Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Practice Test 4-5
Hochgeladen von
Nguyễn Thị Hồng YếnOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Practice Test 4-5
Hochgeladen von
Nguyễn Thị Hồng YếnCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Practice Test 4-5
Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 1. A competitive market is one in which a. there is only one seller of the product. b. each seller of the product is free to set the price of his product. c. each seller attempts to compete with other sellers, causing fewer sellers in the market. d. there are so many buyers and many sellers that each has a negligible impact on price. 2. Buyers and sellers who have no influence on market price are referred to as a. price makers. b. market pawns. c. price takers. d. powerless. 3. Generally, the market for ice cream would be considered a. a monopolistic market. b. a competitive market. c. more organized than an auction. d. a market where individual sellers have significant pricing power. 4. A market with only a few sellers would be a. a monopoly. b. an oligopoly. c. a competitive market. d. a monopolistically competitive market. 5. Which of the following would NOT be a determinant of demand? a. the price of related goods b. income c. tastes d. the prices of the inputs used to produce the good 6. If the price of a substitute to good X increases, then the a. demand for good X will decrease. b. market price of good X will decrease. c. demand for good X will increase. d. quantity demanded for good X will increase. 7. Two goods are substitutes if a decrease in the price of one good a. increases the demand for the other good. b. reduces the demand for the other good. c. reduces the quantity demanded of the other good. d. increases the quantity demanded of the other good. 8. Suppose you like banana cream pie made with vanilla pudding. Assuming all other things are constant, you notice that the price of bananas is higher. How would your demand for vanilla pudding be affected by this? a. It would decrease. b. It would increase. c. It would be unaffected. d. There is insufficient information given to answer the question. 9. Which of the following is NOT a determinant of demand? a. the price of a resource
____
____
____
____
____
____
____
____
b. the price of a complementary good c. the price of the good next month d. the price of a substitute good ____ 10. The downward-sloping line which relates prices and quantity demanded is called the a. demand schedule. b. demand curve. c. quantity demanded line. d. quantity demanded curve. ____ 11. A demand curve is a. the downward-sloping line relating the price of the good to the quantity demanded. b. the upward-sloping line relating price to quantity supplied. c. the curve that relates income to quantity demanded. d. showing the same relationship between two goods as a production possibilities frontier. ____ 12. Morgan tells you that the price of DVDs at the video store will be going up next week. You will probably respond by a. decreasing your current demand for DVDs. b. increasing your current demand for DVDs. c. not changing your current demand for DVDs. d. refusing to ever buy anymore DVDs at that store. Figure 4-2
____ 13. Refer to Figure 4-2. If the demand curve shifts from D1 to D, then a. firms would be willing to supply less than before. b. people are less willing to buy the product at any price than before. c. people are now more willing to buy the product at any price than before. d. the price of the product has decreased, causing consumers to buy more of the product. Figure 4-4
____ 14. Refer to Figure 4-4. Which graph could be used to show the result of 5 percent of the country's smokers deciding to stop smoking? a. A b. B c. C d. Each graph could be used to show the result. ____ 15. If the price of a good is low a. firms would increase profit by increasing output. b. quantity supplied could be zero. c. the supply curve for the good will shift to the left. d. firms should raise the price of the product. ____ 16. Which of the following determines a market supply curve but not an individual supply curve? a. number of sellers b. expectations c. input prices d. technology ____ 17. Lead is an important input in the production of crystal. If the price of lead decreases, all else equal, we would expect the supply of a. crystal to be unaffected. b. crystal to decrease. c. crystal to increase. d. lead to increase. ____ 18. Holding the nonprice determinants of supply constant, a change in price would a. result in a change in supply. b. have no effect on the quantity supplied. c. result in a shift of demand. d. result in a movement along a stable supply curve. ____ 19. All else constant, an increase in the number of cattle delivered to an auction to be marketed would a. represent an increase in the supply of cattle at the auction.
