Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Interfacing With Intel 8251a
Hochgeladen von
Santhosh KumarOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Interfacing With Intel 8251a
Hochgeladen von
Santhosh KumarCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
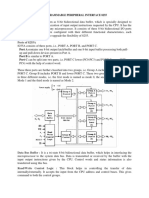
INTERFACING WITH INTEL 8251A (USART)
The 8251A is a programmable serial communication interface chip designed for synchronous and asynchronous serial data communication.
It supports the serial transmission of data.
It is packed in a 28 pin DIP.
Read/Write control logic:
The Read/Write Control logic interfaces the 8251A with CPU, determines the functions of the 8251A according to the control word written into its control register.
It monitors the data flow.
This section has three registers and they are control register, status register and data buffer.
The active low signals RD, WR, CS and C/D(Low) are used for read/write operations with these three registers.
When C/D(low) is high, the control register is selected for writing control word or reading status word.
When C/D(low) is low, the data buffer is selected for read/write operation.
When the reset is high, it forces 8251A into the idle mode.
The clock input is necessary for 8251A for communication with CPU and this clock does not control either the serial transmission or the reception rate.
Transmitter section:
The transmitter section accepts parallel data from CPU and converts them into serial data.
The transmitter section is double buffered, i.e., it has a buffer register to hold an 8-bit parallel data and another register called output register to convert the parallel data into serial bits.
When output register is empty, the data is transferred from buffer to output register. Now the processor can again load another data in buffer register.
If buffer register is empty, then TxRDY is goes to high.
If output register is empty then TxEMPTY goes to high.
The clock signal, TxC (low) controls the rate at which the bits are transmitted by the USART.
The clock frequency can be 1,16 or 64 times the baud rate.
Receiver Section:
The receiver section accepts serial data and convert them into parallel data
The receiver section is double buffered, i.e., it has an input register to receive serial data and convert to parallel, and a buffer register to hold the parallel data.
When the RxD line goes low, the control logic assumes it as a START bit, waits for half a bit time and samples the line again.
If the line is still low, then the input register accepts the following bits, forms a character and loads it into the buffer register.
The CPU reads the parallel data from the buffer register.
When the input register loads a parallel data to buffer register, the RxRDY line goes high.
The clock signal RxC (low) controls the rate at which bits are received by the USART.
During asynchronous mode, the signal SYNDET/BRKDET will indicate the break in the data transmission.
During synchronous mode, the signal SYNDET/BRKDET will indicate the reception of synchronous character.
MODEM Control:
The MODEM control unit allows to interface a MODEM to 8251A and to establish data communication through MODEM over telephone lines.
This unit takes care of handshake signals for MODEM interface.
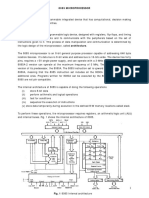
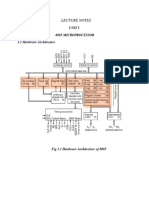
Block Diagram:
The functional block diagram of 825 1A consists five sections. They are:
Read/Write control logic Transmitter Receiver Data bus buffer Modem control.
The functional block diagram is shown in fig:
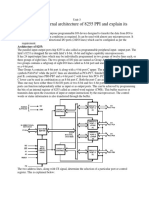
The 825 1A can be either memory mapped or I/O mapped in the system.
8251A in I/O mapped in the system is shown in the figure.
Using a 3-to-8 decoder generates the chip select signals for I/O mapped devices.
The address lines A4, A5 and A6 are decoded to generate eight chip select signals (IOCS-0 to IOCS-7) and in this, the chip select signal IOCS-2 is used to select 8251A.
The address line A7 and the control signal IO / M(low) are used as enable for decoder.
The address line A0 of 8085 is connected to C/D(low) of 8251A to provide the internal addresses.
The data lines D0 - D7 are connected to D0 - D7 of the processor to achieve parallel data transfer. The RESET and clock signals are supplied by the processor. Here the processor clock is directly connected to 8251A. This clock controls the parallel data transfer between the processor and 8251A.
The output clock signal of 8085 is divided by suitable clock dividers like programmable timer 8254 and then used as clock for serial transmission and reception.
