Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Tissue Table
Hochgeladen von
Marcie BooneOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Tissue Table
Hochgeladen von
Marcie BooneCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
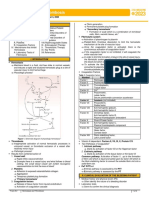
TISSUE TYPE Simple Squamous Epithelium Simple Cuboidal Epithelium Simple columnar Epithelium
LOCATION Air sacs, lining of heart blood vessels, lining of ventral body cavity, (serosae) Kidney tubules, ducts, small glands
Nonciliated: lines digestive tract, gall bladder, excretory ducts of some glands Ciliated: line small bronchi, uterine tubes some of uterus Psuedostratified Nonciliated: sperm ducts Columnar Ciliated: lines trachea Epithelium and upper respiratory tract Nonkernatinized: Stratified moist lining of Squamous esophagus, mouth epithelium and vagina Kernatinized : epidermis of skin, dry membranes
DESCRIPTION 1 layer of fatten cells, disc shaped, central nuclei and sparse cytoplasm 1 layer of cube like cells, large spherical central nuclei 1 layer of tall cells with round to oval nuclei, some have cilia; layers may contain mucus secreting unicellular glands. 1 layer of cells of different hts, nuclei seen at different levels may bear mucus secreting cells or cilia. 2 or more layers of metabolically active membrane, surface cells are squamous & deeper layers are cuboidal or columnar. Keratinized are full of keratin and are dead. Basal cells are active in mitosis produce cells of more superficial layers
CELLS FUNCTION Squamous Allows passage of material by diffusion and epithelium cells filtration in sites where protection is not important, secrete lubricating substance in serosae Simple Secretion and Absorption cuboidal epithelium cells Goblet , simple Absorption, secrete mucus, enzymes; ciliated columnar propel mucus or reproductive cells by ciliary epithelium, action. reproductive cells
Pseudostratified Secretion, mucus propulsion by ciliary action columnar epithelium
Basal cells, squamous cells
Protects underlying tissue in areas of subjected abrasion
TISSUE TYPE Stratified Columnar Epithelium
LOCATION Male urethra & large ducts of some glands
Traditional Epithelium
Lines the ureters urinary bladder part of urethra
Embryonic connective tissue: Mesenchyme
Embryo
Connective Tissue Proper: Loose Connective tissue Areolar Connective Tissue Proper: Loose Connective tissue: ADIPOSE
Under Epithelia of body, packages organs, surrounds capillaries
DESCRIPTION Several cell layers, basal cells usually cuboidal superficial cells of elongated and columnar Resembles both stratified squamous and stratified cuboidal basal cells, cuboidal or columnar surface cells, dome shaped, or squamous like, depending on degree of organ stretch Embryonic connective tissue , gel like ground substance containing fibers, star shaped mesenchyme cells Gel like matrix, all three fiber types,
CELLS FUNCTION Basal cells, Protection & secretion stratified columnar epithelium cells Basal cells, cuboidal or columnar Stretches readily and permits distension of urinary organ by contained urine.
Mesenchyme cells
Arises during early weeks of embryonic development and eventually differentiates (specialize) into all other connect tissue.
Fibroblasts, macrophages, mast, and some wbc
Wraps and cushions organs, plays role in inflammation process holds and convey tissue fluid
Under skin, around kidneys, eyeballs; within abdomen, and in breast
Matrix as in areolar, very sparse closely packed adipocytes or fat cells have nucleus pushed to side by large fat droplets
Adipocytes
Provides reserve fuel, insulates against heat loss, supports and protects organs.
TISSUE TYPE Connective Tissue Proper: Loose Connective tissue: RETICULAR Connective Tissue Proper: Dense Connective Tissue: DENSE REGULAR Connective Tissue Proper: Dense Connective tissue: Dense IRREGULAR Connective Tissue Proper: Dense Connective tissue: Elastic Hyaline Cartilage
LOCATION Lymphatic organs
DESCRIPTION Network of reticular fibers in loose ground substances, cells lie on network
CELLS FUNCTION Reticular cell, Fibers form an internal skeleton stoma that WBC, mast, supports other cell types, macrophages
Tendons, ligaments
Parallel collagen fibers, a few elastic fibers
Fibroblast
Attaches to muscles to bones or to muscles, attaches bone to bone, withstand great tensile stress when pulling force is applied on direction.
Fibrous capsules of organs and joints, dermis of skin, submucosa of digestive tract Walls of large Arteries, within ligaments associated with vertebral column; within walls of bronchial tubes
Irregularly arranged collagen fibers, some elastic fibers
Fibroblast
Able to withstand tension exerted in many directions; provides structural strength
DENSE REGULAR connective tissue contain high proportion of elastic fibers
Fibroblast
Allows recoiling of tissue following stretching, maintains pulsatile flow of blood through arteries, aids in passive recoil of lungs following inspiration.
