Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Convert Ion of Galvanometer Into Voltmeter
Hochgeladen von
hrpatel31Originalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Convert Ion of Galvanometer Into Voltmeter
Hochgeladen von
hrpatel31Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Page 1 of 3
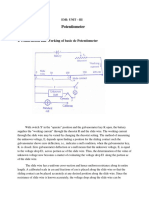
Conversion of galvanometer into voltmeter
Aim : - To convert galvanometer into voltmeters of different ranges which can be used
to measure the potential differences in electrical circuits.
Apparatus : - Galvanometer, voltmeter, variable resistor, variable power supply and
connecting terminals.
Description : - A galvanometer can be converted in to a voltmeter by connecting a high
resistance ( R ) in series with the galvanometer as shown in the figure. The value of resistance ( R ) connected in series decides the range of the voltmeter. The scale is calibrated in volts, so as to read the potential difference directly. To measure the potential difference between two points, the voltmeter must be connected in parallel across those two points in the circuit. When a high value of resistance is connected in series to the galvanometer, only a small fraction of the total current will flow through the galvanometer. So, this does not cause any damage to the galvanometer. More over, as the current flow in the galvanometer, which is connected in parallel in the circuit, is very small, it causes no effect in the current of the main circuit.
Procedure : - Connect the circuit as shown in the figure. The variable power supply
connected gives the required potential difference to the circuit. Also select and connect the required resistance ( R ) in series with the galvanometer, to convert the
galvanometer into voltmeter of required range. The selection of the resistance that should be connected in series to the galvanometer is in such away that the galvanometer shows full deflection for the required range. By increasing the supply voltage, the galvanometer reading is increased in steps of 5 divisions, starting from zero, the corresponding voltmeter readings are noted, in the table.
Page 2 of 3
Graph : - A graph is drawn, by taking galvanometer reading on X- axis and the
corresponding voltmeter reading on Y-axis. It gives a straight line passing through the origin. The graph is useful to know the potential difference across any two points in the circuit if the galvanometer reading is known.
The experiment is repeated by connecting another resistance (R)in series with the galvanometer to get a voltmeter of a different range. So the same galvanometer can be used to get voltmeters of different ranges, just by changing the series resistance (R).
Precautions : - 1) The series resistance should be so selected such that for the required
range of voltmeter, the galvanometer shows full the deflection with in the scale. 2) The continuity experiment. of connecting terminals should be checked before going to the
Results : -
Page 3 of 3
Table
Voltmeter range =
Value of resistance connected in series to galvanometer =
S.No.
Galvanometer reading ( n divisions )
Voltmeter reading (V)
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
*****
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Fans and Blowers PapstDokument108 SeitenFans and Blowers PapstvitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multimeter VIMPDokument61 SeitenMultimeter VIMPSysu KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Potential TransformerDokument27 SeitenPotential TransformerVijay Pandit100% (1)
- Avr Gavr-8a DatasheetDokument3 SeitenAvr Gavr-8a Datasheetkhhoa0% (1)
- Napolcom Exam ReviewerDokument15 SeitenNapolcom Exam ReviewerIrene FriasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulic ActuatorDokument55 SeitenHydraulic ActuatorMASOUD75% (4)
- Voltage and Current TransformersDokument27 SeitenVoltage and Current TransformersRebekah Powell100% (1)
- Electronic Scale ArduinoDokument8 SeitenElectronic Scale ArduinoKathryn WorkmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mapua EE101-1L Exp 1Dokument3 SeitenMapua EE101-1L Exp 1Bob Laurence CaridadNoch keine Bewertungen
- APM303Dokument20 SeitenAPM303Goran Jovanovic100% (5)
- Physics Project: ON Moving Coil GalvanometerDokument22 SeitenPhysics Project: ON Moving Coil GalvanometerRISHIK100% (5)
- DL24P Schematic DiagramDokument1 SeiteDL24P Schematic DiagramLAN JR HOUSE0% (1)
- Te Unit-2 MCQ PDFDokument10 SeitenTe Unit-2 MCQ PDFRajNoch keine Bewertungen
- VHDL Based Circuits Design and Synthesis On FPGA: A Dice Game Example For EducationDokument6 SeitenVHDL Based Circuits Design and Synthesis On FPGA: A Dice Game Example For EducationRam RajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sensitivity TestDokument12 SeitenSensitivity Testratnaraj_kanungoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1082-LAB 10 Voltmeters and AmmetersDokument9 Seiten1082-LAB 10 Voltmeters and AmmetersNghi TranNoch keine Bewertungen
- 07 Galvanometer - 2Dokument2 Seiten07 Galvanometer - 2Muhammad SufyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- VoltmeterDokument2 SeitenVoltmetervijay kumar honnaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparison Methods of Measurements: UNIT-3Dokument27 SeitenComparison Methods of Measurements: UNIT-3jenitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 16052020 045213pm 19062023 052331pmDokument49 SeitenChapter 6 16052020 045213pm 19062023 052331pmAbdullah ZamirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3Dokument6 SeitenUnit 3dhub324Noch keine Bewertungen
