Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
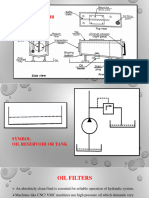
Gun-Type Burners (Pressure Gun)
Hochgeladen von
Siva AnubhamOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Gun-Type Burners (Pressure Gun)
Hochgeladen von
Siva AnubhamCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
http://www.youtube.com/watch?
feature=player_detailpage&v=w-_2aCVvStM
An oil burner is a mechanical device that combines fuel oil with proper amounts of air before delivering the mixture to the point of ignition in a combustion chamber. It is essential for the efficiency of the combustion process that the oil/air mixture is well homogenized and with as few pure droplets of fuel oil as possible. A fuel oil burner either
vaporize and/or atomize
the fuel oil. Fuel oil burners can in general categorized as
gun-type (atomizing ) burners (pressure gun) pot-type (vaporizing) burners rotary-type fuel oil burners
Gun-type Burners (pressure gun)
A gun-type burner atomize the fuel oil by forcing the oil through a nozzle and spraying it into to an gun-like airflow atomic nozzle. The liquid forms microscopic particles or globules which is well mixed and partly evaporated before ignited in the combustion chamber. A residential gun-type burner normally requires a oil 80 - 130 psi oil pressure. Commercial and industrial burners requires 100 - 300 psi. The gun-type is very flexible and can be used within a large range of applications, from relative small residential heaters to larger industrial heating applications.
Pot-type burners
In a pot-type fuel burner the fuel evaporates into the combustion air. There are in general
natural draft burners forced draft burners sleeve burners
In an atmospheric pot type heaters the gravity causes the oil to flow to the burner. The natural draft burner relies on the natural draft in the chimney for air supply. The forced draft burner relies on a mechanical fan and/or the chimney for air supply. The perforated sleeve burner is only used in small applications. The pot-type burner is the most inexpensive of the fuel oil burners and has the lowest operating cost. A disadvantage of the pot-type is a limited capacity. This type is in general most suited for smaller applications.
Rotary fuel burners
Rotary burners operates with low-pressure gravity and the fuel oil is supplied on and thrown of a rotary disc in a fine spray by the centrifugal force. Rotary burners can be classified as
rotary nozzle rotary cup
With the rotary nozzle burner the nozzle assembly rotate at high speed and oil is supplied through the shaft. The rotary cup oil burner contains a cone shaped cup that rotates around a central tube where fuel oil is supplied. The following types of rotary oil burners are available
vertical rotary burners horizontal rotary burners wall-flame rotary burners
The rotary fuel burner has in general its advantage in large applications.
Oil-fired burners are used in many parts of the country as the basic heat source for warm air and hot water heating systems. Most of the home oil systems in use today are called pressure burners. In this type of system, oil is sprayed into a combustion chamber at high pressure, propelled by a blower, and ignited by an electric spark. The oil continues to burn as the mist is sprayed.
2006 Publications International, Ltd. Most oil furnaces in use today are called pressure burners. In this type of system, oil is sprayed into a combustion chamber at high pressure.
An oil furnace is a complex assembly. The maintenance and repair work for this type of furnace is limited to simple parts: the filters, the blower, the motor belts, the switches, and the thermostat. Electrodes, an oil nozzle, air tubes, a transformer, a pump, and other components require special tools and testing equipment and are best left to a professional for service. To become familiar with your oil furnace, remove the access panel covering the burner blower by removing the retaining screws around the rim of the housing. You can access the air blower and filter through a metal panel on one side of the furnace. The panel is held by either hooks or retaining bolts; slip the panel up and off the hooks or remove the bolts and lift the panel off. Most furnaces have switches and reset buttons located on the motor or in a switch box outside the furnace housing. These are usually identified with stampings or labels, such as DISCONNECT SWITCH, RESET, and so on. The stack control sensor, a safety device that monitors burner operation, is positioned in the stack and held with a series of retaining bolts. There's not much you can do to fix an oil furnace, but routine maintenance can forestall many problems. On the next page you'll find a list of tips to keep your furnace running smoothly. For more articles on home repair, check out the following links. Furnace Maintenance: Save yourself time and money by learning the steps to keep youor furnace in prime condition. Major Appliance Repair: If the furnace isn't the only thing in your house on the fritz, you can learn how to fix other machines in this article. Small Appliance Repair: Once you've tackled the furnace, a toaster or blender seems like child's play. Find out how to fix them here. Thermostat Maintenance: To make sure there's actually a problem with your heating system, you may want to check the thermostat, too. Learn how to calibrate a thermostat.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Burn BodyDokument32 SeitenBurn BodyMahmoud Ahmed Ali AbdelrazikNoch keine Bewertungen
- 15.10 Lubrication SystemDokument19 Seiten15.10 Lubrication SystemMoin KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Turbine Start UpDokument131 SeitenGas Turbine Start UpBaharudin Bin Kamarul Baharin100% (3)
