Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Akshay Company Analysis
Hochgeladen von
Mansimran KaurOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Akshay Company Analysis
Hochgeladen von
Mansimran KaurCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
COMAPNY ANALYSIS Introduction Axis Bank Limited, formerly UTI Bank, is an Indian financial services firm that had
begun operations in 1994, after the Government of India allowed new private banks to be established. The Bank was promoted jointly by the Administrator of the Specified Undertaking of the Unit Trust of India (UTI-I), Life Insurance Corporation of India (LIC), General Insurance Corporation Ltd., National Insurance Company Ltd., The New India Assurance Company, The Oriental Insurance Corporation and United India Insurance Company UTI-I holds a special position in the Indian capital markets and has promoted many leading financial institutions in the country. The bank changed its name to Axis Bank in April 2007 to avoid confusion with other unrelated entities with similar name. On 24 February 2010, Axis Bank announced the launch of 'AXIS CALL & PAY on atom', a unique mobile payments solution using Axis Bank debit cards. Axis Bank is the first bank in the country to provide a secure debit card-based payment service over IVR.
Branch Network The Bank's Registered Office is at Ahmadabad and its Central Office is located at Mumbai. At the end of March 2012, the Bank has a very wide network of 1,622 domestic branches and extension counters and at end of March 2012 there were 9,924 ATMs situated in 1,050 cities and town. The Bank today is capitalized to the extent of 4.099 billion with the public holding (other than promoters and GDRs) at 53.63%. It is also listed in the top 100 most trusted brands of India in the Brand Trust report. Axis Bank operates the worlds highest ATM site at Thegu, Sikkim at 13,200 feet above sea level.
Company Profile Axis Bank Limited is an India-based bank. The Bank operates in four segments: treasury operation, which includes investments in sovereign and corporate debt, equity and mutual funds, trading operations, derivative trading and foreign exchange operations on the account, and for customers and central funding; retail banking, which includes lending to individuals/small businesses subject to the orientation, product and granularity criterion, and also includes liability products, card services, Internet banking, automated teller machines (ATM) services, depository, financial advisory services, and non-resident Indian services (NRI); corporate/wholesale banking, which includes corporate relationships not included under retail banking, corporate advisory services, placements and syndication, management of publics issue, project appraisals, capital market related services, and cash management services, and other banking business, which includes para banking activities.
SERVICES 1. Retail Banking Deposit Schemes Loans and Advances (i).Personal Loans (ii).Housing Loans (iii).Cards (iv).Auto Loans 2. Personal Banking Term Deposits Fixed Deposits Recurring Deposits Different variants of cards Gold plus cards, silver and silver plus cards 3. Corporate Banking Accounts (i).Normal Current a/c (ii).NGO savings a/c Services (i).Private Equity, mergers and acquisitions (ii).Advisory services (iii).Capital market funding (iv).E-broking
CAPITAL STRUCTURE The capital structure of a company refers to the mix of the long term finances used by the firm. It is the financing plan of the company. Features of an Optimal Capital Structure (i). ProfitabilityThe use of fixed charges sources of funds such as preference shares, debentures and term loans along with equity capital in the capital structure is described as financial leverage. The company should make maximum use of leverage at a minimum cost. (ii). FlexibilityThe capital structure should be flexible. The company should be able to raise funds whenever required and also pay-off debts whenever it becomes too costly to continue with that particular source.
(iii). ControlThe capital structure should involve minimum dilution of the company. (iv). SolvencyThe use of excessive debt threatens the solvency of the company. Companies now prefer public issues with the sole purpose of reducing debt.
