Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Or Writeup Phaco
Hochgeladen von
hakhak013Originalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Or Writeup Phaco
Hochgeladen von
hakhak013Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
I.
Patients Profile A. Demographic data Name: Mr. Y Age: 85 y/o Sex: Mali Civil Status: married Religion: Roman Catholic Address: Poblacion Centro, Tubao, La Union Date of birth: April 29, 1927 Nationality: Filipino B. Environmental Status Their community is set in a rural environment where peace and order is well maintained by the barangay. The patient said, as he asked by the group to describe the house lamang that sa she lives in May gawa isang sa bungalow at na may ng yari sa concreto ang aming bahay pero sa banding kusina ay gawa kawayan. As he kwarto dalawang lote na bintana. continued, ang sukat
kinatatayuan ng bahay namin ay humigit kumulang seventy-two square meters. The patient is the one who maintains the cleanliness of their house which he does religiously every morning and after breakfast. Instead, They use mosquito with her nets as deterrent for mosquitoes. They dont have their own toilet bathroom. they share husbands parents near their house. As with the water pump, they have it at the back of their house located approximately 10 feet away. According furnace using to him, he as cooks fuel. their They food do in not a clay a
charcoal
have
refrigerator; instead, they buy their food daily from the market. their Her husband is usually far does from the the marketing market because other
location
quite
and
facilities. According to the patient, he is contented with
the security that the barangay officials are providing ion their community and the environment where he is currently residing.
C. Lifestyle The patient usually wakes at around six to seven oclock in the morning. he is also fond of chatting and socializing with neighbors. The patient as he claimed is omnivorous. She likes to drink coffee right after meal. he is also fond of eating salty and sweet foods like, as verbalized, salted peanuts, seafoods, junk foods, noodles, kakanin, and drink pop cola. As verbalized, Hindi ako naninigarilyo at umiinom ng alak. Wala akong bisyo magmula ng bata pa ako. The patient usually sleeps at around 9 oclock in the evening after watching televisio D. Family Health History According to the patient, they have a family history of cataract, hypertension, breast cancer, diabetes mellitus and asthma. E. History of Past Illness F. History of Present Illness The patients symptoms started last 2002. he experienced difficulty of seeing things and blurry visions. At first he ignored it but as he experiences it more often she worried for her health condition. of her Even his The relatives patient noticed that the the
enlargement
neck.
said
palpitations
occur
every
day
and
he
had
difficulty
of
sleeping at night.
II.
Anatomy and Physiology
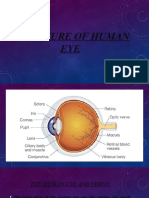
Orbit - refers to the bony socket of the skull that contains the eyeball or globe, and the surrounding nerves, blood vessels, fat, connective tissue, and muscle. Precorneal tear film - The precorneal tear film is produced by the meibomian glands (outer fat layer), the lacrimal and nictitans
glands (watery layer), and the conjunctiva (inner fat layer). The tear film provides an optically smooth surface to the cornea, helps deliver nutrition to the cornea, and contains vitamins, enzymes, and other substances that affect corneal health. The cornea is one of the most sensitive tissues in the body. Corneal nerves are concentrated in the superficial (outer) cornea, with no nerves present in the Descemet's membrane. The limbus is located at the peripheral edge of the cornea and forms the transition zone between the clear cornea and the white sclera. In most horses, there is an obvious gray line at the limbus where ligaments bridging the iris and cornea are visible. The sclera is connected to the cornea and constitutes the major portion of the outer layer of the eyeball. Pupil--The pupil (hole in the iris) changes in size depending upon environmental light intensity-- it constricts in bright light and dilates in dim light to control the amount of light entering the lens. The lens is a transparent structure located behind the iris and held in place by ligaments. The horse uses the lens to focus on nearby objects. Optic disk--The horse's optic disk (which is also called the optic papilla or optic nerve head)contains ganglion cell nerve fibers and can be seen with the ophthalmoscope. Retina--The retina is the most complex structure of the eye and is the most metabolically active tissue in the body. It converts light energy into chemical energy to generate the electrical signal that is conducted to the brain in order for the horse to see.
III.
