Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Exercise 2
Hochgeladen von
jamjamaeOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Exercise 2
Hochgeladen von
jamjamaeCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Exercise 2.
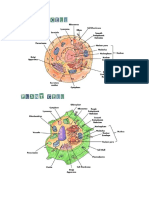
Plant Cells Cell o Basic unit of life capable of metabolizing and reproducing independently from other living entities History o Robert Hooke (1665) Discovered that a cork and plant tissues are made up of small cavities separated by walls Cavities = cells from Latin term cella meaning storerooms/chambers o Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann Cell Theory All living things are made up of cells Life processes eg. metabolism take place within the cells Cells arise from pre-existing cells Cells contains the hereditary unit w/c can be passed on from generation to generation Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes o Prokaryotes before nucleus o Eukaryotes with a true nucleus Criteria Cell size Nuclear Envelope DNA Prokaryotes 1-10 um Absent Circular in nucleoid and not associated with proteins to form chromosomes Absent Eukaryotes 5-100 um and above Present Linear in nucleus
Specialized membrane bound structures or organelles
Present
Parts of the Plant Cells:
plant cell
CW
protoplast
plasma membrane
nucleus
cytoplasm
membrane-bound organelles (mitochondria, plastids, vacuole)
membrane systems (ER, Golgi bodies)
non-membrane entities (ribosomes, cytoskeletons)
Cell wall- gives rigidity and shape to the plant cell as well as protection o Made up of cellulose, pectin, cutin, waxes, hemicelluloses, lignin and suberin o Parts associated with the CW:
middle lamella cements/sticks together two adjacent plant cells - Made up of pectin or calcium pectate pits holes/depressions in cell wall wherein plasmodesmata pass through plasmodesmata channel-like structures that serve as interconnections between protoplasts of two adjacent cells
Protoplast- plant cell without the cell wall o Living part of the plant cell Plasma/cell membrane- semi-permeable, lipid bilayer structure o regulates the entry of chemicals/substances in and out of the cell Nucleus- serves as the control system of the cell containing the DNA Cytoplasm- jelly-like substance inside the cell wherein organelles and other parts lie Mitochondria- provides energy (ATP) to the cell Plastids- stores food and pigment o Membrane-bound organelles unique to plants o Classification according to color or content: Leukoplasts colorless, for storage o Amyloplasts - starch o Proteinoplast proteins o Elaioplast fats Chromoplasts pigments (yellow, red, orange); to attract pollinators Chloroplast chlorophyll (chlorenchyma parenchyma cells w/ chlorophyll) Proplasts undifferentiated plastids Large central vacuole- Surrounded by a single membrane tonoplast o contains water, salts, sugar, proteins and minerals o Takes up much of cells interior (90% vol. of mature cell) o Storage of pigments (eg. anthocyanin) and metabolic products o Also stores ergastic substances (salts of organic acids) like crystals o Forms of crystals: Raphide needle-like Druse star or flower- like Cystolith irregular or grape-like Rhombohedron diamond-like Endoplasmic reticulum for lipid synthesis and their transport o Smooth ER o Rough ER with bounded ribosomes responsible for protein synthesis
Golgi bodies packaging center of the cell Ribosomes- synthesizes proteins to be transported to neighboring cells Cytoskeletons- microfilaments and microtubules give support to plant cells
Plant Cell Types Parenchyma thin primary cell walls; usually have large vacuoles o Commonly with intercellular spaces o Carry out most of the plants metabolic functions (photosynthesis, storage, cell division) o Living at maturity (protoplast intact) Collenchyma thicker primary walls that are evenly thickened at corners o Lacks secondary walls, no lignin; in primary cell wall with pectin o Living protoplasm at maturity o Support young and elongating leaves and stems (flexible) Sclerenchyma much more rigid o With primary and secondary walls; thick secondary walls strengthen by lignin o Supporting elements of the plant o Mature cells cannot elongate o Lack protoplast at maturity dead o For support and protection of mature parts of the plant (eg. sclereids or stone cells) as well as water and food conduction (eg. vascular tissues, xylem and phloem) Lab work Plant Cell Types Fresh mount of Colocasia esculenta