Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Aids
Hochgeladen von
Patrice AlexanderOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Aids
Hochgeladen von
Patrice AlexanderCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
AIDS (acquired immune deficiency syndrome) is a severe illness caused by HIV (human immunodeficiency virus).
HIV works within the body by harming the immune system, so it is unable to fight infection(s). HIV is considered a sexually transmitted disease. It is spread to others via tainted blood, mother to baby, and bodily fluids. When the immune system is destroyed enough by HIV, the illness turns into AIDS. There is currently no cure for HIV/AIDS, but there are medications available that offset its progression.
HIV destroys CD4 cells. To be diagnosed with AIDS you must have a CD4 count that is under 200, or experience an AIDS complication. There are several of these complications. A few are Pneumocystis pneumonia, Cytomegalovirus, Tuberculosis, Toxoplasmosis, and Cryptosporidiosis.
The symptoms of HIV/AIDS can vary on a case by case basis. Most individuals develop flu symptoms a month or so after they have been exposed to the virus. Other symptoms include, but are but limited to fever, swollen lymph glands, night sweats, and diarrhea. HIV progresses to AIDS in about 10 years without treatment. Symptoms then begin to include wasting syndrome, unexplained fatigue, skin rashes, and mouth lesions.
A common misconception is that you can become infected with HIV/AIDS through ordinary contact. You cannot become infected from simple things such as, shaking hands or hugs. You can however become infected during sex, blood transfusions (less common), sharing needles, and from mother to child during pregnancy, birth, or breast feeding.
Anyone can contract HIV/AIDS. It is not just limited to a select group of people. Risk factors of contracting the illness include unprotected sex, having another STI (where open sores are present), and intravenous drug use. These risk factors mean they put you at a higher risk of contracting HIV/AIDS, not that you already have.
There are more serious complications that can arise due to a weakened immune system. They are Lymphomas, Kaposis sarcoma, Wasting syndrome, Cryptococcal Meningitis, and Candidiasis. Confirmatory tests (EIA and Western Blot) of the blood and saliva are used to test for antibodies to HIV/AIDS. If the test is positive there are numerous treatment regimens available, they prolong life longer and better then past treatments.
Web Links: http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/hiv-aids/DS00005 http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/hiv-aids/DS00005/DSECTION=symptoms, http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/hiv-aids/DS00005/DSECTION=causes. http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/hiv-aids/DS00005/DSECTION=risk-factors, http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/hiv-aids/DS00005/DSECTION=complications
1. AIDS: A disease in which there is a severe loss of the bodys cellular immunity, greatly lowering the resistance to infection and malignancy. 2. HIV: A retrovirus that causes AIDS. 3. Pneumocystis Pneumonia: An opportunistic infection, caused by yeast like fungus. A major cause of death in patients with late stage AIDS. 4. Cytomegalovirus: A kind of herpes virus that usually produces very mild symptoms in an infected person but may cause severe neurological damage in people with weakened immune systems and in the newborn 5. Tuberculosis: An infectious bacterial disease characterized by the growth of nodules (tubercles) in the tissues, esp. the lungs 6. Candidiasis: An infection caused by a species of the yeast Candida, usually Candida albicans. This is a common cause of vaginal infections in women. Also, Candida may cause mouth infections in people with reduced immune function, or in patients taking certain antibiotics. 7. Lymphoma: Cancer of the lymph nodes. 8. Kaposis sarcoma: A form of cancer involving multiple tumors of the lymph nodes, or skin occurring chiefly in people with depressed immune systems. 9. Cryptococcal Meningitis: A fungal infection of the membranes covering the brain and spinal cord (meninges). 10. Wasting Syndrome: Involuntary weight loss (at least 10% of body mass) in combination with diarrhea, fever, or weakness lasting at least 30 days. The bulk of what is lost is lean body cell mass, meaning that while it may be a combination of muscle, fat, and bone, it is mostly muscle.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Mapeh 9 4th Quarter ExamDokument6 SeitenMapeh 9 4th Quarter ExamAple Rigor100% (2)
