Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
5.5 Component Values: DSS DS
Hochgeladen von
Gauhar Aftab KhanOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
5.5 Component Values: DSS DS
Hochgeladen von
Gauhar Aftab KhanCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
5.
5 Component values
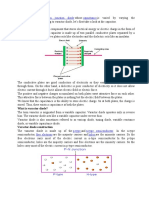
Slightly modified royal oscillator (it is an electronic oscillator which has the advantages of simplicity, low component count, sinusoidal waveforms and easy transformer isolation). Input voltage Input voltage was limited to 12V for safety and because the circuit tends to become unstable at higher voltages. Mosfets The metaloxidesemiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET, MOS-FET, or MOS FET) is a transistor used for amplifying or switching electronic signals. Although the MOSFET is a four-terminal device with source (S), gate (G), drain (D), and body (B) terminals,[1] the body (or substrate) of the MOSFET often is connected to the source terminal, making it a threeterminal device like other field-effect transistors. When two terminals are connected to each other (short-circuited) only three terminals appear in electrical diagrams. The MOSFET is by far the most common transistor in both digital and analog circuits, though the bipolar junction transistor was at one time much more common. We use IRFZ44 which is a power Mosfet and has VDSS = 55v, RDS = 17.5 m ohm and ID = 49 A Resistors Two resistors 100 ohms, which is enough and wastes less power. And it was rated at least 1 watt to handle high current. Two resistors 10K ohms and one resistor 1K ohms. Toroid (coil inductor) Toroidal inductors and transformers are electronic components, typically consisting of a circular ring-shaped magnetic core of iron powder, ferrite, or other material around which wire is coiled to make an inductor. Toroidal coils are used in a broad range of applications, such as high-frequency coils and transformers. Toroidal inductor scan have higher Q factors
and higher inductance than similarly constructed solenoid coils. This is due largely to the smaller number of turns required when the core provides a closed magnetic path. The magnetic flux in a high permeability Toroid is largely confined to the core; the confinement reduces the energy that can be absorbed by nearby objects, so toroidal cores offer some selfshielding. Radio frequency chokes (RFC) were 500uH has ferrite cores to produce much better results. Diodes In electronics, a diode is a two-terminal electronic component with asymmetric transfer characteristic, with low (ideally zero) resistance to current flow in one direction, and high (ideally infinite) resistance in the other. A semiconductor diode, the most common type today, is a crystalline piece of semiconductor material with a p-n junction connected to two electrical terminals. A vacuum tube diode, now rarely used except in some high-power technologies and by enthusiasts, is a vacuum tube with two electrodes, a plate (anode) and cathode. Diodes are 1N4144 which is small high-speed ones. Capacitors A capacitor (originally known as condenser) is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store energy in an electric field. The forms of practical capacitors vary widely, but all contain at least two electrical conductors separated by a dielectric (insulator); for example, one common construction consists of metal foils separated by a thin layer of insulating film. Capacitors are widely used as parts of electrical circuits in many common electrical devices. 8 paralleled 6.8nF Capacitors with ratings 1600V wima FKP1 are used in primary side to handle the heavy current circulates in LC bank while keeping losses tolerable, the capacitors are polypropylene dielectric .and 100nf 63v capacitor. Receiver side In receiver side one metalized polypropylene capacitor, chosen for suitable resonant frequency which is 47 nF.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Capacitor: Some Publications Still Use The Old Resistor SymbolDokument6 SeitenCapacitor: Some Publications Still Use The Old Resistor SymbolSarah Jane EgeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesVon EverandDiode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (7)
- Resistor Capacitor Inductor Transistor DiodeDokument2 SeitenResistor Capacitor Inductor Transistor Diodelekz re100% (2)
- Components 1. Diode: Semiconductor DiodesDokument8 SeitenComponents 1. Diode: Semiconductor DiodesVaranasi RamakrishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PrintDokument3 SeitenPrintAnnie VieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic ElecteonicsDokument40 SeitenBasic ElecteonicsShakir RahmaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Electronics ComponentsDokument54 SeitenBasic Electronics ComponentselquintogatoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Varactor Diode DefinitionDokument6 SeitenVaractor Diode DefinitionMohit BhavsarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Semiconductor DevicesDokument18 SeitenSemiconductor DevicesNawal MunifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project in TLe 3Dokument5 SeitenProject in TLe 3RG PrinceRed Ripalda BorlagdanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Semiconductor DeviceDokument6 SeitenSemiconductor DeviceGilberto ManhattanNoch keine Bewertungen
