Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Errors
Hochgeladen von
Samira OlyaieOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Errors
Hochgeladen von
Samira OlyaieCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
A.
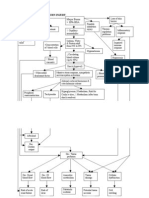
GOUGING at the labiocervical caused by failure to complete convenience extension toward the incisal prior to entrance of the shaft of the bur. B. GOUGING of the labial wall caused by failure to recognize the 20-degree lingual-axial angulation of the tooth. C. GOUGING of the distal wall caused by failure to recognize the 17-degree mesial-axial angulation of the tooth. D. FAILURE to explore, dbride, or fill the second canal caused by inadequate incisogingival extension of the access cavity. E. DISCOLORATION of the crown caused by failure to remove pulp debris. The access cavity is too far to the gingival with no incisal extension. F. LEDGE formation caused by complete loss of control of the instrument passing through the access cavity prepared in proximal restoration.
A. PERFORATION at the distogingival caused by failure to recognize that the premolar has tilted to the distal. B. INCOMPLETE preparation and possible instrument breakage caused by total loss of instrument control. Use only occlusal access, never buccal or proximal access. C. BIFURCATION of a canal completely missed, caused by failure to adequately explore the canal with a curved instrument. D. APICAL PERFORATION of an invitingly straight conical canal. Failure to establish the exact length of the tooth leads to trephination of the foramen. E. PERFORATION at the apical curvature caused by failure to recognize, by exploration, buccal curvature. A standard buccolingual radiograph will not show buccal or lingual curvature. PLATE 19 Mandibular Premolar Teeth ERRORS in Cavity Preparation
A. OVEREXTENDED preparation undermining enamel walls. The crown is badly gouged owing to failure to observe pulp recession in the radiograph. B. PERFORATION into furca caused by using a longer bur and failing to realize that the narrow pulp chamber had been passed. The bur should be measured against the radiograph and the depth to the pulpal floor marked on the shaft with Dycal. C. PERFORATION at the mesial-cervical caused by failure to orient the bur with the long axis of the molar severely tipped to the mesial. D. DISORIENTED occlusal outline form exposing only the mesiobuccal canal. A faulty cavity has been prepared in full crown, which was placed to straighten up a lingually tipped molar (D1). E. FAILURE to find a second distal canal owing to lack of exploration for a fourth canal. F. LEDGE FORMATION caused by faulty exploration and using too large of an instrument. G. PERFORATION of the curved distal root caused by using a large straight instrument in a severely curved canal. PLATE 27 Mandibular Molar Teeth ERRORS in Cavity Preparation
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- En Defensa de Los NiñosDokument10 SeitenEn Defensa de Los NiñosIliana GarcíaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Chloe Ting - 2 Weeks Shred Challenge - Free Workout ProgramDokument18 SeitenChloe Ting - 2 Weeks Shred Challenge - Free Workout ProgramNanciya LoomphaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Effectiveness of An Anterior Mini-Screw in Achieving Incisor IntrusionDokument10 SeitenEffectiveness of An Anterior Mini-Screw in Achieving Incisor IntrusionAbdel Hadi KanjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Pathophys BURNDokument2 SeitenPathophys BURNpaupaulala83% (6)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- ScribdDokument29 SeitenScribdeshasohail789Noch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Physical Examination:-: Vital SignsDokument4 SeitenPhysical Examination:-: Vital SignspriyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- 45764bos35945 Icitss GuidelinesDokument7 Seiten45764bos35945 Icitss GuidelinesTarun BhardwajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Arbonne Essentials Energy Fizz Sticks: Meet The ProductDokument1 SeiteArbonne Essentials Energy Fizz Sticks: Meet The ProductAnnaJenningsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Acupuntura y Tui Na en DismenorreaDokument3 SeitenAcupuntura y Tui Na en DismenorreaCristian Dionisio Barros OsorioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluoride The Aging Factor PDFDokument151 SeitenFluoride The Aging Factor PDFkate bastidasNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Enterprise Risk Management 2014Dokument5 SeitenEnterprise Risk Management 2014DSunte WilsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- PeadiatricDokument49 SeitenPeadiatricMARIA JAVED BSN-FA20-022Noch keine Bewertungen
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Soal Tes 1 Sem 6 S1 Reg 2021Dokument3 SeitenSoal Tes 1 Sem 6 S1 Reg 2021arka jrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Gynecology Reconstructive Surgery - Volume 2Dokument318 SeitenGynecology Reconstructive Surgery - Volume 2Bharti Pant GahtoriNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Silkpeel DermalInfusion Patient BrochureDokument12 SeitenSilkpeel DermalInfusion Patient BrochureRogier van der HeideNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACLS Advanced Cardiac Life Support, Iridia MedicalDokument54 SeitenACLS Advanced Cardiac Life Support, Iridia MedicalYu Lin ZhangNoch keine Bewertungen
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Method StatementDokument20 SeitenMethod StatementCharles IkenyeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5SDokument5 Seiten5SKakek SugionoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- 5 Elements Qi GongDokument1 Seite5 Elements Qi GongBill HonakerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kriptorchid Billateral Anjing-DikonversiDokument8 SeitenKriptorchid Billateral Anjing-Dikonversidessy yulianiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Process Recording: Nurse Inference Client AnalysisDokument4 SeitenProcess Recording: Nurse Inference Client AnalysisLemuel GuevarraNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Bartleby and Infantile AutismDokument4 SeitenBartleby and Infantile AutismAlyna Marya IoaneiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Swedish Group - ProgrammeDokument3 SeitenSwedish Group - Programmemarudo01Noch keine Bewertungen
- 02 Revman Exercise Caffeine Articles JournalsDokument8 Seiten02 Revman Exercise Caffeine Articles JournalsKenneth TorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hammer Down Training Program For Mixed Martial ArtDokument40 SeitenHammer Down Training Program For Mixed Martial ArtOng-Art PollockNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHCCCS007 Learner Guide V1.1Dokument71 SeitenCHCCCS007 Learner Guide V1.1rasna kc100% (1)
- Bookshelf NBK401552Dokument24 SeitenBookshelf NBK401552Hanina mamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- EPA Emission StandardsDokument5 SeitenEPA Emission StandardsSyed Zain AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- No.40 Vocabulary & Structures B/ Stocky C/ PretextDokument5 SeitenNo.40 Vocabulary & Structures B/ Stocky C/ PretextMai Phương Nguyễn ThịNoch keine Bewertungen
- Legendary Enlargement E Mail SwipesDokument13 SeitenLegendary Enlargement E Mail SwipesJc Fort0% (1)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)