- Aerobic Exercise Dos and DontsDokument2 SeitenAerobic Exercise Dos and DontsSandy NodadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- GATS 2 FactSheetDokument4 SeitenGATS 2 FactSheetAsmi MohamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Ana Surgery WardDokument11 SeitenDrug Ana Surgery WardJames QuilingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Test - Mid TermDokument2 SeitenPractice Test - Mid Termngaanhc2ngtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2Dokument15 SeitenChapter 2Daniel John LingamenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Formulary HospitalDokument98 SeitenDrug Formulary HospitalahmshmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iec Obg CareDokument16 SeitenIec Obg CareBlessy Madhuri100% (1)
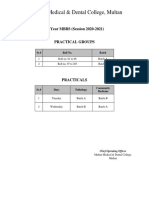
- 4th Year MBBS Batches & GroupsDokument2 Seiten4th Year MBBS Batches & GroupsSohail Abbas KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Informative Speech OutlineDokument3 SeitenInformative Speech Outlineapi-250554127100% (1)
- Determinan Gejala Mental Emosional Pelajar SMP-SMA Di Indonesia Tahun 2015Dokument11 SeitenDeterminan Gejala Mental Emosional Pelajar SMP-SMA Di Indonesia Tahun 2015NurLestariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sarcopenia, European Definition and DiagnosisDokument12 SeitenSarcopenia, European Definition and DiagnosisRémi DelauzunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essential Care of Newborn at BirthDokument32 SeitenEssential Care of Newborn at Birthastha singh100% (1)
- Approach To The History and Evaluation of Vertigo and DizzinessDokument24 SeitenApproach To The History and Evaluation of Vertigo and DizzinessPAULA GABRIELA ABAD POLONoch keine Bewertungen
- The Factories Act 1948Dokument96 SeitenThe Factories Act 1948NIKITHAA ASHWINNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accredited Social Health Activist: Ms - Neethu Vincent Asst Professor KVM College of NursingDokument18 SeitenAccredited Social Health Activist: Ms - Neethu Vincent Asst Professor KVM College of NursingNeethu VincentNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Filipino Worker's Resilience Amidst Covid-19 PandemicDokument15 SeitenA Filipino Worker's Resilience Amidst Covid-19 PandemicVin Nicole Salazar Revilla67% (3)
- Mock Oral CasesDokument6 SeitenMock Oral Casestcbarot100% (1)
- Tmi Lumbar Fusion Rehabilitation ProtocolDokument2 SeitenTmi Lumbar Fusion Rehabilitation ProtocolJackyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nooriya Prabhakaran Visualcv Resume 2017Dokument2 SeitenNooriya Prabhakaran Visualcv Resume 2017api-372799602Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mitchell H. Katz-Evaluating Clinical and Public Health Interventions - A Practical Guide To Study Design and Statistics (2010)Dokument176 SeitenMitchell H. Katz-Evaluating Clinical and Public Health Interventions - A Practical Guide To Study Design and Statistics (2010)Lakshmi SethNoch keine Bewertungen
- Can Cognitive Therapy Be Conducted by Computers. Eells, Barrett, Wrigh, ThaseDokument7 SeitenCan Cognitive Therapy Be Conducted by Computers. Eells, Barrett, Wrigh, ThaseAylin Lidsay Feria GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Education and Health 3 Grade 12 Module 3.docx 1Dokument19 SeitenPhysical Education and Health 3 Grade 12 Module 3.docx 1Iesha Rhaye Alonzo100% (2)
- Anthropometric ResultDokument2 SeitenAnthropometric ResultNaveed AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nutrisi Bedah: Dr. Dr. Ishandono Dachlan, M.SC., SP.B., SP - BP-RE (K)Dokument69 SeitenNutrisi Bedah: Dr. Dr. Ishandono Dachlan, M.SC., SP.B., SP - BP-RE (K)Tiara MonicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Temy Dlya Napisania Esse V EGE Po Angliyskomu YazykuDokument7 SeitenTemy Dlya Napisania Esse V EGE Po Angliyskomu YazykuElena StepanovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Irene Gee Regidor BSED-English Conditions of Developmental Delay 1. Mental RetardationDokument3 SeitenIrene Gee Regidor BSED-English Conditions of Developmental Delay 1. Mental RetardationAliana CabalunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ethical & Legal Issues in Canadian NursingDokument950 SeitenEthical & Legal Issues in Canadian NursingKarl Chelchowski100% (1)
- PG DissertationDokument39 SeitenPG Dissertationavikalmanitripathi2023Noch keine Bewertungen
- Figure 1. New Criteria For AKI Diagnosis Are Displayed. in Order To Diagnose AKIDokument8 SeitenFigure 1. New Criteria For AKI Diagnosis Are Displayed. in Order To Diagnose AKIMayra Alejandra Prada SerranoNoch keine Bewertungen