The TTL logic levels of the serial data lines and the control signals necessary for serial transmission and reception are converted to RS232 logic levels using MAX232 and then terminated on a standard 9-pin D-.type connector.
In 8251A the transmission and reception baud rates can be different or same. The device which requires serial communication with processor can be connected to this 9-pin D-type connector using 9-core cable
The signals TxEMPTY, TxRDY and RxRDY can be used as interrupt signals to initiate interrupt driven data transfer scheme between processor and 8251 A.
I/O addresses of 8251A interfaced to 8085 is,
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Preliminary Specifications: Programmed Data Processor Model Three (PDP-3) October, 1960Von EverandPreliminary Specifications: Programmed Data Processor Model Three (PDP-3) October, 1960Noch keine Bewertungen
- Serial Data Transmission Vs Parallel Data Transmission: Unit 5Dokument16 SeitenSerial Data Transmission Vs Parallel Data Transmission: Unit 5achuu1987Noch keine Bewertungen
- Practical Reverse Engineering: x86, x64, ARM, Windows Kernel, Reversing Tools, and ObfuscationVon EverandPractical Reverse Engineering: x86, x64, ARM, Windows Kernel, Reversing Tools, and ObfuscationNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8251 - Usart Serial Communication InterfaceDokument17 Seiten8251 - Usart Serial Communication InterfaceVignesh GuruNoch keine Bewertungen
- MPMC IiiDokument106 SeitenMPMC IiiMani Kumar AmarlapudiNoch keine Bewertungen
- UsartDokument13 SeitenUsartksanthiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8251A USART - Programmable Communication InterfaceDokument15 Seiten8251A USART - Programmable Communication InterfaceShreerama Samartha G BhattaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit3 MicroprocessorDokument27 SeitenUnit3 MicroprocessorAshishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Peripheral InterfacingDokument32 SeitenPeripheral Interfacingsulekha saxenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit IIIDokument42 SeitenUnit IIISoundarrajan RajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8251 & 8253 Programmable Communication Interface &programmable Interval TimerDokument47 Seiten8251 & 8253 Programmable Communication Interface &programmable Interval Timersree2728Noch keine Bewertungen
- 8251A Universal Synchronous Asynchronous Receiver TransmitterDokument8 Seiten8251A Universal Synchronous Asynchronous Receiver TransmitterPratibha SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Minimum and Maximum ModesDokument21 SeitenMinimum and Maximum ModesSubash BasnyatNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8251A USART - Programmable Communication InterfaceDokument15 Seiten8251A USART - Programmable Communication InterfaceselvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8251 - UsartDokument24 Seiten8251 - UsartAvanish NiranjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MP-MC R16 - Unit-3Dokument21 SeitenMP-MC R16 - Unit-3yasshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microprocessors: BY: Prof. Dileep J Dept. of TCE K.S.I.TDokument16 SeitenMicroprocessors: BY: Prof. Dileep J Dept. of TCE K.S.I.TsenthilNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8085 MaterialDokument12 Seiten8085 MaterialsameerNoch keine Bewertungen
- By K. Praveen Kumar Asst. Prof in ECE Dept. GITAM University-HyderabadDokument24 SeitenBy K. Praveen Kumar Asst. Prof in ECE Dept. GITAM University-HyderabadHariTejNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8085 Features, Signal DescriptionDokument13 Seiten8085 Features, Signal DescriptionRakesh Kumar DNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation 1Dokument23 SeitenPresentation 1khushalee.chavadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8251 UsartDokument19 Seiten8251 UsartkadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ¡ Semiconductor: MSM80C85AHRS/GS/JSDokument29 Seiten¡ Semiconductor: MSM80C85AHRS/GS/JSdanielhoseaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microprocessor System: Session # 7Dokument13 SeitenMicroprocessor System: Session # 7Aamir BhuttoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8251A Programmable Communication InterfaceDokument25 Seiten8251A Programmable Communication InterfaceRohith YerrabachalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8086 Section 3-4Dokument4 Seiten8086 Section 3-4Jaspreet KaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- USARTDokument17 SeitenUSARTtharunvenkataNoch keine Bewertungen