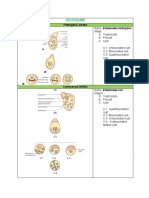
TISSUE TYPE Elastic Cartilages
Fibrocartilage
LOCATION Forms most of embryonic skeleton, ends of long bones in joint cavities, forms costal cartilages of ribs, cartilages of nose, trachea and larynx External ear, epiglottis Intervertebral discs, pubic symphysis, discs of knee joints Bones
DESCRIPTION Amorphous but firm matrix, collagen fibers form an imperceptible network;
CELLS FUNCTION Chondroblasts, Support and reinforces, has resilient chondrocytes cushioning , resists compressive stress
Bone: Osseous tissue
Blood
Similar to hyaline cartilage, but more elastic fibers in matrix Similar but less firm than the hyaline cartilage, thick collagen fibers predominate Hard, calcified matrix contains many collagen fibers & vascularized Red and white cells within matrix plasma
Chondroblasts, chondrocytes Chondroblasts, chondrocytes
Maintains the shape of structure while allowing great flexibility Tensile strength with the ability to absorb compressive shock
Osteocytes, Osteoblasts
Within blood vessels
RBC WBC
Supports and protects by enclosing, provides levers for muscles, stores calcium and minerals and fats, marrow inside bones is site for blood cell formation (hematopoiesis Transport of respiratory gases, nutrients, wastes, other substances
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- HS202 Pathology ExamDokument6 SeitenHS202 Pathology ExamJulio dR AltavasNoch keine Bewertungen
- BloodDokument9 SeitenBloodSheena PasionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leptospires General Characteristics:: Bacteriology: SpirochetesDokument5 SeitenLeptospires General Characteristics:: Bacteriology: SpirochetesJaellah MatawaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Molecular Biology and Diagnostic Intro To CytogeneticsDokument6 SeitenMolecular Biology and Diagnostic Intro To Cytogeneticselijah montefalcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemistry (1-20)Dokument30 SeitenBiochemistry (1-20)Stetho LoveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bacteriostatic Agents: Drugs Which Bind To The 50s Ribosomal UnitDokument3 SeitenBacteriostatic Agents: Drugs Which Bind To The 50s Ribosomal UnitJoshua TrinidadNoch keine Bewertungen
- HemopoiesisDokument22 SeitenHemopoiesisSheena PasionNoch keine Bewertungen
- AUB - Renal DiseasesDokument2 SeitenAUB - Renal DiseasesJeanne RodiñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ConnectivetissuepptDokument20 SeitenConnectivetissuepptChicco De AngelisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hemostasis and Thrombosis: OutlineDokument11 SeitenHemostasis and Thrombosis: OutlineManila MedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immunoserology ReviewDokument45 SeitenImmunoserology ReviewJacqueline RoijardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiology Lecture - Dr. ManaloDokument3 SeitenPhysiology Lecture - Dr. ManaloJayricDepalobosNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2023.LabDx - Trans02.Hemostasis and ThrombosisDokument4 Seiten2023.LabDx - Trans02.Hemostasis and ThrombosisstellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.entamoeba Histolytica - Is The Major Pathogen in This GroupDokument14 Seiten1.entamoeba Histolytica - Is The Major Pathogen in This GroupJoseph De JoyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISBBhandoutDokument55 SeitenISBBhandoutRed GillianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fasciolopsis Buski: F Hepatica F. BuskiDokument4 SeitenFasciolopsis Buski: F Hepatica F. BuskiGela ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parasitology Laboratory Questionnaires 2TDokument21 SeitenParasitology Laboratory Questionnaires 2TJen CANoch keine Bewertungen
- Nervous System - HistologyDokument8 SeitenNervous System - HistologyambercrisologoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Normal Haemopoiesis: Dr. Tariq M. Roshan Department of Hematology PPSPDokument29 SeitenNormal Haemopoiesis: Dr. Tariq M. Roshan Department of Hematology PPSPyamanassafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vitamin B12 and FolateDokument12 SeitenVitamin B12 and FolateAllessandria DimaggioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intro To ImmunohematoDokument48 SeitenIntro To Immunohematojong188Noch keine Bewertungen
- Capillary Fragility/ Resistance Test: Tourniquet or Rumpel-Leede or Hess TestDokument4 SeitenCapillary Fragility/ Resistance Test: Tourniquet or Rumpel-Leede or Hess TestGerly MaglangitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Staphylococci: Streptococcus PyogenesDokument20 SeitenStaphylococci: Streptococcus PyogenesPharmacy2015100% (2)