- Uh 60 ManualDokument241 SeitenUh 60 ManualAnonymous ddjwf1dqpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Radiant Manual Updated 2013Dokument19 SeitenRadiant Manual Updated 2013api-251989125Noch keine Bewertungen
- Aircrafft Lubrication SystemDokument8 SeitenAircrafft Lubrication SystemshyamsundarsrNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01.main Engine ManualDokument64 Seiten01.main Engine ManualwilfredNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 4Dokument11 SeitenAssignment 4levitranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gasoline Engine Performance TestDokument35 SeitenGasoline Engine Performance TestaljhonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Furnace Design and Operation: Fuel Handling SystemsDokument45 SeitenFurnace Design and Operation: Fuel Handling SystemskINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Small Engine: A Step-By-Step Guide To Maintaining Your Small EngineDokument8 SeitenSmall Engine: A Step-By-Step Guide To Maintaining Your Small EngineBez ImenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boiler Manual Updated 20131Dokument50 SeitenBoiler Manual Updated 20131api-251989125Noch keine Bewertungen
- Turbocharger BasicsDokument5 SeitenTurbocharger BasicstaonglantsaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Fuel Oil System For A Diesel EngineDokument8 SeitenThe Fuel Oil System For A Diesel EngineYvonne Pearl Delos SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity 1 ME LabDokument29 SeitenActivity 1 ME LabIanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boiler Manual UpdatedDokument50 SeitenBoiler Manual UpdatedJimi DbonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- AVIM 105A and 106A Combustion Heater Operation and MaintenanceDokument13 SeitenAVIM 105A and 106A Combustion Heater Operation and Maintenance13594Noch keine Bewertungen
- Report On Generator Installation For The Fishing Boat at Neil Marine (PVT) LTD, BeruwalaDokument16 SeitenReport On Generator Installation For The Fishing Boat at Neil Marine (PVT) LTD, BeruwalaChanna AshanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lubrication and Cooling SystemDokument11 SeitenLubrication and Cooling Systemrongphar9alon100% (1)
- Overhaul Engine and Its Associated ComponentsDokument36 SeitenOverhaul Engine and Its Associated ComponentsBiruk Tilahun100% (3)
- Furnace Manual 120v Updated 2013Dokument21 SeitenFurnace Manual 120v Updated 2013api-251989125Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fuel System of A Gas Turbine EngineDokument4 SeitenFuel System of A Gas Turbine EngineZayarlwinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Questions For OralDokument17 SeitenQuestions For OralQaiser khanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3 Fuel SystemDokument58 SeitenUnit 3 Fuel SystemuthiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oil SepratorsDokument4 SeitenOil SepratorsMohammad Amer0% (1)
- Vocab and SentencesDokument6 SeitenVocab and SentencesYannick PakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diesel Fa19Dokument35 SeitenDiesel Fa19Muhammad JunaidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amt 1201 - Prelim - Module 2 - DelgadoDokument4 SeitenAmt 1201 - Prelim - Module 2 - DelgadoBrendan Lewis DelgadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATS ComBased Training - PPTX MONDokument155 SeitenATS ComBased Training - PPTX MONDEATHSTAR GAMINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bashar Sir FAQDokument92 SeitenBashar Sir FAQMehedy MasudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diesel Engine Operational SafetyDokument12 SeitenDiesel Engine Operational SafetyYohannes DennisNoch keine Bewertungen
- LubricationsDokument9 SeitenLubricationsSamarth SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lubrication of MachineryDokument13 SeitenLubrication of Machinerysimba8661Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cooling System Troubleshooting: PurposeDokument15 SeitenCooling System Troubleshooting: Purposedmc constructionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module g11Dokument60 SeitenModule g11Roderick M. DomioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Components of Hydraulic SystemDokument42 SeitenComponents of Hydraulic SystemShrikant BorseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flame Safeguard Controls in Multi-Burner EnvironmentsDokument33 SeitenFlame Safeguard Controls in Multi-Burner EnvironmentsManish KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engine Lubrication SystemDokument2 SeitenEngine Lubrication SystemYemaneDibetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bowl MillDokument10 SeitenBowl MillAvtarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Turbine CourseDokument54 SeitenGas Turbine CourseMgn San100% (1)
- Lub of Bolero SLXDokument21 SeitenLub of Bolero SLXRohit PantNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fuel Injection System For Ci Engines PDFDokument6 SeitenFuel Injection System For Ci Engines PDFmark mutimushiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research Work Week 11Dokument2 SeitenResearch Work Week 11jonas lintagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engine ComponentsDokument9 SeitenEngine ComponentsRadamirNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Gas and Oil FuelsDokument20 Seiten3 Gas and Oil FuelsCristhian Garcia VillarroelNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Characteristics of Gas TurbineDokument13 SeitenGeneral Characteristics of Gas Turbineart estacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Main Diesel Engine Cooling SystemDokument4 SeitenMain Diesel Engine Cooling SystemconcernizationNoch keine Bewertungen
- Role of Hydrogen in GeneratorDokument33 SeitenRole of Hydrogen in GeneratorVasudev Agrawal100% (1)