petiole o Parenchyma and collenchyma cells Prepared slide of Eleusine indica stem sclerenchyma cells of vascular tissues (xylem and phloem) Prepared slide of scrapings from C. nucifera endocarp o Sclerenchyma sclereid with lumen Cellular parts and processes Fresh mount A. cepa epidermal peel of bulb + 0.15 M I2KI Fresh mount C. annuum in water - carotenoid pigment in the chromoplast Fresh mount R. spathacea dorsal side of the leaf + water o Stomata and guard cells with chloroplasts Adjacent cells violet, anthocyanin in the vacuole 0.30 M I2KI (minutes) plasmolysis protoplast separates from CW; cell loses water Hydrilla verticillata leaf chloroplasts and movement of chloroplast cytoplasmic streaming (cyclosis) Ergastic Substances non-living inclusions; crystals seen in the vacuoles Prepared slides - shiny structures against darkened background o Begonia petiole rhombohedron o F. elastica cystolith o Nerium oleander druse o C. esculenta - Raphide
Starch grains Zea mays endosperm scrapings in I2KI parenchyma cells w/ stored particles that are bluish/black in color (starch grains)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Biology 1st DiscussionDokument52 SeitenBiology 1st DiscussionBea BulasaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Cytology or Cell BiologyDokument63 SeitenIntroduction To Cytology or Cell BiologyChemMANoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Structure and Function 2012Dokument69 SeitenCell Structure and Function 2012gpranay4100% (1)
- CHAPTER 2 Plant CellDokument68 SeitenCHAPTER 2 Plant CellAiman Haikal100% (1)
- @MedicalBooksStoreS 2017 Acute IschemicDokument273 Seiten@MedicalBooksStoreS 2017 Acute IschemicAditya Perdana Dharma Wiguna100% (1)
- Plant and Animal Cell DemoDokument2 SeitenPlant and Animal Cell DemoAnnaTeresaCalayagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cells: Structure and FunctionDokument51 SeitenCells: Structure and FunctionmalaitamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reviewer in BiologyDokument8 SeitenReviewer in BiologyMikaela EvangelistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animal and Plant Cell Anatomy Detailed NotesDokument5 SeitenAnimal and Plant Cell Anatomy Detailed NotesMadeleine AgiusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hematology ReviewerDokument15 SeitenHematology ReviewerNichol Villalba100% (1)
- Cell Parts and Their FunctionsDokument9 SeitenCell Parts and Their FunctionsMlshin LaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Four Test - Cell Structure and FunctionDokument8 SeitenChapter Four Test - Cell Structure and FunctionDonald BrownNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Cell Structure FunctionDokument124 Seiten1 Cell Structure FunctionIntoy, Stephanie Mae100% (1)
- Cells Structure and FunctionDokument56 SeitenCells Structure and FunctionAnnisa DiyanabilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Note About CellsDokument17 SeitenBiology Note About CellsEK TubeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology RevisionDokument29 SeitenBiology RevisionelsybelsyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study Notes - Topic 1 A'sDokument11 SeitenStudy Notes - Topic 1 A'sJenniffer SmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cells - Structure and Function: Important Events in The Discovery of CellsDokument10 SeitenCells - Structure and Function: Important Events in The Discovery of CellsHassinMarkLariosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochem PrelimDokument42 SeitenBiochem PrelimFaith RochaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio Notes on ClassificationDokument5 SeitenBio Notes on ClassificationShasha WiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Robert Hooke's Discovery of Cells Using a MicroscopeDokument7 SeitenRobert Hooke's Discovery of Cells Using a MicroscopelorinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Structure and its EnvironmentDokument50 SeitenCell Structure and its EnvironmentCarol FernandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class Notes For Upper Biology MasterclassDokument2 SeitenClass Notes For Upper Biology MasterclassYehia Khaled Essam Fawaz ICSBR1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Notes Science CellsDokument12 SeitenNotes Science CellsHina SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brief History Cytology Hierarchy of Structural Organization - Cell Structure - MitosisDokument52 SeitenBrief History Cytology Hierarchy of Structural Organization - Cell Structure - MitosisPJ PomarNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPM Form 4Dokument23 SeitenSPM Form 4tqahazliNoch keine Bewertungen
