Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Thesis With Margin
Hochgeladen von
Dada Malicsi LandichoOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Thesis With Margin
Hochgeladen von
Dada Malicsi LandichoCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
lyceum of the Philippines university cabrini
College of Allied Medicine Inc.
Maharlika St., Sto. Tomas, Batangas PAGE 1
SCHOOL OF NURSING
THE PERCEPTION OF THE RESIDENTS OF BARANGAY DARASA IN BASIC LIFE SUPPORT IMPLEMENTATION AND ITS RELATION TO THEIR COMPLIANCE
A Thesis Presented to The Faculty of the College of Nursing LPU- St. Cabrini College of Allied Medicine In Partial Fulfillment Of the Requirements for the Degree Bachelor of Science in Nursing
By: Aguinaldo, Arvin L. Alquizalas, April Ariane H. Angeles, Edwin C. Balancio, Amy Lou Joy R. Intal, Ma. Cecillia B
lyceum of the Philippines university cabrini
College of Allied Medicine Inc.
Maharlika St., Sto. Tomas, Batangas PAGE 2
SCHOOL OF NURSING
CHAPTER I THE PROBLEM AND ITS BACKGROUND Introduction Keeping every individuals safe is the top priority. People should learn how to protect themselves and their family inside the house and out. They should know what to do in an emergency, how to stock a first-aid kit, where to call for help, and more. Being prepared for an emergency on campus, at home, or when traveling in the wilderness is a must but people have to make sure that they have the proper training to safeguard themselves and others. People must have awareness of how to recognize and treat life-threatening emergencies, including cardiac arrest and choking for adults and children. There is also a must for them to learn to recognize the warning signs of heart attack and stroke in adults and breathing difficulties in children. However, to provide effective, life-saving first aid interventions requires instruction and practical training. This is especially true where it relates to potentially fatal illnesses and injuries, such as those that require cardiopulmonary resuscitation. CPR and an approved first aid education can help people prepare to handle a first aid emergency
lyceum of the Philippines university cabrini
College of Allied Medicine Inc.
Maharlika St., Sto. Tomas, Batangas PAGE 3
SCHOOL OF NURSING
First aid is the provision of initial care for an illness or injury. It is usually performed by non-expert, but trained personnel to a sick or injured person until definitive medical treatment can be accessed. It generally consists of a series of simple and in some cases, potentially life-saving techniques that an individual can be trained to perform with minimal equipment. Certain skills are considered essential to the provision of first aid and are taught ubiquitously. Particularly the "ABC"s of first aid, which focuses on critical life-saving intervention, must be rendered before treatment of less serious injuries. ABC stands for Airway, Breathing, and Circulation. Some organizations add a fourth step of "D" for Deadly bleeding or Defibrillation, while others consider this as part of the Circulation step. This kind of tool helps individuals in emergency situations and gives them the knowledge on how to cope with and intervene to such situations. Basic Life Support along with first aid can readily help prevent life threatening emergencies. And as nurses, it is our responsibility to help educate ourselves and the public about the proper application of Basic Life Support.
Statement of the Problem
lyceum of the Philippines university cabrini
College of Allied Medicine Inc.
Maharlika St., Sto. Tomas, Batangas PAGE 4
SCHOOL OF NURSING
This study aimed to determine the perception of the residents in Barangay Darasa, Tanauan City, Batangas with regards to Basic Life Support. Specifically, the study sought to answer the following questions: 1. What is the perception of the respondents about basic life support and its relation to their safety? 2. What is the profile of the following respondents according to their: 2.1 Age 2.2 Sex 2.3 Highest educational attainment 2.4 Civil status 3. What are the information needs of residents to be answered with regards to Basic Life Support? 4. Is there a significant relationship between the demographic profile and the perception of the residents of Barangay Darasa, Tanauan City, Batangas to Basic Life Support?
lyceum of the Philippines university cabrini
College of Allied Medicine Inc.
Maharlika St., Sto. Tomas, Batangas PAGE 5
SCHOOL OF NURSING
Statement of Hypotheses The researchers tested the null hypotheses based on the theory or literature. 1. There is a significant relationship between the perception and the level of compliance of the residents in basic life support in Barangay Darasa. 2. There is no significant relationship between the perception and the level of compliance of the residents in basic life support in Barangay Darasa.
Significance of the Study The findings of this study will be of great help to the following: The clients (individuals, families, groups, communities) who are the direct recipients of care and the most important reason for the existence of nursing profession will benefit directly through the improvement in their knowledge and skills about Basic Life Support brought about by the identification of the strengths and weaknesses of their knowledge and skills and feedback on the results of this study.
lyceum of the Philippines university cabrini
College of Allied Medicine Inc.