b. represent an increase in demand for cattle at the auction. c. represent a decrease in the number of sellers at the auction. d. have no effect on the demand or supply at the auction. Figure 4-6
____ 20. Refer to Figure 4-6. The movement from S to S1 is called a. a decrease in supply. b. a decrease in quantity supplied. c. an increase in supply. d. an increase in quantity supplied. ____ 21. The unique point at which the supply and demand curves intersect is called a. market unity. b. an agreement. c. cohesion. d. equilibrium. Figure 4-9
____ 22. Refer to Figure 4-9. In this market, equilibrium price and quantity would be a. $15,400. b. $20,600. c. $25,500. d. $25,800. ____ 23. Refer to Figure 4-9. At a price of $20, which would NOT be true?
a. b. c. d.
The market would be in equilibrium. Equilibrium price would be equal to equilibrium quantity. There would be no pressure for price to change. 600 units would be bought and sold.
Figure 4-10
____ 24. Refer to Figure 4-10. Graph A shows which of the following? a. an increase in demand b. an increase in quantity demanded c. an increase in quantity supplied d. All of the above are correct. e. Both a and c are correct. ____ 25. If the demand for a product decreases, we would expect equilibrium price a. to increase and equilibrium quantity to decrease. b. to decrease and equilibrium quantity to increase. c. and equilibrium quantity to both increase. d. and equilibrium quantity to both decrease. Table 4-3 An Increase in Demand A Decrease in Demand An Increase in Supply A C A Decrease in Supply B D
____ 26. Refer to Table 4-3. The space that would represent a decrease in equilibrium quantity and an indeterminate change in equilibrium price would be a. A. b. B. c. C.
____ 27.
____ 28.
____ 29.
____ 30.
____ 31.
____ 32.
____ 33.
____ 34.
d. D. What will happen to the equilibrium price and quantity of new cars if the price of gasoline rises, the price of steel rises, public transportation becomes cheaper and more comfortable, and auto-workers negotiate higher wages? a. Price will fall and the effect on quantity is ambiguous. b. Price will rise and the effect on quantity is ambiguous. c. Quantity will fall and the effect on price is ambiguous. d. Quantity will rise and the effect on price is ambiguous. What will happen to the equilibrium price of new textbooks if more students attend college, paper becomes cheaper, textbook authors accept lower royalties and fewer used textbooks are sold? a. Price will rise. b. Price will fall. c. Price will stay exactly the same. d. The price change will be ambiguous. Consider the market for new DVDs. If DVD players became cheaper, buyers expected DVD prices to fall next year, used DVDs became more expensive, and DVD production technology improved, then we could safely conclude that the equilibrium price of a new DVD would a. rise. b. fall. c. stay the same. d. We couldn't be sure what it might do. The price elasticity of demand measures a. a buyer's responsiveness to a change in the price of a good. b. the increase in demand as additional buyers enter the market. c. how much more of a good consumers will demand when incomes rise. d. the increase in demand that will occur from a change in one of the nonprice determinants of demand. The concept of elasticity is used to a. analyze how much the economy is capable of expanding. b. determine the level of government invention in the economy. c. analyze supply and demand with greater precision. d. calculate consumer credit purchases. A person who has high cholesterol and must exercise an hour every day has what type of demand for exercise equipment? a. elastic b. unit elastic c. inelastic d. weak Holding all other forces constant, when the price of gasoline rises, the number of gallons of gasoline demanded would fall substantially over a ten-year period because a. buyers tend to be much less sensitive to a change in price when given more time to react. b. buyers will have substantially more income over a ten-year period. c. buyers tend to be much more sensitive to a change in price when given more time to react. d. None of these answers are correct. Suppose the price of Twinkies is reduced from $1.45 to $1.25 and, as a result, the quantity of Twinkies demanded increases from 2,000 to 2,200. Using the midpoint method, the price elasticity of demand for Twinkies in the given price range is a. 2.00. b. 1.55.
