Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Project
Hochgeladen von
Pradeep VadlaOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Project
Hochgeladen von
Pradeep VadlaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE
AT KARNATAKA POWER CORPORATION LIMITED
Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements Bangalore University for the award of the Degree in
MASTER OF BUSINESS ADMINISTRATION BANGALORE UNIVERSITY
SUBMITTED BY,
N.S.HARISH
REG. NO: 09TUCMA024
UNDER THE GUIDANCE OF
Dr. Y.NAGRAJU, MBA, M.com, M.phil, PhD
READER, CBSMS
2009-2011
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES DEPARTMENT OF MANAGEMENT, BANGALORE UNIVERSITY BANGALORE - 560001
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY: The project was intended to have an exposure of working environment and to conduct evaluation of financial performance and to know the financial health of the company. The project was taken over for a period of 8 weeks. It covered the area starting from the company profile until analysis, findings, suggestions and conclusion about the problem of the study. The chief objective in this study was to understand the financial performance of the company. To study the financial ability, growth and profitability of KPCL. In this study secondary data was collected. The relevant information was taken from annual reports, journals and internet. The data collected from secondary sources were tabulated and analyzed. I used the tool ratios &Trend analysis to analyze the financial performance of the company. The analysis and interpretation have been presented in the tables followed by appropriate graphs which are followed by findings, recommendations and conclusions.
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
CHAPTER-I INTRODUCTION
The figures given in financial statements do not speak anything themselves, hence financial tools and techniques are applied for easy interpretations and for quick decision. The financial analysis is to classify the data in simple form given in financial statements and to compare with each other to find out the strengths and weaknesses of the business and to take the decision for future. For instance, if all items relating to current assets are placed in one group while all items relating to current liabilities are placed in another group, the comparison between two groups will provide useful information.
1.1 MEANINGS AND DEFINITIONS
IN THE WORDS OF FINNEY AND MILLER: Financial analysis consist in separating facts according to some definite plan, Arranging them in groups according to certain circumstances and then presenting them in a convenient and easily read and understandable form.
IN THE WORD OF JOHN.N.MYRES: Financial statement analysis is largely a study of relationships among the various financial factors in a business, as disclosed by a single set of statements and a study of the trends of these factors as shown in a series of statements.
Financial statement analysis involves analyzing the forms financial statement to extract the information that can facilitate decision making. For ex:- an analysis of the financial statement can reveal whether the form will be able to meet its long term debt commitment, weather the firm is financially distressed, whether the company is using its physical assets efficiently, whether the firm as an optimal financing mix, whether the firm is generating adequate return for its shareholders, whether the firm can
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
sustain its competitive advantage etc; while the information used is historical, the instant is clearly to arrive at recommendations and forecast for the feature rather than provide a picture of the past. Financial analysis is performed by both internal
management and external groups. Firms would perform such an analysis in order to evaluate their overall current performance, identify problem/opportunity areas, develop budgets and implement strategies for the future. External group (such as investors, regulators, lenders, suppliers, customers) also perform financial analysis in deciding whether to invest in a particular firm, whether to extend credit etc. There are several rating agencies (such as Moodys, Standard & Poor) that routinely perform financial analysis of firms in order to arrive at a composite rating. FINANCIAL STATEMENT ANALYSIS
The basis for financial statement planning, analysis and decision making is the financial information. Financial information is needed to predict, compare and evaluate the firms earning ability. It is also required to aid in economic decision making investment and financing decision making. The financial statements or accounting reports helps in communicating performance of company to its stakeholders. Three basic financial statements of great significance to owners, management and investors are balance sheet, profit and loss account and cash flow statement. Financial Statement analysis is the process of identifying the financial strength and weakness of the firm by properly establishing relationship between the items of balance sheet and the profit and loss account. Metcalf and Titard define Financial statement analysis as a process of evaluating the relationship between components parts of the financial statement to obtain a better understanding of a firms position and performance.
1.2 FINANCIAL ANALYSIS TECHNIQUES
There are various techniques for the financial performance of the company. Through these one can clearly assess the real capability of the company provided. The financial statement has to depict the true and fair view of the state of affairs of the company. The various tools or techniques of financial analysis are as follows:
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
1. Ratio analysis 2. Trend analysis 3. Fund flow analysis 4. Cash flow analysis 5. Working capital management 6. Capital structure 7. Capital budgeting 8. Cost of capital 9. Comparative statement analysis
1.3 MEANINGS AND DEFINITIONS: RATIO ANALYSIS: Ratio analysis is a process of identifying the financial strengths and weaknesses of the firm. RATIO: A ratio is simple arithmetical expression of the relationship of one number to another. It may be defined as the indicated quotient of two mathematical expressions. According to Accountants Handbook by Wixom, Kell and Bedford, a ratio is an expression of the quantitative relationship between two numbers.
STEPS INVOLVED IN RATIO ANALYSIS: Selection of the relevant data from the financial statements depending upon the objectives of analysis. Calculation of appropriate ratios from the above data. Comparison of the calculated ratios with the ratios of the same firm in the past, or the ratio developed from the projected financial statements or the ratios of some other firms or the comparison with the ratios of the industry to which the firm belongs. Interpretation of the ratios.
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
SIGNIFICANCE OF RATIO ANALYSIS: Ratio analysis simplifies the complex financial data. It reveals the change in financial conditions of the business. Ratio analysis helps the management in decision making. It throws light on the degree of efficiency of management and utilization of assets. It helps in forecasting and planning. Over a period of time the firm develops certain norms which may indicate future success or failure. Ratio may be used as instruments of management control, particularly in area of sales and control. Ratios facilitate the function of communication and enhance the value of financial statements. Ratios are helpful in assessing the financial position and the profitability of the concern. Ratio analysis also helps in effective control of business measuring performance, control of cost etc, effective control is a key stone of better management. Ratio analysis helps the investors in making investment decision to make a profitability investment. It helps to know the relationship between different related items of financial statements. It helps in investigating the factors responsible for financial soundness / deterioration of particular situation. It helps in analyzing and interpreting the financial health of the enterprise. The ratios are calculated based upon past values. So it helps management to frame sound business policies for business in future.
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
1.4 OBJECTIVES OF RATIO ANALYSIS: To study the profitability: Accounting ratio help to measure the profitability of the business by calculating the various profitability ratios. To study the solvency: With the help of solvency ratios, solvency of the company can be measured. These ratios show the relationship between the liabilities and assets. To analyze the financial statement of the company: Ratio analysis help the outsiders just like creditors, shareholders, debenture-holders, bankers to Know about the profitability and ability of the company to pay them interest and dividend etc. To study the operating efficiency: Ratio analysis helps to work out the operating efficiency of the company with the help of various turnover ratios. To analyze the performance of the company: With the help of ratio analysis a company may have comparative study of its performance to the previous years. To provide recommendations and suggestions based on findings: Accounting ratios are very useful as they briefly summaries the result of detailed and complicated computations. 1.5 ADVANTAGE OF RATIO ANALYSIS: Helpful in analysis of Financial Statements. Helpful in comparative Study. Helpful in locating the weak spots of the business. Helpful in Forecasting. Estimate about the trend of the business. Fixation of ideal Standards. Effective control.
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
1.6 LIMITATIONS OF RATIO ANALYSIS: Comparison not possible if different firms adopt different accounting policies. Ratio analysis becomes less effective due to price level changes Ratio may be misleading in the absence of absolute data. Limited use of a single data. Lack of proper standards. False accounting data gives false ratio. Ratios alone are not adequate for proper conclusions. Effect of personal ability and bias of the analysts. 1.7 OPERATIONAL DEFINITIONS: CURRENT ASSETS: Current assets include cash and those assets, which can be converted into cash within a year, such as marketable securities, debtors, inventories and prepaid expenses. LIQUID OR QUICK ASSETS: Liquid assets are those assets which can be converted into cash immediately or reasonable soon without loss of value. Liquid assets include all current assets except stock and prepaid expenses. CURRENT LIABILITIES: Current liabilities include all obligations maturing within a year such as creditors, bills payable, accrued expenses, proposed dividend. QUICK LIABILITIES: A quick liability refers to all those liabilities which should necessarily be paid within a shorter period of time, which is within one year. INVENTORY: The term inventory includes the stock of raw materials, work in progress and finished stock. WORKING CAPITAL: Working capital is the excess of current assets over current liabilities. OPERATING PROFITS:
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
Operating profit is the net profit from the business for which the concern is started. In other words, it is the excess of net sales over the operating cost. It is the net profit plus non operating expenses minus non operating incomes. CAPITAL EMPLOYED: Capital includes net fixed assets (fixed assets- depreciation) and current assets. OPERATING COST: Operating cost refers to all expenses incurred for operating or running a business. It comprises cost of goods sold plus operating expenses such as office and administration expenses, selling and distribution expenses. DEBTORS: A debtor is a person who owes money to us or person who has to pay. CREDITORS: A creditor is a person to whom we have to pay. TOTAL ASSETS: A total asset refers to all realizable assets which can be realized. They include all tangible assets and intangible assets include patent rights, copy rights, and trademarks. NET WORTH: Net worth means the excess of total assets over total liabilities, in other words it means owners funds. RESERVES: Reserves are those amounts of money, which have been earned in previous year. These reserves include statutory reserve and balance of profits.
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
CLASSIFICATION OF RATIO/ TYPES OF RATIOS: Broadly the operation and financial position of firm can be described by studying its short term liquidity position, profitability and its operational activities. Therefore, ratios can be classified in to following four broad categories: I. II. III. IV. Liquidity ratios Capital structure/leverage ratio Activity ratio Profitability ratio
LIQUIDITY RATIO: The term liquidity and short term solvency are used synonymously. Liquidity or short term solvency means ability of the business to its short term liabilities .inability to pay off short term liabilities affects its credibility as well as its credit rating. Continuous default on the part of the business leads to commercial bankruptcy. Eventually such commercial bankruptcy may lead to its sickness and dissolution. Short term lenders and creditors of a business are very much interested to know its state of liquidity because of their financial stake. Traditionally two ratios are used to highlight the business liquidity. These are current ratio and quick ratio. Other ratios include cash ratio, interval measure ratio and net working capital ratio. CURRENT RATIO: The current ratio is one of the best known measures of the financial strength. The main question this ratio addresses is: does the business have enough current assets to meet the payment schedule of its current debts with a margin of safety for possible losses in current assets? a generally acceptable current ratio is 2:1 but whether or not a specific ratio is satisfactory depends on the
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
10
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
nature of the business and the characteristics of its current assets and liabilities. QUICK RATIO: The quick ratio is also called the acid-test ratios and one of the best measures of liquidity. The quick ratio is much more exacting measure than the current ratio by excluding inventories it concentrates on the really liquid assets with value that is fairly certain. Quick assets consist of only cash and near cash assets. QUICK RATIO = LIQUID ASSETS / CURRENT LIABILITIES. CASH RATIO: Absolute liquid assets include cash in hand and cash at bank and marketable securities or temporary investments. It is the real measure of the liquidity or short-term solvency of a concern, the actual absolute liquid ratio is compared with the standard or ideal absolute liquid ratio of 1:2.