Pathophysiology Cataract Senile Main problem: the lens ages, its weight and thickness increases while its accommodative power decreases
Risk factors: Female gender Older than 40 years old heriditary Low iodine intake African-Americans seem to have nearly twice the risk of developing cataracts Over exposure to sunlight Smoking and alcohol use
Diagnostic tests and laboratory results: Visual Acuity: A visual acuity test measures your quality of vision at certain distances. Your doctor will ask you to read letters of various sizes from a chart. Your eyes will be tested individually and together to measure the accuracy of your eyesight at different distances. A visual acuity test is an easy, painless, and quick way to diagnosis cataracts, although more tests will be needed to make sure cataracts are the cause of your vision problems. Contrast Sensitivity: Contrast sensitivity testing is similar to visual glare acuity caused testing by the but places Eye greater doctors emphasis consider on how cataracts can decrease image contrast due to light scattering and cataract. contrast sensitivity testing to be a more realistic measurement of true quality of vision.
Slit Lamp: A slit lamp is a special type of microscope that magnifies your eye so your doctor can examine the lens to determine the presence and severity of a cataract. Your doctor will ask you to place your chin on the chin rest of the slit lamp. A light will then be directed at your eye. By looking through the slit lamp, your doctor can examine the lens to determine the degree to which it is clouded. Pupil Dilation: Pupil dilation is a common test used in
diagnosing cataracts. Clouding of
the lens is
not noticeable
until a cataract reaches an advanced stage. When your eye is dilated, however, the pupil increases in size, offering a view of your entire lens. By thoroughly examining the lens, a doctor can determine whether or not a cataract is affecting your quality of vision.
Signs and Symptoms: decrease in clarity of vision, not fully correctable with glasses loss of contrast sensitivity Haloes may be observed around lights Night vision will be diminished will look grey or white to the observer shadows and color vision are less vivid
Treatment: Surgery (Anterior chamber implants, Posterior chamber implants, Small Incision Cataract Surgery, Intracapsular surgery, Phacaemulsification, Cataract Surgery, Extracapsular surgery)
IV.
Patients Preparation A. Skin preparation The skin around the eye was cleansed with antiseptic solution. B. Drapings Sterile C. Position The patient was placed in a supine position with the head turned to the side. (eyeto be operated is up and the dependent ear is well padded) stabilized ina padded, foam, or gel headrest D. Anesthesia used The thyroid surgery was performed with general anesthesia. The specific type using of general anesthesia tube a using was endotracheal by the Before anesthesia endotracheal inserted sheets or towels were draped above the head, keeping only eye visible.
anesthesiologist
(intubation)
laryngoscope.
intubation, the anesthesiologist put the patient to sleep and prevented muscle spasm. other pre-anesthetic drugs were given through IV before the intubation. After inserting the tube, the anesthesiologist checked the patency and the level of the tube until it was inserted and when its intact the tube was connected to the breathing circuit connected to the anesthesia machine. V. Operative procedure After the patient was anesthetized, the surgeon determined the very small incision line measuring bilaterally from the eye. Then he made about 1/8 inch in the white of the eye near the outer edge of the cornea. A small ultrasonic probe is inserted through this opening and, oscillating at 40,000 cycles per minute, is used to break up (emulsify) the cataract into tiny pieces. The emulsified material is simultaneously suctioned from the eye by the open tip of the same instrument. The hard central core of the cataract (the nucleus) is removed first, followed by
extraction of the softer, peripheral cortical fibers that make up the remainder of the lens. The front (anterior) section of the lens capsule is removed along with the fragments of the natural lens. The back (posterior) portion of the capsule is left in place to hold and maintain the correct position for the implanted intraocular lenses. Next, After removal of the cataract, a prescription intraocular lens, or IOL, is permanently implanted in the lens capsule to replace the natural crystalline lens of the eye that was removed during the surgery. This lens is rolled inside a tiny hollow tube and inserted through the same incision that was used to remove the cataract. The folded lens is pushed out of the tube by a tiny plunger and, as it unfolds, is positioned by the surgeon in the center of the lens capsule. The new lens is held in place by microscopic, spring-like wires that are attached to the implant. Finally, he closed the incision and applied dressing on top. VI. OR instruments used
1. This lens is designed for wide angle viewing of phakic, fluid filled eyes during vitrectomy and helps in visualization of the posterior and peripheral fundus in phakic and aphakic eyes. It is also useful in endolaser of peripheral fundus. 2. These flexible nylon hooks retract the iris with minimal damage to the tissue and provide a fast and simple method for temporary pupil enlargement. 3. This helps in safe back flushing of the incarcerated tissue during passive aspiration of intra ocular fluids. 4. Circular expansion and stabilization of the periphery of the capsular bag Reduced risk of capsular fibrosis Reduced risk of capsular shrinking Safe IOL centration in eyes with zonular dehiscence Stabilized conditions during (phaco emulsification) surgery 5. Helps in stabilizing the nucleus in cases of PC rupture. 6. It helps to insert the endocapsular ring in the capsular bag in a very controlled manner, making it extremely easy to use. 7. Useful for atraumatic brushing of the retinal surface with simultaneous aspiration. Useful for repositioning of retinal folds or breaks. 8. Maintains the position of the capsule during phaco. Supports the fornix as well as the capsulorhexis rim, so that the peripheral capsule isn't attracted towards the phaco tip. Avoids the problem of the capsular tension ring trapping cortex. Prevents zonular stress during nuclear rotation. Makes it possible to perform posterior chamber phaco even with subluxated lenses having minimum zonular support.