- Duo Range Type PotentiometerDokument19 SeitenDuo Range Type Potentiometersaikarthick023Noch keine Bewertungen
- Practical Conversion G in VDokument10 SeitenPractical Conversion G in VLOKESH CHANDRA JOSHINoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical and Electronics Measurement 4th Sem B.Tech.Dokument41 SeitenElectrical and Electronics Measurement 4th Sem B.Tech.Saksham KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cha:4 Potentiometers: Principal of D.C. Potentiometer Crompton's Potentiometer Application of DC PotentiometerDokument16 SeitenCha:4 Potentiometers: Principal of D.C. Potentiometer Crompton's Potentiometer Application of DC PotentiometerNirav ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Galvanometer Ammeter by Dr. Gaurav KarnatakDokument14 SeitenGalvanometer Ammeter by Dr. Gaurav KarnatakRose ytNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 1 Familiarization With Electrical Measuring InstrumentsDokument10 SeitenExperiment 1 Familiarization With Electrical Measuring InstrumentsCorps LaroprocNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER 2 InstrumentationDokument11 SeitenCHAPTER 2 InstrumentationhariNoch keine Bewertungen
- EMI 3rd PDFDokument53 SeitenEMI 3rd PDFKeshav Kumar Pushpam100% (1)
- PotentiometersDokument23 SeitenPotentiometersbhaskaratarun239bNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conversion of Galvanometer Into VoltmeterDokument1 SeiteConversion of Galvanometer Into VoltmeterKhadim ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Objective 5-Understand The Use of Potentiometer For The Measurement of Electrical Quantities in D.C and A.C Circuits.Dokument33 SeitenGeneral Objective 5-Understand The Use of Potentiometer For The Measurement of Electrical Quantities in D.C and A.C Circuits.canal abdulNoch keine Bewertungen
- PotentiometerDokument3 SeitenPotentiometerammuluhai333Noch keine Bewertungen
- Potentiometer: 1. Construction and Working of Basic DC PotentiometerDokument11 SeitenPotentiometer: 1. Construction and Working of Basic DC PotentiometerKumar SanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wheatstone BridgeDokument2 SeitenWheatstone BridgeMohamed ElsayedNoch keine Bewertungen
- LU1.2.Use Basic Electric MetersDokument23 SeitenLU1.2.Use Basic Electric Metersnguemaabraham1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ece014 - Electronics 3 - Experiment 3Dokument10 SeitenEce014 - Electronics 3 - Experiment 3John Wilfredd CurimoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Galvanometer ConversionDokument7 SeitenGalvanometer Conversionashwin_airNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analog Electronic WattmetrDokument2 SeitenAnalog Electronic WattmetrKaran AnejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Project On Convertion of Gslvanometer To AmmeterDokument15 SeitenPhysics Project On Convertion of Gslvanometer To Ammeterharshilsapariya501Noch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment # 5Dokument7 SeitenExperiment # 5Abdullah TahirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 05 - Voltmeter and Ammeter Design Using GalvanometerDokument7 SeitenLab 05 - Voltmeter and Ammeter Design Using GalvanometerK.Ramachandran40% (5)
- Galvanometer's Conversion To Ammeter and VoltmeterDokument1 SeiteGalvanometer's Conversion To Ammeter and Voltmeteranshvishwakarma2005Noch keine Bewertungen
- Potentiometers: Nstrument Ransformers ANDDokument26 SeitenPotentiometers: Nstrument Ransformers ANDDIVYA PRASOONA CNoch keine Bewertungen
- VoltmeterDokument6 SeitenVoltmeterAndi DelimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of ExperimentsDokument6 SeitenList of ExperimentsNishika GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- LVDT and Capacitance Strain GuagesDokument13 SeitenLVDT and Capacitance Strain GuagesJignesh P Korat100% (1)
- Cable Fault DetectorDokument25 SeitenCable Fault DetectorHarshalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Four Terminal ResistanceDokument9 SeitenFour Terminal ResistanceAline RochaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 1 UpdatedDokument22 SeitenExperiment 1 Updatedyoho hohoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASSIGNMENTDokument16 SeitenASSIGNMENTAkshat JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relay Setting (Directional) : Leakage FluxDokument8 SeitenRelay Setting (Directional) : Leakage Fluxjyoti kachareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2Dokument19 SeitenUnit 2VIDYA SAGAR KAKARLANoch keine Bewertungen
- Galvanometer Into Ammeter 29122023 022143pmDokument3 SeitenGalvanometer Into Ammeter 29122023 022143pmsikandarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experimental Physics 102Dokument84 SeitenExperimental Physics 102Third ChanceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emmi LabDokument48 SeitenEmmi LabRamesh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 UnitDokument36 Seiten3 Unitbitseee RandDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analog Electrical Devices and MeasurementsDokument21 SeitenAnalog Electrical Devices and MeasurementsGabriel MarzinottoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical & Electronic InstrumentationDokument26 SeitenElectrical & Electronic InstrumentationKamal PhyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment No - Measurement of ResistanceDokument5 SeitenExperiment No - Measurement of ResistanceAppu ParoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measurement of High Voltages and CurrentsDokument35 SeitenMeasurement of High Voltages and Currentssyed1188Noch keine Bewertungen