CASH RATIO = ABSOLUTE LIQUID ASSETS / QUICK LIABILITY.
LEVERAGE RATIO/ CAPITAL STRUCTURE: The capital structure leverage ratio may be defined as those financial ratios which measure the long term stability and structure of the firm. these ratio indicate the mix of fund provided by owners lenders and assure the lenders of the long term funds with regard to: I. Periodic payment interest during the period of the long and II. Repayment of principle amount on maturity Therefore average ratio of two types I. Capital structure ratio and II. Coverage ratio
CAPITAL STRUCTURE RATIO These ratios provide an insight into the financing techniques used by business and focus, as consequences on the long term solvency position. From the balance sheet
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
11
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
one can get only the absolute fund employed and its sources, but only capital structure ratios show the relative weight of different sources. In the balance sheet one may find shareholders ` fund loan fund and current liabilities and provisions these are very often classified as owners equities and external equities owners equity means share capital both equity share capital and preference share capital and reserve and surplus. External equity means all outside liabilities (inclusive of current liabilities and provisions). Also these are sometimes classified as equity and debt. equity means shareholder fund and debt means long term borrowed funds (so short term loans, current liabilities and provisions are excluded). As per guidelines for issue of debenture by public limited company debenture and bonds with an initial maturity period of five years or more, including interest accrued thereon. It also includes all deferred payment liabilities but it does not include short term bank borrowing and advances, unsecured deposits or loans from the public, shareholders and employees, and unsecured loans and deposits from others. It should also include proposed debenture issues. Equity means paid up share capital including preference share capital and reserves. Three popularly used capital structure ratios are:
I. EQUITY RATIO- this ratio indicates the proportion of owners fund to total fund invested in the business. Traditionally, it is believed that higher the proportion of owner fund lower is the degree of risk.
II. DEBT RATIO - total debt includes short and long term borrowings from financial institution, debenture / bonds, deferred payment arrangement for buying capital equipment, bank borrowing, public deposits and any other interest bearing loans. Capital employed includes total debt and net worth. Thus ratio is used to analyze the long term solvency of the firm.
III. DEBT TO EQUITY RATIO- debt equity ratio is the indicator of leverage. According to traditional school, cost of capital firstly decreases due to higher doses of leverage, reaches minimum and thereafter increases. So infinite increases in leverage in leverage (i.e. debt-equity ratio) is not possible. But according to Modigliani- miller theory, cost of capital and leverage are
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
12
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
independent of each other. But Modigliani-miller theory is based on certain restrictive assumption, namely, perfect capital market, homogeneous expectation by the present and prospective investors, presence of homogeneous risk class firm, 100% dividend payout, no tax situation, etc. and most of this assumption is viewed as unrealistic. It is believed that leverage and cost of capital are not unrelated.
A high ratio means less protection for creditor. A low ratio on the other hand, indicates a wider safety cushion (i.e. , creditor feel the owner funds can help absorb possible losses of income and capital)
This ratio indicates the proportion of debt fund in the relation to equity. This ratio is very often referred in capital structure decision as well as in legislation dealing with the capital structure decision (i.e. Issue of shares and debentures). Lender and also keen to know this ratio since it show the relative weight of debt and equity.
A. ACTIVITY RATIOS: If a business does not use its assets effectively, investors in the business would rather take their Money and place it somewhere else. In order for the assets to be used effectively, the business needs a high turnover; it includes the following ratios they are, INVENTORY OR STOCK TURNOVER RATIO: This ratio indicates the relationship between the cost of goods during the year and average stock Kept during that year. INVENTORY TURNOVER RATIO = COST OF GOODS SOLD / AVERAGE INVENTORY. DEBTORS OR RECEIVABLE TURNOVER RATIO: This ratio indicates the relationship between credit sales and Average debtors during the year. DEBTOR TURNOVER RATIO = NET CREDIT SALES / AVERAGE DEBTORS + B/R.
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
13
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
AVERAGE COLLECTION PERIOD: This ratio indicates the time with in which the amount is collected from debtors and bills Receivables. AVERAGE COLLECTION PERIOD = AVERAGE TRADE DEBTORS / SALES PER DAY. CREDITOR TURNOVER RATIO: This ratio indicates the relationship between credit purchases and average creditors during the Year. CREDITOR TURNOVER RATIO = NET CREDIT ANNUAL PURCHASES / AVERAGE TRADE CREDITORS + B/P. AVERAGE PAYMENT PERIOD RATIO: This ratio indicates the period which is normally taken by the firm to make payment to its Creditors. AVERAGE PAYMENT PERIOD = CREDITORS + B/P / CREDIT PURCHASE PER DAY. WORKING CAPITAL TURNOVER RATIO: This ratio reveals how efficiently working capital has been utilized in making sales. WORKING CAPITAL TURNOVER RATIO = COST OF GOODS SOLD /WORKING CAPITAL.
FIXED ASSET TURNOVER RATIO: This ratio reveals how efficiently the fixed assets are being utilized. FIXED ASSETS TURNOVER RATIO = COGS / NET FIXED ASSETS.
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
14
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
B. SOLVENCY RATIOS: It indicate the ability of the company to meet its long-term obligations on a continuing basis and thus to survive over a long period of time. In judging how well on a company is doing, analysts typically compare a company's ratios to industry statistics as well as to its own past performance. Following are some of solvency ratios: DEBT EQUITY RATIO: This ratio expresses the relationship between long Term debts and shareholders fund. The standard ratio for debt equity ratio is 2:1
DEBT- EQUITY RATIO = SHAREHOLDER FUND / NET WORTH. DEBT TO TOTAL FUNDS RATIO: This Ratio is a variation of the debt equity ratio and gives the same indication as the debt equity Ratio. In the ratio, debt is expressed in relation to total funds, i.e., both equity and debt. DEBT TO TOTAL FUNDS RATIO = LONG TERM LOANS /
SHAREHOLDER FUNDS. PROPRIETARY RATIO: This ratio indicates the proportion of total funds provide by owners or shareholders. PROPRIETRY RATIO = SHAREHOLDER FUNDS / SHAREHOLDER FUNDS + LONG TERM LOANS SOLVENCY RATIO: The ratio indicates the relationship between the total liabilities to outsiders to total assets of a Firm and can be calculated as follows: SOLVENCY RATIO = TOTAL LIABILITY TO OUTSIDERS / TOTAL ASSETS.
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
15
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
D.PROFITABILITY RATIOS: Profitability ratios are gauges of the company's operating success for a given period of time. It includes the following ratios GROSS PROFIT RATIO: This ratio shows the relationship between gross profit and sales. GROSS PROFIT RATIO = GROSS PROFIT / NET SALES *100. NET PROFIT RATIO: This ratio shows the relationship between net profit and sales. NET PROFIT RATIO = NET PROFIT / NET SALES *100. RETURN ON EQUITY SHAREHODER FUNDS: Equity Shareholders of a company are more interested in knowing the earning capacity of their funds in the business. RETURN ON EQUITY SHAREHOLDER FUNDS = NPAIT / EQUITY SHAREHOLDER FUNDS *100. EARNING PER SHARE: This ratio measures the profit available to the equity shareholders on a per share basis. All profit left after payment of tax and preference dividends are available to equity shareholders. EPS = NET PROFIT DIVIDEND ON PREFERNCE SHARE / NUMBER OF EQUITY SHARE. DIVIDEND PER SHARE: Profits remaining after payment of tax and preference dividend are available to equity shareholders. D.P.S = DIVIDEND PAID TO EQUITY SHAREHOLDERS/ NUMBER OF EQUITY SHARES *100.
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
16
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
RETURN ON CAPITAL EMPLOYED: This ratio reflects the overall profitability of the business. It is calculated by comparing the profit earned and the capital employed to earn it. This ratio is usually in percentage and is also known as Rate of Return or Yield on Capital. RETURN ON CAPITAL EMPLOYED = PBIT DIVIDENDS / CAPITAL EMPLOYED *100. DIVIDEND PAYOUT RATIO: It measures the relationship between the earning available to equity shareholders and the Dividend distributed among them. DIVIDEND PAYOUT RATIO NET = DIVIDEND PAID TO TO EQUITY EQUITY
SHAREHOLDERS/TOTAL SHAREHOLDERS.
PROFIT
BELONGS
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
17
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
CHAPTER-II
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
2.1. TITLE OF THE PROJECT:
Analysis of Financial Performance at KPCL
2.2. STATEMENT OF THE PROBLEM:
The main objective of any organization is to maximize the profit. Profitability or financial soundness of the organization, it can be ascertained with the help of ratio analysis and trend analysis. An analysis of Financial Performance at KARNATAKA POWERGENERATION CORPORATION LTD using ratios & trend analysis as tools Financial statement no doubt contain a large number of accounting data or figures but the accounting data or financial figures are not more than the group of financial figures. They do not much convey much information. However they may give a clear picture of the financial adventures of the firm if they are analyzed and interpreted. Through analysis and interpretation of the financial statements, we can reduce the story of the actual progress and financial position of the firm in clear and simple language which can be easily understood by a layman.
2.3. OBJECTIVES OF THE STUDY: The study is undertaken to achieve the following objectives. To find out the factors influencing the financial performance of the company. To analyse the financial performance of the company. To check the efficiency of the organization in terms of its profits and turnovers. To study the trend of the companys profits, assets, liabilities and other financial components through trend analysis.
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
18
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
2.4 SCOPE OF THE STUDY The scope is limited to published information received from company website. The study was limited to few important financial techniques of the firm. It covers the financial analysis of KPCL only. The study covers 2006-2010 balance sheet & cash flow statements items only. The study is to analyze the financial performance with reference to financial statements like balances sheet, cash flow statements etc.