UNIVERSITY OF BAGUIO SCHOOL OF NURSING
University of Baguio School of Nursing
OR WRITE-UP: Phacoemulsification
SUBMITTED BY: Marion Dela Vega Rinwa Guiang
-NPA2-
SUBMITTED TO: Ms.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Glaucoma 180813151731Dokument24 SeitenGlaucoma 180813151731malathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eye and Ear Assessment and DisordersDokument374 SeitenEye and Ear Assessment and DisordersFirifan DiribaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zacks, Jeffrey M - Flicker - Your Brain On Movies (2015, Oxford University Press)Dokument361 SeitenZacks, Jeffrey M - Flicker - Your Brain On Movies (2015, Oxford University Press)Annie B.Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Case Presentation of CataractDokument16 SeitenA Case Presentation of CataractDoneva Lyn Medina100% (1)
- Binocular VisionDokument35 SeitenBinocular Visiongargi.c100% (3)
- Assessment of The Eyes and VisionDokument8 SeitenAssessment of The Eyes and Visionmary krisNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Project On " Human Eye": Submitted To-Submitted byDokument13 SeitenA Project On " Human Eye": Submitted To-Submitted byaman1990100% (1)
- Presented by Carmelita Ramos, RNDokument81 SeitenPresented by Carmelita Ramos, RNMela De Jesus RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reffractive ErrorsDokument13 SeitenReffractive ErrorsSagiraju SrinuNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Simple Guide to the Eye and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsVon EverandA Simple Guide to the Eye and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human EyeDokument72 SeitenHuman EyeDhananjayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic Presentation CataractDokument11 SeitenTopic Presentation Cataractjyoti singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Retina Detachment, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionVon EverandRetina Detachment, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vision Therapy PDFDokument72 SeitenVision Therapy PDF4nsan4o4luNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ico Inst BK Visual SC 2018 Rev2Dokument20 SeitenIco Inst BK Visual SC 2018 Rev2drlawrencekindoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Investigatory Project (On Eye Diseases)Dokument22 SeitenBiology Investigatory Project (On Eye Diseases)diya65% (49)
- Eye, Ear, Nose and Throat Assessment and Disorders Final PPT, NursingDokument489 SeitenEye, Ear, Nose and Throat Assessment and Disorders Final PPT, NursingFirifan Diriba100% (1)
- Juvenile CataractDokument44 SeitenJuvenile CataractArvindan SubramaniamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Low Vision: Assessment and Educational Needs: A Guide to Teachers and ParentsVon EverandLow Vision: Assessment and Educational Needs: A Guide to Teachers and ParentsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Presentation of E.CDokument8 SeitenCase Presentation of E.CRichard AbucayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Special Sensors PDFDokument45 SeitenSpecial Sensors PDFSwarna JayarathnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marginal KeratitisDokument23 SeitenMarginal KeratitisKumar RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Makalah Miopi Bahasa InggrisDokument16 SeitenMakalah Miopi Bahasa InggrisDhewii Amelya MiissLoversNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disorders of EyeDokument40 SeitenDisorders of Eyepslokesha84Noch keine Bewertungen
- Examination of The EyeDokument16 SeitenExamination of The EyeRoxana SurliuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Eye Disorders-1Dokument11 SeitenIntroduction To Eye Disorders-1bhavani GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eye Diseases: An Investigatory Project by Shrikanth Pillai XII BDokument11 SeitenEye Diseases: An Investigatory Project by Shrikanth Pillai XII BCR7STUDIO 7100% (1)
- Cataract SenilisDokument54 SeitenCataract Senilismayo djitroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Main Sensory OrgansDokument33 SeitenMain Sensory OrgansKKhowardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundoscopy Made Easy Ming 2009Dokument34 SeitenFundoscopy Made Easy Ming 2009Laura100% (1)
- Final TouchDokument49 SeitenFinal TouchmalathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structure of Human Eye DipiyDokument10 SeitenStructure of Human Eye Dipiyvineet_knwrNoch keine Bewertungen
