Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Urea Agar Base Differentiates Enterobacteria
Hochgeladen von
vaibhavOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Urea Agar Base Differentiates Enterobacteria
Hochgeladen von
vaibhavCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
UREA AGAR BASE (CHRISTENSEN) ISO 6579
CAT N: 1110
FORMULA IN g/l
Urea Sodium Chloride Monopotassium Phosphate 20.00 5.00 2.00 Gelatin Peptone Dextrose Phenol Red 1.00 1.00 0.012
For the differentiation of Enterobacteria on the basis of urease production
Final pH 6.8 0.2 at 25C
PREPARATION
Dissolve 29 grams of the medium in 100 ml of distilled water. Sterilize by filtration. Separately dissolve 15 grams of agar in 900 ml of distilled water by boiling. Sterilize in autoclave at 121 C for 15 minutes. Cool to 50C and add to the 100 ml of the sterile Urea Agar Base. Mix well and dispense aseptically in sterile tubes. Leave the medium to set in a slanted position so as to obtain deep butts. Do not remelt the slanted agar. The prepared medium should be stored at 2-8C. The color at a pH of 6.8 to 7.0 should have a light pinkish-yellow color. The dehydrated medium should be homogeneous, free-flowing and orange-red in color. If there are any physical changes, discard the medium.
USES
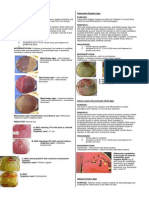
UREA AGAR BASE (Christensen) may be used as an aid in the differentiation of microorganisms, particularly enteric Gram-negative Enterobacteria, on the basis of urea hydrolysis, from clinical samples and other materials. The formula is according to ISO 6579. Urea Agar Base, with TSI Agar (Cat. 1046), may be used as a screening medium for the selection of Salmonella and Shigella. Urea Agar Base is used in spot tests for the rapid detection of urease activity and, when combined with results of other quick screening tests, it is the most common method to detect urease production by Enterobacteria. It is particularly recommended for the differentiation of members of the genus Proteus from those of Salmonella and Shigella in the diagnosis of enteric infections. Gelatin peptone provides nitrogen, vitamins, minerals and amino acids essential for growth. Dextrose is the fermentable carbohydrate providing carbon and energy. Sodium chloride maintains the osmotic balance. Monopotassium phosphate provides buffering capacity. Urea is a source of nitrogen for those organisms producing urease. Phenol red is the pH indicator. To obtain good results, inoculate heavily over the slant as the speed of the reaction depends on the relation of organism amount and medium surface. Do not inoculate the butt of this medium as it is used as a negative color control. ISO 6579 reccomends to incubate at 35 2C for 24 3 hours. A positive test is denoted by a change in color, due to urease production, from yellow (pH 6.8) to a deep purple or bluish-red (pH 8.1) on the slant surface. Observations of the tubes should be made at 2 4 hours. Proteus and a few other organisms give a positive (purple) reaction. Reincubate all negative cultures daily for up to 7 days for positives such as Brucella.
MICROBIOLOGICAL TEST
The following results were obtained in the performance of the medium from type cultures after incubation at a temperature of 35 2C and observed after 243 hours.
1
LABORATORIOS CONDA, S.A.
www.condalab.com
Microorganisms
Growth Good Good Good Good Good
Urease - (no change of color in the medium) - (no change of color in the medium) + (red or purple medium) + (red or purple medium) - (no change of color in the medium)
Enterobacter aerogenes ATCC 13048 Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 Klebsiella pneumoniae ATCC 13883 Proteus vulgaris ATCC 13315 Salmonella typhimurium ATCC 14028
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Christensen J. Bact. 52:641. 1946. Thal and Chen J. Bact. 69:10. 1955. Ewing Enterobacteriaceae. USPHS, Publication 734. Norma UNE-EN-ISO 6579. Microbiology of food and animal feeding stuffs -- Horizontal method for the detection of Salmonella spp.
ISO
STORAGE
Once opened keep powdered medium closed to avoid hydration.
