Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Electric Current Quiz For X
Hochgeladen von
Sharad SrivastavaOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Electric Current Quiz For X
Hochgeladen von
Sharad SrivastavaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
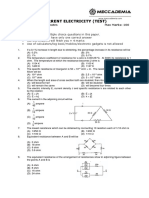
PHYSICS QUIZ M.M. 48 INSTRUCTIONS :ATTEMPT ALL QUESTIONS.
EACH CORRECT ANSWER CARRIES +3 MARKS , WRONG ANSWER -1 MARK AND ZERO MARK IF LEFT UNATTEMPTED.
1.
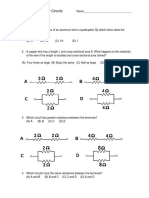
V-I graphs for parallel and series combination of two metallic resistors are as shown in the fig. which graph represents parallel combination (a) A (b) B (c) A and B both (d) neither
2.
The current in the arm CD of the network in the fig. (a)
I1 I 2
(b)
I2 I3
(c)
I1 I 3
(d)
I1 I 2 I 3
3.
The effective between A and B is (a) 3 R (b)
R 3
(c)
3R 2
(d)
2R 3
4.
In the circuit shown in the fig. the current I through ammeter A has a value equal to (a) 1A (b)
10 A 9
(c) 4 A
(d) 3.5 A
5.
The diagram shows two squares, x and y cut from a sheet of metal of uniform thickness . x and y reesistances have sides of length L and 2L respectively. The resistance Rx and Ry of the square are measured between opposite faces in the diagram, What is the value of (a)1/4 (b)1/2 (c) 4 (d) 2
Rx RY
6.
A battery of emf E and negligible internal resistance is connected to two resistor of resistance R1 and R2 as shown in the circuit diagram. What is The potential difference across the resistor of Resistance R2 (a)
(c)
E ( R1 R2 ) R1 E ( R1 R2 ) R2
(b) 24
(b)
ER2 R1 R2 ER2 R1
(d)
7.
A wire of resistance 36 (a) 12
is bent in the form of an equilateral triangle. The resistance between any two vertices is (c) 8 (d) 36
(c) 50 (d) 150
8.
Find out the value of resistance R in the fig. (a) 100 (b) 200
FIITJEE Mumbai Centre (Andheri, Chembur, Dadar, Kandivali, Thane, Vashi) Phone: 022- 42378100, 32911892, 32383438, 41617777, 41581500, 9987686970 email: academics.mumbai@fiitjee.com web: www.fiitjee.com
9.
You have three equal resistances. How many different combinations can you have with these three resistances taken simultaneously (a) 2 (b) 3 (c) 4 (d) 6 Two wires of same length and material have radii r and 2r. The ratio of their specific resistance is (a) 1:2 (b) 1:1 (c) 1:4
10.
(d) 4:1
11.
In the network shown in the figure, the equivalent resistance between A and B is (A) 10R (B) (6/11) R (C) (25/12 R (D) 50/11 R
2R B 3R
R A 4R
12.
In the circuit shown in figure below the current through (A) the 3 resistor is 1 A (B) the 3 resistor is 0.2 A (C) the 3 resistor is 0.50 A (D) the 3 resistor is 0.25 A
9V 2
8 2
8 2
13.
A current of flows in a system of conductor as shown in figure. The potential difference VB VD will be (A) 2 V (B)+2V (C)+1 V (D) zero.
B 3 3A A 2 D 6 4 C 3A
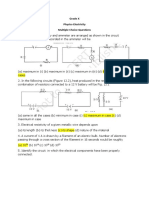
14.
A wire of resistance R is cut into n equal parts. These parts are then connected in parallel. The equivalent resistance of the resultant combination is 2 (A) nR (B)R/n (C) n/R (D) R/n . A wire has a resistance of 10. It is stretched by 1/10 of its original length. Then its resistance will be (A) 9 (B) 10 (C) 11 (D) 12.1
15.
16.