DIVIDEND
FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE
SHARE PERFORMANCE
INVESTMENT PORTFOLIO The book value of the Banks investment portfolio as on 31st March 2012 was `93,192 crores, of which, 58,533 crores related to government securities while `34,659 crores were invested in other securities such as corporate bonds, equities, preference shares, mutual funds etc. 73% of the government securities have been classified in the HTM category while 99% of the Bonds & Debentures portfolio have been classified in the AFS category. The distribution of the investment portfolio in the three categories as on 31st March 2012 in each category was as follows:
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Corporate Finance DecisionsDokument3 SeitenCorporate Finance DecisionsPua Suan Jin RobinNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Generation Banking in IndiaDokument9 SeitenNew Generation Banking in IndiaGanesh TiwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- MD Wasim Ansari, Paytm, PPTDokument20 SeitenMD Wasim Ansari, Paytm, PPTMd WasimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1Dokument34 SeitenChapter 1Aira Nhaira MecateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering EconomicsDokument2 SeitenEngineering EconomicsGoverdhan ShresthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Momo Statement ReportDokument2 SeitenMomo Statement ReportHolybabyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Bank For Essentials of Corporate Finance 9th Edition by RossDokument24 SeitenTest Bank For Essentials of Corporate Finance 9th Edition by Rosspauljohnstonapgsoemyjk98% (45)
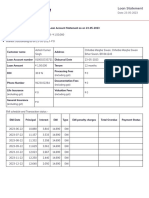
- Navi Loan Account StatementDokument2 SeitenNavi Loan Account Statementashish singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pe Saudi-1Dokument38 SeitenPe Saudi-1alamctcNoch keine Bewertungen
- MoD Constructive Delivery-vl&c-PCSDokument6 SeitenMoD Constructive Delivery-vl&c-PCSVishal BhardwajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indigo PaperDokument75 SeitenIndigo Papernxoxoxrx xxxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functions of IfciDokument4 SeitenFunctions of IfciKŕiśhñą Śińgh100% (1)
- CII InvoiceDokument1 SeiteCII InvoicesambasivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NSE Yield Curve and Implied Yields ReportDokument2 SeitenNSE Yield Curve and Implied Yields ReportCarl RossNoch keine Bewertungen
- Free Cash FlowDokument6 SeitenFree Cash FlowAnh KietNoch keine Bewertungen
- PF Withdrawal Application (Sample Copy)Dokument5 SeitenPF Withdrawal Application (Sample Copy)Ashok Mahanta100% (1)
- Practice set instructionsDokument36 SeitenPractice set instructionsMaureen D. FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- HomeCredit Loan Payment ScheduleDokument2 SeitenHomeCredit Loan Payment ScheduleKylyn JynNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toa Valix Vol 1Dokument451 SeitenToa Valix Vol 1Joseph Andrei BunadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- SECURITIZATION AUDIT - A Waste of Foreclosure Victim MoneyDokument9 SeitenSECURITIZATION AUDIT - A Waste of Foreclosure Victim MoneyBob Hurt50% (2)
- Asc 830Dokument5 SeitenAsc 830Leandro RabinovichNoch keine Bewertungen
- Working Report 2022 30 June English Single Page Artwork Low ResDokument36 SeitenWorking Report 2022 30 June English Single Page Artwork Low ResAparajita RB SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sharekhan: Your Guide To Financial JungleDokument19 SeitenSharekhan: Your Guide To Financial JungleAnil VishwakarmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mt103 Qonto Bank 100 e EuroDokument2 SeitenMt103 Qonto Bank 100 e Eurohaleighcrissy49387Noch keine Bewertungen
- Coprate FinanceDokument114 SeitenCoprate FinanceHrishita AnandNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Markets MmsDokument202 SeitenFinancial Markets MmsJigar ModyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical Investment Management by Robert.A.Strong Slides ch08Dokument28 SeitenPractical Investment Management by Robert.A.Strong Slides ch08mzqaceNoch keine Bewertungen
- SHORT WRITE ABOUT STOCK SHARE AND RISK Electiva CPCDokument7 SeitenSHORT WRITE ABOUT STOCK SHARE AND RISK Electiva CPCyarima paterninaNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Financial Instruments Chapter 11Dokument16 SeitenNew Financial Instruments Chapter 11Dipali DavdaNoch keine Bewertungen
- E Banking Questionaire - Google Forms 33Dokument6 SeitenE Banking Questionaire - Google Forms 33Manish JangidNoch keine Bewertungen