Maharlika St., Sto. Tomas, Batangas PAGE 6
SCHOOL OF NURSING
The results of this study will help reduce the work of health care providers insofar that clients will be taught about proper implication of Basic Life Support and through that, Health care providers can spend more time in caring for the most vulnerable patients and will further improve nursing care in terms of the risk factors and complications brought by the accidents. The Department of Health. Information on the performance of the residents with regards to Basic Life Support will serve as an addition to the baseline data for them to look into the needs of the people and provide the necessary source of motivation in gaining more knowledge and improve their skills. The value of networking in the utilization of health services can also be facilitated. The future Researchers. This will give them the opportunity to determine the information needs of the subjects (residents of Brgy Darasa) about the Basic Life Support and to find out the needs or requirements that must be achieved. The students of Lyceum of the Philippines University-St. Cabrini College of Allied Medicine. This study fosters an enhancement of knowledge, skills, and attitudes towards the implementation of Basic Life Support.
Definition of Terms Basic Life Support is the level of medical care which is used for patients with lifethreatening illnesses or injuries until the patient can be given full medical care at a hospital. It can be provided by trained medical personnel, including emergency medical technicians,
lyceum of the Philippines university cabrini
College of Allied Medicine Inc.
Maharlika St., Sto. Tomas, Batangas PAGE 7
SCHOOL OF NURSING
paramedics, and by laypersons who have received BLS training. BLS is generally used in the pre-hospital setting, and can be provided without medical equipment. Barangay Darasa A barangay situated more than 1Km from the public market of Tanauan, Batangas. It has a population of 14,805. Community A group of people living in the same locality Compliance Respondents willingness to follow Disaster is a natural or man-made (or technological) hazard resulting in an event of substantial extent causing significant physical damage or destruction, loss of life, or drastic change to the environment Emergency - is a situation that poses an immediate risk to health, life, property or environment. Middle Adult is a human being or living organism that is of relatively mature age (33-45 years old), typically associated with sexual maturity and the attainment of reproductive age. Perception the act or faculty of apprehending by means of the sense or the mind; cognition; understanding. Young Adult - an age group including persons from about 19 years to 32 years old
lyceum of the Philippines university cabrini
College of Allied Medicine Inc.
Maharlika St., Sto. Tomas, Batangas PAGE 8
SCHOOL OF NURSING
Scope and Delimitations The study focuses on the perception of the residents of Barangay Darasa in basic life support implementation and its relation to their compliance during accidents and lifethreatening situations. The respondents were young adults and middle adults who are 18 years old and above. They have been chosen because they are the ones who are very much able to intervene and perform the procedure in case of emergencies The researchers selected 25 respondents, divided equally to both age groups to assess their knowledge on providing BLS. This study was conducted only among the residents of Brgy. Darasa, Tanauan City, Batangas. Therefore, the result of the study may only be true for Barangay Darasa and its residents and may not be true on other Barangays and residents in Tanauan, Batangas or to other barangay of other municipalities in the Philippines. Lastly, the result of the study may only be reliable on the year the study was conducted and may no longer be in succeeding years.
lyceum of the Philippines university cabrini
College of Allied Medicine Inc.
Maharlika St., Sto. Tomas, Batangas PAGE 9
SCHOOL OF NURSING
CHAPTER II REVIEW OF LITERATURE Pre-hospital care is an essential part of the treatment process in many acute diseases and trauma. Pre-hospital care is usually classified into ALS- (advanced life support) and BLS-(basic life support) treatment levels according to the methods used. ALS refers to sophisticated pre-hospital care using invasive methods, such as intravenous fluids, medications and intubation. Basic Life Support (BLS) on the other hand is used to assure patient's vital functions until the patient has been transported to appropriate medical care. ALS-level pre-hospital care has usually been implemented by physicians or paramedics, while BLS-level care is given by paramedics or emergency medical technicians. BLS is the components for chain of survival for people who is in under life-threatening situation. (Kerim Hakan Altintas., Dilek Aslan., Ali Naci Yildiz., Nuket Subasi., Meli Elcin., Orhan Odabasi., Nazmi Bilir., Iskender Sayek 2005).In many cases, ACLS and BLS has been compared on which is most beneficial to those people in emergency situations. There are various trainings and courses in the Philippines that are conducted to help victims of Cardiac Arrest to survive. One in which the Philippine National Red Cross provides wherein their goal is to help people whether you are a medical personnel,a student or just a bystander. Cardiovascular disease or heart disease has been one of the
lyceum of the Philippines university cabrini
College of Allied Medicine Inc.