- 18ecc203j - Unit 3 Edit Session 11 - 13Dokument38 Seiten18ecc203j - Unit 3 Edit Session 11 - 13Ankur JhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.7 Timer/counter 8253/8254Dokument15 Seiten3.7 Timer/counter 8253/8254skarthikmtechNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microprocessor - 8085 Internal ArchitectureDokument25 SeitenMicroprocessor - 8085 Internal ArchitectureTanveer Ahmed HakroNoch keine Bewertungen
- MicroprocessorDokument7 SeitenMicroprocessorSanoxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dmacontroller 8257Dokument27 SeitenDmacontroller 8257satyanarayana12Noch keine Bewertungen
- 8085 Microprocessor - Functional Units: AccumulatorDokument5 Seiten8085 Microprocessor - Functional Units: AccumulatorDeep KambleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit Iii I/O Interfacing Reference: Chapter 9 Microcomputer Systems, Cheng Liu, Glenn GibsonDokument337 SeitenUnit Iii I/O Interfacing Reference: Chapter 9 Microcomputer Systems, Cheng Liu, Glenn GibsonGomathi PsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ec6504 MPMC Unit 3Dokument337 SeitenEc6504 MPMC Unit 3dkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Remote Controlled Digital Audio Processor - Full Project AvailableDokument3 SeitenRemote Controlled Digital Audio Processor - Full Project AvailableK Raja SekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Programmable Communication InterfaceDokument44 SeitenProgrammable Communication InterfaceBETHWEL KIPROTICHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit I PDFDokument25 SeitenUnit I PDFSomnath2014Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 6 2Dokument25 SeitenUnit 6 2Venkatesh RachaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ii Microprocessor - 8085 ArchitectureDokument6 SeitenIi Microprocessor - 8085 ArchitectureYohannis DanielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microprocessor & Interfacing Tittle: Interfacing Pheripheral 8251 With 8086Dokument19 SeitenMicroprocessor & Interfacing Tittle: Interfacing Pheripheral 8251 With 8086odaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dma Controller 8257Dokument27 SeitenDma Controller 8257Rathore Yuvraj SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8259 PIC AND 8237 DMA: by Harjot Kaur (2203448) Isha (2203461)Dokument13 Seiten8259 PIC AND 8237 DMA: by Harjot Kaur (2203448) Isha (2203461)Harjot KaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ee8551 8085 NotesDokument31 SeitenEe8551 8085 NotesKUMARANSCRNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8259 Programmable Interrupt Controller T.Srikrishna, M.SC, M.Tech, GVPDokument4 Seiten8259 Programmable Interrupt Controller T.Srikrishna, M.SC, M.Tech, GVPAbhayNoch keine Bewertungen
- MPMC NotesDokument301 SeitenMPMC NotesVarinder KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maximum Mode 8086 SystemDokument9 SeitenMaximum Mode 8086 Systemchenna838Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit II Special Purpose Programmable Peripherals and Their InterfacingDokument10 SeitenUnit II Special Purpose Programmable Peripherals and Their InterfacingPraveen RathnamNoch keine Bewertungen
- MC8085Dokument7 SeitenMC8085Bhavani BhavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operating Modes of 8086 MicroprocessorDokument9 SeitenOperating Modes of 8086 MicroprocessorMOHAMMED ASLAM CNoch keine Bewertungen
- DatasheetDokument16 SeitenDatasheetAmmu PuniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Features and Modes of 8086Dokument11 SeitenFeatures and Modes of 8086ABHishekNoch keine Bewertungen
- MPDokument34 SeitenMPAbhinandan JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3 Interfacing: InterfaceDokument21 SeitenUnit 3 Interfacing: Interfacechirag khandelwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8282,8286,8284Dokument23 Seiten8282,8286,8284Relan Soniia100% (1)
- 8251 - UsartDokument26 Seiten8251 - UsartSreekanth PagadapalliNoch keine Bewertungen
- April 14Dokument167 SeitenApril 14Santhosh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Finance Xii SP New SyllabusDokument21 SeitenBusiness Finance Xii SP New SyllabusSanthosh Kumar100% (1)