In the given circuit, when galvanometer shows no deflection, the current in 2 resistance is (A) 1.4 A (B) 1.2 A (C)1.0 A (D) 0.4 A
10 1.4A G 25
FIITJEE Mumbai Centre (Andheri, Chembur, Dadar, Kandivali, Thane, Vashi) Phone: 022- 42378100, 32911892, 32383438, 41617777, 41581500, 9987686970 email: academics.mumbai@fiitjee.com web: www.fiitjee.com
ANSWER 1. A 2. B 3. B 4. A 5. C 6. B 7. C 8. A 9. C 10. B 11. B 12. A 13. B 14. D 15. D 16. C
FIITJEE Mumbai Centre (Andheri, Chembur, Dadar, Kandivali, Thane, Vashi) Phone: 022- 42378100, 32911892, 32383438, 41617777, 41581500, 9987686970 email: academics.mumbai@fiitjee.com web: www.fiitjee.com
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- MCQ Physics 3Dokument5 SeitenMCQ Physics 3Sugaraj SamuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics SampleDokument102 SeitenPhysics Sampleshrutianand8915Noch keine Bewertungen
- 14 - Current ElectricityDokument7 Seiten14 - Current ElectricityGurpal SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam 2 CH 1 All PDFDokument20 SeitenExam 2 CH 1 All PDFAhmed Taha Bebo0% (1)
- ElectricityDokument4 SeitenElectricityaishwarya meenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Current Electricity - CC - E - WADokument12 SeitenCurrent Electricity - CC - E - WAHussain Ali PioneerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Current Electricity - 01 Page 16-18Dokument3 SeitenCurrent Electricity - 01 Page 16-18maddy449Noch keine Bewertungen
- Class10 Electricity Module 3Dokument4 SeitenClass10 Electricity Module 3Dr-Swarnima AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Current ElectricityDokument33 SeitenCurrent ElectricityKapil_1983100% (4)
- DPP-4 (Current Electricity)Dokument11 SeitenDPP-4 (Current Electricity)Mriganga SarmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric-Current Class NotesDokument34 SeitenElectric-Current Class NotesPraxxmNoch keine Bewertungen
- QN CollectionDokument96 SeitenQN Collectionபொறிஞன்Noch keine Bewertungen
- Revision Sheet of ElectricityDokument7 SeitenRevision Sheet of ElectricityPRVLNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Current Electricity MCQDokument7 SeitenPhysics Current Electricity MCQHimanshu VasisthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Current Electricity - Minu SinghDokument11 SeitenCurrent Electricity - Minu SinghADITYA SINGHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Student Copy. DPP No. 21 - Current ElectrictyDokument5 SeitenStudent Copy. DPP No. 21 - Current ElectrictyCraftoastNoch keine Bewertungen
- Direct Current Circuits (QB)Dokument48 SeitenDirect Current Circuits (QB)Mohammed Aftab AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Current Circuits Practice ProblemsDokument14 SeitenElectric Current Circuits Practice ProblemsSrihith MarakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Current 1Dokument4 SeitenCurrent 1Devansh DuhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Circuits (Cengage Questions)Dokument21 SeitenElectric Circuits (Cengage Questions)Phantom1699Noch keine Bewertungen
- Circuits MC Practice ProblemsDokument29 SeitenCircuits MC Practice ProblemsMark CalixtoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12th Unit Test Sankalp ObjectiveDokument6 Seiten12th Unit Test Sankalp ObjectiveJatin ChouhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Current-Electricity MCQ 2Dokument9 SeitenCurrent-Electricity MCQ 2Anant KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tamer All PDFDokument124 SeitenTamer All PDFevernote accountNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Current and Ohm's LawDokument34 SeitenElectric Current and Ohm's LawArpit JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Practice Paper - 8 Term-1Dokument11 SeitenPhysics Practice Paper - 8 Term-1JatinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 623a5c67-4398-4e1b-8b41-da8a83ae2872Dokument9 Seiten623a5c67-4398-4e1b-8b41-da8a83ae2872Vidhi ShekhawatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz 23: Multiple-Choice Questions On Series and Parallel NetworksDokument2 SeitenQuiz 23: Multiple-Choice Questions On Series and Parallel Networksravichan_2010Noch keine Bewertungen
- Csec Electrical and Electronic TechnolohyDokument9 SeitenCsec Electrical and Electronic TechnolohyDanel75% (8)
- Current ElectricityDokument16 SeitenCurrent ElectricityNavya RastogiNoch keine Bewertungen
- UnitTest - D03 Aug 2023 (1) K.Dokument61 SeitenUnitTest - D03 Aug 2023 (1) K.krishgj19ab3232Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Current and Ohm McqsDokument77 SeitenElectric Current and Ohm McqsEngrAneelKumarAkhani100% (2)
- Electricity QPDokument13 SeitenElectricity QPrishiop405Noch keine Bewertungen
- 11a-Circuits MC Practice ProblemsDokument37 Seiten11a-Circuits MC Practice Problemsminviking25Noch keine Bewertungen