Maharlika St., Sto. Tomas, Batangas PAGE 10
SCHOOL OF NURSING
Philippines leading top killer with the ratio of 1:5 deaths in the past year according to National Statistics Office. The NSO said heart disease was cited as the cause of 100,908 deaths or 21% percent of the 480,820 deaths reported from January 2009 to March 2010. (http://www.abs-cbnnews.com/lifestyle/10/20/11/heart-disease-phs-top-killernso). Globally, 30% of all deaths are due to cardiovascular disease. The most common mechanism of death due to ischemic heart disease is Cardiac Arrest the majority of which occurs outside the hospital anytime. With this said, knowledge and the ability to perform BLS whether youre qualified medical personnel or not, providing BLS can be very beneficial to those who are in this situation. In the event of out-of hospital cardiac arrest, it takes time for emergency professionals to arrive at the site of medical emergency. This time gap involves the presence of bystanders and if this people are trained and have the knowledge about basic life support, the victim can survive and can even be provided with proper interventions after the incident by the health providers. Within the area of cardiac arrest, Basic Life Support encompasses the recognition of cardiac arrest, opening of airways and performing ventilations and chest compressions i.e. performance of CPR with no equipment. ( Thoren 2007). In 1974, American Heart Association defined the concept as an emergency first aid procedure that consists of the recognition of airway obstruction,respiratory arrest and the proper application of cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR). (page 838). Later on, prevention was added to that concept. Prevention can be obtained by providing immediate intervention, early recognition of arrest to the victim and immediate response of medical team to emergency.
lyceum of the Philippines university cabrini
College of Allied Medicine Inc.
Maharlika St., Sto. Tomas, Batangas PAGE 11
SCHOOL OF NURSING
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) can save life during this event, maintaining a small but necessary circulation until the arrival of the ambulance and /or further treatment possibilities such as arrival of defribrillator with operator. (Thoren 2007). CPR is a technique of basic life support for the purpose of oxygenating the heart and brain until it backs into normal. This is done for those suffering cardiac and respiratory arrest. That is necessary to clear first any airway obstructions like the tip of the tongue or a tooth before CPR can be performed. Proper/clear teaching and simulation are really beneficial for the lay rescuers who are training Basic Life Support. Knowledge about the the process can be instilled in their minds in a good way. Gender preference are said to be one factor that affects layman rescuers ability to provide or perform BLS. According to a study, results have shown that, women less frequently declare their willingness to provide first aid before the course. Among the most common reasons for not performing by stander CPR, the following factors can be named: fear of disease, visible bleeding, victims poor hygiene, sense of danger, and also: panic, fear of doing harm, belief that the victim is dead, necessity of doing mouth to mouth breathing to a stranger and fear of legal sanctions. A bystander is more willing to take proper action if they know the victim, if it is certain that the victim is not likely to survive unless CPR is performed and if they have necessary CPR skills. ( Bartczak., Barzdo 2011)
lyceum of the Philippines university cabrini
College of Allied Medicine Inc.
Maharlika St., Sto. Tomas, Batangas PAGE 12
SCHOOL OF NURSING
Additionally, the study showed, that people more willing to perform CPR constitute the following type: young men, in a relationship, smokers and organ donors. Willingness to perform CPR also depends on whether a respondent has attended first aid training and their experience. Male genders are considered to be more eligible to provide help during lifethreathening situations. A survey showed that male gender was associated with good compression, greater self-confidence was also associated with good ventilation and with good compression. A short time since last BLS training was associated with a higher number of ventilations/min. A short time since last experience of CPR was associated with a higher number of compressions. They conclude that male gender, greater self-confidence, recent BLS training and recent CPR were associated with better quality of BLS. (http://ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18083286) Another factor is the age of lay rescuer. Those people who have a history of disease such as heart diseases and diseases that comes with age are the ones given priority when theyre about to give BLS. Observational studies of training or actual CPR performance have described rare occurrences of muscle strain, back symptoms, shortness of breath, hyperventilation, and case reports of pneumothorax, chest pain, myocardial infarction and nerve injury. The incidence of these events is very low, and CPR training and actual performance is safe in most circumstances. Individuals undertaking CPR training should be advised of the nature and extent of the physical activity required during the training programme. Learners and rescuers who develop
lyceum of the Philippines university cabrini
College of Allied Medicine Inc.