- CataractDokument7 SeitenCataractaltfanz_044454Noch keine Bewertungen
- Humans, and Other Animals, Are Able To Detect A Range of Stimuli From The External Environment, Some of Which Are Useful For CommunicationDokument13 SeitenHumans, and Other Animals, Are Able To Detect A Range of Stimuli From The External Environment, Some of Which Are Useful For CommunicationYouieeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Breakthrough in Health-GACDokument25 SeitenBreakthrough in Health-GACdolly29100% (1)
- (L-2) - Eye - Nov 12, 2019Dokument54 Seiten(L-2) - Eye - Nov 12, 2019Sejal PrasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- EENT Instillation and IrrigationDokument13 SeitenEENT Instillation and Irrigationplebur100% (1)
- Eye RobicsDokument28 SeitenEye RobicsIsmi Raudha0% (1)
- Glaucoma CruzDokument5 SeitenGlaucoma CruzPaola CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- WPR 2Dokument5 SeitenWPR 2ishika mohanNoch keine Bewertungen
- D.A.V Senior Secondary School: Biology Investigatory ProjectDokument22 SeitenD.A.V Senior Secondary School: Biology Investigatory ProjecthashimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essay Healthy Eyes and EarsDokument8 SeitenEssay Healthy Eyes and EarsMell Brigitte Cordova AlmonteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 3 2nd Quarter Unit 3 Lesson 1 Sense Organs and How To Care For ThemDokument89 SeitenGrade 3 2nd Quarter Unit 3 Lesson 1 Sense Organs and How To Care For ThemRaul Rivera SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Occupational Health Tips On Eye Protection For Good Visual HealthVon EverandOccupational Health Tips On Eye Protection For Good Visual HealthNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIO-Project InvestigatoryDokument83 SeitenBIO-Project InvestigatoryAyush BhattNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sense OrgansDokument26 SeitenSense OrgansArpan AdhikariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sense Organs NotesDokument13 SeitenSense Organs NotesVijay Laxmi MundhraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Ophthalmology: by DR - Bakhtiar Q. JafDokument41 SeitenIntroduction To Ophthalmology: by DR - Bakhtiar Q. JafChristian JaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Examination of The RetinaDokument3 SeitenExamination of The RetinaGus LionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Certificate: Study of Eye DiseasesDokument20 SeitenCertificate: Study of Eye DiseasesDhruvNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCM104 MS2 - Course Unit 13 - Review of The Anatomy and Physiology of The Eyes & AssessmentDokument5 SeitenNCM104 MS2 - Course Unit 13 - Review of The Anatomy and Physiology of The Eyes & AssessmentJordz PlaciNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sense of VisionDokument34 SeitenSense of VisionqqqqqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Examination of The Eye in The Emergency Room: Christopher Calandrella D.O - Pgy2Dokument104 SeitenExamination of The Eye in The Emergency Room: Christopher Calandrella D.O - Pgy2Alexandra Mendoza100% (1)
- Working of Human EyeDokument13 SeitenWorking of Human EyeVikashKeshavNoch keine Bewertungen
- CommunicationDokument16 SeitenCommunicationbitchass niggaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Binocular Indirect Ophthalmoscopy - Funduskopi InderekDokument5 SeitenBinocular Indirect Ophthalmoscopy - Funduskopi InderekMario JohanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Göz AnatomiDokument4 SeitenGöz AnatomiArdaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bates' Visual Guide To Physical Examination Vol. 7: Head, Eyes, and EarsDokument9 SeitenBates' Visual Guide To Physical Examination Vol. 7: Head, Eyes, and EarsArlene DaroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eye & Ear Stations ONLYDokument6 SeitenEye & Ear Stations ONLYVictoria WarrenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marie Belen C. Tamayor, RNDokument42 SeitenMarie Belen C. Tamayor, RNrein_seanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9 Sensory Organs - Eye and EarDokument41 Seiten9 Sensory Organs - Eye and Earbabaaijaz01Noch keine Bewertungen
