Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Test 1 Solution
Hochgeladen von
Jake WischnefskiOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Test 1 Solution
Hochgeladen von
Jake WischnefskiCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
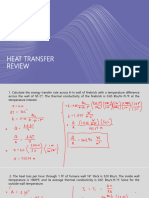
PROBLEM 1.
63
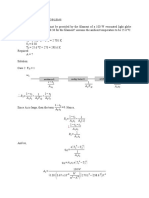
KNOWN: Dimensions and emissivity of a cell phone charger. Surface temperature when plugged in. Temperature of air and surroundings. Convection heat transfer coefficient. Cost of electricity. FIND: Daily cost of leaving the charger plugged in when not in use. SCHEMATIC:
Tsur = 20C
Ts = 33C = 0.92
qconv
50 mm Air T = 22C h = 4.5 W/m2K
Eg
45 mm 20 mm
qrad
ASSUMPTIONS: (1) Steady-state conditions, (2) Convection and radiation are from five exposed surfaces of charger, (3) Large surroundings, (4) Negligible heat transfer from back of charger to wall and outlet.
& & & ANALYSIS: At steady-state, an energy balance on the charger gives Ein + E g = 0 , where E g
represents the conversion from electrical to thermal energy. The exposed area is A = (50 mm 45 mm) + 2(50 mm 20 mm) + 2(45 mm 20 mm) = 6050 mm2. Thus,
4 & E g = ( qconv + qrad ) = hA(Ts T ) + A(Ts4 Tsur )
= 4.5 W / m 2 K(33C 22C) + 0.92 5.67 108 W/m 2 K 4 ( (306 K)4 (293 K)4 ) 6050 106 m 2 = 0.74 W This is the total rate of electricity used while the charger is plugged in. The daily cost of electricity is Cost = 0.74 W $0.18/kWh 1 kW/1000 W 24 h/day = $0.0032/day
<
COMMENTS: (1) The radiation and convection heat fluxes are 73 W/m2 and 50 W/m2, respectively. Therefore, both modes of heat transfer are important. (2) The cost of leaving the charger plugged in when not in use is small.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Om He163 230-0210-HeDokument40 SeitenOm He163 230-0210-HeShahrizatSmailKassim100% (1)
- Design of Helical SpringsDokument32 SeitenDesign of Helical SpringsAHMAD FIRDAUS ILIAS100% (1)
- Basic Design and Concepts To Industrial Plant SystemsDokument39 SeitenBasic Design and Concepts To Industrial Plant SystemsCj SiguenzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shear and Moment Diagrams - Including The 3 Moment Equation and ExamplesDokument300 SeitenShear and Moment Diagrams - Including The 3 Moment Equation and Examplessoulsell100% (7)
- 7 Quencher DesignDokument8 Seiten7 Quencher DesignJozsef Acs100% (1)
- Chapter 15 ProblemsDokument3 SeitenChapter 15 ProblemsJoshua Phillip Austero FederisNoch keine Bewertungen
- CombinepdfDokument108 SeitenCombinepdfAlessandra TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multi ModeDokument73 SeitenMulti ModeShalinee KavadiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical Engineering Review 2 Fundamentals ThermodynamicsDokument5 SeitenMechanical Engineering Review 2 Fundamentals ThermodynamicsIvy Joy UbinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Refrigeration Engineering: MerefengDokument62 SeitenRefrigeration Engineering: MerefengPrecious Gallardo DerainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 1& 2 - SolDokument10 SeitenTutorial 1& 2 - SolAli ZaghloulNoch keine Bewertungen
- HW 1Dokument5 SeitenHW 1Yohan ManaligodNoch keine Bewertungen
- REFSYS - 3ME-8 (2ND SEM/ A.Y. 2020-2021) Midterm ExaminationDokument3 SeitenREFSYS - 3ME-8 (2ND SEM/ A.Y. 2020-2021) Midterm ExaminationRobert GarlandNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emittance R Emittance R Config. Factor RDokument6 SeitenEmittance R Emittance R Config. Factor RAJNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Transfer Problem Sheet PDFDokument3 SeitenHeat Transfer Problem Sheet PDFDerek101johnson100% (1)
- Steam Power Plant PDFDokument21 SeitenSteam Power Plant PDFJan Rangel Sabado De VeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermodynamics Exam SolutionsDokument5 SeitenThermodynamics Exam SolutionsAugi Reader50% (2)
- DEFINITIONS (Machine Shop-Design)Dokument19 SeitenDEFINITIONS (Machine Shop-Design)Marcial Jr. MilitanteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1Dokument8 SeitenChapter 1Von A. Damirez0% (1)
- CHE 306 - Solved Problems-9Dokument1 SeiteCHE 306 - Solved Problems-9Garcia Raph100% (1)
- Module Iii Refrigeration CycleDokument16 SeitenModule Iii Refrigeration CycleDiether RigorNoch keine Bewertungen
- BSABE2 - Blasquez - Lab Report 2Dokument7 SeitenBSABE2 - Blasquez - Lab Report 2Lorenzo Niño BlasquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final hmt-1 PDFDokument211 SeitenFinal hmt-1 PDFPoyyamozhi Nadesan RanjithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat TransferDokument27 SeitenHeat TransferLurking RogueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Problem Stirling CycleDokument2 SeitenSample Problem Stirling CycleJaniz TumambingNoch keine Bewertungen