2.5 METHODOLOGY / RESEARCH TOOL:
Financial statement can be subjected to two types of analysis. They are: TREND ANALYSIS OR DYNAMIC ANALYSIS: which is made by analyzing the financial statement over a period of two years. This indicates the trend of such variable, as sales, cost of production profits, assets and liabilities. For this purpose comparative financial statement are prepared horizontally.
RATIO ANALYSIS: The financial performance was done over a period of four years. Analysis was done through calculation of ratios form the financial statements. Interpretations was done by thorough analysis and comparing with a standard ratio. Ratios are often classified using the following terms: Liquidity ratios. Solvency ratios. Activity ratios. Profitability ratios.
SOURCES OF DATA COLLECTION
COLLECTION OF PRIMARY DATA The following methods were used for collection of primary data. Interacting with the Finance Manager by asking general questioners. Observation at KPCL.
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
19
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
COLLECTION OF SECONDARY DATA: Secondary Data- Annual reports of company, Published articles, journals, magazines and in house reports.
SAMPLE TECHNIQUE: The sample technique cannot be applied for the available data.
SAMPLE SIZE: The financial statements of the year, 2006-07, 2007-08, 2008-09, and 2009-10 of the KPCL have been taken as sample size.
2.6 LIMITATIONS OF THE STUDY: This study suffers from following limitations: Limited DATA provided by KPCL, The scope of the study is limited for the information supplied and data made available. The scope of this study is limited to critical evaluation. No full disclosure A\Cs.
Limited Information provided by finance manager.
2.7 CHAPTERS SCHEME: 1. Introduction and Background. 2. Research Design. 3. Profiles of Industry, Companies and Products. 4. Analysis and interpretation. 5. Summary of Findings, Conclusions and Suggestions.
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
20
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
CHAPTER: III
PROFILES
A. INDUSTRY PROFILE
When India became independent the country had a power generating capacity of 1360 MW. The power sector has registered significant progress since the process of planned development of the economy in1950 Hydro power and Coal based thermal power have been the main source of generating electricity. Primarily private utility company carries out generation and distribution of electric power. Notable amongst them and still in existence is Calcutta Electric Power now, Kolkata Electric Power was available only in a few urban centres, rural areas and villages did not have electricity.
After 1950, all new generation, transmission and distribution in the rural sector and the urban centres [which was not served by private utilities] came under the purview of state and central government agencies. State Electricity Boards [SEB] were found in all the states. Traditionally, Indias power sector has been dominated by central and state governments. Usually State Electricity Boards play an important role in the generation, transmission as well as distribution of power. Private players have a limited presence in this sector. Poor financial health of State Electricity Board has deterred the private investors from investing in the sector even though the have been assured.
The players in this sector are 65 out of which 15 companies are listed. Nuclear Power Company and the Power Grid Corporation are among biggest non-listed companies. Apart from these, there are many small players like Tulsyan power and Vadina Power who contribute only 0.1% of the total capacity. Among the listed company NTPC has the highest sales and profits. NTPC is one of the major players in the power industry of the country.
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
21
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
3.1 GROWTH OF INDIAN POWER SECTOR
Power development is the key to the economic development. It has been receiving adequate priority ever since the process of planned development began in 1950. The power sector has been getting 18-20% plan periods. Remarkable growth and progress have led to extensive use of electricity in all the sectors of economy in the successive five year plans. Over the year since 1950 the installed capacity of power plants was 1713 (utilities) has increased to 89090 MW (31.3.2007), registering a 52nd fold increase in 48 years.
3.2 CURRENT PROBLEMS OF POWER INDUSTRY
The most important cause of the problem being faced in the power sector is the irrational and unremunerative tariff structure. Although the tariff is fixed and realized by SESs, the state government have constantly interfered in tariff setting without subsidising SEBs for the losses arising out of state government desire to provide power at concessional rates to certain sectors, especially agriculture. Power supply to agriculture and domestic consumers is heavily subsidised. Only a part of this subsidy is recovered by SEBs through cross subsidisation of tariff from commercial and industrial consumers. The SEBs in the process have been incurring heavy loss. If SEBs were to continue to operate on the same lines their internal resources generated during next 10 year will be negative Future of Power Industry
India is a developing nation, there is a heavy demand for power in the country, but the current situation in the power industry shows that there are several factors which prohibit the successful fulfilment of demand for power. However the country has several opportunities through which improvement in the power industry can be made. India aims at elevating the share of renewable energy source in power generation to10% by 2012. Trading of power will be an important source of revenue in power market. Potentially, India is one of the largest power markets in the world. Utilization of power will not only improve this sector but also boom countrys GDP.
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
22
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
B.COMPANY PROFILE
3.3 BACKGROUND OF THE COMPANY Karnataka Power Corporation limited is the sole administrator for the power generation in the state. From the Mysore Power Corporation Limited 1970 (A successor to the Hydro Electric Construction Department of Mysore state) to Karnataka Power Corporation. Karnataka Power Corporation Limited (KPCL) was incorporated in 1970 as a wholly owned undertaking of the Government of Karnataka engaged in the construction, operation and maintenance of power generating stations in Karnataka. The Karnataka Power Corporation has been a prime mover and catalyst behind key power sector reforms in the state - measures that have spiraled steady growth witnessed in both industrial and economic areas.
KPCL was the first power generating company to be registered under the Companies Act 1956. It came into existence on 20th July 1970 with an authorized capital of Rs.56crores and capacity of 746MW, entirely contributed by the Government of Karnataka. It has expanded its capacity to 5726MW and in future poised to add 789MW from its on-going projects. Revenue of Rs.41480Million in 2009 as compared to Rs.1.30Million in 1971, speaks volumes about KPCLs progress. The KPCLs stock in trade is industry proven - well-established infrastructure & modern, progressive management concepts and a commitment to excel, helping it meet the challenges of the rising energy demands of Karnataka. The leverage point of KPCL initiatives are its resource management strengths right across planning, financing and project engineering. KPCL also has a high rating in terms of project completion and commissioning within the implementation calendar.
3.4 OBJECTIVES BEHIND ESTABLISHMENT OF KPCL To carry on the operation of Electric Power Corporation and to construct and establish necessary power stations. To construct and maintain reservoirs, dams etc, which will directly and indirectly contribute to such operations
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
23
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
NATURE OF BUSINESS CARRIED AT KPCL KPCL is engaged in generation of power. Through hydel, thermal, wind sources generation of power is done. They construct the necessary projects for the generation of power. Even it provides consultancy services to various companies on the activities like Operation and maintenance services, Feasibility studies / evaluation and the compilation of detailed project reports, Renovation, modernization and updating of hydro stations etc.
3.5 VISION, MISSION AND QUALITY POLICY VISION STATEMENT Ensuring energy security for Karnataka through diversified energy portfolio KPCL is committed to becoming a world class organization. To translate this commitment in to reality it uses a dynamic approach that adopts three driving forces Build-in-efficiency, cost effectiveness and ensure that progress is in harmony with environment.
MISSION STATEMENT The mission of KPCL is to maximize Power Generation by: Identifying and developing opportunities in power generation Establishing and operating power plants Constant up gradation of technical competence and systems, developing human resources capabilities of empowerment are the ways to achieve these objectives. KPCL seeks to be a world class organization emphasizing efficiency, cost effectiveness and harmony with environment.
QUALITY POLICY Implementation of quality management system Continual process and product performance Adherence to committed delivery schedule Constant up-gradation of technical competence and system. Review and continual improvement
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
24
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
3.6 PRODUCT/SERVICES PROFILE The KPCL is set up for the power generation. Even it undertakes Consultancy Services on feasible study of the projects.
TYPES OF ELECTRICITY GENERATION The KPCL generates power through: Hydro Energy Thermal Energy Wind Energy Diesel Plant
3.1 TABLE.1 KPCL GENERATION DATA IN MILLION UNITS
GENERATION / YEAR THERMAL DIESEL + HYDRO + WIND +SOLAR TOTAL
2009-10 13263 12757 26020
2008-09 11717 13363 25080
2007-08 10876 14737 25613
2006-05 11484 15151 26635
2005-04 9165 10724 19889
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
25
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
3.1 GRAPH SHOWING KPCL GENERATION OF DATA IN MILLION UNITS
30000
KPCL Power Generation
M25000 I L 20000 L
15000
Thermal Diesel+Hydro+ Wind+Solar Total
U N 10000 I 5000 T S
0 2009-10 2008-09 2007-08 2006-07 2005-06
Year
(Sources collected by the annual report of the company) CONSULTANCY SERVICES KPCL today has the capability to undertake large scale power projects from concept to commissioning. It can also operate the plant on an EPC (Engineering Procurement and Construction) basis, with a host of exclusive auxiliary services.
KPCLs Consultancy and Engineering Services Division, an offshoot of its core competency, offers its clients a wide spectrum of consultancy inputs across the complete cycle of power project development. It has the expertise in analysis and design of structures using Finite Element package, micro station and in-house developed software packages for reservoir operation, Stability of Dams etc.
These include: Feasibility studies / evaluation and the compilation of detailed project reports Design, Engineering, procurement and construction services Consultancy on both Thermal and Hydel Power Stations, including handling of international competitive bids
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
26
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
Rehabilitation of dams in distress Renovation, modernization and updating of hydro stations Overall project and performance management.
CLIENT PORTFOLIO Supervision & Quality testing of concreting works at KSRTC/BMTC Bus Stations, Bangalore (M/s Karnataka Road Transport Corporation & Bangalore Metro Transport Corporation).Review of DPR, preparation of bid documents for fixing up EPC contractor, verification of designs and drawings, advisory supervision at site for 120 MW hydro project on Rummam river in West Bengal (M/s NTPC Hydro Limited)
Project review and assessment construction monitoring, performance testing and operation view of Malana Hydro Project at Himachal Pradesh -86 MW (M/s Malana Power Corporation Ltd., Himachal Pradesh)
AREA OF OPERATION The KPCL main motto of establishment is to electrify the Karnataka State. So the boundaries of KPCL are restricted only to Karnataka. KPCL currently has 34 dams & 25 power stations across the State with profiles that range from 0.35 MW to 1035 MW. The total installed capacity logged by KPCL is 5509 MW across a project canvas that covers expansions, renovations and upgrading of existing plants. Almatti dam power house Kali Hydel project. Kappadagudda wind farm Sharavathi Hydel project Varahi power station Raichur thermal power station Bellary thermal power station Bidadi combined cycle power station
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
27
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
3.7 AREA OF OPERATIONS OF KPCL
Ownership Pattern KPCL was the first power generating company to be registered under the Companies Act 1956. It came into existence on 20th July 1970 with an authorized capital of Rs.56 crores entirely contributed by the Government of Karnataka. The Chairman of the Company will be the Honorable Chief Minister of Karnataka.