- I. Passive ComponentsDokument7 SeitenI. Passive Componentsdare beastNoch keine Bewertungen
- 21BCE5419 Exp1Dokument12 Seiten21BCE5419 Exp1Anshika RaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- BXE Practical Journal (Experiment No. 1 To 8) - 1Dokument55 SeitenBXE Practical Journal (Experiment No. 1 To 8) - 1kakashi hatakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Studying basic components and devicesDokument12 SeitenStudying basic components and devicesAnshika RaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic of ElectronicsDokument14 SeitenBasic of ElectronicsRahul DubeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical & Electronics Components GuideDokument15 SeitenElectrical & Electronics Components GuidejohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiments EPLDokument24 SeitenExperiments EPLMonicaSekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Electric Resistance?Dokument39 SeitenWhat Is Electric Resistance?Abdelrhman ElkholyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communication With Laser BeamDokument17 SeitenCommunication With Laser BeamJagruti MulayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 4Dokument7 SeitenUnit 4binukirubaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab No. 01: TitleDokument10 SeitenLab No. 01: TitleArbab AslamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronic ComponentsDokument6 SeitenElectronic ComponentsEmey SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- FM TransmitterDokument24 SeitenFM Transmitterrethunkb5548100% (2)
- AbstractDokument2 SeitenAbstractVivek SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basics of ElectronicsDokument15 SeitenBasics of ElectronicsAtul KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical ParametersDokument16 SeitenElectrical Parametersapi-295377694Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1: Domestic Electrical Equipment Maintenance Section 2Dokument11 SeitenAssignment 1: Domestic Electrical Equipment Maintenance Section 2Ganabpaty ThiagarajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diode Types and Applications in 40 CharactersDokument11 SeitenDiode Types and Applications in 40 Charactersusama saleemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Em ReportDokument7 SeitenEm Reportkashafnasir9977Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cebu Institute of Technology University: ECE 162 W1Dokument8 SeitenCebu Institute of Technology University: ECE 162 W1meshin yuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laser Torch ProDokument9 SeitenLaser Torch ProTarun SachanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 4-1Dokument67 SeitenModule 4-1john paulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design a Clap Activated SwitchDokument37 SeitenDesign a Clap Activated SwitchSenthil KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diode:: Cutoff VoltageDokument3 SeitenDiode:: Cutoff VoltageÆmmar AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- BEC Notes Lecture 2 by Ur Engineering FriendDokument7 SeitenBEC Notes Lecture 2 by Ur Engineering Friendapjvlogs0Noch keine Bewertungen
- Circuits & Resistors: Conductors & InsulatorsDokument10 SeitenCircuits & Resistors: Conductors & InsulatorsH Aries OñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microelectronics Devices: Yao-Joe YangDokument17 SeitenMicroelectronics Devices: Yao-Joe YangŞemsettin karakuşNoch keine Bewertungen
- Passive Components (Compatibility Mode)Dokument102 SeitenPassive Components (Compatibility Mode)gauravNoch keine Bewertungen
- LED Bulb Circuit GuideDokument33 SeitenLED Bulb Circuit GuideDebashishParidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DiodesDokument3 SeitenDiodeslitrakhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transistor: Transistor As A SwitchDokument12 SeitenTransistor: Transistor As A SwitchBharat SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Semiconductor DiodeDokument9 SeitenTypes of Semiconductor Diodezain aliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fire Fighting RobotDokument40 SeitenFire Fighting RobotHarvinder SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronic EngeeniringDokument11 SeitenElectronic EngeeniringMuataz ZyadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- InductorDokument28 SeitenInductorDean Bryan BaylonNoch keine Bewertungen