c. 1.00. d. .64. Figure 5-1
____ 35. Refer to Figure 5-1. The section of the demand curve labeled A represents the a. elastic section of the demand curve. b. inelastic section of the demand curve. c. unit elastic section of the demand curve. d. perfectly elastic section of the demand curve. Figure 5-2
____ 36. Refer to Figure 5-2. The elasticity of demand from point B to point C, using the midpoint method would be a. 0.5. b. 0.75. c. 1.0. d. 1.3. ____ 37. Elasticity of demand is closely related to the slope of the demand curve. The more responsive buyers are to a change in price, the demand curve will be a. steeper. b. further to the right. c. flatter. d. closer to the vertical axis. ____ 38. A perfectly inelastic demand curve will be a. negatively sloped, because buyers decrease their purchases when the price rises.
b. vertical, because buyers purchase the same amount whether the price rises or falls. c. positively sloped, because buyers respond by increasing their purchases when price rises. d. horizontal, because buyers increase their purchases by huge amounts with slight changes in price. ____ 39. Which of the following would have the most elastic demand? a. clothing b. blue jeans c. Levi jeans d. All three would have the same elasticity of demand since they are all related. Figure 5-6
____ 40. Refer to Figure 5-6. The price elasticity of this demand curve between $10 and $15 is a. unit elastic. b. elastic. c. inelastic. d. perfectly elastic. ____ 41. Moving up a linear demand curve, we know that total revenue a. increases, then decreases. b. decreases, then increases. c. increases. d. decreases. Figure 5-8
____ 42. Refer to Figure 5-8. Between point A and point B we know that a. the slope is equal to 1/4 and elasticity is equal to 2/3. b. the slope is equal to 1/4 and elasticity is equal to 3/2. c. the slope is equal to 3/2 and elasticity is equal to 1/4. d. the slope is equal to 2/3 and elasticity is equal to 1/4. ____ 43. Refer to Figure 5-8. Between point A and point B on the graph, the elasticity of demand is a. perfectly elastic. b. inelastic. c. unit elastic. d. elastic. ____ 44. If an increase in income results in a decrease in the quantity demanded of a good, then the good is a. an inferior good. b. a necessity. c. a normal good. d. a luxury. ____ 45. You and your college roommate eat three packages of Ramen noodles each week. After graduation last month, both of you were hired at several times your college income. You still enjoy Ramen noodles very much and buy even more, but your roommate plans to buy other foods she prefers more. When looking at income elasticity of demand for Ramen noodles, yours would a. be negative and your roommate's would be positive. b. be positive and your roommate's would be negative. c. be zero and your roommate's would approach infinity. d. approach infinity and your roommate's would be zero. Table 5-1 Income $30,000 $40,000 Quantity of Good X Purchased 2 5 Quantity of Good Y Purchased 20 10
____ 46. Refer to Table 5-1. Good X is a. very price elastic. b. an inferior good. c. underpriced. d. a normal good. ____ 47. In the long run which of the following would NOT be a reason why the elasticity of supply is elastic? a. Firms can build new factories. b. Firms can hire additional workers. c. New firms can enter the market. d. Firms can sell less at lower prices without losing profits. ____ 48. If sellers do not respond at all to a change in price, a. technological advancement must be great. b. supply must be perfectly elastic. c. a long period of time must have elapsed. d. supply must be perfectly inelastic. Figure 5-10
____ 49. Refer to Figure 5-10. Which of the following would be most elastic? a. from A to B b. from C to D c. from E to F d. from D to F Figure 5-12
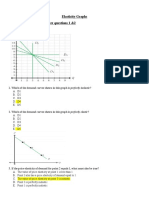
____ 50. Refer to Figure 5-12. Which supply curve is perfectly inelastic? a. S1 b. S2 c. S3 d. It is impossible to tell without more information. Short Answer 51. You own a small town movie theatre. You currently charge $5 per ticket for everyone who comes to your movies. Your friend who took an economics course in college tells you that there may be a way to increase your total revenue. Given the demand curves shown, answer the following questions.
a. b. c. d. e. f.
What is your current total revenue for both groups? The elasticity of demand is more elastic in which market? Which market has the more inelastic demand? What is the elasticity of demand between the prices of $5 and $2 in the adult market? Is this elastic or inelastic? What is the elasticity of demand between $5 and $3 in the children's market? Is this elastic or inelastic? Given the graphs and what your friend knows about economics, he recommends you increase the price of adult tickets to $8 each and lower the price of a child's ticket to $3. How much could you increase total revenue if you take his advice?