- 311 ThermoDynamics ThermoDynamicsDokument5 Seiten311 ThermoDynamics ThermoDynamicsmozam haqNoch keine Bewertungen
- 23radiation Heat Transfer - Heat Exchange Between Surfaces - Formulae ProblemsDokument13 Seiten23radiation Heat Transfer - Heat Exchange Between Surfaces - Formulae Problemsananth2012Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 9-Hydroelectric Plant PDFDokument118 SeitenChapter 9-Hydroelectric Plant PDFsindyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fans and Blowers Practice ProblemsDokument2 SeitenFans and Blowers Practice ProblemsFour AyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Transfer: Precious Arlene Villaroza-MelendrezDokument33 SeitenHeat Transfer: Precious Arlene Villaroza-MelendrezMark Jake RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5Dokument25 SeitenChapter 5dickinaround87100% (1)
- A Propeller Shaft As Shown Is To Receive 300 HP at 315 RPM From The Right Through A Flexible CouplingDokument5 SeitenA Propeller Shaft As Shown Is To Receive 300 HP at 315 RPM From The Right Through A Flexible CouplingMark AgusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercises Problem 1 Ref and Air Con MamaclayRADokument3 SeitenExercises Problem 1 Ref and Air Con MamaclayRALeyzer MalumayNoch keine Bewertungen
- From Table AT7 - Design of Machine Elements of Faires For AISI C1045 - S 96 Ksi - S 59 Ksi - E 30 x10 Psi A) Based On Ultimate StrengthDokument4 SeitenFrom Table AT7 - Design of Machine Elements of Faires For AISI C1045 - S 96 Ksi - S 59 Ksi - E 30 x10 Psi A) Based On Ultimate StrengthMark AgusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Procedure For Flat BeltDokument2 SeitenDesign Procedure For Flat BeltKutty AravindNoch keine Bewertungen
- JJJJJJJJJJDokument4 SeitenJJJJJJJJJJJoshua UmaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Turbine PowerplantDokument1 SeiteGas Turbine PowerplantVon A. DamirezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rac Problems Set 1Dokument6 SeitenRac Problems Set 1Mohammad Umair100% (1)
- Mechanics (Dynamics)Dokument2 SeitenMechanics (Dynamics)Earl JennNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanics of Material-1-5 PDFDokument252 SeitenMechanics of Material-1-5 PDFkhan janNoch keine Bewertungen
- MD-1 BearingsDokument2 SeitenMD-1 BearingsEleisa SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.0 Band Brake Example ProblemsDokument10 Seiten2.0 Band Brake Example Problemsmanalo.jonmeloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Balingt - Prelim ExamDokument21 SeitenBalingt - Prelim ExamRene Niño Macamay BalingitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ref Systems Lecture Notes 1Dokument9 SeitenRef Systems Lecture Notes 1Retro GamerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulic AnsweranssDokument11 SeitenHydraulic AnsweranssJanelle D. Puti-anNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pipe Problems Part 1Dokument100 SeitenPipe Problems Part 1Sheena BejasaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diesel Power Plant ProblemsDokument2 SeitenDiesel Power Plant ProblemsMaribethCanesoMappeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plate 1, 2 3 No AnsDokument4 SeitenPlate 1, 2 3 No AnsRika MaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- PME9 Heat TransferDokument8 SeitenPME9 Heat TransferKAL ELNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 5Dokument63 SeitenUnit 5RajeshKumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Refrigeration-Systems Part 1Dokument11 SeitenRefrigeration-Systems Part 1Sean GuanzonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name: Obias, Ricci Eugenia Date: August, 31 2021 Exercise No. 1Dokument4 SeitenName: Obias, Ricci Eugenia Date: August, 31 2021 Exercise No. 1Ricci ObiasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 1Dokument10 Seiten4 1Miguel Dominic BernardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worked Examples H. ExchangersDokument5 SeitenWorked Examples H. ExchangersBryan ScofieldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foundry TerminologyDokument5 SeitenFoundry Terminologyahmish kabbaxeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Number 1Dokument82 SeitenQuestion Number 1Ryan Llona FernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- HMTDokument37 SeitenHMTVaibhav Vithoba NaikNoch keine Bewertungen