- Xi Rasi Phy Iit WPT 19.02.24Dokument5 SeitenXi Rasi Phy Iit WPT 19.02.24Deena chemistNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jeep 112Dokument7 SeitenJeep 112Ishan LakhwaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- X Science Worksheet Electricity Module 2Dokument5 SeitenX Science Worksheet Electricity Module 2Janhavi KawadeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10113163Dokument36 Seiten10113163Anonymous hDKqasfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revision DPP - JEE Advance - DPP-3 - P - DPP-3 - DPP - 03 PDFDokument11 SeitenRevision DPP - JEE Advance - DPP-3 - P - DPP-3 - DPP - 03 PDFvijay kakarlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 3 MCQ PHYSICS CLASS 12TH ASSIGNMENTDokument3 SeitenCH 3 MCQ PHYSICS CLASS 12TH ASSIGNMENTPatel 0786Noch keine Bewertungen
- DC Circuit XII A1Dokument4 SeitenDC Circuit XII A1UJWALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Engineering Model Questions For IBPS Technical Officer Paper 2Dokument29 SeitenElectrical Engineering Model Questions For IBPS Technical Officer Paper 2Rohit Raj60% (5)
- Physics Classes: Topic: - Current ElectricityDokument3 SeitenPhysics Classes: Topic: - Current Electricitydnyanada patankarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pre Board 1 PhysicsDokument6 SeitenPre Board 1 PhysicsMohit KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 3 - MCQ QN AloneDokument34 SeitenCH 3 - MCQ QN Alonexefayo4337Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1212441515electricity WorksheetsDokument6 Seiten1212441515electricity Worksheetsaayush619_com3918Noch keine Bewertungen
- 12th Physic One MarksDokument17 Seiten12th Physic One MarksKirthik Reshan.S 12'A'Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 3rd Sec EgyptDokument39 SeitenPhysics 3rd Sec Egyptabdelrahman mohamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- 07-11-23 Current Electricity Rept.Dokument11 Seiten07-11-23 Current Electricity Rept.Jashan DoleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Current and Circuits Practice ProblemsDokument15 SeitenCurrent and Circuits Practice ProblemsAnthony HuiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Current Electricity (Test)Dokument3 SeitenCurrent Electricity (Test)ChetanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Electric Circuits and Ohm With AnsDokument22 Seiten1 Electric Circuits and Ohm With AnsIncst BhaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electricity - Formative AssessmentDokument4 SeitenElectricity - Formative AssessmentNagulan MadhavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electra Quiz: Time - Marks - +3 (Correct), - 1 (Incorrect)Dokument3 SeitenElectra Quiz: Time - Marks - +3 (Correct), - 1 (Incorrect)RohitRajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yub 7Dokument395 SeitenYub 7shamshad100% (1)
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesVon EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reviews in Computational ChemistryVon EverandReviews in Computational ChemistryAbby L. ParrillNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tables of Racah Coefficients: Mathematical Tables SeriesVon EverandTables of Racah Coefficients: Mathematical Tables SeriesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Android App: Https://Goo - Gl/Ls8Qra Telegram: Https://T.Me/NeetprepationDokument20 SeitenAndroid App: Https://Goo - Gl/Ls8Qra Telegram: Https://T.Me/NeetprepationSharad SrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.motion in A Straight LineDokument44 Seiten3.motion in A Straight LineSharad SrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Android App: Https://Goo - Gl/Ls8Qra Telegram: Https://T.Me/NeetprepationDokument44 SeitenAndroid App: Https://Goo - Gl/Ls8Qra Telegram: Https://T.Me/NeetprepationSharad SrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- For Students of Classes 5th To 10th Indian National Junior Science Olympiad (Injso) Answer Key, 27 January 2018Dokument1 SeiteFor Students of Classes 5th To 10th Indian National Junior Science Olympiad (Injso) Answer Key, 27 January 2018Sharad SrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motion TestDokument6 SeitenMotion TestSharad SrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Key INJSO (IJSO Stage - II) - Test Date - 02 Feb. 2019: For Students of Classes 5th To 10thDokument1 SeiteAnswer Key INJSO (IJSO Stage - II) - Test Date - 02 Feb. 2019: For Students of Classes 5th To 10thSharad SrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kvpy SB Solutions PDFDokument34 SeitenKvpy SB Solutions PDFSharad SrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CalorimetryDokument12 SeitenCalorimetrySharad SrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution To Thepretical Problem 1 PDFDokument6 SeitenSolution To Thepretical Problem 1 PDFSharad SrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SHM TestDokument5 SeitenSHM TestSharad SrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabus of The International Junior Science Olympiad - IJSODokument7 SeitenSyllabus of The International Junior Science Olympiad - IJSOrunnymeadowNoch keine Bewertungen
- NSEP 2013 Solution 1.0Dokument27 SeitenNSEP 2013 Solution 1.0Sharad SrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maharashtra State Board - HSC - 2017-2018 - March - PhysicsDokument9 SeitenMaharashtra State Board - HSC - 2017-2018 - March - PhysicsSharad SrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NSEP 2007 PhysicsDokument19 SeitenNSEP 2007 PhysicsSharad Srivastava0% (2)