- Artifact 4 Parts Small Engines PowerpointDokument56 SeitenArtifact 4 Parts Small Engines Powerpointapi-240922530Noch keine Bewertungen
- Generator AuxiliariesDokument4 SeitenGenerator AuxiliariesNilesh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kenneth Sleight - Engine Room ExploredDokument10 SeitenKenneth Sleight - Engine Room Explorednf_azevedoNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Information: Scope and Use of This ManualDokument27 SeitenGeneral Information: Scope and Use of This ManualJose Maces Del FoyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engine Lubrication and Cooling SystemDokument36 SeitenEngine Lubrication and Cooling SystemJunaid YNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aero Engines Assignment 2Dokument9 SeitenAero Engines Assignment 2Malik Abdullah AwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lubricating SystemDokument25 SeitenLubricating SystemmelissaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jeppesen Oral QsDokument47 SeitenJeppesen Oral QsDavid DoughtyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tugas 1 Written and TranslateDokument7 SeitenTugas 1 Written and TranslateAdiet ScwaezenegersamdNoch keine Bewertungen
- محركاتDokument20 SeitenمحركاتYasmin RedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Small Engines and Outdoor Power Equipment: A Care & Repair Guide for: Lawn Mowers, Snowblowers & Small Gas-Powered ImplementsVon EverandSmall Engines and Outdoor Power Equipment: A Care & Repair Guide for: Lawn Mowers, Snowblowers & Small Gas-Powered ImplementsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Installation and Operation Instructions For Custom Mark III CP Series Oil Fired UnitVon EverandInstallation and Operation Instructions For Custom Mark III CP Series Oil Fired UnitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Micro - Systemic Bacteriology Questions PDFDokument79 SeitenMicro - Systemic Bacteriology Questions PDFShashipriya AgressNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02 Chapter 2 - Corporate Governance MechanismDokument19 Seiten02 Chapter 2 - Corporate Governance MechanismHanis ZahiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shaqlawa Technical College: IT DepartmentDokument20 SeitenShaqlawa Technical College: IT Departmentbilind_mustafaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IbmautomtiveDokument38 SeitenIbmautomtiveMeltz NjorogeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yarn HairinessDokument9 SeitenYarn HairinessGhandi AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bathinda - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokument4 SeitenBathinda - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaBhuwan GargNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contemp Person Act.1Dokument1 SeiteContemp Person Act.1Luisa Jane De LunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- For ClosureDokument18 SeitenFor Closuremau_cajipeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catalogue of Archaeological Finds FromDokument67 SeitenCatalogue of Archaeological Finds FromAdrinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Perturbation MethodsDokument29 SeitenPerturbation Methodsmhdr100% (1)
- Introduction To AmplifierDokument8 SeitenIntroduction To AmplifierElaine BicolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bustax Midtem Quiz 1 Answer Key Problem SolvingDokument2 SeitenBustax Midtem Quiz 1 Answer Key Problem Solvingralph anthony macahiligNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uts Cmo Module 5Dokument31 SeitenUts Cmo Module 5Ceelinah EsparazNoch keine Bewertungen
- BluePrint & High Pressure Pascalization (HPP)Dokument3 SeitenBluePrint & High Pressure Pascalization (HPP)Prof C.S.PurushothamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- DOST-PHIVOLCS Presentation For The CRDRRMC Meeting 15jan2020Dokument36 SeitenDOST-PHIVOLCS Presentation For The CRDRRMC Meeting 15jan2020RJay JacabanNoch keine Bewertungen
- SahanaDokument1 SeiteSahanamurthyarun1993Noch keine Bewertungen
- Design Practical Eden Swithenbank Graded PeDokument7 SeitenDesign Practical Eden Swithenbank Graded Peapi-429329398Noch keine Bewertungen
- Economizer DesignDokument2 SeitenEconomizer Designandremalta09100% (4)
- Astm D2000 PDFDokument38 SeitenAstm D2000 PDFMariano Emir Garcia OdriozolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Specimen Signature FormDokument27 SeitenSpecimen Signature FormnandukyNoch keine Bewertungen
- SRS Document Battle Royale Origins - V2Dokument36 SeitenSRS Document Battle Royale Origins - V2Talha SajjadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mobile Services: Your Account Summary This Month'S ChargesDokument3 SeitenMobile Services: Your Account Summary This Month'S Chargeskumarvaibhav301745Noch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Optimization of A Medium Altitude Long Endurance UAV Wingbox StructureDokument8 SeitenDesign and Optimization of A Medium Altitude Long Endurance UAV Wingbox StructureamirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thesis On Retail Management of The Brand 'Sleepwell'Dokument62 SeitenThesis On Retail Management of The Brand 'Sleepwell'Sajid Lodha100% (1)
- Cpar ReviewerDokument6 SeitenCpar ReviewerHana YeppeodaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 13507Dokument5 Seiten13507Abinash Kumar0% (1)
- Biscotti: Notes: The Sugar I Use in France, Is CalledDokument2 SeitenBiscotti: Notes: The Sugar I Use in France, Is CalledMonica CreangaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marieb ch3dDokument20 SeitenMarieb ch3dapi-229554503Noch keine Bewertungen
- Datos Adjuntos Sin Título 00013Dokument3 SeitenDatos Adjuntos Sin Título 00013coyana9652Noch keine Bewertungen