- BiochemDokument108 SeitenBiochemJangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cells NotesDokument3 SeitenCells NotesmisosoupNoch keine Bewertungen
- CellsDokument5 SeitenCellsLhey JesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.1 Cell Structure and FunctionDokument51 Seiten2.1 Cell Structure and FunctionNigel Subhash BakkerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio11-Plant AnimalcomparisonDokument5 SeitenBio11-Plant Animalcomparisonapi-246377724Noch keine Bewertungen
- Plant StructureDokument33 SeitenPlant Structurevioleotero850Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cells Structure FunctionDokument8 SeitenCells Structure FunctionRameesha RanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Structure and OrganisationDokument106 SeitenCell Structure and Organisationwienna1987Noch keine Bewertungen
- Components of Animal and Plant CellsDokument4 SeitenComponents of Animal and Plant CellsYukiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CellDokument4 SeitenCellPrincess MillanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology: Cell StructuresDokument12 SeitenBiology: Cell Structurescarl gamingNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Following Is A Glossary of Plant Cell Anatomy Terms.: Plant Cells Cristae Mitochondria ChloroplastsDokument6 SeitenThe Following Is A Glossary of Plant Cell Anatomy Terms.: Plant Cells Cristae Mitochondria ChloroplastsHitesh MoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Organelles 11Dokument32 SeitenCell Organelles 11Mamalumpong NnekaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cells - Basic Unit of LifeDokument45 SeitenCells - Basic Unit of Lifeapi-202349222Noch keine Bewertungen
- CellDokument32 SeitenCellSagita RahayuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity No.1 - The CellDokument3 SeitenActivity No.1 - The CellCelestine MambulaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 Biology Revision Study Material Chapter 8Dokument8 Seiten11 Biology Revision Study Material Chapter 8Saurav SoniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Structure & Function: Endoplasmic Reticulum ERDokument2 SeitenCell Structure & Function: Endoplasmic Reticulum ERLiling CassiopeiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- STM123 OutlineDokument19 SeitenSTM123 OutlineNur-Aiza AlamhaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3: Cell Biology & GeneticsDokument7 SeitenChapter 3: Cell Biology & GeneticsansleybarfieldNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Living Cell: A Guide to Its History, Parts, Functions and TypesDokument49 SeitenThe Living Cell: A Guide to Its History, Parts, Functions and TypesDaezel DeuxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of LifeDokument5 SeitenChapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of LifeDHAIRYA KASAR100% (1)
- Biology Exam #1 Study GuideDokument12 SeitenBiology Exam #1 Study GuideKevin TranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animal CellDokument2 SeitenAnimal CellRjvm Net Ca FeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life: What Are Living Organisms Made Up Of?Dokument5 SeitenChapter 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life: What Are Living Organisms Made Up Of?HeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 2 Cell Structure and FunctionsDokument31 SeitenModule 2 Cell Structure and FunctionsConcepcion, Jemaelah P.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Animal and Plant Cell OrganellesDokument3 SeitenAnimal and Plant Cell OrganellesKent Orriele FadriquelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cells - Structure and Function: Important Events in The Discovery of CellsDokument24 SeitenCells - Structure and Function: Important Events in The Discovery of CellsJaspher Joshua CallangaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CellsDokument19 SeitenCellsAulia Safri NahriyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Biology Notes For Grade 11 (1st Semester)Dokument37 SeitenGeneral Biology Notes For Grade 11 (1st Semester)shieeesh.aNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8 Cell The Unit of LifeDokument7 SeitenChapter 8 Cell The Unit of LifeAli WarisNoch keine Bewertungen