52. Recently, in Smalltown, the price of Twinkies fell from $0.80 to $0.70. As a result, the quantity demanded of Ho-Ho's decreased from 120 to 100. What would be the appropriate elasticity to compute? Using the midpoint method, compute this elasticity. What does your answer tell you?
Practice Test 4-5 Answer Section
MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. ANS: D there are so many buyers and many sellers so that each has a negligible impact on price. DIF: 2 2. ANS: C price takers. REF: SECTION: 1 OBJ: TYPE: M
DIF: 1 REF: SECTION: 1 3. ANS: B a competitive market. DIF: 1 4. ANS: B an oligopoly. REF: SECTION: 1
OBJ: TYPE: M
OBJ: TYPE: M
DIF: 1 REF: SECTION: 1 5. ANS: D the prices of the inputs used to produce the good DIF: 1 REF: SECTION: 2 6. ANS: C demand for good X will increase. DIF: 2 REF: SECTION: 2 7. ANS: B reduces the demand for the other good. DIF: 3 8. ANS: A It would decrease. REF: SECTION: 2
OBJ: TYPE: M
OBJ: TYPE: M
OBJ: TYPE: M
OBJ: TYPE: M
DIF: 2 REF: SECTION: 2 9. ANS: A the price of a resource DIF: 1 10. ANS: B demand curve. REF: SECTION: 2
OBJ: TYPE: M
OBJ: TYPE: M
DIF: 1 REF: SECTION: 2 OBJ: TYPE: M 11. ANS: A the downward-sloping line relating the price of the good to the quantity demanded. DIF: 2 REF: SECTION: 2 OBJ: TYPE: M
12. ANS: B increasing your current demand for DVDs. DIF: 2 REF: SECTION: 2 OBJ: TYPE: M 13. ANS: C people are now more willing to buy the product at any price than before. DIF: 2 14. ANS: C C REF: SECTION: 2 OBJ: TYPE: M
DIF: 3 REF: SECTION: 2 15. ANS: B quantity supplied could be zero. DIF: 2 16. ANS: A number of sellers DIF: 2 17. ANS: C crystal to increase. REF: SECTION: 3
OBJ: TYPE: M
OBJ: TYPE: M
REF: SECTION: 3
OBJ: TYPE: M
DIF: 3 REF: SECTION: 3 18. ANS: D result in a movement along a stable supply curve. DIF: 2 REF: SECTION: 3 19. ANS: A represent an increase in the supply of cattle at the auction. DIF: 2 REF: SECTION: 3 20. ANS: C an increase in supply. DIF: 2 21. ANS: D equilibrium. DIF: 1 22. ANS: B $20,600. REF: SECTION: 3
OBJ: TYPE: M
OBJ: TYPE: M
OBJ: TYPE: M
OBJ: TYPE: M
REF: SECTION: 4
OBJ: TYPE: M
DIF: 2 REF: SECTION: 4 23. ANS: B Equilibrium price would be equal to equilibrium quantity. DIF: 2 REF: SECTION: 4 24. ANS: E Both a and c are correct.