Maharlika St., Sto. Tomas, Batangas PAGE 13
SCHOOL OF NURSING
significant symptoms (e.g. chest pain or severe shortness of breath) during CPR training should be advised to stop. Several manikin studies have found that chest compression depth can decrease as little as 2 min after starting chest compressions. An in-hospital patient study showed that, even while using real-time feedback, the mean depth of compression deteriorated between 1.5 and 3 min after starting CPR. It is therefore recommended that rescuers change about every 2 min to prevent a decrease in compression quality due to rescuer fatigue. Changing rescuers should not interrupt chest compressions. ( http://resuscitation-guidelines.articleinmotion.com/article/S0300-9572%2810%29004351/fulltext) CPR training of laypersons should follow an organized plan of implementation that targets 2 ends of the age spectrum. First are persons most likely to encounter someone in cardiac arrest, typically persons 40 years of age and older. Second, as a valuable long-term investment, instruction of schoolchildren is important because they are at an age when knowledge and skills are well retained; they are also relatively immune to social pressures and the fear of involvement that can be a negative influence in later years. Thus, the symposium participants strongly recommended that instruction in CPR be incorporated as a standard part of the curriculum. (http://circ.ahajournals.org/content/108/20/2575.full)
lyceum of the Philippines university cabrini
College of Allied Medicine Inc.
Maharlika St., Sto. Tomas, Batangas PAGE 14
SCHOOL OF NURSING
The persons highest educational attainment is also necessary when providing help to the people as well as the marital status. Those with people who have higher achieved status in education are said to be better in identifying crisis and can provide help and immediate response. On the other hand, marital status of a rescuer can also affect because of the importance of the victim to the one who is giving help. For example, the relative or a family member of the rescuer is the victim and he has the possibility to prioritize him/her first than other people. Synthesis What is Basic Life Support? It refers to life-saving skills, emergency procedures performed to sustain life that includes cardiopulmonary resuscitation, control of bleeding, and treatment of shock, stabilization of injuries and wounds, and first aid. Initial recognition and response to heart attack and stroke are also considered part of Basic Life Support. BLS occurs usually in community and out-of-hospital settings and always has been compared to ACLS which is given and common in hospital settings. Basically, BLS are not only limited to medical practitioners or any people in the medical field. An attack can occur anytime at any place, whenever you are doing something or whether you are just walking on the street, anyone can help if they are capable and confident of what they are doing. That is why programs and trainings are given and provided for those people in the community or out-of-hospital areas who wants to learn and gain knowledge for them to help other people who are victims of cardiac arrest. Having
lyceum of the Philippines university cabrini
College of Allied Medicine Inc.
Maharlika St., Sto. Tomas, Batangas PAGE 15
SCHOOL OF NURSING
the knowledge even though they are not qualified medical personnel can increase their confidence and thus can have good outcome. Conceptually, some factors such as age, sex educational attainment and civil status have been the areas that said to be affecting in providing basic life support. But awareness of the event or life threatening situations is what mostly prioritized. The rescuers perception and cognitive reaction to a condition or event is important in how he copes up or intervenes despite all the factors cited. In our studies, adults perception and knowledge regarding Basic Life Support greatly influenced the implementation of this program. So knowledge in Basic Life Support is essential and improving this knowledge and correct their perceptions can be of great help in saving lives.
Conceptual Framework In this study, the researchers focused on the perception of the residents (Young Adults and Middle Adults) in Barangay Darasa, Tanauan City, Batangas with regards to Basic Life Support. The perception will be tested and will grade according to their current respond to disaster.
lyceum of the Philippines university cabrini
College of Allied Medicine Inc.
Maharlika St., Sto. Tomas, Batangas PAGE 16
SCHOOL OF NURSING
INDEPENDENT VARIABLE 1. Demographic Profile of the respondent 1.1 Age 1.2 Sex 1.3 Highest Educational Attainment 1.4 Civil Status DEPENDENT VARIABLE 1. Perception on Basic Life Support of the respondent
lyceum of the Philippines university cabrini
College of Allied Medicine Inc.
Maharlika St., Sto. Tomas, Batangas PAGE 17
SCHOOL OF NURSING
CHAPTER III RESEARCH METHODOLOGY In this chapter, the methods that are going to be utilized in the study are explained. The methodologies used will elicit information about the study problem. Explain further the plans and strategies that the researchers used for gathering data. Research Design This study used descriptive approach of research. Descriptive Research Approach raises questions based on the ongoing events of the present (Brown, Little et.al. 1996). This type of research design is used to observe, assess, describe and document the respondents perception in providing help during emergencies that occurs around their community or even on their own homes. The study will help the residents of Barangay Darasa Tanauan City Batangas to acquire knowledge about basic life support and how it can benefit them in case of emergencies. Subject of the Study The researchers utilized 100% of the target respondents (n=50), the respondents in this study were young adult ages old 18-40 and middle adult ranging from 33-45 years of age from each household. The respondents belong to Brgy. Darasa Tanauan City Batangas, a barangay that has a population of 14,805 as of the year 2011. Regardless of the gender, educational attainment, economic and civil status, the researcher just utilized the number of respondents to assure validity of the information
lyceum of the Philippines university cabrini
College of Allied Medicine Inc.