Authorized capital: This is the major type of capital secured by KPCL. At present, it is having Rs. 7,432 Million on which equity shares of Rs. 1,000 each. Authorized capital of the organization is 1, 15, 00,000 equity shares of Rs. 1,000 each. Being a government body, all the shares are owned by government of Karnataka.
The chief minister himself is the chairman of Karnataka Power Corporation limited. The managing director and other government nominee director are senior IAS officers
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
28
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
besides being senior technocrats with proven record. Under the managing director are the other chief executives, directors, engineers etc.
Karnataka Power Corporation today realizes that if one sits on the lid of progress they will be blown by it. The organization believes that competing for the future is competing for the opportunity shares with the current portfolio of core competencies. It today challenges the logic that public office is the last refuge of the incompetent. Change has become a way of life for this organization.
Competitors Information KPCL produces 59% of Electricity in Karnataka. As it is owned by State Government there is always a upper hand than rivalries. Karnataka is facing a shortage of power supply, so the government itself is encouraging the Private Players to invest in the power sector.
3.2 TABLE SHOWING INSTALLED CAPACITY & GENERATION AS ON 31 MARCH 2010 REGION INDIA KARNATAKA KPCL MEGA WATT 159968 10534 6000 MILLION UNITS 767846 50563 26020
3.3 TABLE SHOWING THE COMPETITORS INFORMATION Products Competitors Neyveli Lignite Reliance Power Corporation Larsen And
29
Hydro
Thermal Gas
Diesel
Wind
Solar
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
Turbo Talcher Power Corporation Oglethorpe Power Atria Power Corporation
INFRASTRUCTURE FACILITIES KPCL is a highly IT Savvy company among the all other public sector units in the state at large and power sector in particular and has the distinction of being the first state owned company in the power sector to have established SHAKTINET- a satellite based communication network through VSATs among all its power stations and Bangalore.
Local Area Networks have been established at all Project locations and about 800 officials have been wired to corporate office with reliable VSAT (Very Small Aperture Thermal) back bone. All the activities of the corporation are computerized and KPCL has the unique distinction among power utilities of establishing voice and data communication between its projects and Bangalore through the new generation. The computer services department of KPCL with fully dedicated engineers and software professionals has developed and implemented all the software required for its business activities and is geared to offer consultancy services in the field of software development and networking. Comfortable infrastructure in its work place. Every division of the company is computerized. Adequate lighting facility. Well furnished with spaciously to get work fast in smooth manner. Separate office for each department.
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
30
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
NEW INITIATIVES: Established 2 MBPS MPLS circuits between Bangalore and two of its major projects via Raichur Thermal Power Station and Bellary Thermal power station for speedy communication Extension of the above facility to other project locations in the near future. Established Video Conferencing facility at Major project locations. Providing reliable communication facility at major project locations through Fiber Optic Cabling using state of the art technology.
ACHIEVEMENT/AWARDS: 2008-2009 KARNATAKA RATNA award by government of Karnataka for best overall performance. 2008 - first prize for unit-6 of RTPS - best safe power boiler from director of factories and boilers 2008-2009 - gold medal for varahi hydro electric project for early completion of the project 2007-2008 - bronze medal for gerusoppa dam power house third best performing Hydel station 2006-2007 - bronze medal for kodasalli dam power house(kali) third best performing Hydel station 2005-2006 - certificate for varahi hydro electric project - best performance in Hydel station 2004-2005 - certificate for Almatti dam power house unit 3 best execute. 2003-04 - Gold Shield & Certificate for Outstanding Performance - 88.23% PLF 2002-03 - Gold Shield & Certificate for Outstanding Performance -90.39% PLF 2000-01 and 2001-02 - Certificate & Silver Shield For Good Performance
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
31
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
2000, 2002 - Certificate for Reduction in Auxiliary Consumption 2001, 2002, 2003 Certificate for Reduction in Secondary Fuel Oil 1999-2000 Rs 22.82 lakhs for Reduction in Secondary Fuel, Oil, Auxiliary Consumption & High PLF of 81.52% 1998-99 Rs 6.65 lakhs for Cash Award & Bronze Medal for Achieving High PLF of 81.65%
FUTURE GROWTH AND PROSPECTS KPCL took the lead in mapping potential sites for non conventional energy sources such as mini hydel locations & windy spots. KPCL established pilot mini hydel & wind projects of 10.75 MW & 4.55MW respectively. This endeavor & the database created, has facilitate significant participation by independent power producers in their areas. Today capacity of over 186MW in mini hydel & 258MW of wind projects has been possible in Karnataka.
The Karnataka government has initiated reforms package in the power sector to improve viability & customer standards. The appointed of an independent regulator to user in greater transparency, efficiency & accountability in the working of power utilities like KPCL. KPCL recognizes the changing environment as part of global movement & has geared itself to the market driven & customer friendly, meeting he expectation of all stake holders.
KPCL consultancy and engineering services division, an offshoot of its core competency, offers its clients a wide spectrum of consultancy inputs across the complete cycle of power project development. It has the expertise in analysis and design of structures using STADPRO- 2006, NISA finite element package, AUTOCAD -2006, micro station and in-house developed software packages for reservoir operation stability of dams etc. Feasibility studies/ evaluation & the compilation of detailed projects reports
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
32
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
Design, engineering, procurement and construction services Consultancy on both thermal and Hydel power stations, including handling of internal competitive bids Project management from project scheduling to preparation of final invoice and certification. Operation and maintenance Renovation, modernization and updating of hydro station Overall project and performance management COMPETITORS:
The major competitors of KPCL: National Thermal Power Corporation Naively Lignite corporation Reliance Energy TATA Power Suzlon Energy Torrent Power Jindal Thermal Essar Power
INFRASTRUCTURAL FACILITY:
KPCL Head office is situated at No.82, Shakti Bhavan, and Race Course Road, Bangalore. KPCL has build many Hospitals, Residential Quarters, Apartments, Schools, Jr. College, Degree College, Clubs, Swimming pools, Temples, Gardens etc. for the benefits of its employees in various concerned project areas.
IT INFRASTRUCTURE
KPCL is a highly IT Savvy company among the public sector units in the state at large and power sector in particular and has the distinction of being the first state owned company in the power sector to have established SHAKTINET- a satellite
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
33
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
based communication network through VSATs among all its power stations and Bangalore. Local Area Networks have been established at all Project locations and about 800 officials have been wired to corporate office with reliable VSAT back bone. All the activities of the corporation are computerized and KPCL has the unique distinction among power utilities of establishing voice and data communication between its projects and Bangalore through the new generation DAMA V-SATS on KPTCLs "VIDYUTNET". The computer services department of KPCL with fully dedicated engineers and software professionals has developed and implemented all the software required for its business activities and is geared to offer consultancy services in the field of software development and networking. Some of the software developed in-house are:
Fuel Management system Human resource Information System Cash and Compilation Management system Establishment Integrated Inventory Management System Public Deposit System Generation Management System Billing software for Bellary Thermal power station Medicine Procurement system
NEW INITIATIVES:
Established 2 MBPS MPLS circuits between Bangalore and two of its major projects viz Raichur Thermal Power Station and Bellary Thermal power station for speedy communication.
Extension of the above facility to other project locations in the near future. Established Video Conferencing facility at Major project locations. Exploring possibilities of establishing SCADA facility at corporate office, Bangalore for real time data monitoring.
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
34
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
STRUCTURE OF KPCL
CHAIRMAN
BOARD OF DIRECTORS
MANAGING DIRECTOR
Technical Director
Finance Director
HR Director
Internal Audit
E.D G.M. (F) G.M (A)
(DY. GM HR)
G.M (I.A)
C.E
DY.G.M (F)
DY.G.M.(A)
A.G.M (HR1) DY.G.M
S.E
A.G.M (F)
A.G.M (A)
P.O (HR2)
A.G.M E.E A.O A.O J.P.O
A.E.E
A.A.O
A.A.O
S.A
A.O
A.E.
S.E.
S.A
A.A.O
J.E.
A S.A
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
35
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
E.D: Executive Director C.E: Chief Engineer Manager S.E: Senior Engineer E.E: Executive Engineer A.E.E: Assistant Executive Engineer A.E: Assistant Engineer J.E: Junior Engineer J.P.O: Junior Personal Office
G.M (F):General Manager Finance Dy.G.M: Deputy General
A.G.M: Assistant General A.O: Accounts Officer S.A: Senior Assistant A: Assistant P.O: Personal Officer
3.8 FINANCE DEPARTMENT
FINANCE DEPARTMENT CHART
Director of Finance
Tariffs and Billings Chief Finance manager Budgeting Chief Accounts Manager
Cash management
Compilation
Sales Tax
PF/GPF
Establishment Section
3.8 FINANCE DEPARTMENT: Finance is the life blood of all industry. The same applies to KPCL, much of the funds are self generated by the sale of power from KPCL, rising of equity capital, debenture capital, public deposits and also term loans from other financial institutions. The organisation though being a government of Karnataka Enterprises does not rely on any of the funds/ grants from the government treasury. Chief Finance Manager who is under the direct control
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
36
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
of Finance Director Heads, finance department in KPCL next in the order are Senior Executive, Divisional Officers and Account Officers followed by Senior Assistants and Assistants. Budgetary activities are centralized in this department. It consolidates all the activities of budget, budget estimation activity and the actual budget will be analyzed by each department.
TARIFFS AND BILLING SYSTEM The main function of tariff and billing section is to fix traffic for hydel, thermal and wind power station as per guidelines of ministry of government of India and Karnataka Electricity Regulatory Commission (KERC) and guidelines prescribed by state and central government authorities.