OBJ: TYPE: M
OBJ: TYPE: M
DIF: 3 REF: SECTION: 4 25. ANS: D and equilibrium quantity to both decrease. DIF: 2 26. ANS: D D. REF: SECTION: 4
OBJ: TYPE: M
OBJ: TYPE: M
DIF: 3 REF: SECTION: 5 27. ANS: C Quantity will fall and the effect on price is ambiguous. DIF: 3 REF: SECTION: 4 28. ANS: D The price change will be ambiguous. DIF: 3 REF: SECTION: 4 29. ANS: D We couldn't be sure what it might do. DIF: 3 REF: SECTION: 4 30. ANS: A a buyer's responsiveness to a change in the price of a good. REF: SECTION: 1 OBJ: TYPE: 1 31. ANS: C analyze supply and demand with greater precision. DIF: 2 32. ANS: C inelastic REF: SECTION: 1
OBJ: TYPE: M
OBJ: TYPE: M
OBJ: TYPE: M
OBJ: TYPE: M
OBJ: TYPE: M
DIF: 2 REF: SECTION: 1 OBJ: TYPE: M 33. ANS: C buyers tend to be much more sensitive to a change in price when given more time to react. DIF: 2 34. ANS: D .64. REF: SECTION: 1 OBJ: TYPE: M
DIF: 3 REF: SECTION: 1 35. ANS: A elastic section of the demand curve. DIF: 2 36. ANS: B 0.75. DIF: 2 REF: SECTION: 1
OBJ: TYPE: M
OBJ: TYPE: M
REF: SECTION: 1
OBJ: TYPE: M
37. ANS: C flatter. DIF: 2 REF: SECTION: 1 OBJ: TYPE: M 38. ANS: B vertical, because buyers purchase the same amount whether the price rises or falls. DIF: 3 39. ANS: C Levi jeans DIF: 2 40. ANS: C inelastic. REF: SECTION: 1 OBJ: TYPE: M
REF: SECTION: 1
OBJ: TYPE: M
DIF: 3 REF: SECTION: 1 41. ANS: A increases, then decreases. DIF: 3 REF: SECTION: 1 42. ANS: B the slope is equal to 1/4 and elasticity is equal to 3/2. DIF: 3 43. ANS: D elastic. DIF: 2 44. ANS: A an inferior good. REF: SECTION: 1
OBJ: TYPE: M
OBJ: TYPE: M
OBJ: TYPE: M
REF: SECTION: 1
OBJ: TYPE: M
DIF: 1 REF: SECTION: 1 45. ANS: B be positive and your roommate's would be negative. DIF: 2 46. ANS: D a normal good. REF: SECTION: 1
OBJ: TYPE: M
OBJ: TYPE: M
DIF: 1 REF: SECTION: 1 47. ANS: D Firms can sell less at lower prices without losing profits. DIF: 2 REF: SECTION: 2 48. ANS: D supply must be perfectly inelastic. DIF: 2 49. ANS: A REF: SECTION: 2
OBJ: TYPE: M
OBJ: TYPE: M
OBJ: TYPE: M
from A to B DIF: 2 50. ANS: A S1 DIF: 1 SHORT ANSWER 51. ANS: a. b. c. d. e. f. Total revenue from children's tickets is $100 and from adult tickets is $250. Total revenue from all sales would be $350. the demand for children's tickets is more elastic. The adult ticket market has the more elastic demand. The elasticity of demand between $5 and $2 is 0.26 or inelastic. The elasticity of demand between $5 and $3 is 1.33 or elastic. If price is increased to $8 for adult tickets (maximum for the graph) and price decreased to $3 for child tickets (minimum for graph), total revenue would increase to $440 ($8 ( 40 + $3 ( 40) or $90 more than before. REF: SECTION: 2 OBJ: TYPE: M
REF: SECTION: 2
OBJ: TYPE: M
REF: SECTION: 1 OBJ: TYPE: S 52. ANS: The appropriate elasticity to compute would be cross-price elasticity. The cross-price elasticity for this example would be 1.36. The two goods are substitutes because the cross-price elasticity is positive. REF: SECTION: 1 OBJ: TYPE: S
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 0870117564idiomatic American EnglishDokument122 Seiten0870117564idiomatic American EnglishvietmenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microeconomics - ECO402 Final Term QuizDokument28 SeitenMicroeconomics - ECO402 Final Term QuizSuleyman KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spiritual Fitness Assessment: Your Name: - Date: - InstructionsDokument2 SeitenSpiritual Fitness Assessment: Your Name: - Date: - InstructionsLeann Kate MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Bank for Introductory Economics: And Introductory Macroeconomics and Introductory MicroeconomicsVon EverandTest Bank for Introductory Economics: And Introductory Macroeconomics and Introductory MicroeconomicsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- AP Econ Practice Test #2, Chapters 5-9Dokument83 SeitenAP Econ Practice Test #2, Chapters 5-9Rodger12100% (1)
- Economics Practice ExamDokument33 SeitenEconomics Practice ExamMelissa Douglas100% (1)