- 3 SEMR421 Bacteriology Part 3Dokument14 Seiten3 SEMR421 Bacteriology Part 3Micah Daniel TapiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parasite Trematodes PDFDokument2 SeitenParasite Trematodes PDFGougle MuteNoch keine Bewertungen
- HAEMOPOIESISDokument6 SeitenHAEMOPOIESISDiyana ZahariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medtech Laws DelfinDokument16 SeitenMedtech Laws DelfinNeririNoch keine Bewertungen
- CM Review Notes 2Dokument22 SeitenCM Review Notes 2USMAN JuhaminNoch keine Bewertungen
- MTAP ISBB - Sir JJ (Merged)Dokument9 SeitenMTAP ISBB - Sir JJ (Merged)Nathan DrakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hematology ReviewerDokument10 SeitenHematology ReviewerAldren BeliberNoch keine Bewertungen
- Robbins - 12 The HeartDokument5 SeitenRobbins - 12 The HeartCM NajitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immuno Serology ReviewDokument16 SeitenImmuno Serology ReviewM CNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENZYMOLOGYDokument2 SeitenENZYMOLOGYCarla Lagar FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity Tabulation ParasitologyDokument18 SeitenActivity Tabulation ParasitologyStephen YorNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.5 PHARMA ANTI MYCOBACTERIAL AGENTSpdfDokument18 Seiten3.5 PHARMA ANTI MYCOBACTERIAL AGENTSpdfJanet SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- MycoViro - Complete Handouts (AMCC)Dokument46 SeitenMycoViro - Complete Handouts (AMCC)Martin Clyde100% (1)
- Lecture 10 Vibrio, Aeromonas, Campylobacter and HelicobacterDokument4 SeitenLecture 10 Vibrio, Aeromonas, Campylobacter and HelicobacterRazmine RicardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NO Hazard Slight Moderate Serious Extreme: Hazard Hazard Hazard HazardDokument74 SeitenNO Hazard Slight Moderate Serious Extreme: Hazard Hazard Hazard HazardCristy Jean100% (1)
- Methods of Studying Fungi: Dr. Alice Alma C. BungayDokument74 SeitenMethods of Studying Fungi: Dr. Alice Alma C. BungayKaycee Gretz LorescaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathology 1st Practical ExamDokument101 SeitenPathology 1st Practical Examjeffrey_co_1Noch keine Bewertungen
- CC Bishop QuestionsDokument3 SeitenCC Bishop QuestionsJohanna Kate DiestroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microbiology Mock Board RationalizationDokument228 SeitenMicrobiology Mock Board RationalizationCla NuvalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immuno SeroDokument80 SeitenImmuno SeroDocAxi Maximo Jr AxibalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Student Notes: Clinchem1: Davao Doctors College Medical Laboratory Science DepartmentDokument5 SeitenStudent Notes: Clinchem1: Davao Doctors College Medical Laboratory Science DepartmentMelody PardilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- HEMOSTASIS Coagulation PathwayDokument3 SeitenHEMOSTASIS Coagulation PathwayGianna SablanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immunology and Serology TestsDokument2 SeitenImmunology and Serology TestsPearlregine Cianne MirandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aubf Trans PrelimDokument18 SeitenAubf Trans PrelimSarah EugenioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic Outline: Elements of Parasitology (3P's) Types of Association of Living OrganismsDokument6 SeitenTopic Outline: Elements of Parasitology (3P's) Types of Association of Living OrganismsJhunrick Corpuz TumpalanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nematodes: 2. Enterobius VermicularisDokument2 SeitenNematodes: 2. Enterobius VermicularisCia QuebecNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immunoserology Review CompleteDokument41 SeitenImmunoserology Review CompleteAndrea Faye MONTERONANoch keine Bewertungen
- MedtechDokument7 SeitenMedtechLyudmyla GillegoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microbiology - Bacteria Summary (Updated)Dokument26 SeitenMicrobiology - Bacteria Summary (Updated)moZZeltovNoch keine Bewertungen
- Molbio HandoutDokument29 SeitenMolbio HandoutHazel FlorentinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 23 SummaryDokument4 SeitenChapter 23 SummaryMartin ClydeNoch keine Bewertungen
- CiullahemaDokument60 SeitenCiullahemaMariel AbatayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- MT LawsDokument8 SeitenMT LawsKathleen Javier AngcayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calcium, Magnesium, and Potassium Homeostasis: OutlineDokument10 SeitenCalcium, Magnesium, and Potassium Homeostasis: OutlineMigs MedinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anti-Anemia and Hematopoietic Growth FactorsDokument8 SeitenAnti-Anemia and Hematopoietic Growth FactorsIsabel CastilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- CLINICAL CHEMISTRY: Passbooks Study GuideVon EverandCLINICAL CHEMISTRY: Passbooks Study GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- 13.histology LectureDokument64 Seiten13.histology LecturepashaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Auditory Pathway PDFDokument3 SeitenAuditory Pathway PDFShruthi DanielNoch keine Bewertungen