2C
25C
LABORATORIOS CONDA, S.A.
www.condalab.com
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Violet Red Bile Glucose Agar (V.R.B.G.A.) : Enterobacteriaceae in Foodstuffs With MPN Technique WithoutDokument7 SeitenViolet Red Bile Glucose Agar (V.R.B.G.A.) : Enterobacteriaceae in Foodstuffs With MPN Technique WithoutThandie KehleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agar Sps2012Dokument2 SeitenAgar Sps2012Erick GaleanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- الترشيح الغشائيDokument1 Seiteالترشيح الغشائيsami algradeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- R2A Agar (European Pharmacopoeia) Plate Count MediumDokument2 SeitenR2A Agar (European Pharmacopoeia) Plate Count MediumRiyon FajarprayogiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Isolation and Characterization of Rhizobacteria From ChilliDokument15 SeitenIsolation and Characterization of Rhizobacteria From ChillisauravNoch keine Bewertungen
- E.Coli Coliforms Chromogenic Medium: CAT Nº: 1340Dokument2 SeitenE.Coli Coliforms Chromogenic Medium: CAT Nº: 1340Juan Manuel Ramos ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urease Test Protocol 3223Dokument7 SeitenUrease Test Protocol 3223vitorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 3 BacteDokument7 SeitenLec 3 BacteMitchee ZialcitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mediu de Cultura Cromogen ColiformiDokument2 SeitenMediu de Cultura Cromogen ColiformiGeoemilia1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Microbiology ReviewerDokument8 SeitenMicrobiology ReviewerSteph Vee100% (6)
- MCB2010L Final Notes PDFDokument12 SeitenMCB2010L Final Notes PDFTotalMeanGirlNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3Bmt MICR 231 LEC - BacteriologyDokument2 Seiten3Bmt MICR 231 LEC - BacteriologyroseannequyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urease Test - Principle, Media, Procedure and ResultDokument11 SeitenUrease Test - Principle, Media, Procedure and ResultAlisha KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 201020120500-CLED Agar With Andrade IndicatorDokument3 Seiten201020120500-CLED Agar With Andrade Indicatorsofimar sanzNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1062Dokument2 Seiten1062Nisadiyah Faridatus ShahihNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enterobacter Sakazakii Isolation Chromogenic AGAR (ESIA) ISO 22964Dokument2 SeitenEnterobacter Sakazakii Isolation Chromogenic AGAR (ESIA) ISO 22964Js OrendaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catalase TestDokument12 SeitenCatalase Testshiva121294Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1010_en_3Dokument2 Seiten1010_en_3Penny HuynhNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1076Dokument2 Seiten1076Ernesto Romero FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAT Nº: 1405: Saline Peptone Water Iso 6887Dokument2 SeitenCAT Nº: 1405: Saline Peptone Water Iso 6887Bldjl HichemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Identification of Pseudomonas SPDokument20 SeitenIdentification of Pseudomonas SPUttam Kr Patra100% (4)
- Cetrimide Agar BaseDokument3 SeitenCetrimide Agar BaseDip MajumderNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAT Nº: 1208: Lysine Decarboxylase BrothDokument2 SeitenCAT Nº: 1208: Lysine Decarboxylase BrothNguyễnVinhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antibiotic Senstivity of Various Pathogenic Bacteria in Case of Uti and Throat InfectionsDokument25 SeitenAntibiotic Senstivity of Various Pathogenic Bacteria in Case of Uti and Throat InfectionsMishel AroraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catalog # URS-10: 100 Strips Per BoxDokument4 SeitenCatalog # URS-10: 100 Strips Per BoxLey100% (1)
- AGAR CHROMOCULT Merck Rebrand - 110426 - 1906Dokument6 SeitenAGAR CHROMOCULT Merck Rebrand - 110426 - 1906Luz Katherine MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 8Dokument28 SeitenLab 8Mustafa A. DawoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Caldo UreaDokument4 SeitenCaldo UreaDiego AriasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Identifying Bacteria Using Selective MediaDokument35 SeitenIdentifying Bacteria Using Selective Mediatutu totoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAT Nº: 1407: Alkaline Peptone WaterDokument2 SeitenCAT Nº: 1407: Alkaline Peptone WaterAbe NavellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Production of Protease Enzyme by Aspergillus Niger ThroughDokument12 SeitenProduction of Protease Enzyme by Aspergillus Niger ThroughAbhishek PrakashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Violet Red Bile Agar: CompositionDokument2 SeitenViolet Red Bile Agar: CompositionMuhammad AdnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trypticasein Soy Broth (TSB) European Pharmacopoeia: CAT Nº: 1224Dokument2 SeitenTrypticasein Soy Broth (TSB) European Pharmacopoeia: CAT Nº: 1224unknownxpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Selective Media for Gram Positive and Gram Negative IsolationDokument8 SeitenSelective Media for Gram Positive and Gram Negative IsolationJescika BarretoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arginineglucose Yeast Extract Agar - Technicaldetails - 9720210526.050253Dokument3 SeitenArginineglucose Yeast Extract Agar - Technicaldetails - 9720210526.050253MSc Penélope MeloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alkaline Peptone Broth or Alkaline Peptone WaterDokument5 SeitenAlkaline Peptone Broth or Alkaline Peptone WaterAAdriyaniTenriolaAkbarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 3 Quality Control Sterilization and Disinfection ModuleDokument23 SeitenLesson 3 Quality Control Sterilization and Disinfection ModuleTinNoch keine Bewertungen
- GB 4789.4 2010 National Food Safety Standard Food Microbiological Examination Salmonella PDFDokument24 SeitenGB 4789.4 2010 National Food Safety Standard Food Microbiological Examination Salmonella PDFmmoradi55Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sterility Testing: B. K. SajeebDokument23 SeitenSterility Testing: B. K. SajeebSadia AfrinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemical TestsDokument41 SeitenBiochemical TestsChinthikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sabouraud Dextrose Agar (European Pharmacopoeia) : CAT Nº: 1024Dokument0 SeitenSabouraud Dextrose Agar (European Pharmacopoeia) : CAT Nº: 1024Fred GreenNoch keine Bewertungen
- ErgovalinDokument4 SeitenErgovalinDiegoSampietroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multistix Reagent StripDokument3 SeitenMultistix Reagent StripFrancis TorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sterility TestingDokument41 SeitenSterility TestingpratikNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAT Nº: 1216: Nutrient BrothDokument2 SeitenCAT Nº: 1216: Nutrient BrothTran TuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detection of E - 3BOaRnPSfLDokument20 SeitenDetection of E - 3BOaRnPSfLabdolu531Noch keine Bewertungen
- Clostridium perfringens BAM ChapterDokument5 SeitenClostridium perfringens BAM ChapterReyhan EgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bacterial endotoxins test methodsDokument8 SeitenBacterial endotoxins test methodsCeangoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Streptococcus Agalactiae: Biochemical TestingDokument8 SeitenStreptococcus Agalactiae: Biochemical TestingAki OtaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Media Biochemical TestsDokument36 SeitenMedia Biochemical TestsIsmail Bazly ZarirNoch keine Bewertungen
- EMB Agar Isolates Gram-Negative Enteric BacilliDokument2 SeitenEMB Agar Isolates Gram-Negative Enteric Bacillisigit the pembalapNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemical - TestsDokument5 SeitenBiochemical - TestsMohsen Haleem100% (1)
- Microbiology Staining and Culture Media TechniquesDokument23 SeitenMicrobiology Staining and Culture Media TechniquesSɪʟᴇɴᴛ GᴀᴍɪɴɢNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Culture Media: Phenyl Ethyl Alcohol Agar Selective MediaDokument18 SeitenTypes of Culture Media: Phenyl Ethyl Alcohol Agar Selective MediaJulián CastroNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4th Year Biotech Students Lab Practicals On Enzyme TechnologyDokument5 Seiten4th Year Biotech Students Lab Practicals On Enzyme TechnologyABU LoasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chromocult Coliform PDFDokument4 SeitenChromocult Coliform PDFAndres GalárragaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 005-Clinical MicroDokument15 Seiten005-Clinical Micro04051914001Noch keine Bewertungen
- Plant and Animal Bio-Chemistry - Including Information on Amino Acids, Proteins, Pigments and Other Chemical Constituents of Organic MatterVon EverandPlant and Animal Bio-Chemistry - Including Information on Amino Acids, Proteins, Pigments and Other Chemical Constituents of Organic MatterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 9Dokument3 SeitenExperiment 9aditi_joshee419Noch keine Bewertungen
- Calendar of Hindu Festivals 2012Dokument1 SeiteCalendar of Hindu Festivals 2012vaibhavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enzymology IntroductionDokument21 SeitenEnzymology IntroductionvaibhavNoch keine Bewertungen