- Insurance OperationsDokument5 SeitenInsurance OperationssimplyrochNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam1 Practice Exam SolutionsDokument37 SeitenExam1 Practice Exam SolutionsSheehan T Khan100% (3)
- Different Complex Multipliers - Government, Expenditure, Tax and Balanced Budget MultiplierDokument15 SeitenDifferent Complex Multipliers - Government, Expenditure, Tax and Balanced Budget MultiplierArundhuti RoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- MBA - Business Eco - 1Dokument10 SeitenMBA - Business Eco - 1Nikesh MunankarmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Examination Paper: Instruction To CandidatesDokument8 SeitenExamination Paper: Instruction To CandidatesNikesh MunankarmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 04Dokument40 SeitenCH 04Mohammed Aljabri100% (1)
- Week 6 Practice 101Dokument19 SeitenWeek 6 Practice 101David LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECON 201 Practice Test 2 (Chapter 5, 6 and 21)Dokument9 SeitenECON 201 Practice Test 2 (Chapter 5, 6 and 21)Meghna N MenonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elasticity Graphs Use The Graph Below To Answer Questions 1 &2Dokument6 SeitenElasticity Graphs Use The Graph Below To Answer Questions 1 &2SaadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of EconomicsDokument27 SeitenPrinciples of EconomicsAqil Siddiqui100% (2)
- Small Hydro Power Plants ALSTOMDokument20 SeitenSmall Hydro Power Plants ALSTOMuzairmughalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elasticity of DemandDokument38 SeitenElasticity of DemandimadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 01Dokument14 SeitenChap 01Syed Hamdan100% (1)
- Testbank Chapter5 NewDokument13 SeitenTestbank Chapter5 NewAhmadYaseenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4: (Market Forces of Supply and Demand) Section ADokument11 SeitenChapter 4: (Market Forces of Supply and Demand) Section APhạm HuyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revision QuestionDokument19 SeitenRevision QuestionSharina DailamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Bank of Managerial Economics - 4 MarkDokument23 SeitenQuestion Bank of Managerial Economics - 4 MarklakkuMS100% (4)
- Multiple Choice Tutorial: Demand, Supply and MarketsDokument62 SeitenMultiple Choice Tutorial: Demand, Supply and Marketssorrylex100% (1)
- Econ Q and ADokument93 SeitenEcon Q and AGel Mi Amor100% (1)
- Supply-Demand Practice QuestionsDokument5 SeitenSupply-Demand Practice QuestionsSajid Anzar100% (1)
- Elasticity and InelasticityDokument2 SeitenElasticity and InelasticityKarl BrattNoch keine Bewertungen
- Price ElasticityDokument2 SeitenPrice ElasticityKinNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAF 02 CHP Wise Mcqs PDFDokument79 SeitenCAF 02 CHP Wise Mcqs PDFAtta SoomroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homework MicroeconomicsDokument4 SeitenHomework MicroeconomicsNguyễn Bảo Ngọc100% (1)
- CHAPTER 4 Economic151 Sample TestDokument13 SeitenCHAPTER 4 Economic151 Sample TestDiem Suong100% (1)
- Elasticity Is A Measure of ResponsivenessDokument7 SeitenElasticity Is A Measure of ResponsivenessAlesiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Managerial Economics (Quiz) Subject Code: 12MCEC01 MBA-Trimester - IDokument4 SeitenManagerial Economics (Quiz) Subject Code: 12MCEC01 MBA-Trimester - IShivani PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- More Multiple Choice Questions With AnswersDokument14 SeitenMore Multiple Choice Questions With AnswersJudz Sawadjaan100% (2)
- HomeworkDokument3 SeitenHomeworkMihaela Gavrilita50% (2)
- QuizDokument36 SeitenQuizStormy88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Managerial EconomicsDokument10 SeitenManagerial EconomicsDipali DeoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 03Dokument16 SeitenChap 03Syed Hamdan100% (1)