- SLD 2Dokument48 SeitenSLD 2madev21413Noch keine Bewertungen
- PotentiometerDokument7 SeitenPotentiometerCarmella Mae QuidiligNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measurement of ResistanceDokument20 SeitenMeasurement of ResistanceWanjala WilliamNoch keine Bewertungen
- EMMI Lab PDFDokument31 SeitenEMMI Lab PDFSarithareddy AvuluriNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Factories Act, 1948: ObjectivesDokument24 SeitenThe Factories Act, 1948: Objectiveshrpatel31Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment-2.Doc Unit 1Dokument1 SeiteAssignment-2.Doc Unit 1hrpatel31Noch keine Bewertungen
- Communication: Effective Rural For DevelopmentDokument74 SeitenCommunication: Effective Rural For Developmenthrpatel31Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Use of Financial Ratios Analyzing Liquidity Analyzing Activity Analyzing Debt Analyzing Profitability A Complete Ratio AnalysisDokument19 SeitenThe Use of Financial Ratios Analyzing Liquidity Analyzing Activity Analyzing Debt Analyzing Profitability A Complete Ratio Analysiskowsalya18Noch keine Bewertungen
- Labour LawsDokument44 SeitenLabour LawsSreeja VarmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Life Insurance PolicyDokument4 SeitenLife Insurance Policyhrpatel31Noch keine Bewertungen
- Trade UnionsDokument26 SeitenTrade UnionsdiddianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Blue Copper ProteinsDokument15 Seiten3 Blue Copper ProteinsSergio BetancurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Testo 175 H1 INDokument2 SeitenTesto 175 H1 INsundarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pyro MeterDokument6 SeitenPyro Meterseeralan balakrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Logical EffortDokument223 SeitenLogical Effortgmahajan0100% (6)
- General Physics 2 Q3 ADM Module 5 7 1Dokument24 SeitenGeneral Physics 2 Q3 ADM Module 5 7 1Abigail FlorendoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rbs/Bts Signal Cabling: DF PanelDokument1 SeiteRbs/Bts Signal Cabling: DF PanelMayuSalanggaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jumo Aquis 500 PH: Transmitter/Controller For PH, ORP and NH - (Ammonia) Concentration Type 202560Dokument108 SeitenJumo Aquis 500 PH: Transmitter/Controller For PH, ORP and NH - (Ammonia) Concentration Type 202560Dennis Gamarra RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- GPIO Initialization For ARM MicroprocessorDokument25 SeitenGPIO Initialization For ARM MicroprocessorCristian Santana RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conductor and Insulator 1Dokument11 SeitenConductor and Insulator 1John Paul RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Building A Thermocouple Vacuum GaugeDokument8 SeitenBuilding A Thermocouple Vacuum Gaugealessandro8265Noch keine Bewertungen
- + 5V 10 K - 5V + 5V 10 K + 5V + 5V - V 10 K : ECGR 3131: Fundamentals of Electronics & SemiconductorsDokument5 Seiten+ 5V 10 K - 5V + 5V 10 K + 5V + 5V - V 10 K : ECGR 3131: Fundamentals of Electronics & SemiconductorsDavidRubeomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modification To AMP REV1Dokument14 SeitenModification To AMP REV1augustinetezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamini Series Adhesive Supply UnitDokument2 SeitenDynamini Series Adhesive Supply UnitITWDynatecNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Nation Ank-523-18-19 Tech Bid PDFDokument80 SeitenLab Nation Ank-523-18-19 Tech Bid PDFRadhakrishna MadabhushiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Attenuation and DispersionDokument92 SeitenAttenuation and Dispersionscribd01Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 16 Automated SystemsDokument9 SeitenUnit 16 Automated Systemsapi-339083063Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tai Lieu SmallCell BTS3911E Installation Guide (04) (PDF) - enDokument98 SeitenTai Lieu SmallCell BTS3911E Installation Guide (04) (PDF) - enduongsonvnptNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scotle Technology Group Ltd. Scotle IR6000 V3. BGA Rework Station. User Manual.Dokument17 SeitenScotle Technology Group Ltd. Scotle IR6000 V3. BGA Rework Station. User Manual.zigmund zigmundNoch keine Bewertungen
- Baumuller ExtrusoraDokument368 SeitenBaumuller ExtrusoraJoelson MeneghelliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinetec Spectra Knee CPM Service ManualDokument30 SeitenKinetec Spectra Knee CPM Service ManualGerardo AntonioNoch keine Bewertungen
- V-Log/V-Gamut: Reference ManualDokument7 SeitenV-Log/V-Gamut: Reference ManualPufa DjuartonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modern Power Electronics and AC Drives by Bimal K Bose PDFDokument738 SeitenModern Power Electronics and AC Drives by Bimal K Bose PDFsurendrNoch keine Bewertungen