- CellDokument5 SeitenCellapi-267979304Noch keine Bewertungen
- What is a Cell? The Building Block of LifeDokument6 SeitenWhat is a Cell? The Building Block of LifeWaleed Bin KhalidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Subcellular & DiseasesDokument123 SeitenCell Subcellular & Diseasesnasreenshaker0Noch keine Bewertungen
- The CellsDokument28 SeitenThe CellsRhea GulayNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIO ReviewerDokument14 SeitenBIO ReviewerRenjyl Gay DeguinionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quarter 1 - GenBio 1-Week 1 (23-24)Dokument41 SeitenQuarter 1 - GenBio 1-Week 1 (23-24)Adrienne Skyle SibalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparing Immobilized Kinase Inhibitors and Covalent ATP Probes For Proteomic Profiling of Kinase Expression and Drug Selectivity.Dokument9 SeitenComparing Immobilized Kinase Inhibitors and Covalent ATP Probes For Proteomic Profiling of Kinase Expression and Drug Selectivity.Darkill JackNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - Biochemistry and The Organization of CellsDokument24 Seiten1 - Biochemistry and The Organization of CellsJobelle MalihanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Olympiad Exam Syllabus (Final)Dokument4 SeitenBiology Olympiad Exam Syllabus (Final)NumayrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microsoft Word - Chapter 3Dokument4 SeitenMicrosoft Word - Chapter 3hjhjkhdsafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cambridge Small Template Class FileDokument5 SeitenCambridge Small Template Class FileFresh Prince Of NigeriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2nd Lecture On Action Potential by Dr. Roomi.Dokument14 Seiten2nd Lecture On Action Potential by Dr. Roomi.Mudassar Roomi100% (1)
- 04 - 2reproduction in ProtozoaDokument5 Seiten04 - 2reproduction in ProtozoaDipankar RoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood LecturesDokument128 SeitenBlood LecturessrhrenaissanceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1: Bacterialcell Structure, Physiology, Metabolism, and GeneticsDokument19 SeitenChapter 1: Bacterialcell Structure, Physiology, Metabolism, and GeneticsNico Loko100% (1)
- Bautista 2007 NatureDokument6 SeitenBautista 2007 NatureRoberta StoicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bais Manish DVM PHD Nov 23sDokument3 SeitenBais Manish DVM PHD Nov 23smanish.bais114017Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Transport Review 2Dokument2 SeitenCell Transport Review 2api-233187566Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1 BIO LP 5 EditedDokument5 Seiten1 BIO LP 5 EditedRosemarie Soldevilla LanderoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osmosis and Diffusion ExperimentDokument8 SeitenOsmosis and Diffusion ExperimentCharles MacleanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ohns D29527 en F - M3 - 2016 09 29 - 094835 - 1475507735280Dokument24 SeitenOhns D29527 en F - M3 - 2016 09 29 - 094835 - 1475507735280Δημήτριος ΙωαννίδηςNoch keine Bewertungen
- DB 170826Dokument12 SeitenDB 170826Nanthicha KrajangpawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Expression Pattern of S1R MRNA and Protein in Mammalian Retina - Ola2001Dokument16 SeitenExpression Pattern of S1R MRNA and Protein in Mammalian Retina - Ola2001nienminhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Absorption by RootsDokument7 SeitenAbsorption by Rootsshreya morajkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Meiosis Karyotype Revision2 NondisjuncDokument2 SeitenMeiosis Karyotype Revision2 NondisjuncKerem Sezai BaşNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gen Bio Module 3 Q2Dokument3 SeitenGen Bio Module 3 Q2Hero PantiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genetic Code 2020Dokument20 SeitenGenetic Code 2020PAVITHRA SNoch keine Bewertungen
- USMLE 1 Hematology BookDokument368 SeitenUSMLE 1 Hematology BookPRINCENoch keine Bewertungen
- Enhancing Bone Regeneration with Platelet-Rich FibrinDokument7 SeitenEnhancing Bone Regeneration with Platelet-Rich FibrinCarlosWaitforitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio 140 Lab BeetsDokument9 SeitenBio 140 Lab Beetsflawson0078970100% (2)
- M.sc. Biotech Credit CourseDokument101 SeitenM.sc. Biotech Credit CourseStephen MooreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discussion Bio460Dokument2 SeitenDiscussion Bio460MUHAMMAD SYAHMI BIN AZMINoch keine Bewertungen