- Measuring A Nation'S Income: Questions For ReviewDokument4 SeitenMeasuring A Nation'S Income: Questions For ReviewNoman MustafaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapt 2 MICDokument13 SeitenChapt 2 MICAkkamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Macroeconomics Midterm 2013Dokument19 SeitenMacroeconomics Midterm 2013Daniel Welch100% (1)
- Chap 029Dokument74 SeitenChap 029d-fbuser-63413751100% (1)
- ADL 04 Managerial Economics V3Dokument6 SeitenADL 04 Managerial Economics V3solvedcare100% (1)
- EC101 Revision Questions - Graphical Analysis - SolutionsDokument10 SeitenEC101 Revision Questions - Graphical Analysis - SolutionsZaffia AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4Dokument445 Seiten4lilylikesturtle75% (4)
- Chap 04Dokument16 SeitenChap 04Syed Hamdan100% (1)
- Midterm and SolutionsDokument9 SeitenMidterm and SolutionswillvxdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aditional Problems MCQ SupplydemandDokument19 SeitenAditional Problems MCQ SupplydemandHussein DarwishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discounts, Markup and MarkdownDokument3 SeitenDiscounts, Markup and MarkdownYannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple Choice Questions Chapter 11 Perfect CompetitionDokument26 SeitenMultiple Choice Questions Chapter 11 Perfect CompetitionAfrose KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- EC102 - Problem Set 1 - Answer KeyDokument19 SeitenEC102 - Problem Set 1 - Answer KeyEd ZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Law of Demand and SupplyDokument16 SeitenLaw of Demand and SupplyRitu RoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz6 MEAcctg1102 - 91 E0Dokument17 SeitenQuiz6 MEAcctg1102 - 91 E0Saeym SegoviaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 26 Ad & AsDokument25 SeitenCH 26 Ad & AsAli HussinNoch keine Bewertungen
- MacroEconomics Written Assignment 2Dokument6 SeitenMacroEconomics Written Assignment 2Thais HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter1 2Dokument6 SeitenChapter1 2Young Joo MoonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Econ 100.1 Exercise Set No. 1Dokument2 SeitenEcon 100.1 Exercise Set No. 1Charmaine Bernados BrucalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Managerial Economics Ch3Dokument67 SeitenManagerial Economics Ch3Ashe BalchaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 06Dokument12 SeitenChap 06Syed Hamdan50% (2)
- Chapter 1: Economics For Managers (Question Bank & Answers)Dokument13 SeitenChapter 1: Economics For Managers (Question Bank & Answers)tk_atiqah100% (1)
- Review For MidtermDokument34 SeitenReview For MidtermTexanskie Kupony100% (1)
- Elasticity Practic QuizDokument5 SeitenElasticity Practic QuizMariana MogîldeaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economy KeyDokument12 SeitenEconomy KeyCristiSantínNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple Choice: Identify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDokument7 SeitenMultiple Choice: Identify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionNguyen Hai AnhNoch keine Bewertungen
- AllDokument8 SeitenAllNguyễn Thị Hồng YếnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Absorption V Variable Costing Video LectureDokument11 SeitenAbsorption V Variable Costing Video LecturenajmulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review ch.1 2Dokument21 SeitenReview ch.1 2Nguyễn Thị Hồng YếnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 12 - Income - Table by VanDokument10 SeitenChapter 12 - Income - Table by VanNguyễn Thị Hồng YếnNoch keine Bewertungen
