Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Periodic Trends of The Element
Hochgeladen von
Ankit GandhiOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Periodic Trends of The Element
Hochgeladen von
Ankit GandhiCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
CHM 3609 - Inorganic Chemistry
Chapter 8: Periodic Table of the elements Types of Elements and Compounds: Elemental forms: Solid, Liquids and Gases
Mark D. Jackson
jacksonm@fau.edu
Monatomic gases: rare gases (non reactive under most conditions; F compounds) Diatomic elements: halogens, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen Discrete molecular units: S (cyclic S8), P, Se, C60 (fullerenes) Extended covalent structures: C (diamond, graphite); Si, P, S; Ge, As, Se; Sn, Sb, Te; Bi Metals: most common type of element High coordination; CCP, HCP (12x), BCC (8 + near 6; center of a cube) Nuclei + delocalized electrons; AOs form electronic bands Some overlap in molecular - extended - metal categories Chemical compounds: Ionic-covalent- metallic bonding spectrum Ionic compounds, some soluble in water, others insoluble. Molecular solids and molecular units. Complex anions and cations Transition metal compounds: non-bonding ligand and metal-ligand bonded Overview of periodicity: * The chemistry of an element depends almost solely on the number of valence electrons, with only slight variations as you pass down a column/family of elements. * Cation and anions change size a bit, but over all properties are very similar; the addition of d-orbitals can lead to some new properties, such as an expanded octet. * Cause: Inner electrons screen (diminish) the nuclear-valence-electron interaction; roughly, the outermost n th electron feels much less than +n charge, it may feel an effective nuclear charge of +2 or +3. Review periodic trends: 1. Comparable valence electronic structure for elements in the same family; therefore similar chemical and physical properties. Atoms or ions simply get a bit larger as you go down the column. 2. Ionization energies - most obvious variable to examine; trends validate Noble Gases as most stable. Show the effect of inner shell electron screening and Z-dependence of energy. 3 .Atomic radii and ionic radii - These are not really properties of the atom, since they must be calculated from experimental structural data; how do you define the limit of the electron cloud? Ionic radii always depend on the ionic charge, the counter ion, and coordination (crystal type). Atomic radii: you must consider covalent radii based on either diatomic molecules or solids (the latter may also vary with structural form - metal or extended solid).
Beware the chemical form of the element..... density (g or s?); physical properties (metal or diatomic or ?) Development of the Periodic Table: some elements were predicted based on holes in the Periodic Table.
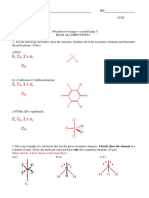
Types of problems: i. Major types of elemental forms ii. Understand trends in the ionization potential, ionic and covalent radii. iii. Compare covalent, ionic and metallic bonding. iv. Recognize the diverse range of structures found for the elements.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5795)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1091)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Inductively Coupled Plasma SpectrosDokument1 SeiteInductively Coupled Plasma SpectrosBoonGen GeamNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Typical Schematic Diagram of UvDokument2 SeitenA Typical Schematic Diagram of UvBalqis yasinNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT-2 Chem Bonding-2Dokument13 SeitenUNIT-2 Chem Bonding-2KARTIKAY LADDHANoch keine Bewertungen
- Virtual Experiment 2: Instrumentation and Working Principles of Infrared (IR) SpectrosDokument10 SeitenVirtual Experiment 2: Instrumentation and Working Principles of Infrared (IR) SpectrosBernadette Virola CuevasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Light Purple and Yellow Gradient Marketing Plan Presentation-DikonversiDokument15 SeitenLight Purple and Yellow Gradient Marketing Plan Presentation-DikonversiLilianty nurdinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculation of Δ0, Inter Electronic Repulsion Parameter (B) & β for d1, d9, d4, d6, d2 & d8 ComplexesDokument32 SeitenCalculation of Δ0, Inter Electronic Repulsion Parameter (B) & β for d1, d9, d4, d6, d2 & d8 Complexesramukaka100% (2)
- Chemical BondingDokument38 SeitenChemical Bondingsmileworker utkarshsinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnetic RadiationDokument22 SeitenElectromagnetic RadiationSelva Kumar0% (1)
- Flame SpectrosDokument20 SeitenFlame SpectrosMustafa KhandgawiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Principles of AASDokument22 SeitenBasic Principles of AASShaira CogollodoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Set 6 UV Vis Absorption Spectroscopy1Dokument10 SeitenProblem Set 6 UV Vis Absorption Spectroscopy1Konata OzumiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 InorgDokument29 SeitenChapter 5 InorgMauritiusFeliciano100% (2)
- Accelerate EducationDokument11 SeitenAccelerate EducationThomas DyeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch. 2 Resonance Structures and Aromatic CompoundsDokument27 SeitenCh. 2 Resonance Structures and Aromatic CompoundsCollo KarisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dipoles and Intermolecular ForcesDokument14 SeitenDipoles and Intermolecular Forcesspidy warriorsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ligand Field Theory-IDokument19 SeitenLigand Field Theory-IMeyga Evi Ferama Sari100% (1)
- PhosphorescenceDokument18 SeitenPhosphorescencejaanabhenchodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction and ConclusionDokument2 SeitenIntroduction and ConclusionKiara De LeonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2Dokument3 SeitenChapter 2叶震森Noch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 9 Chemistry Test ReviewDokument1 SeiteGrade 9 Chemistry Test ReviewEric Hill0% (1)
- Chapter 19 NMRDokument126 SeitenChapter 19 NMRMuchammad RofiiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Or Molecular Structure Is The Three-Dimensional Arrangement of Atoms Within A MoleculeDokument38 SeitenOr Molecular Structure Is The Three-Dimensional Arrangement of Atoms Within A MoleculeGael Forbes RealNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ex IrDokument7 SeitenEx IrVinh HoangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handout For Russell-Saunders Coupling PDFDokument12 SeitenHandout For Russell-Saunders Coupling PDFAditiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Master Card - Coordination CompoundsDokument2 SeitenMaster Card - Coordination CompoundsgudiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analytical EXP 7 Cigarette ICP-AESDokument15 SeitenAnalytical EXP 7 Cigarette ICP-AESHanyszShal100% (1)
- Exam1 121 KeyDokument5 SeitenExam1 121 KeyAl 12Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fluorescein Dye PDFDokument7 SeitenFluorescein Dye PDFLaura FajardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChromophoresDokument28 SeitenChromophoresangelalee20002Noch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Instrumental Analysis Experiment 2: Uv-Visible Determination of An Unknown Concentration of Kmno4 SolutionDokument7 SeitenBasic Instrumental Analysis Experiment 2: Uv-Visible Determination of An Unknown Concentration of Kmno4 SolutionSiti Maizatul AkmaNoch keine Bewertungen