- ReadmeDokument1 SeiteReadmewashyngttonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 800-40 Suspencion ChalmersDokument7 Seiten800-40 Suspencion ChalmersJhonatan Velasquez CastellanosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Journal of Cleaner Production: S.M. Ashekuzzaman, Patrick Forrestal, Karl Richards, Owen FentonDokument10 SeitenJournal of Cleaner Production: S.M. Ashekuzzaman, Patrick Forrestal, Karl Richards, Owen FentonSenthil KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- FINS 2624 Quiz 2 Attempt 2 PDFDokument3 SeitenFINS 2624 Quiz 2 Attempt 2 PDFsagarox7Noch keine Bewertungen
- IB Chemistry HL Test 2nd FEBDokument13 SeitenIB Chemistry HL Test 2nd FEBprasad100% (1)
- Solving Rational Equations and InequalitiesDokument5 SeitenSolving Rational Equations and InequalitiesJaycint - Rud PontingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Real Possibility of Future ConditionDokument3 SeitenReal Possibility of Future ConditionHusNoch keine Bewertungen
- AkzoNobel-Trigonox 239Dokument6 SeitenAkzoNobel-Trigonox 239Wafa AjiliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Function and Definite Integrals ExplainedDokument7 SeitenFunction and Definite Integrals Explainedana maharaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- US Army TV Course - Documentation Cinematography SS0536Dokument49 SeitenUS Army TV Course - Documentation Cinematography SS0536innerethosNoch keine Bewertungen
- 25f8e d64fDokument6 Seiten25f8e d64fapi-233604231Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mast Bending Stress Calculation: Antenna 1Dokument6 SeitenMast Bending Stress Calculation: Antenna 1Vinay KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Etabloc Technical DataDokument108 SeitenEtabloc Technical Dataedward ksbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Railway Electrification Projects Budget 2019-20Dokument9 SeitenRailway Electrification Projects Budget 2019-20Muhammad Meraj AlamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steam Turbine Unloading and Shut-Down of Operation Turbine/Generator Shut-Down Diagram (General)Dokument1 SeiteSteam Turbine Unloading and Shut-Down of Operation Turbine/Generator Shut-Down Diagram (General)parthibanemails5779Noch keine Bewertungen
- Improving Students' Science Process SkillsDokument9 SeitenImproving Students' Science Process SkillsNovia RahmawatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Numerical Simulation of Screw Displacement Pile Interaction With Non-Cohesive SoilDokument12 SeitenNumerical Simulation of Screw Displacement Pile Interaction With Non-Cohesive Soilmohamed magdyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Projects in the Autonomous Region in Muslim MindanaoDokument4 SeitenProjects in the Autonomous Region in Muslim MindanaoMark montebonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instrukcja Pellets Fuzzy Logic - ENGDokument53 SeitenInstrukcja Pellets Fuzzy Logic - ENGxilef84Noch keine Bewertungen
- Proteccion Contra Sobretensiones PDFDokument84 SeitenProteccion Contra Sobretensiones PDFgilbertomjcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eb4069135 F enDokument13 SeitenEb4069135 F enkalvino314Noch keine Bewertungen
- Macroeconomics II: Search and Matching: Luiz BrotherhoodDokument18 SeitenMacroeconomics II: Search and Matching: Luiz BrotherhoodMartin GutovskieNoch keine Bewertungen
- LearnEnglish Video Zone How These Women Changed Science ForeverDokument3 SeitenLearnEnglish Video Zone How These Women Changed Science ForeverDaniella MensatoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name: Amir Bin Rossaifuddin Id: 2016307153 Group: Emd2M2ADokument2 SeitenName: Amir Bin Rossaifuddin Id: 2016307153 Group: Emd2M2AamirossaifuddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Mathematics 9709/13Dokument20 SeitenCambridge International AS & A Level: Mathematics 9709/13Justin OngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indian War of Independence 1857 - Part 2Dokument150 SeitenIndian War of Independence 1857 - Part 2BISWAJIT MOHANTYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basicline BL 21t9stDokument28 SeitenBasicline BL 21t9stgabriel6276Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lock Out Tag Out ProceduresDokument9 SeitenLock Out Tag Out ProceduresyawarhassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prob Stats Module 4 2Dokument80 SeitenProb Stats Module 4 2AMRIT RANJANNoch keine Bewertungen
- DPT ProcedureDokument3 SeitenDPT ProcedureAmit HasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chocolate - Useful Physical ConstantsDokument2 SeitenChocolate - Useful Physical ConstantsJuan CNoch keine Bewertungen