- HBP AnsReviewQuestionDokument33 SeitenHBP AnsReviewQuestionTea WonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9-December 2008 AsiaDokument403 Seiten9-December 2008 AsiaNguyễn Thị Hồng YếnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final ExamsDokument54 SeitenFinal ExamsNguyễn Thị Hồng YếnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Selection Letter Abhishek TodkarDokument1 SeiteSelection Letter Abhishek TodkarDipak GiteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discussion: Functions, Advantages and Disadvantages of BIOPOT Cassava Peel and Husk CharcoalDokument4 SeitenDiscussion: Functions, Advantages and Disadvantages of BIOPOT Cassava Peel and Husk CharcoalAhmad BurhanudinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Suffolk County Substance Abuse ProgramsDokument44 SeitenSuffolk County Substance Abuse ProgramsGrant ParpanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Baggage Handling Solutions LQ (Mm07854)Dokument4 SeitenBaggage Handling Solutions LQ (Mm07854)Sanjeev SiwachNoch keine Bewertungen
- B. Contract of Sale: D. Fraud in FactumDokument5 SeitenB. Contract of Sale: D. Fraud in Factumnavie VNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mormond History StudyDokument16 SeitenMormond History StudyAndy SturdyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Presentation and Analysis - Operations JollibeeDokument7 SeitenCase Presentation and Analysis - Operations JollibeeDonnabie Pearl Pacaba-CantaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theodore L. Sendak, Etc. v. Clyde Nihiser, Dba Movieland Drive-In Theater, 423 U.S. 976 (1975)Dokument4 SeitenTheodore L. Sendak, Etc. v. Clyde Nihiser, Dba Movieland Drive-In Theater, 423 U.S. 976 (1975)Scribd Government DocsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prayer For World Teachers Day: Author: Dr. Anthony CuschieriDokument1 SeitePrayer For World Teachers Day: Author: Dr. Anthony CuschieriJulian ChackoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cases in Political Law Review (2nd Batch)Dokument1 SeiteCases in Political Law Review (2nd Batch)Michael Angelo LabradorNoch keine Bewertungen
- RAN16.0 Optional Feature DescriptionDokument520 SeitenRAN16.0 Optional Feature DescriptionNargiz JolNoch keine Bewertungen
- SEBI Management Summary SheetsDokument398 SeitenSEBI Management Summary SheetsPriyanka ChandakNoch keine Bewertungen
- sc2163 ch1-3 PDFDokument40 Seitensc2163 ch1-3 PDFSaeed ImranNoch keine Bewertungen
- WHO in The Philippines-Brochure-EngDokument12 SeitenWHO in The Philippines-Brochure-EnghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urban Transportation System Design and Feasibility Analysis A Case Study of Lagos Mega-CityDokument8 SeitenUrban Transportation System Design and Feasibility Analysis A Case Study of Lagos Mega-CityKaren EstradaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 13th Format SEX Format-1-1: Share This DocumentDokument1 Seite13th Format SEX Format-1-1: Share This DocumentDove LogahNoch keine Bewertungen
- RF05 UAMS and School ConcernsDokument8 SeitenRF05 UAMS and School ConcernsAngel Ann Pascua LuibNoch keine Bewertungen
- JTW Programm Kyushu UniversityDokument10 SeitenJTW Programm Kyushu Universitykokii_2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Pricing of Deposit ServicesDokument37 SeitenDesign and Pricing of Deposit ServicesThe Cultural CommitteeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 - How To Calculate Present ValuesDokument21 SeitenChapter 2 - How To Calculate Present ValuesTrọng PhạmNoch keine Bewertungen
- CV - Parisi - UChileDokument5 SeitenCV - Parisi - UChileFen_udechileNoch keine Bewertungen
- Barrier Solution: SituationDokument2 SeitenBarrier Solution: SituationIrish DionisioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microplastic Occurrence Along The Beach Coast Sediments of Tubajon Laguindingan, Misamis Oriental, PhilippinesDokument13 SeitenMicroplastic Occurrence Along The Beach Coast Sediments of Tubajon Laguindingan, Misamis Oriental, PhilippinesRowena LupacNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIDO EIP Achievements Publication FinalDokument52 SeitenUNIDO EIP Achievements Publication FinalPercy JacksonNoch keine Bewertungen
- ICargo Mobility QantasDokument4 SeitenICargo Mobility QantasViswateja KrottapalliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Level 2 TocDokument5 SeitenLevel 2 TocStephanie FonsecaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PoetryDokument5 SeitenPoetryKhalika JaspiNoch keine Bewertungen