- Syllabus of The International Junior Science Olympiad - IJSODokument7 SeitenSyllabus of The International Junior Science Olympiad - IJSOrunnymeadowNoch keine Bewertungen
- SL Pho Test 2010 PDFDokument7 SeitenSL Pho Test 2010 PDFBHAAJI0001Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1994e.pdf CANADIAN OLYMPIADDokument5 Seiten1994e.pdf CANADIAN OLYMPIADSharad SrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 1 - APhO 2013Dokument1 SeiteProblem 1 - APhO 2013Lâm Văn Sa HuỳnhNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2013e PDFDokument7 Seiten2013e PDFSharad SrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conservation of MomentumDokument1 SeiteConservation of MomentumSharad SrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- OpticsDokument3 SeitenOpticsSharad SrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Untitled X Paper1Dokument7 SeitenUntitled X Paper1Sharad SrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conservation of MomentumDokument1 SeiteConservation of MomentumSharad SrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conservation of MomentumDokument1 SeiteConservation of MomentumSharad SrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Task Basis JurisprudenceDokument10 SeitenTask Basis JurisprudenceKerwin LeonidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Public BudgetingDokument15 SeitenPublic BudgetingTom Wan Der100% (4)
- Not For Profit Governance WeilDokument224 SeitenNot For Profit Governance WeillkjhmnvbNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Global StudyDokument57 SeitenA Global StudyRoynal PasaribuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chan Sophia ResumeDokument1 SeiteChan Sophia Resumeapi-568119902Noch keine Bewertungen
- Danculos - M1 - L3 - Activity TasksDokument2 SeitenDanculos - M1 - L3 - Activity TasksAUDREY DANCULOSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Managing Ambiguity and ChangeDokument7 SeitenManaging Ambiguity and ChangeTracey FeboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spyderco Product Guide - 2016Dokument154 SeitenSpyderco Product Guide - 2016marceudemeloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Internship PPTDokument19 SeitenSample Internship PPTSangeeta JamadarNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Machine StopsDokument14 SeitenThe Machine StopsMICHAEL HARRIS USITANoch keine Bewertungen
- Life in The Past - Year 6 WorksheetsDokument11 SeitenLife in The Past - Year 6 WorksheetstinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unsung Ancient African Indigenous Heroines and HerosDokument27 SeitenUnsung Ancient African Indigenous Heroines and Herosmsipaa30Noch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of Low-Frequency Passive Seismic Attributes in Maroun Oil Field, IranDokument16 SeitenAnalysis of Low-Frequency Passive Seismic Attributes in Maroun Oil Field, IranFakhrur NoviantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rectification or Correction of Sale DeedDokument4 SeitenRectification or Correction of Sale Deedsumanth_0678Noch keine Bewertungen
- Navamsa Karma and GodDokument9 SeitenNavamsa Karma and GodVisti Larsen50% (2)
- Software Project Management PDFDokument125 SeitenSoftware Project Management PDFUmirNoch keine Bewertungen
- AS 1 Pretest TOS S.Y. 2018-2019Dokument2 SeitenAS 1 Pretest TOS S.Y. 2018-2019Whilmark Tican MucaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To The Field of Organizational BehaviorDokument22 SeitenIntroduction To The Field of Organizational BehaviorSayyid Al ArizieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scribe FormDokument2 SeitenScribe FormsiddharthgamreNoch keine Bewertungen
- The ReformationDokument20 SeitenThe ReformationIlyes FerenczNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fascinating Numbers: Some Numbers of 3 Digits or More Exhibit A Very Interesting PropertyDokument2 SeitenFascinating Numbers: Some Numbers of 3 Digits or More Exhibit A Very Interesting PropertyAnonymous JGW0KRl6Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ylarde vs. Aquino, GR 33722 (DIGEST)Dokument1 SeiteYlarde vs. Aquino, GR 33722 (DIGEST)Lourdes Loren Cruz67% (3)
- Class 12 Accountancy HHDokument58 SeitenClass 12 Accountancy HHkomal barotNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Conference On Basic Science (ICBS)Dokument22 SeitenInternational Conference On Basic Science (ICBS)repositoryIPBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 Foundations of CurriculumDokument20 SeitenUnit 2 Foundations of CurriculumKainat BatoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plastique: Art and EducationDokument7 SeitenPlastique: Art and EducationJackStevensonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bug Tracking System AbstractDokument3 SeitenBug Tracking System AbstractTelika Ramu86% (7)
- Context: Lesson Author Date of DemonstrationDokument4 SeitenContext: Lesson Author Date of DemonstrationAR ManNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pakistan List of Approved Panel PhysicianssDokument5 SeitenPakistan List of Approved Panel PhysicianssGulzar Ahmad RawnNoch keine Bewertungen
- India Marine Insurance Act 1963Dokument21 SeitenIndia Marine Insurance Act 1963Aman GroverNoch keine Bewertungen