BUDGETING SECTION Budgeting is the blue print of future needs of company, budget refers to forecast of future need. KPCL involves 2 types of budget: 1. Revenue Budget 2. Cash Budget
REVENUE BUDGET INVOLVES Establishment & General Expenses Operation & Maintenance Fuel & Chemicals Royalty Financial Charges Depreciation
CASH BUDGET is helpful in estimating cash requirement, planning short term financing and scheduling payments in connection with capital expenditure project, purchase planning of materials. CASH MANAGEMENT SECTION Cash is the life blood of a business enterprise. Hence the finance manager should establish reliable forecasting and reporting system improve cash collections and
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
37
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
disbursement and achieve optional conservation and utilization of funds. KPCL prepares daily cash reports. In daily cash reports they prepare all the receipt and payments, they have made in a day. In this department cash management officers have the responsibility to maintain all the cash reports comes under project execution.
COMPILATION SECTION In this section they prepare a consolidated Balance sheet and Profit & Loss account. KPCL have various power stations and each of them prepare a Profit and Loss account and Balance sheet and send it to the Head Office. In Head Office every month Accounts department prepares the consolidated reports.
SALES TAX SECTION Every business organisation is liable to pay tax either through direct tax or through indirect tax, which is also mandatory to KPCL. In this section KPCL prepares monthly sales tax based on monthly return statement. There are 3 types of tax which is paid by KPCL, they are: 1. Karnataka Sales Tax [KST] 2. Central Sales Tax [CST] 3. Karnataka Tax an Entry of Goods.[KTEG]
BILLING SECTION The main function of billing section is, payment of all expenditure incurred for executing the project. There are different types of bills, They are: 1. Supplies bills 2. Workers bills 3. Contractors bills. They also prepare the accounts comes under the payment of bills. There are 2 heads of accounts which includes all these bills.
HEADS OF ACCOUNTS: I. II. Revenue Head Capital Head
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
38
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
REVENUE HEAD: it includes preparing Advertisement bills Telephone bills Printing & Stationery bills
CAPITAL HEAD: It includes preparing Machine bills Furniture bills Land & Building bills
ESTABLISHMENT SECTION: It gives some benefits to employees and taking the responsibility of promoting the welfare of employees. Functions of the Establishment Section are: Disbursement of salary to employees Housing Allowances Pension Reimbursement of Medical Expenses Other Establishment Expenses
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
39
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
CHAPTER IV
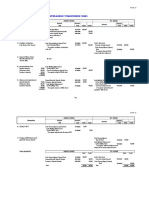
ANALYSIS AND INTERPRETATION OF DATA The analysis of data includes analysis of financial statements of firm using ratios and trend analysis as a tools and techniques. The financial analysis is to classify the data in simple form given in financial statements and to compare with each other to find out the strengths and weaknesses of the business and to take the decision by the finance managers. This chapter includes various ratios which analyses the firms profitability, solvencies etc and trend analysis of financial statements of .KPCL to analyze change in profits, turnover, assets, liabilities and comparing them with one another using base year data. The trend of KPCL is calculated using financial elements of Balance Sheets & Profit & Loss accounts and having 2006-07data as a base year. 4.1 TABLE SHOWING CURRENT RATIO (Rs. 000) CURRENT RATIO = CURRENT ASSETS \ CURRENT LIABILITIES
PARTICULARS CURRENT ASSETS CURRENT LIABILITIES CURRENT RATIO
2006-2007 33819087 9092055
2007-2008 35507765 8192262
2008-2009 54672179 10373311
2009-2010 65265078 8592033
3.71
4.33
5.27
7.59
ANALYSIS AND INTERPRETATION: The ideal or standard current ratio is 2:1. The current year ratio is 7.59 which is higher than previous year KPCL has shown very good performance in terms of the current ratio as it has been increasing year by year which is a good sing. In the year 2009 2010 the company current ratio is very high which will have an adverse impact on the profitability of organization. Very high current ratio is not desirable it means less efficient use of funds. High current ratio means excessive dependence on long term source of funds.
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
40
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
4.1 GRAPH SHOWING THE CURRENT ASSETS AND LIABILITIES
70000000 60000000 50000000 40000000 30000000 20000000 10000000 0 2006-2007 2007-2008 2008-2009 9092055 8192262 10373311
65265078 54672179 CURRENT ASSETS
33819087
35507765 CURRENT LIABILITIES
8592033
Linear (CURRENT ASSETS)
2009-2010
4.1a GRAPH SHOWING CURRENT RATIO
CURRENT RATIO
8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 2006-2007 2007-2008 2008-2009 2009-2010
CURRE NT RATIO
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
41
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
QUICK RATIO: QUICK RATIO OR ACID TEST RATIO = Quick assets = current assets-inventories Quick liabilities = current liabilities- bank overdraft-cash credit 4.2 TABLE SHOWING QUICK RATIO (Rs. 000) Quick assets/Quick liability
PARTICULARS 2006-2007 QUICK ASSETS QUICK LIABILITIES QUICK RATIO 3.46 9092055 31416318
2007-2008 33212554
2008-2009 49811595
2009-2010 61909888
8192262
10373311
8592033
4.05
4.80
7.21
ANALYSIS AND INTRPRETATION: The ideal quick ratio is 1:1. The quick ratio for the KPCL is increasing from year to year. In the year 2009-2010 it is 7.21 which are far above ideal standard. It has increased by 2.41from the last year. This ratio indicates financial soundness of the firm if the ratio above the standard. This ratio reflects the financial soundness of the firm in terms liquidity.
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
42
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
4.2 GRAPH SHOWING QUICK ASSET AND QUICK LIABILITIES
70000000 61909888 60000000 50000000 40000000 31416318 30000000 20000000 10000000 0 2006-2007 2007-2008 2008-2009 2009-2010 9092055 8192262 10373311 8592033 Linear (QUICK ASSETS) 33212554 QUICK LIABILITIES 49811595 QUICK ASSETS
4.2a GRAPH SHOWING QUICK RATIO:
QUICK RATIO
8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 2006-2007 2007-2008 2008-2009 2009-2010 QUICK RATIO
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
43
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
4.3 TABLE SHOWING SHAREHOLDER EQUITY AND CAPITAL EMPLOYEE (Rs. 000):
EQUITY RATIO = Shareholder equity\ Total capital employed
PARTICULARS SHAREHOLDER EQUITY CAPITAL EMPLOYED EQUITY RATIO
2006-07 29253546 75615056 0.39
2007-08 31139600 83015026 0.38
2008-09 38738632 107702544 0.36
2009-10 47810194 125766678 0.38
ANALYSES AND INTERPRETATION There has been a rise in the number of equity share of KPCL from the year 2008-2009 which is a very good sign for investors and creditors as it implies minimization of risk. The equity ratio of the company is declining from the year to year. In the year 2009- 2010 it is 0.38.
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
44
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
4.3 GRAPH SHOWING SHAREHOLDER EQUITY AND CAPITAL EMPLOYEE
140000000 120000000 100000000 80000000 60000000 40000000 20000000 0 2006-07 2007-08 2008-09 29253546 31139600 38738632 75615056 83015026 107702544
125766678
SHAREHOLDE R EQUITY
CAPITAL EMPLOYED
47810194
Linear (SHAREHOLD ER EQUITY)
2009-10
Linear (CAPITAL EMPLOYED)
4.3a TABLE SHOWING EQUITY RATIO
EQUITY RATIO
0.395 0.39 0.385 0.38 0.375 0.37 0.365 0.36 0.355 0.35 0.345 0.34 2006-2007 2007-2008 2008-2009 2009-2010 EQUITY RATIO
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
45
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
4.4 TABLE SHOWING DEBT RATIO (Rs. 000):
DEBT RATIO =
Total debt\ Capital employed 2007-08 49832132 83015026 2008-09 66326949 107702544 2009-10 73819763 125766678
PARTICULARS 2006-07 TOTAL DEBT CAPITAL EMPLOYED DEBT EQUITY RATIO 0.44 33425678 75615056
0.60
0.62
0.59
ANALYSIS INTERPRETATION:
The debt ratio of the company increasing from the 2006-2007 but in the year 20092010 there has been a decline by 0.03 the debt ratio in the first three years is increasing which means more of debt was being used for financing the operation. This implies that more of interest charges have to be paid by the firm. The decline in the ratio is due to more of capital being employed in comparison to usage of debt funds. The company is using internal source of financing its operation.
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
46
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
4.4 GRAPH SHOWING TOTAL DEBT AND CAPITAL EMPLOYED
140000000 120000000 100000000 80000000 60000000 40000000 20000000 0 2006-07 2007-08 2008-09 33425678 75615056 83015026 66326949 49832132 107702544
125766678
TOTAL DEBT
73819763
CAPITAL EMPLOYE D Linear (TOTAL DEBT) Linear (CAPITAL EMPLOYE D)
2009-10
4.4a GRAPH SHOWING DEBT RATIO:
DEBT RATIO
0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 2006-2007 2007-2008 2008-2009 2009-2010 DEBT EQUITY RATIO
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
47
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
4.5 TABLE SHOWING DEBT TO EQUITY RATIO (Rs. 000) DEBT TO EQUITY RATIO = Debt preferred long term\Shareholders equity
PARTICULARS DEBT
2006-07 33425678
2007-08 49832132 31139600
2008-09 66326949 38738632
2009-10 73819763 47810194
SHAREHOLDERS 29253546 EQUITY DEBT TO EQUITY 1.14 RATIO
1.60
1.71
1.54
ANALYSIS AND INTERPRETATION: The company debt to equity ratio is decreasing after year. Debt equity ratio is the indicator of leverage. This ratio should be less. Higher the ratio indicates less cushion for creditors and ability of the firm to absorb future losses of income and capital. In the year 2009-2010 the ratio is 1.54 which has decreased by 0.17 from the creditors point of view this ratio is satisfactory as every year the ratio is more than ideal 2:3 but from the shareholders point of view it is not satisfactory except for the year 2009-2010 in which it is 1.54. The company should try to keep this ratio up in coming years. The company should try to reduce this ratio as this will increase the confidence of the investors. A low ratio is generally viewed as favorable from long term creditors point of view. Low ratio may be taken as quite unsatisfactory by the shareholders because they find neglected opportunity for using low cost outsiders fund to acquire fixed assets that could earn a high return. Keeping in the view the interest of both(shareholders and long term creditors).