- S3 ME FEE Notes Mod 4 FINALDokument25 SeitenS3 ME FEE Notes Mod 4 FINALAmal MonichanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Condenser.: Capacitor - in A Way, A Capacitor Is A Little Like A Battery. Although They Work in Completely Different WaysDokument8 SeitenCondenser.: Capacitor - in A Way, A Capacitor Is A Little Like A Battery. Although They Work in Completely Different WaysJuan DelacruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- MOSFET: A Guide to the Metal-Oxide Semiconductor Field-Effect TransistorDokument21 SeitenMOSFET: A Guide to the Metal-Oxide Semiconductor Field-Effect TransistorthesumitsinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schottky DiodeDokument5 SeitenSchottky Diodeilg1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Semiconductor Diode: Avalanche DiodesDokument15 SeitenTypes of Semiconductor Diode: Avalanche DiodesAsr ARNoch keine Bewertungen
- ? ? ? 6/PERO ? ? ? RqvwuxfwlrqDokument7 Seiten? ? ? 6/PERO ? ? ? RqvwuxfwlrqLasam CagayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reg. # 2014-ch-215Dokument20 SeitenReg. # 2014-ch-215Atif MehfoozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electroniccomponents 190105072037 PDFDokument29 SeitenElectroniccomponents 190105072037 PDFsatyaveetr singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Robotics 3205Dokument7 SeitenRobotics 3205api-295212456Noch keine Bewertungen
- Wire Fuse and SwitchDokument47 SeitenWire Fuse and SwitchMacy RiegoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ConnectorsDokument9 SeitenConnectorsROHININoch keine Bewertungen
- Capacitor, Reed Relay & Reed SwitchDokument5 SeitenCapacitor, Reed Relay & Reed SwitchCt HajarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Circuit ComponentsDokument3 SeitenBasic Circuit ComponentsJhoker SudzNoch keine Bewertungen
- 16SEE - Schedule of PapersDokument36 Seiten16SEE - Schedule of PapersPiyush Jain0% (1)
- Detect Plant Diseases Using Image ProcessingDokument11 SeitenDetect Plant Diseases Using Image Processingvinayak100% (1)
- CHM 127 Exp 1Dokument4 SeitenCHM 127 Exp 1shelby hartwigNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3000 Most Common Words in EnglishDokument85 Seiten3000 Most Common Words in Englishapi-575590272100% (1)
- Y06209 November 2015Dokument28 SeitenY06209 November 2015Fredy CoyagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CommunicationDokument5 SeitenCommunicationRyan TomeldenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astm A105, A105mDokument5 SeitenAstm A105, A105mMike Dukas0% (1)
- Phenomenal Consciousness and Cognitive Access: ResearchDokument6 SeitenPhenomenal Consciousness and Cognitive Access: ResearchAyşeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mock DataDokument56 SeitenMock DataAnonymous O2bvbOuNoch keine Bewertungen
- ADII11 Metode Deteksi OutlierDokument50 SeitenADII11 Metode Deteksi Outlier21-A-2-19 Nazli Amaliya RamadhaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Naaqs 2009Dokument2 SeitenNaaqs 2009sreenNoch keine Bewertungen
- AWS D1.5 PQR TitleDokument1 SeiteAWS D1.5 PQR TitleNavanitheeshwaran SivasubramaniyamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Report 1Dokument8 SeitenLab Report 1Hammad SattiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dball-Gm5 en Ig Cp20110328aDokument18 SeitenDball-Gm5 en Ig Cp20110328aMichael MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- CLOZE TEST Fully Revised For SSC, Bank Exams & Other CompetitiveDokument57 SeitenCLOZE TEST Fully Revised For SSC, Bank Exams & Other CompetitiveSreenu Raju100% (2)
- AR Adjustments: Details, Setup, Flow, Accounting and API: September 5th, 2008Dokument5 SeitenAR Adjustments: Details, Setup, Flow, Accounting and API: September 5th, 2008John SmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- COP Oil: For Epiroc Components We Combine Technology and Environmental SustainabilityDokument4 SeitenCOP Oil: For Epiroc Components We Combine Technology and Environmental SustainabilityDavid CarrilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overhead Water Tank Structural AnalysisDokument28 SeitenOverhead Water Tank Structural Analysiscollins unanka100% (3)
- Calculating Molar MassDokument5 SeitenCalculating Molar MassTracy LingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calibration Method For Misaligned Catadioptric CameraDokument8 SeitenCalibration Method For Misaligned Catadioptric CameraHapsari DeviNoch keine Bewertungen
- DRM 25Dokument14 SeitenDRM 25Anantha RajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 C's of Business LetterDokument3 Seiten7 C's of Business LetterGladys Forte100% (2)
- I2E: Embedding Innovation as Organizational StrategyDokument11 SeitenI2E: Embedding Innovation as Organizational StrategyDeepak PanditNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparison of Waste-Water Treatment Using Activated Carbon and Fullers Earth - A Case StudyDokument6 SeitenComparison of Waste-Water Treatment Using Activated Carbon and Fullers Earth - A Case StudyDEVESH SINGH100% (1)