- Role of A Secretary in Capital Formation Xii Commerce SP New SyllabusDokument28 SeitenRole of A Secretary in Capital Formation Xii Commerce SP New SyllabusSanthosh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sources of Business Finance Xii Commerce SP New SyllabusDokument30 SeitenSources of Business Finance Xii Commerce SP New SyllabusSanthosh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- AHM 250 SummaryDokument116 SeitenAHM 250 SummarySanthosh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- OPTCL Management Trainee Question PaperDokument7 SeitenOPTCL Management Trainee Question PaperSanthosh Kumar0% (1)
- WHO Partograph Study Lancet 1994Dokument6 SeitenWHO Partograph Study Lancet 1994Dewi PradnyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Small Signal Analysis Section 5 6Dokument104 SeitenSmall Signal Analysis Section 5 6fayazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Writing Task The Strategy of Regional Economic DevelopementDokument4 SeitenWriting Task The Strategy of Regional Economic DevelopementyosiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ms Microsoft Office - WordDokument3 SeitenMs Microsoft Office - WordFarisha NasirNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBC Building Wiring Installation NC IIDokument72 SeitenCBC Building Wiring Installation NC IIFaysbuk KotoNoch keine Bewertungen
- HP Sustainability Impact Report 2018Dokument147 SeitenHP Sustainability Impact Report 2018Rinaldo loboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lexington School District Two Return To School GuideDokument20 SeitenLexington School District Two Return To School GuideWLTXNoch keine Bewertungen
- NIELIT Scientist B' Recruitment 2016 - Computer Science - GeeksforGeeksDokument15 SeitenNIELIT Scientist B' Recruitment 2016 - Computer Science - GeeksforGeeksChristopher HerringNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scope of Internet As A ICTDokument10 SeitenScope of Internet As A ICTJohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise 23 - Sulfur OintmentDokument4 SeitenExercise 23 - Sulfur OintmentmaimaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- MSA Chair's Report 2012Dokument56 SeitenMSA Chair's Report 2012Imaad IsaacsNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCoal Coal July Investor SlidesDokument26 SeitenMCoal Coal July Investor SlidesMCoaldataNoch keine Bewertungen
- YeetDokument8 SeitenYeetBeLoopersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Windsor Machines LimitedDokument12 SeitenWindsor Machines LimitedAlaina LongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Awais Inspector-PaintingDokument6 SeitenAwais Inspector-PaintingMohammed GaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Codex Standard EnglishDokument4 SeitenCodex Standard EnglishTriyaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Certification and LettersDokument6 SeitenCertification and LettersReimar FerrarenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Item Description RCVD Unit Price Gross Amt Disc % Ta Amount DeptDokument1 SeiteItem Description RCVD Unit Price Gross Amt Disc % Ta Amount DeptGustu LiranNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISP Flash Microcontroller Programmer Ver 3.0: M Asim KhanDokument4 SeitenISP Flash Microcontroller Programmer Ver 3.0: M Asim KhanSrđan PavićNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tate Modern London, Pay Congestion ChargeDokument6 SeitenTate Modern London, Pay Congestion ChargeCongestionChargeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science News Explores-June July 2023Dokument36 SeitenScience News Explores-June July 2023Tobei AchimNoch keine Bewertungen
- IEEE Conference Template ExampleDokument14 SeitenIEEE Conference Template ExampleEmilyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Staircase and Lintel As-03Dokument1 SeiteStaircase and Lintel As-03Divith B SannakkiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soneri Bank Compensation PolicyDokument20 SeitenSoneri Bank Compensation PolicySapii MandhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gravity Based Foundations For Offshore Wind FarmsDokument121 SeitenGravity Based Foundations For Offshore Wind FarmsBent1988Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gis Tabels 2014 15Dokument24 SeitenGis Tabels 2014 15seprwglNoch keine Bewertungen
- RCC Design of Toe-Slab: Input DataDokument2 SeitenRCC Design of Toe-Slab: Input DataAnkitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health Informatics SDokument4 SeitenHealth Informatics SnourhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Random Variable N N Mean or Expected Value: Number of Ducks Type of Duck AmountDokument2 SeitenRandom Variable N N Mean or Expected Value: Number of Ducks Type of Duck AmountAngie PastorNoch keine Bewertungen