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
48
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
4.5 GRAPH SHOWING SHAREHOLDERS EQUITY AND DEBT
90000000 80000000 70000000 60000000 50000000 40000000 30000000 20000000 10000000 0 2006-07 2007-08 2008-09 2009-10 Linear (SHAREHOLDE RS EQUITY) 33425678 29253546 49832132 38738632 31139600 Linear (DEBT) 47810194 66326949 SHAREHOLDER S EQUITY DEBT 73819763
4.5a GRAPH SHOWING DEBT TO EQUITY RATIO SHAREHOLDERS EQUITY
60000000 50000000 40000000 30000000 20000000 10000000 0 2006-2007 2007-2008 2008-2009 2009-2010 SHAREHO LDERS EQUITY
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
49
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
4.6 TABLE SHOWING FIXED ASSET TO LONG TERM FUND (Rs. 000)
FIXED ASSETS TO LONG TERM FUND = Fixed Asset\ Long Term Fund
PARTICULARS
2006 - 2007
2007 - 2008
2008 - 2009
2009-2010
FIXED ASSETS
54899996
55614923
63435127
68999929
LONG TERM FUND FIXED ASSETS TO LONG TERM FUND RATIO
48666588
49832132
66326949
73819763
1.12
1.11
0.96
0.93
ANALYSIS & INTERPRETATION: This ratio should be less than 1. In KPCL this ratio has been declining continuously which indicates that the company is now reducing the use or method of financing fixed assets through the short term funds. In the year 2006 2007 the ratio is 1.12 which has come down to 0.93 in 2009 2010. The high ratio in the initial years may be due to expansion purpose in which short term funds were utilized.
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
50
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
4.6 GPAPH SHOWING FIXED ASSETS AND LONG TERM FUNDS
80000000 70000000 60000000 50000000 40000000 30000000 20000000 10000000 0 2006 - 2007 2007 - 2008 2008 - 2009 54899996 55614923 49832132 48666588 66326949 63435127
73819763 68999929
FIXED ASSETS
LONG TERM FUND
Linear (FIXED ASSETS ) Linear (LONG TERM FUND )
2009-2010
4.6a GRAPH SHOWING FIXED ASSET TO LONG TERM FUND RATIO:
FIXED ASSETS TO LONG TERM FUND RATIO
1.2 1 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 2006-2007 2007-2008 2008-2009 2009-2010 FIXED ASSETS TO LONG TERM FUND RATIO
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
51
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
4.7. TABLE SHOWING POPRIETARY RATIO (Rs. 000)
PROPRIETARY RATIO = Proprietary Fund\Total Assets
PARTICULAR PROPRIETARY FUND TOTAL ASSETS PROPRIETARY FUND TO TOTAL ASSETS RATIO
2006 - 2007 75615056
2007 - 2008 83015026
2008 - 2009 107702544
2009 -2010 125766678
80023454
91136188
117594656
134328507
0.93
0.91
0.92
0.94
ANALYSIS & INTERPRETATION: This ratio focuses the attention on the general financial strength of the business enterprise. The ideal ratio is 0:5:1. In every year the ratio is satisfactory. It is above the ideal norm. The ratio is highest in the year 2009-2010 which is 0.94. This indicates there is less risk to creditors in the event of losses their money wont be lost and they would be paid. Though there was a decline in the year 2007-2008 from 0.94 to 0.91 but since then it has been increasing steadily. The company should try to improve this more and more.
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
52
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
4.7 GRAPH SHOWING PROPRIETARY FUND AND TOTAL ASSETS:
160000000 140000000 120000000 100000000 80023454 80000000 60000000 40000000 20000000 0 2006 - 2007 2007 - 2008 2008 - 2009 2009 -2010 Linear (TOTAL ASSETS ) Linear (PROPRIETA RY FUND ) 91136188 117594656 TOTAL ASSETS 134328507 PROPRIETAR Y FUND
4.7a GRAPH SHOWING PROPRIETARY RATIO:
PROPRIETARY FUND TO TOTAL ASSETS RATIO
0.945 0.94 0.935 0.93 0.925 0.92 0.915 0.91 0.905 0.9 0.895 2006-2007 2007-2008 2008-2009 2009-2010 PROPRIETARY FUND TO TOTAL ASSETS RATIO
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
53
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
4.8 TABLE SHOWING CAPITAL TURNOVER RATIO (Rs. 000):
CAPITAL TURNOVER RATIO =
Sales\Capital Employed
PARTICULARS SALES CAPITAL EMPLOYED
2006-07
2007-08
2008-09
2009-10 43972451
34338100 33448576 41478976
75615056 83015026 107702544 125766678 0.40 0.39 0.35
CAPITAL TURNOVER RATIO 0.45
ANALYSIS & INTERPRETATION: The higher the ratio, the more efficient the utilization of owners and long term creditors fund. This ratio indicates the firm ability of generating sales per rupee of long term investments. As per the graph the capital turnover ratio of the company has been decreasing year after year. From 0.45 in 2006 -2007 this ratio is now 0.35 in 2009 - 2010 which indicates that the company should try to convert the debtors and receivables into cash very frequently so that the working capital cycle is not stagnated. It is advised to the company to improve this ratio.
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
54
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
4.8 GRAPH SHOWING SALES AND CAPITAL EMPLOYED:
140000000 125766678 120000000 100000000 83015026 80000000 60000000 41478976 40000000 20000000 0 2006-07 2007-08 2008-09 2009-10 Linear (CAPITAL EMPLOYED ) 34338100 33448576 43972451 Linear (SALES ) 75615056 CAPITAL EMPLOYED 107702544 SALES
4.8a GRAPH SHOWING CAPITAL TURNOVER RATIO
CAPITAL TURNOVER RATIO
0.5 0.45 0.4 0.35 0.3 0.25 0.2 0.15 0.1 0.05 0 2006-2007 2007-2008 2008-2009 2009-2010
CAPITAL TURNOVER RATIO
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
55
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
4.9 TABLE SHOWING FIXED ASSETS TURNOVER RATIO (Rs. 000)
FIXED ASSETS TURNOVER RATIO = Sales\Capital Assets
PARTICULARS SALES CAPITAL ASSETS ASSETS TURNOVER RATIO
2006-07
2007-08
2008-09
2009-10 43972451 68999929 0.64
34338100 33448576 41478976 54899996 55614923 63435127 0.62 0.60 0.65
ANALYSIS & INTERPRETATION:
A high assets turnover ratio indicates more efficient utilization of fixed assets in generating sales. As per the graph there was a decline of 0.02 in the year 2007-2008. From that year onwards there is continuous increase in the ratio. In 2009-2010 the ratio is 0.64 and indicates that all the assets are being effectively utilized.
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
56
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
4.9 GRAPH SHOWING SALES AND CAPITAL ASSETS:
80000000 70000000 60000000 50000000 41478976 40000000 30000000 20000000 10000000 0 2006-07 2007-08 2008-09 2009-10 34338100 33448576 Linear (SALES ) 54899996 55614923 43972451 CAPITAL ASSETS 68999929 63435127 SALES
Linear (CAPITAL ASSETS )
4.9a GRAPH SHOWING FIXED ASSETS TURNOVER RATIO
FIXED ASSETS TURNOVER RATIO
0.66 0.65 0.64 0.63 0.62 0.61 0.6 0.59 0.58 0.57 2006-2007 2007-2008 2008-2009 2009-2010 ASSETS TURNOVER RATIO
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
57
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
4.10 TABEL SHOWING CAPITAL TURNOVER RATIO:
WORKING CAPITAL TURNOVER = Sales\Working Capital
PARTICULAR SALES WORKING CAPITAL WORKING CAPITAL TURNOVER RATIO
2006-2007 34338100
2007-2008 33448576
2008-2009 41478976
2009-2010 43972451
24727032
27315503
44222350
56673045
1.38
1.22
0.94
0.78
ANALYSIS & INTERPRETATION:
Working capital turnover ratio indicates the efficiency and inefficiency of the management in the utilization of working capital. Higher the working capital turnover ratio indicates the efficiency and low turnover ratio indicates the inefficiency of the management. There has been a continuous decline in this ratio which is not a good sign and which shows lag in converting of receivables into cash the company should take immediate steps to improve this else in the long run this will have a bad impact on the firm. The ratio of the company has come down to 0.78 in 2009 -2010 from 1.38 in 2006-2007. The company should try to improve this ratio
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
58
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
4.10 GRAPH SHOWING SALES AND WORKING CAPITAL:
60000000 50000000 40000000 30000000 20000000 10000000 0 2006-2007 2007-2008 2008-2009
56673045
SALES
44222350 43972451 41478976 34338100 24727032 33448576 27315503 Linear (SALES ) WORKING CAPITAL
2009-2010
Linear (WORKING CAPITAL)
4.10a GRAPH SHOWING WORKING CAPITAL TURNOVER RATIO:
WORKING CAPITAL TURNOVER RATIO
1.6 1.4 1.2 1 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 2006-2007 2007-2008 2008-2009 2009-2010 WORKING CAPITAL TURNOVER RATIO
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
59
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
4.11 TABLE SHOWING INVENTORY TURNOVER RATIO: (Rs. 000)
INVENTORY TURNOVER RATIO= Sales\Average inventory
PARTICULAR SALES AVERAGE INVENTORY INVENTORY TURNOVER RATIO
20062007 34338100 1812956 13.42
20072008 33448576 2348990 14.24
20082009 41478976 3577898 11.59
20092010 43972451 4107887 10.70
ANALYSIS & INTERPRETATION: The inventory turnover ratio of KPCL has been increasing from year to year. It has increased to 10.70 in 2009 - 2010 from 11.59 in 2008-2009. This indicates that there is no stoppage iii the generation to distribution stage. This helps in increasing sales. The company should try to keep this performance.
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
60
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
4.11 GRAPH SHOWING SALES AND AVERAGE INVENTORY:
50000000 45000000 40000000 35000000 30000000 25000000 20000000 15000000 10000000 5000000 0 2006-2007 2007-2008 2008- 2009 2009- 2010 1812956 2348990 3577898 4107887 34338100 33448576 43972451 41478976
SALES
AVERAGE INVENTOR Y Linear (SALES)
Linear (AVERAGE INVENTOR Y)
4.11a GRAPH SHOWING INVENTORY TURNOVER RATIO:
INVENTORY TURNOVER RATIO
16 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 2006-2007 2007-2008 2008-2009 2009-2010 INVENTORY TURNOVER RATIO
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
61
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
4.12 TABLE SHOWING DEBTORS TURNOVER RATIO: (Rs. 000)
PARTICULARS SALES AVERAGE ACCOUNTS RECEIVABLE DEBTORS TURNOVER RATIO
2006-2007 34338100
2007-2008 33448576
2008-2009 41478976
2009-2010 43972451
21932835
27583305
35040904
46464357
1.57
1.21
1.18
0.95
ANALYSIS & INTERPRETATION:
This ratio indicates the speed with which the receivables are collected from the debtors. It affects the liquidity position of the company. As per the graph those has been a decline in this ratio froth 1.18 in 2008 - 2009 to 0.95 in 2009 - 2010 which indicates that there has been a delay in conversion or collection. The company should try to collect the dues as frequently as possible so that it doesnt affect the liquidity. Else the company has to resort to external source of financing for financing its operations.