- Course-PM SSY135 Wireless Communications 21-22Dokument7 SeitenCourse-PM SSY135 Wireless Communications 21-22Amirhossein MohsenianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rules For Assigning Activity Points: Apj Abdul Kalam Technological UniversityDokument6 SeitenRules For Assigning Activity Points: Apj Abdul Kalam Technological UniversityAnonymous KyLhn6Noch keine Bewertungen
- GCSE H3 02g4 02 3D TrigonometryDokument2 SeitenGCSE H3 02g4 02 3D TrigonometryAndrei StanescuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scan & Pay Jio BillDokument22 SeitenScan & Pay Jio BillsumeetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Individual Moving Range (I-MR) Charts ExplainedDokument18 SeitenIndividual Moving Range (I-MR) Charts ExplainedRam Ramanathan0% (1)
- E Requisition SystemDokument8 SeitenE Requisition SystemWaNi AbidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Machinery Lubrication Technician (MLT) I and II Certification Exam GuideVon EverandMachinery Lubrication Technician (MLT) I and II Certification Exam GuideBewertung: 2 von 5 Sternen2/5 (1)
- Fire in the Night: The Piper Alpha DisasterVon EverandFire in the Night: The Piper Alpha DisasterBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (5)
- Asset Integrity Management for Offshore and Onshore StructuresVon EverandAsset Integrity Management for Offshore and Onshore StructuresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flow Analysis for Hydrocarbon Pipeline EngineeringVon EverandFlow Analysis for Hydrocarbon Pipeline EngineeringNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prevention of Valve Fugitive Emissions in the Oil and Gas IndustryVon EverandPrevention of Valve Fugitive Emissions in the Oil and Gas IndustryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oil and Gas Pipelines and Piping Systems: Design, Construction, Management, and InspectionVon EverandOil and Gas Pipelines and Piping Systems: Design, Construction, Management, and InspectionBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (16)
- Industrial Piping and Equipment Estimating ManualVon EverandIndustrial Piping and Equipment Estimating ManualBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (7)
- Pipeline Integrity: Management and Risk EvaluationVon EverandPipeline Integrity: Management and Risk EvaluationBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (6)
- Well Control for Completions and InterventionsVon EverandWell Control for Completions and InterventionsBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (10)
- Pocket Guide to Flanges, Fittings, and Piping DataVon EverandPocket Guide to Flanges, Fittings, and Piping DataBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (22)
- Risk Management in the Oil and Gas Industry: Offshore and Onshore Concepts and Case StudiesVon EverandRisk Management in the Oil and Gas Industry: Offshore and Onshore Concepts and Case StudiesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Black Gold Stranglehold: The Myth of Scarcity and the Politics of OilVon EverandBlack Gold Stranglehold: The Myth of Scarcity and the Politics of OilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deepwater Drilling: Well Planning, Design, Engineering, Operations, and Technology ApplicationVon EverandDeepwater Drilling: Well Planning, Design, Engineering, Operations, and Technology ApplicationBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (2)
- Hydraulic Fracturing in Unconventional Reservoirs: Theories, Operations, and Economic AnalysisVon EverandHydraulic Fracturing in Unconventional Reservoirs: Theories, Operations, and Economic AnalysisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical Wellbore Hydraulics and Hole Cleaning: Unlock Faster, more Efficient, and Trouble-Free Drilling OperationsVon EverandPractical Wellbore Hydraulics and Hole Cleaning: Unlock Faster, more Efficient, and Trouble-Free Drilling OperationsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Internal Combustion: How Corporations and Governments Addicted the World to Oil and Subverted the AlternativesVon EverandInternal Combustion: How Corporations and Governments Addicted the World to Oil and Subverted the AlternativesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (2)
- Oil & Gas Design Engineering Guide Book: Useful Practices and Equipment & SystemsVon EverandOil & Gas Design Engineering Guide Book: Useful Practices and Equipment & SystemsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subsea Valves and Actuators for the Oil and Gas IndustryVon EverandSubsea Valves and Actuators for the Oil and Gas IndustryBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Enhanced Oil Recovery Handout: A Focus on WaterfloodingVon EverandEnhanced Oil Recovery Handout: A Focus on WaterfloodingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Petroleum Rock Mechanics: Drilling Operations and Well DesignVon EverandPetroleum Rock Mechanics: Drilling Operations and Well DesignBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Compression Machinery for Oil and GasVon EverandCompression Machinery for Oil and GasKlaus BrunBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (4)