Maharlika St., Sto. Tomas, Batangas PAGE 18
SCHOOL OF NURSING
needed for the study. To determine the ideal sample size for a population, the Slovens formula is used:
Where: n = sample size N = population size e = margin of error
Data Gathering Procedure The study used a combination of surveying and interviewing. Interviews were done to verify if the respondents meet the conditions set for this study. We, the researchers also used other references such as the same studies done abroad and published papers in reputable journals. These helped us in predicting the most likely outcome of the study. We have also used this to create the questions for the survey. Survey was done through handing out questionnaires that serve as pre-test to the respondents and letting them answer it for about 20 minutes. The data gathering was done on weekend where they have no work. This was the chosen time to ensure that the respondents would be able to answer the questions properly and clearly to get the best results from this study.
lyceum of the Philippines university cabrini
College of Allied Medicine Inc.
Maharlika St., Sto. Tomas, Batangas PAGE 19
SCHOOL OF NURSING
After having the pre-test, a group of trained first aiders conducted a seminar about basic life support. This was done to put on and/or enhance the respondents knowledge about basic life support. A post-test was also done to get a feedback on what did the respondents learned after attending the seminar. This is useful in determining if there is a progress in their perception about basic life support and their compliance
Questionnaire
lyceum of the Philippines university cabrini
College of Allied Medicine Inc.
Maharlika St., Sto. Tomas, Batangas PAGE 20
SCHOOL OF NURSING
1. May mga ilang bagay na kailangann ninyong gawin kapag nakaengkwentro tayo ng taong nangangailangan. Ano ang una mong gagawin? a. Tukuyin ang kakayahang tumugon b. Suriin kung may panganib c. Tumawag nang tulong d. Impisahang magCPR (Cardiac Pulmonary Resuscitation) 2. Pinapayo ba na suriin kung mayroong tanda ng sirkulasyon sa mga matatanda sa pamamagitan ng pagtingin sa Carotid Pulse (Litid) a. Oo b. Hindi 3. Para sayo, ano ang ibig sabihin ngWalang Buhay a. Walang malay, hindi tumutugon, hindi gumagalaw b. Walang pulso 4. Alin sa mga ito ang ibig sabihin ng CPR (Cardiac Pulmonary Resuscitation) a. Paraan ng pagsalbang hininga, pagbibigay nang pwersa sa dibdib b. Basic Life Support 5. Alin sa mga ito ang angkop na pamamaraan para makahinga ang batang biktima? a. Panatilihin ang neutral na posisyon (Tuwid na ulo) b. Pag-angat nang ulo at baba
lyceum of the Philippines university cabrini
College of Allied Medicine Inc.
Maharlika St., Sto. Tomas, Batangas PAGE 21
SCHOOL OF NURSING
6. Kapag nagsasagawa nang CPR, gaano kadaming paunang hininga (mouth to mouth) ang binibigay mo? a. Dalawa b. Lima c. Tatlo 7. Ibang paraan sa pagtingin ng proporsyon ng kompresyon ay a. Bilang ng kompresyon binibigay pagitan ng paghinga b. Bilang ng kompresyon kada minuto 8. Ano ang inirerekumendang proporsyon ng kompresyon sa paghinga a. 100 kompresyon sa bawat 2 panghinga b. 30 kompresyon sa bawat 2 panghinga c. 30 kompresyon kada dalawang minuto 9. Ang inirerekumindang proporsyon ng kompresyon sa paghinga (30:2) ay na angkop sa a. sangol b. bata c. matanda 10. Kailangan pa bang bilangin kung gaano kadami ng pagbibigay ng CPR? a. Oo b. Hindi
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Project Proposa-WPS OfficeDokument3 SeitenProject Proposa-WPS OfficeAbordo IricNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tittle: Narrative Report of RevalidaDokument4 SeitenTittle: Narrative Report of RevalidaAllysa MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- RESEARCH 1 (Copy)Dokument13 SeitenRESEARCH 1 (Copy)Charry Anne de GuzmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Descriptive Research About The About First Aid Procedure Known by CEU-SHS Grade 11 STEM Students S.Y 2017-2018Dokument34 SeitenA Descriptive Research About The About First Aid Procedure Known by CEU-SHS Grade 11 STEM Students S.Y 2017-2018Fatrick BernardinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Raot Si CherryDokument28 SeitenRaot Si CherryElaiza Eline LaguaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Letter For DeanDokument1 SeiteLetter For DeanfitnessbopNoch keine Bewertungen
- NSTP Module 9: Emergency Response Training: ObjectivesDokument11 SeitenNSTP Module 9: Emergency Response Training: ObjectivesNovel LampitocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dance Sports Workshop Activity ProposalDokument3 SeitenDance Sports Workshop Activity ProposalAya Sismondo100% (1)