- MENG4662 Chapter 2 Rankine CycleDokument67 SeitenMENG4662 Chapter 2 Rankine CycleSamuel GeorgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Example Question FinalDokument22 SeitenExample Question Finalgazile0% (1)
- Assignment 5Dokument2 SeitenAssignment 5hossamkandil7Noch keine Bewertungen
- HW 1 SolDokument9 SeitenHW 1 SolNatalia AlvaradoNoch keine Bewertungen
- HW 3Dokument14 SeitenHW 3Mark LutherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solución Problemas Extra Tema 5 - Nivel 2Dokument7 SeitenSolución Problemas Extra Tema 5 - Nivel 2SpanishRacingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 - TutorialDokument4 SeitenChapter 3 - TutorialDavidNoch keine Bewertungen
- s355j2g3 Material PropertyDokument9 Seitens355j2g3 Material PropertyAmrut KajveNoch keine Bewertungen
- FE/Pipe: Finite Element AnalysisDokument2 SeitenFE/Pipe: Finite Element AnalysisChirag ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Verification and Validation of Turbulent Flow Around A Clark-Y AirfoilDokument16 SeitenVerification and Validation of Turbulent Flow Around A Clark-Y AirfoilKarthik AbhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solid Mechanics Plane Stress and Plane StrainsDokument8 SeitenSolid Mechanics Plane Stress and Plane StrainskingstonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Three Point and Four Point StarterDokument7 SeitenThree Point and Four Point Starterkaran nirmala gajanan shindeNoch keine Bewertungen
- MEGAWRAP-200: Unidirectional Carbon Fabric For Structural StrengtheningDokument2 SeitenMEGAWRAP-200: Unidirectional Carbon Fabric For Structural StrengtheningMarli MaksutiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 16th Numerical Towing Tank SymposiumDokument189 Seiten16th Numerical Towing Tank SymposiumBrenno Moura MouraNoch keine Bewertungen
- BALANCEDDokument13 SeitenBALANCEDJennifer dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Witte Poly PumpsDokument5 SeitenWitte Poly Pumpsy.s.6saputroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bus Stop Steel FinalDokument33 SeitenBus Stop Steel FinalanuarNoch keine Bewertungen
- GasesDokument38 SeitenGaseshNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.0 Imperfections in Solids: "Crystals Are Like People, It Is The Defects in Them Which Tend To Make Them Interesting!"Dokument29 Seiten4.0 Imperfections in Solids: "Crystals Are Like People, It Is The Defects in Them Which Tend To Make Them Interesting!"Williams AkandiNoch keine Bewertungen
- IOT Practical FileDokument37 SeitenIOT Practical FileFiroz AnsariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mse 315aDokument23 SeitenMse 315aMuhammad Bilal SahiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annie Fang - Research PosterDokument1 SeiteAnnie Fang - Research PosterAnnie FangNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2022 Acoustic Metamaterials For Noise Reduction A ReviewDokument23 Seiten2022 Acoustic Metamaterials For Noise Reduction A Reviewrunze zhangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual de Aceros Inoxidables EspecialesDokument12 SeitenManual de Aceros Inoxidables EspecialesErick OlavarriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical Engineering Important MCQ PDF-Fluid Mechanics 2Dokument8 SeitenMechanical Engineering Important MCQ PDF-Fluid Mechanics 2kibrom atsbhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TPU Technical DatasheetDokument2 SeitenTPU Technical Datasheetromi supriyonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem Ib PaperDokument18 SeitenChem Ib Paperembededodin0% (1)
- MTC Spec 1916Dokument3 SeitenMTC Spec 1916Indwell RaigarhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp # 1 Melting PointDokument11 SeitenExp # 1 Melting PointjamesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grillage Voided BoxculvertsDokument32 SeitenGrillage Voided BoxculvertsNaga Manikanta TatikondaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Lightning Arrest Ers For Electrical Power Systems ProtectionDokument11 SeitenDesign of Lightning Arrest Ers For Electrical Power Systems ProtectionMohammad KhodadadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 59E - Agitator - Seals - in Chemical-EN-18.09.2008 PDFDokument24 Seiten59E - Agitator - Seals - in Chemical-EN-18.09.2008 PDFTiago Carnovali PessoaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SuperconductorDokument12 SeitenSuperconductorAchmad Salafudin BerdurasiNoch keine Bewertungen