- Exp 11Dokument3 SeitenExp 11Soler HeusaffNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structure and Function of The Human EyeDokument6 SeitenStructure and Function of The Human EyeAljhon DelfinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Care of Clients With Problems in Visual and Auditory Perception EYEDokument4 SeitenCare of Clients With Problems in Visual and Auditory Perception EYEHershey Cordero BrionesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kuya JayDokument47 SeitenKuya Jayhakhak013Noch keine Bewertungen
- Kuya JayDokument47 SeitenKuya Jayhakhak013Noch keine Bewertungen
- DOH Programs and Calendar Activities: Easter College College of Nursing Guisad Road, Baguio CityDokument9 SeitenDOH Programs and Calendar Activities: Easter College College of Nursing Guisad Road, Baguio Cityhakhak013100% (1)
- DOH Programs and Calendar Activities: Easter College College of Nursing Guisad Road, Baguio CityDokument9 SeitenDOH Programs and Calendar Activities: Easter College College of Nursing Guisad Road, Baguio Cityhakhak013100% (1)
- Examination of Eye PT IIDokument89 SeitenExamination of Eye PT IIGede GiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dr. Jusuf Wijaya - StrabismusDokument32 SeitenDr. Jusuf Wijaya - StrabismusGerry SanjayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Keratitis DisiformDokument4 SeitenKeratitis DisiformmadeemjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Visual Outcome After Cataract Surgery A ReviewDokument5 SeitenVisual Outcome After Cataract Surgery A ReviewRagni MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lens and CataractDokument31 SeitenLens and CataractReinhard TuerahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seragam MPP UnitDokument15 SeitenSeragam MPP UnitKangen HijauNoch keine Bewertungen
- Visual ImpairmentDokument33 SeitenVisual ImpairmentBernadeth Delos ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bionic EyeDokument1 SeiteBionic EyesubhasishcNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5ELEMENTSDokument15 Seiten5ELEMENTSrenuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Downloadophthalmology Cases All Team PDF PDF Free - HTMLDokument23 SeitenDownloadophthalmology Cases All Team PDF PDF Free - HTMLDương Yến TrânNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Study of Prognostic Indicators in Visual Outcome of Adult Traumatic CataractDokument9 SeitenA Study of Prognostic Indicators in Visual Outcome of Adult Traumatic CataractIJAR JOURNALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Primarya Angle Closure Glaucoma 2021Dokument147 SeitenPrimarya Angle Closure Glaucoma 2021robeyeNoch keine Bewertungen
- STAAR Surgical Executive Summary Final - RedactedDokument84 SeitenSTAAR Surgical Executive Summary Final - RedactedLja CsaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FFPL Sample Kit Available: FeaturesDokument2 SeitenFFPL Sample Kit Available: FeaturesSuraj MauryaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Color by Numbers: Composition A: ARTIST: Piet MondrianDokument1 SeiteColor by Numbers: Composition A: ARTIST: Piet MondrianJessi Castellanos100% (1)
- Visual AcuityDokument17 SeitenVisual AcuityKjhnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soal Bahasa Inggris Bab Colors Warna-Warna Dan Kunci JawabanDokument8 SeitenSoal Bahasa Inggris Bab Colors Warna-Warna Dan Kunci JawabanWisma Foto CopyNoch keine Bewertungen
- MicrotropiaDokument6 SeitenMicrotropiaMAJONoch keine Bewertungen
- Glaukoma Sekunder Pada Pasien Anak Dengan Sindrom Sturge Weber: Laporan KasusDokument7 SeitenGlaukoma Sekunder Pada Pasien Anak Dengan Sindrom Sturge Weber: Laporan KasusLordisse WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psych Chap 4+5Dokument26 SeitenPsych Chap 4+5lmaoheartsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 80 Eye-Catching Color Combinations For 2021Dokument1 Seite80 Eye-Catching Color Combinations For 2021Syafiqah FarhainNoch keine Bewertungen
- EGurukul - RetinaDokument23 SeitenEGurukul - RetinaOscar Daniel Mendez100% (1)
- 03 Perspective Depth 070124Dokument39 Seiten03 Perspective Depth 070124Deevya D.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Colour Vision - NajwaDokument52 SeitenColour Vision - NajwaNajwa MansuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathologic Myopia: Kyoko Ohno-MatsuiDokument11 SeitenPathologic Myopia: Kyoko Ohno-MatsuiAnonymous L9D1I7DZNoch keine Bewertungen