- Formal Report On Proteins and Amino AcidsDokument11 SeitenFormal Report On Proteins and Amino AcidsAlthea ValenzuelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Healthcare Reflections, Insights, and Lessons: Proactive/ReactiveVon EverandHealthcare Reflections, Insights, and Lessons: Proactive/ReactiveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Safety Education: Disaster Preparedness and Basic First AidDokument69 SeitenSafety Education: Disaster Preparedness and Basic First AidKatrine Olga Ramones-CastilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Safety and First Aid Teaching GuideDokument8 SeitenSafety and First Aid Teaching GuideNOEL BADECAONoch keine Bewertungen
- FHN MODULE1 PART 2 OVERVIEW of COMMUNITY HEALTH NURSING 1Dokument8 SeitenFHN MODULE1 PART 2 OVERVIEW of COMMUNITY HEALTH NURSING 1ALYSSA MASACAYANNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Awareness Level of Senior High School Student in Applying Occupational Health and Safety ProcedureDokument20 SeitenThe Awareness Level of Senior High School Student in Applying Occupational Health and Safety ProcedureWilliam GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annabella Casungcad Yu - Flash CardsDokument3 SeitenAnnabella Casungcad Yu - Flash CardsannanbNoch keine Bewertungen
- BELODokument7 SeitenBELOmachelle franciscoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Request Letter For Statistician Bon Jasper Angels AcademyDokument2 SeitenRequest Letter For Statistician Bon Jasper Angels AcademyJelo Anievas100% (1)
- Legal Basis of Health Education in The Philippines - PicsHealthDokument13 SeitenLegal Basis of Health Education in The Philippines - PicsHealthAre Pee EtcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analyn Application LetterDokument6 SeitenAnalyn Application Letteranalyn raraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson PlanDokument2 SeitenLesson Planapi-302414155Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Disaster Preparedness Level of Pardo National High School StudentsDokument9 SeitenThe Disaster Preparedness Level of Pardo National High School Studentsmary cris pugoyNoch keine Bewertungen
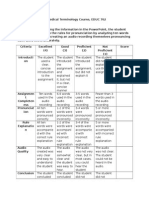
- Rubric-Medical TerminologyDokument2 SeitenRubric-Medical Terminologyapi-268199514100% (1)
- Effect of Instructional Multimedia Methods On Learning Outcomes Among Nursing Students in Selected Topic of Health AssessmentDokument19 SeitenEffect of Instructional Multimedia Methods On Learning Outcomes Among Nursing Students in Selected Topic of Health AssessmentDwi NopriyantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tobacco Lesson PlanDokument4 SeitenTobacco Lesson Planapi-240857737Noch keine Bewertungen
- Reaction Paper in Mental HealthDokument4 SeitenReaction Paper in Mental HealthEduard100% (3)
- 1 Narrative ReportDokument5 Seiten1 Narrative ReportDhon ValeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trace of Oxygen From Nasal Cavity To AlveoliDokument3 SeitenTrace of Oxygen From Nasal Cavity To Alveoliaznknight323Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 ConclusionDokument3 SeitenChapter 5 Conclusionuroosa farooqNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Narrative Report On StudentDokument13 SeitenA Narrative Report On StudentLittleagle100% (2)
- Teachers' Level of Awareness On First Aid and Its Implication On The Dalahican Elementary School'S First Aid PracticesDokument10 SeitenTeachers' Level of Awareness On First Aid and Its Implication On The Dalahican Elementary School'S First Aid PracticesIan AtienzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impact of Various Teaching Methods On Student SatisfactionDokument52 SeitenImpact of Various Teaching Methods On Student SatisfactionDaniyal Khan Muhammad100% (2)
- Syllabus in Chemistry 1 (Nursing)Dokument4 SeitenSyllabus in Chemistry 1 (Nursing)Rodel Matulin Catajay100% (1)
- Rules and Regulation in ICTDokument1 SeiteRules and Regulation in ICTRedjie Redz MigallosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Interview Guide - HA - VIOSDokument9 SeitenNursing Interview Guide - HA - VIOSIra Velle ViosNoch keine Bewertungen
- ResumeDokument4 SeitenResumeAyan MonsterraeNoch keine Bewertungen
- MEynard Castro 1Dokument3 SeitenMEynard Castro 1Meynard Garcia CastroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity-4-1 Salosagcol, Leobert Yancy GDokument2 SeitenActivity-4-1 Salosagcol, Leobert Yancy GLeobert Yancy SalosagcolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 Profile of RespondentsDokument9 SeitenChapter 4 Profile of RespondentsJose BernelNoch keine Bewertungen