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
62
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
4.12 GRAPH SHOWING SALES AND AVERAGE ACCOUNTS RECEIVABLE:
50000000 45000000 40000000 35000000 30000000 25000000 20000000 15000000 10000000 5000000 0 2006-2007 2007-2008 2008-2009 21932835 34338100 33448576 27583305 41478976 35040904
46464357 43972451
SALES
AVERAGE ACCOUNTS RECEIVABLE Linear (SALES )
2009-2010
Linear (AVERAGE ACCOUNTS RECEIVABLE )
4.12a GRAPH SHOWING DEBTORS TURNOVER RATIO:
DEBTORS TURNOVER RATIO
1.8 1.6 1.4 1.2 1 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 2006-2007 2007-2008 2008-2009 2009-2010 DEBTORS TURNOVER RATIO
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
63
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
4.13 TABLE SHOWING RETURN ON EQUITY RATIO: (Rs. 000)
ROE = Profit after taxes /Net Worth
PARTICULARS
2006-07
2007-08 2060000
2008-09 2772948
2009-10 4362472
PROFITS AFTER TAX 1980000 NET WORTH ROE RATIO
75615056 83015026 107702544 146303465 0.03 0.02 0.03 0.03
ANALYSIS & INTERPRETATION: The ROE Ratio has been increasing and decreasing for the company. It has decreased from 0.03 in 2006-2007 to 0.02 in 2007 2008. Again it increased to 0.03 in [year 2008-2009. In the year 2009-2010 this has constant.
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
64
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
4.13. GRAPH SHOWING PAT & NET WORTH:
160000000 140000000 120000000 100000000 80000000 60000000 40000000 20000000 0 2006-07 2007-08 2008-09 1980000 2060000 2772948 75615056 83015026 107702544
146303465
PROFITS AFTER TAX
NET WORTH
Linear (PROFITS AFTER TAX ) 4362472 2009-10
Linear (NET WORTH )
4.13a GRAPH SHOWING ROE RATIO:
ROE RATIO
0.035 0.03 0.025 0.02 0.015 0.01 0.005 0 2006-07 2007-08 2008-09 2009-10 ROE RATIO
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
65
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
II. PROFITABILITY RATIOS BASED ON ASSETS/INVESTMENTS: 4.14 TABLE SHOWING ROA RATIO: (Rs. 000)
ROA= Net Profits after taxes\Average total assets
PARTICULAR NET PAT
2006-07 1980000
2007-08 2060000
2008-09 2770000
2009-10 2890000
AVERAGE TOTAL ASSETS
40011727
45568094
59022144
67422677
RATIO
0.05
0.10
0.06
0.04
ANALYSIS & INTERPRETATION: This ratio should be higher. The higher the ratio the more is the relationship between net profits- and assets employed to earn that profit. This ratio has been declining since the year 2008-2009 i.e. from 0.06 to 0.04 in 2009-2010. The company should try to improve this ratio so that the assets are more efficiently used for earning profits.
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
66
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
4.14 GRAPH SHOWING NET PAT AND AVERAGE TOTAL ASSETS:
80000000 70000000 60000000 50000000 40011727 40000000 30000000 20000000 10000000 1980000 0 2006-07 2007-08 2008-09 2009-10 2060000 45568094 59022144 67422677
NET PAT
AVERAGE TOTAL ASSETS
Linear (NET PAT )
2770000
2890000
Linear (AVERAGE TOTAL ASSETS )
4.14a GRAPH SHOWING ROA RATIO:
ROA
0.12 0.1 0.08 0.06 0.04 0.02 0 2006-07 2007-08 2008-09 2009-10
ROA
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
67
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
III. PROFITABILITY RATIOS BASED ON SALES OF THE FIRM: 4.15. TABLE SHOWING OPERATING PROFIT RATIO: (Rs. 000)
OPERATING PROFIT RATIO = Operating Profit \ Sales X 100
PARTICULARS
2006-07
2007-08
2008-09
2009-10
OPERATING PROFIT
10150000
10270000
13406841
15923141
SALES RATIO
34338100 0.29
33448576 0.31
41478976 0.32
43972451 0.36
ANALYSTS & INTERPRETATION: The operating profit ratio of KPCL has been increasing from year to year. In the year 2009-2010 the ratio is 0.36 there-has been a continuous increasing trend which signifies that the company is not having a very good control over operations. The operating ratio in the KPCL is high. It indicates that the company is left with relatively less amount for meeting the fixed commitments. The low ratio is favorable for the company but the ratio is higher. Hence the company should work to reduce the operating ratio. The operating ratio of the company is high and not satisfactory as there is an effect of net profit by considering sales on it.
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
68
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
4.15 GRAPH SHOWING OPERATING PROFIT AND SALES:
50000000 45000000 40000000 35000000 30000000 25000000 20000000 15000000 10150000 10000000 5000000 0 2006-07 2007-08 2008-09 2009-10 Linear (SALES ) 10270000 13406841 15923141 Linear (OPERATIN G PROFIT ) 34338100 33448576 SALES 43972451 41478976 OPERATIN G PROFIT
4.15a. GRAPH SHOWING OPERATING PROFIT RATIO:
OPERATING PROFIT RATIO
0.4 0.35 0.3 0.25 0.2 0.15 0.1 0.05 0 2006-07 2007-08 2008-09 2009-10 OPERATING PROFIT RATIO
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
69
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
4.16 TABLE SHOWING NET PROFIT RATIO: (Rs.000)
NET PROFIT RATIO = Net Profit /Sales X 100
PARTICULARS
2006-07
2007-08
2008-09
2009-TO
NET PROFIT
1980000
2060000
2772948
4724362
SALES
34338100
33448576
41478976
43972451
RATIO
0.06
0.07
0.07
0.12
ANALYSIS & INTERPRETATION: This ratio indicates profit earned in terms of the sales. There has been a continuous increase in net profit ratio due to lower cost of production and efficiency in operation cost. There is a increasing in the net profit ratio of the company in the year 2009 2010.
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
70
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
4.16 GRAPH SHOWING NET PROFIT AND SALES:
50000000 45000000 40000000 35000000 30000000 25000000 20000000 15000000 10000000 5000000 0 2006-07 2007-08 2008-09 2009-TO 1980000 2060000 2772948 4724362 34338100 33448576 43972451 41478976
NET PROFIT
SALES
Linear (NET PROFIT )
Linear (SALES )
4. 16a GRAPH SHOWING NET PROFIT RATIO:
NET PROFIT RATIO
0.14 0.12 0.1 0.08 0.06 0.04 0.02 0 2006-07 2007-08 2008-09 2009-TO NET PROFIT RATIO
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
71
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
4.17 TABLES SHOWING TREND ANALYSIS OF BALANCE SHEET FOR THE YEARS 2006-2010 TAKING BASE YEAR AS 2006-2007
PARTICULARS I. SOURCES OF FUNDS 1. Shareholders' Funds 2. Loan Funds 3. Deferred Tax liability (Net) II. APPLICATION OF FUNDS 1. FIXED ASSETS 2. INVESTMENTS 3. Current Assets, Loans & Advances 4.CURRENT LIABILITIES 5. Miscellaneous expenditure
2006-07 in 000sRs
2007-08 in 000sRs
2008-09 in 000sRs
2009-10 in 000sRs
29253546 48666588 1888608
31139600 49832132 2043294
38738632 66326949 2636963
54829720 88627045 2846700
54899996 13500 33819087
77614923 13500 35507765
63358609 13500 54672179
64845709 16700 69982945
24727032 168214
23715503 71100
44298868 31567
58916830 32600
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
72
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
PARTICULARS I. SOURCES OF FUNDS 1. Shareholders' Funds 2. Loan Funds 3. Deferred Tax liability (Net) II. APPLICATION OF FUNDS 1. FIXED ASSETS 2. INVESTMENTS 3. Current Assets, Loans & Advances 4.CURRENT LIABILITIES 5. Miscellaneous expenditure
2006-07 in % 100 100 100
2007-08 in % 106 102 108
2008-09 in % 132 136 140
2009-10 in % 187 182 151
100 100 100
141 100 105
115 100 162
118 124 207
100 100
96 42
179 19
238 19
INTERPRETATIONS: 1. The companys balance sheet reveals that share holders net worth is increasing
from 2006 till now i.e. from 100 to 187 an increase in 87%. 2. The long term debt is there it was increasing continuously of 83% i.e. from 100 to 183 this shows that increase in borrowings of company for new projects. 3. The current liabilities are slightly fluctuating it decreased from100 to 96 in 2008 and then again regained which shows that company is relying on its suppliers for raw materials on credit. 4. The fixed assets are reducing year to year from 2008 onwards showing more fluctuations i.e. it reduced from 141 to 118%. 5. The current assets are increasing year by year i.e. increased from 100-207% an increase in 107%.