- WLP Science q2 w3 Nov 28 Dec 2Dokument6 SeitenWLP Science q2 w3 Nov 28 Dec 2Maria Aurea BorjaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theories OF Hallucination: Presenter: DR Rajnarayan M Chair: DR Geetha D Unit IvDokument28 SeitenTheories OF Hallucination: Presenter: DR Rajnarayan M Chair: DR Geetha D Unit Ivamit1109Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hand PositionsDokument1 SeiteHand PositionsReiki RaysNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skin Care ClassDokument16 SeitenSkin Care ClassMuhammad Aliff Abdul RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ICD 10 CM SPECIALIZED CodingWorkbookwithAns v1.1Dokument161 SeitenICD 10 CM SPECIALIZED CodingWorkbookwithAns v1.1AntonSusanto100% (1)
- Pulmonary Complications in Liver DiseaseDokument3 SeitenPulmonary Complications in Liver DiseaseblanquishemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Reproduction PyqsDokument7 SeitenHuman Reproduction PyqsMrityunjay PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 6 AssessmentDokument6 SeitenModule 6 Assessmentapi-98991203Noch keine Bewertungen
- LLENAS - DLL Sci 9 - Sept 5 9 KMLDokument6 SeitenLLENAS - DLL Sci 9 - Sept 5 9 KMLNicole Eve Pelaez-AbarrientosNoch keine Bewertungen
- IMMUNITYDokument5 SeitenIMMUNITYKebbewar KhaledNoch keine Bewertungen
- Addison Ds 9Dokument3 SeitenAddison Ds 9Eden Jay Calija AgoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Update On The Pathogenesis and Treatment of IgADokument12 SeitenAn Update On The Pathogenesis and Treatment of IgAYulius DonyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diploma in Occupational TherapyDokument47 SeitenDiploma in Occupational TherapyAzmi Plus100% (2)
- Theoretical test-PART B-ANSWER KEY FinalDokument10 SeitenTheoretical test-PART B-ANSWER KEY FinalĐồng Ngọc HàNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lobes Structures of The BrainDokument2 SeitenLobes Structures of The BrainCognita CenterNoch keine Bewertungen
- DoNation PowerPoint TemplateDokument11 SeitenDoNation PowerPoint TemplateIvana BunticNoch keine Bewertungen
- 16 Organizing Pneumonia - Libre PathologyDokument4 Seiten16 Organizing Pneumonia - Libre PathologyfadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLL SCIENCE (MELCs) W1Dokument7 SeitenDLL SCIENCE (MELCs) W1MYLEEN P. GONZALESNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tatalaksana Tekanan Tinggi Intrakranial Pada Anak-DikonversiDokument48 SeitenTatalaksana Tekanan Tinggi Intrakranial Pada Anak-DikonversiAbdurrahman Arsyad As SiddiqiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Semi-Final Exam in AnatomyDokument3 SeitenSemi-Final Exam in AnatomyEdmund Lominoque LamelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Bank For Human Biology Concepts and Current Issues 7th Edition JohnsonDokument26 SeitenTest Bank For Human Biology Concepts and Current Issues 7th Edition JohnsonJamesJacksonjbpof100% (74)
- MDCT and MR Urogram Spectrum of Congenital. JurnalDokument11 SeitenMDCT and MR Urogram Spectrum of Congenital. JurnalTamara IstikharaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Space Occupying Lesion: Case ReportDokument31 SeitenSpace Occupying Lesion: Case ReportMaria Margareta HutajuluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology: Human Respiratory SystemDokument3 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology: Human Respiratory SystemVin EighteenthNoch keine Bewertungen
- OpenStax Psychology2e LN03Dokument7 SeitenOpenStax Psychology2e LN03Whitney CartwrightNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slides To Draw and StudyDokument21 SeitenSlides To Draw and StudyAndrea Galang CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Esophagus: Pipe or Gullet, Is An Organ in Vertebrates Through Which Food PassesDokument12 SeitenEsophagus: Pipe or Gullet, Is An Organ in Vertebrates Through Which Food PassesCrow LordNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology of Adrenal GlandsDokument14 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology of Adrenal GlandsEunice CuñadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liceo de Cagayan University R.N Pelaez Blvd. Carmen, Cagayan deDokument46 SeitenLiceo de Cagayan University R.N Pelaez Blvd. Carmen, Cagayan deevanisansNoch keine Bewertungen