- On-The-Job-Training I Isu-Ilagan Auto Care Center City of Ilagan, IsabelaDokument36 SeitenOn-The-Job-Training I Isu-Ilagan Auto Care Center City of Ilagan, IsabelaMaria Pina Barbado PonceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Certificate For AMADO M - CADIONG For UP College of Education WebDokument1 SeiteCertificate For AMADO M - CADIONG For UP College of Education Webbenz cadiongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research Paper in Basic SwimmingDokument17 SeitenResearch Paper in Basic Swimminglrac_adazol0% (2)
- Non Structural Safety ChecklistDokument2 SeitenNon Structural Safety ChecklistGrace CaritNoch keine Bewertungen
- Performance Checklist CPRDokument2 SeitenPerformance Checklist CPRMhel MGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vvsion, MissionDokument7 SeitenVvsion, Missionjan angeli100% (1)
- SkullDokument98 SeitenSkullAl-ajim HadjiliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Major Causes of Visual Impairement For LearnersDokument11 SeitenMajor Causes of Visual Impairement For LearnersAlexCorchNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intro To First AidDokument3 SeitenIntro To First AidKyla SaludoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Discussion For Ethical Considerations Following The 10 DimensionsDokument16 SeitenSample Discussion For Ethical Considerations Following The 10 DimensionsMaria Lorraine AninoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pe-3 PPT#2Dokument19 SeitenPe-3 PPT#2satoukookie100% (1)
- Service Approach To Health EducationDokument2 SeitenService Approach To Health EducationDr. qadeer unnisa begumNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Effects of The Classroom Environment To The BSA Students of STI College BalagtasDokument55 SeitenThe Effects of The Classroom Environment To The BSA Students of STI College BalagtasIan Carlo BayangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Janna Manzano BoadoDokument3 SeitenJanna Manzano BoadosestramitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Relationship Between Speaking in English While Having An Oral Presentation To The Anxiety Level of The Grade 11 Students in Las Piñas City National Senior High SchoolDokument17 SeitenThe Relationship Between Speaking in English While Having An Oral Presentation To The Anxiety Level of The Grade 11 Students in Las Piñas City National Senior High SchoolGui De OcampoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dengue Case School Monitoring ReportDokument1 SeiteDengue Case School Monitoring ReportShalee Carpio Balanquit100% (2)
- Department F Health Plans, Programs, Projects NotesDokument26 SeitenDepartment F Health Plans, Programs, Projects NotesEdgar DumagpiNoch keine Bewertungen
- NSTP 2: Cwts Part 6 - Part 12Dokument36 SeitenNSTP 2: Cwts Part 6 - Part 12Carl GilNoch keine Bewertungen
- ImradDokument17 SeitenImradKEVIN PAGAYAMANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Outcomes-Based-Education: Basis For Enhanced Teacher Education CurriculumDokument24 SeitenOutcomes-Based-Education: Basis For Enhanced Teacher Education CurriculumRhea Tamayo CasuncadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Narrative ReportDokument6 SeitenNarrative ReportMycz DoñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- First Day of ImmersionDokument11 SeitenFirst Day of ImmersionJeprox MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
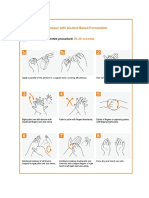
- Alcohol Based HandwashingDokument2 SeitenAlcohol Based HandwashingDada Malicsi LandichoNoch keine Bewertungen
- History BSN CurriculumDokument120 SeitenHistory BSN Curriculumrachelcornites100% (1)
- Cesarean Section CaseStudyDokument23 SeitenCesarean Section CaseStudyDada Malicsi LandichoNoch keine Bewertungen
- History BSN CurriculumDokument120 SeitenHistory BSN Curriculumrachelcornites100% (1)
- Hy DroidsDokument5 SeitenHy DroidsDada Malicsi LandichoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ArtsDokument1 SeiteArtsDada Malicsi LandichoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hy DroidsDokument5 SeitenHy DroidsDada Malicsi LandichoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument2 SeitenAnatomy and PhysiologyDada Malicsi LandichoNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is TaxonomyDokument3 SeitenWhat Is TaxonomyDada Malicsi LandichoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blessed SacramentDokument3 SeitenBlessed SacramentDada Malicsi LandichoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study-Cesarean BirthDokument5 SeitenCase Study-Cesarean BirthDada Malicsi Landicho100% (2)