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
73
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
4.17 GRAPH SHOWING TREND ANALYSIS OF BALANCE SHEET FOR THE YEARS 2006-2010 TAKING BASE YEAR AS 2006-2007
250
200
150
2006-2007 in % 100 2007-2008 in % 2008-2009 in % 2009-2010 in %
50
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
74
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
4.18 TABLE SHOWING TREND ANALYSIS OF PROFIT AND LOSS A\C FOR THE YEARS 2006-2010 TAKING BASE YEAR AS 2006-2007
PARTICULARS Sale of Energy NON OPERATING INCOME TOTAL INCOME : A RAW MATERIALS OOFICE AND ADMINISTRATION EXPENCES Depreciation TOTAL EXPENDITURE : B Profit for the year ( A - B ) LESS: Provision for Taxes PAT
2006-07 34338198 3165576
2007-08
2008-09
2009-10
33910360 41478976 43972451 2973151 2833774 4092926
37503774
36883511 44312750 48065377
17897503 13449060
17520833 25594312 26678713 10794344 11017089 10158063
2446634 33793198
2027435
3785516
3905411
30342613 40396917 40742187
3710576
6540897
3915833
7323190
442297
483696
1142885
2960718
3268279
6057201
2772948
4362472
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
75
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
PARTICULARS Sale of Energy NON OPERATING INCOME TOTAL INCOME : A RAW MATERIALS OOFICE AND ADMINISTRATION EXPENCES Depreciation TOTAL EXPENDITURE : B Profit for the year ( A - B ) LESS: Provision for Taxes PAT
2006-07 100 100
2007-08 2008-09 99 94 121 90
2009-10 128 129
100
98
118
128
100 100
98 80
143 82
149 76
100 100
83 90
155 120
159 121
100
176
106
197
100
109
258
699
100
185
85
133
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
76
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
INTERPRETATIONS: The above table depicts that Sales have been increase year to year, showing an increase in 28% i.e. from 100 to 128%. There is sharp increase in NOI of about 29% compared base year in the 2010 i.e. from 100-129%. Along with sales theres a simultaneous increase in total expenditure of the firm. Profits of the company shows a satisfactory growth and almost doubled in2010 when compared to base year 2007 but in 2009 it shows a big dip in profits of 70% i.e. from 179 to 106. Profit after tax also (PAT) shows high fluctuations it shows an increase in 85%, in 2008 but decrease in 100% in 2009 and theres a recovery of profits with 48%.
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
77
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
4.18 GRAPH SHOWING TREND ANALYSIS OF PROFIT AND LOSS A\C FOR THE YEARS 2006-2010 TAKING BASE YEAR AS 2006-2007
700
600
500
400
300 2006-07 2007-08 200 2008-09 2009-10 100
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
78
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
CHAPTER-5
FINDINGS AND SUGGESTIONS
5.1 FINDINGS:
1.
The KPCL Current ratio is higher than the ideal or standard current ratio is 2:1. It is increasing every year. It shows good financial position of company. The current year ratio is 7.59 which are higher than previous year KPCL has shown very good performance in terms of the current ratio.
2.
KPCL quick ratio has continuously shown an upward trend and the ideal quick ratio is 1:1. In the year 2009-2010 it is 7.21 which are far above ideal standard. It shows companys good liquidity position.
3.
From the equity ratio it can be seen that from the year 2009-2010 the proportion of owners equity is increasing, in the year 2009- 2010 it is 0.38. This is a very good sign as it lowers the degree of risk.
4.
The capital turnover ratio of the company has been decreasing year after year. From 0.45 in 2006 -2007 this ratio is now 0.35 in 2009 - 2010 which indicates that the company should try to convert the debtors and receivables into cash very frequently so that the working capital cycle is not stagnated.
5.
There is an increment in the fixed assets turnover ratio from the year 2008-09. It is good for the company as it indicates efficient utilization of fixed assets in generating sales.
6.
The ideal Proprietary ratio is 0:5:1. In every year the ratio is satisfactory. It is above the ideal norm. The ratio is highest in the year 2009-2010 which is 0.94.
7.
The debt ratio of the company increasing from the 2006-2007 but in the year 20092010 there has been a decline by 0.03 the debt ratio in the first three years is increasing.
8.
There was a decline in asset turnover ratio of 0.02 in the year 2007-2008. From that year onwards there is continuous increase in the ratio. In 2009-2010 the ratio is 0.64 and indicates that all the assets are being effectively utilized.
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
79
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
9.
The return on assets is decreasing from the year 2008-09 which shows under utilization of the current assets
10. The ROI of, the company is consistently been improving which shows the effectiveness of the company. 11. The net profit ratio has been increased year by year which is fair for the company but decreased in the year 2009-10 which is indication for the company to improve its performance. 12. The operating profit ratio of the company is high and satisfactory. 13. Earnings per share value are increasing year by year it shows profitability position to shareholder. 14. The power generation has been depended more on the rainfall and reservoir level and availability of fuel like coal and oil etc. So it tends to be fluctuating. 15. As the new projects are being constructed and power generation capacity of the stations are upgrading, give the way to more operation and maintenance expenses 16. KPCL took the lead in mapping potential sites for non conventional energy sources such as mini Hydel locations & windy spots. KPCL established pilot mini Hydel & wind projects of 10.75 MW & 4.55MW respectively.
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
80
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
5.2 SUGGESTIONS:
1. It is suggested to KPCL to continue the same with respect to the current ratio. 2. It is suggested to KPCL to improve the stock turnover ratio.
3. It is advised to KPCL to improve fixed asset ratio. 4. It is advisable to company go for factoring service for early and hassle free collections from different ESCOMs all over the state so that it will result in convert the debtors and receivables into cash very frequently so that the working capital cycle is not stagnated. 5. It is suggested to KPCL to increase its shareholders fund by issuing shares so that the returns expected by the total asset may increase as the fund may be invested to purchase the assets. 6. They must reduce the financial burden on investment of fixed assets by issuing more number of equity shares and should effectively utilize the fixed assets so that the ratio may increase. 7. It is suggested for KPCL to keep the same increasing trend in order to make its shareholders happy. 8. KPCL should plan while purchasing the assets about there returns so that it can move positive every upcoming year. 9. It is suggested to the company to keep the same with respect to net profit as it indicates the lower cost of production. 10. The MUDRA must increase its sales and have to reduce the cost of production so that it can earn more net profit. 11. It is suggested to the company to increase the investment for meeting the fixed commitments with respect to operating ratio. 12. It is suggested the company to maximize utilization of its fixed assets to overcome the problem of under utilization of resources & also it increases profit, by this the net profit to total asset ratio will increase.
13. Company has to pay tax regularly so that it will not burden the particular period in which it has paid the balance amount of tax.
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
81
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
14. KPCL depends largely in borrowing to finance its fixed assets. In future, the company should use its own earnings to reduce the burden of interest payments.
15. KPCL should also revise their old & tariff of Hydel and Thermal to increase their profitability. 16. Overall performance of company is good it only needs to maintain its status in future and also need to find room to improve.
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
82
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE AT KPCL
5.3 CONCLUSION:
On the basis of the study, we can conclude that the company has made distinctive profits for the past four years and performing well irrespective of the changing conditions and problems like, government regulations, uncertain monsoon rain, and non-realization of dues from ESCOMs etc., Moreover, the frequently changing governments and political conflicts become a threat to the smooth working of company. There is a huge gap between the demand and supply of electricity in the state and this excess demand is being balanced by importing power from other states. So the company has to plan out new plants in the state for achieving self-dependency in the power sector and also go for innovative techniques of producing more megawatts of power from the available resource.
CANARA BANK SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
83
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5782)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (72)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- SDASDDokument9 SeitenSDASDRocelle LAQUINoch keine Bewertungen
- Megaworld CanopyDokument6 SeitenMegaworld CanopyNanam ZaerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shekhar Biz ProfileDokument2 SeitenShekhar Biz ProfileshekharcNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Introduction To Hoshin Kanri, A.K.A. Strategic Goal Deployment - How To Use This Process To Deploy Your Strategic GoalsDokument6 SeitenAn Introduction To Hoshin Kanri, A.K.A. Strategic Goal Deployment - How To Use This Process To Deploy Your Strategic GoalsJairo Castro FlorianNoch keine Bewertungen
- TMForum - EtomDokument61 SeitenTMForum - EtomJosé EvangelistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eng301 Midterm MCQsDokument12 SeitenEng301 Midterm MCQsUsman AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- 15 G Form (Blank)Dokument2 Seiten15 G Form (Blank)nst27Noch keine Bewertungen
- Spyderco v. Classic Blades - ComplaintDokument75 SeitenSpyderco v. Classic Blades - ComplaintSarah BursteinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4a - Pre-Release Material For 2011Dokument6 Seiten4a - Pre-Release Material For 2011Ahmed HamzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3rd Module Consumer BehaviorDokument9 Seiten3rd Module Consumer BehaviorAnantha NagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communication Skills As On 26-10-09Dokument29 SeitenCommunication Skills As On 26-10-09Thakker NimeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acknowledgment Receipt - Loan AgreementDokument51 SeitenAcknowledgment Receipt - Loan AgreementFidelis AijouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paediatric Consumer Health in The Philippines PDFDokument4 SeitenPaediatric Consumer Health in The Philippines PDFMae SampangNoch keine Bewertungen
- CV Resume for Quality Assurance ChemistDokument3 SeitenCV Resume for Quality Assurance Chemistnvvsganesh1984Noch keine Bewertungen
- Asme BPVC BrochureDokument24 SeitenAsme BPVC BrochurekanchanabalajiNoch keine Bewertungen
- SHE Organogram 013Dokument6 SeitenSHE Organogram 013Saif Mohammad KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calf Fattening FeasibilityDokument19 SeitenCalf Fattening FeasibilityMuammad Sanwal100% (2)
- Korea Chocolate Market Report To 2021Dokument12 SeitenKorea Chocolate Market Report To 2021johnnyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 14-2-17 p2Dokument8 Seiten14-2-17 p2immadzaffNoch keine Bewertungen
- HR Practices of Marks and Spencer Selfri PDFDokument46 SeitenHR Practices of Marks and Spencer Selfri PDFbalach100% (1)
- Principles of Marketing Lesson 1Dokument59 SeitenPrinciples of Marketing Lesson 1Lorraine Sambile Arroyo67% (3)
- Sas 1-18Dokument165 SeitenSas 1-18btee2Noch keine Bewertungen
- EMI CalculatorDokument11 SeitenEMI CalculatorPrabhu RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agreements - HTML: Dassault Systemes Biovia Corp.Dokument5 SeitenAgreements - HTML: Dassault Systemes Biovia Corp.Joakin BahamondesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Media Gateway SoftswitchDokument10 SeitenMedia Gateway SoftswitchMahmoud Karimi0% (1)
- Harrison - The Peasant Mode of Production in The Work of AV ChayanovDokument14 SeitenHarrison - The Peasant Mode of Production in The Work of AV ChayanovAndrea LeónNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANNEX O of GAMDokument15 SeitenANNEX O of GAMKelvin CaldinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Date (Value Date) Narration Ref/Cheque No. Debit Credit BalanceDokument5 SeitenDate (Value Date) Narration Ref/Cheque No. Debit Credit BalanceanubhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AirwayBill 0NGKT15231058Dokument1 SeiteAirwayBill 0NGKT15231058halipzramlyzNoch keine Bewertungen
- МСА 2016-2017 частина 2Dokument644 SeitenМСА 2016-2017 частина 2Валентина ЖдановаNoch keine Bewertungen