- Girl Before A MirrorDokument1 SeiteGirl Before A MirrorDada Malicsi LandichoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Republic of The PhilippinesDokument8 SeitenRepublic of The PhilippinesDada Malicsi LandichoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pertemuan 8Dokument3 SeitenPertemuan 8Furi WigitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learning Competency: Distinguishes Between and Among Patterns ofDokument26 SeitenLearning Competency: Distinguishes Between and Among Patterns ofMargie JavierNoch keine Bewertungen
- MG Hse Bulletin 01 2020 The Take 5 For SafetyDokument1 SeiteMG Hse Bulletin 01 2020 The Take 5 For SafetyvivekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acetaminophen TylenolDokument2 SeitenAcetaminophen TylenolKristi WrayNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Prevalence of Malaria Among Pregnant Women On Addmission in Imo State Specialist Hospital OwerriDokument34 SeitenThe Prevalence of Malaria Among Pregnant Women On Addmission in Imo State Specialist Hospital OwerriDaniel ObasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 5 MGCQ Edition The Physical and Sexual SelfDokument28 SeitenModule 5 MGCQ Edition The Physical and Sexual SelfRan Dy MangosingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Material Safety Data Sheet: F112 Surfactant F112Dokument8 SeitenMaterial Safety Data Sheet: F112 Surfactant F112sajad gohariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health Lesson Plan - Nutrition CatapillDokument6 SeitenHealth Lesson Plan - Nutrition Catapillapi-251212131Noch keine Bewertungen
- MacroDokument45 SeitenMacro9zx27kwfgwNoch keine Bewertungen
- NNP2Dokument94 SeitenNNP2Abebe GedamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nutritional Management of The Burn Patient: MicronutrientsDokument4 SeitenNutritional Management of The Burn Patient: MicronutrientsGina KatyanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GEMS Presentation: Health Market InquiryDokument47 SeitenGEMS Presentation: Health Market InquiryYash RohiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Debeb, Simachew Gidey, Et Al. 2021Dokument13 SeitenDebeb, Simachew Gidey, Et Al. 2021priya panaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management of Superficial Phlebitis: Tradition v. ScienceDokument23 SeitenManagement of Superficial Phlebitis: Tradition v. SciencegopscharanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PNM Shaiha KKBB 2023Dokument15 SeitenPNM Shaiha KKBB 2023haslinda84Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hoffmann SignDokument5 SeitenHoffmann SignClaudio Andrés Olmos de AguileraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbohydrates: Nestlé Professional Nutrition MagazineDokument24 SeitenCarbohydrates: Nestlé Professional Nutrition MagazinedenisseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experience of Health Professionals Around An Exorcism: A Case ReportDokument4 SeitenExperience of Health Professionals Around An Exorcism: A Case ReportsorinfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mental Health Clinical Case StudyDokument5 SeitenMental Health Clinical Case Studyapi-546156641Noch keine Bewertungen
- Review Process of Discharge Planning: by Janet BowenDokument11 SeitenReview Process of Discharge Planning: by Janet BowenAfiatur RohimahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leaflet Writing TasksDokument10 SeitenLeaflet Writing TasksNeal ColpittsNoch keine Bewertungen
- GMC Handwara Recruitment 2023Dokument4 SeitenGMC Handwara Recruitment 2023Ummar WaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research-Group-5-Ughhh NiniwDokument39 SeitenResearch-Group-5-Ughhh NiniwTaguno ChrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guide Questions For NCM 107Dokument4 SeitenGuide Questions For NCM 107Miguel LigasNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHE For AdolescentsDokument26 SeitenPHE For AdolescentsSanifa MedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ministry of Health and Family Welfare Pregnancy GuidelinesDokument173 SeitenMinistry of Health and Family Welfare Pregnancy GuidelinesKhushi GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The 5x5 ProgramDokument13 SeitenThe 5x5 ProgramSMO979Noch keine Bewertungen
- Early Metabolic Programming - 1 - InfantNutrition - B.Koletzko PDFDokument10 SeitenEarly Metabolic Programming - 1 - InfantNutrition - B.Koletzko PDFAnnie RealNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proximal Femur Fractures: Sulita Turaganiwai s130364Dokument26 SeitenProximal Femur Fractures: Sulita Turaganiwai s130364Wālē NandNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tor WFP Food Assistance For Assets ProjectDokument15 SeitenTor WFP Food Assistance For Assets Projectsabri HanshiNoch keine Bewertungen