Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
UMTS Overview: Strategy & Support
Hochgeladen von
Mahamed SerwatOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
UMTS Overview: Strategy & Support
Hochgeladen von
Mahamed SerwatCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
UMTS Overview
Strategy & Support
August - 2006
UMTS Overview 2
UMTS Overview
1. Introduction to UMTS
2. UMTS Network Architecture
3. WCDMA Wireless Technology
4. WCDMA Air Interface Principles
5. Coverage and Capacity Principles
August - 2006
UMTS Overview 3
UMTS Overview
Introduction to WCDMA/UMTS
August - 2006
UMTS Overview 4
1980s 1990s 2000 +
same business, new machine new business, new machine
Services
Network
New mobile businesses
Wideband/multimedia
1
2
nd
generation
digital
st
generation
analogue
3
generation
wideband
rd
Basic mobile telephony
Evolution to 3G systems
August - 2006
UMTS Overview 5
Consumer demand for
wideband services
Increased network capacity
More airtime Access anytime, anyplace
Wireless postcard
Imaging
Mobile transactions
More Subscribers
UMTS Drivers
August - 2006
UMTS Overview 6
UMTS Spectrum Allocation
900 MHz 880 915 925 960
EGSM
890 915 935 960
GSM
890 902.5 935 947.5
902.5 915 947.5 960
VFE GSM 900
1800 MHz 1710 1785 1805 1880
GSM
1756 1761 1763.5 1766 1851 1856 1858.5 1861
RX RX TX TX
1751 1756 1761 1763.5 1846 1851 1856 1858.5
RX RX TX TX
1850 1910 1930 1990
1900 MHz GSM/
TDMA/CDMA
1920 1980 2110 2170
UMTS/W-CDMA
MobiNil GSM 900
RX
RX
MobiNil GSM 1800
TX
TX
RX TX
TX
TX
TX RX
RX
TX RX
RX
VFE GSM 1800
August - 2006
UMTS Overview 8
UMTS Overview
UMTS Network Architecture
August - 2006
UMTS Overview 9
3G Radio Access Network - Highlights
UMTS Overview 10
GSM/GPRS Core Network (CN)
I
u
I
u
RNS
RNC
RNS
RNC
Node B Node B Node B Node B
I
ur
I
ub
I
ub
I
ub
I
ub
User Equipment
(UE)
UTRAN
(UMTS
Terrestrial
Radio Access
Network)
PSTN
ISDN
Internet
U
u
3GPP TS 25.401 6.0
MSC
GPRS
Service Node
I
u
I
u
UMTS and UTRAN
August - 2006
UMTS Overview 11
UMTS Overview
CDMA Wireless Technology
August - 2006
UMTS Overview 12
TDMA
Frequency
Time
Time
Frequency
CDMA
Frequency
Code
Frequency
Time
Code
Time
Frequency
FDMA
Frequency
Radio Access Technologies
August - 2006
UMTS Overview 13
|
.
|
\
|
=
Rate Data
Rate Code PN
Both signals combined
in the air interface
PN Code 1 Frequency
A
m
p
l
i
t
u
d
e
Signal 1
PN Code 2
Frequency
A
m
p
l
i
t
u
d
e
Signal 2
Spread Spectrum
Processing Gain
PN Code 1
Signal 1 is reconstructed
Signal 2 looks like noise
Both signals are
received together
AT THE RECEIVER...
Two Transmitters at the same frequency
Spread Spectrum Multiple Access
August - 2006
UMTS Overview 14
In WCDMA, all cells may use the same carrier frequency but different
scrambling codes. This means no frequency planning, but scrambling code
and power planning instead!
FDMA/TDMA (reuse > 1) CDMA/WCDMA (reuse = 1)
One Cell Frequency Reuse
August - 2006
UMTS Overview 15
Correlation of channel codes in receiver
1 Carrier (5MHz)
Power
Own channel correlates well, i.e. peaks (Signal)
Other channels appear as noise (Interference)
More users increased interference
Signal (Eb)
Interference (No)
Power need to be adjusted to retain the Signal to Interference Ratio (SIR)
I.e. fulfilling the BLER requirements for that specific service
CDMA Rx Concept (1/2)
August - 2006
UMTS Overview 16
PN
3
PN
4
PN
5
PN
6
PN
1
PN
1
Cell Site 1 transmits using PN code 1
PN
2
PN
2
Cell Site 2 transmits using PN code 2
Uplink: PN Code used to distinguish each Mobile Station
Downlink: PN Code used to distinguish each Base Station
Scrambling Code Planning
August - 2006
UMTS Overview 17
OC1, OC2
OC3, OC4
OC5, OC6, OC7
OC1 , OC2, OC3
OC1, OC2
OC1, OC2, OC3, OC4
Uplink: Orthogonal Codes used to distinguish data channels
coming from each Mobile Station
Downlink: Orthogonal Codes used to distinguish data channels
Coming from each Base Station
Channelization Codes
August - 2006
UMTS Overview 18
OVSF Code Space: 8 users; one 8-bit code per user
Chip Rate = 3.840 Mcps
480 kb/s 480 kb/s 480 kb/s 480 kb/s 480 kb/s 480 kb/s 480 kb/s 480 kb/s
1
11 10
1111 1100 1010 1001
11111111 11110000 11001100 11000011 10101010 10100101 10011001 10010110
OVSF Codes
August - 2006
UMTS Overview 19
OVSF Code Space: 5 users; one user has 4x data bandwidth
User with 4x Bit Rate
= Unusable Code Space
480 kb/s 480 kb/s 480 kb/s 480 kb/s
1.92 Mb/s
Chip Rate = 3.840 Mcps
1
11 10
1111 1100 1010 1001
11111111 11110000 11001100 11000011 10101010 10100101 10011001 10010110
OVSF Codes
August - 2006
UMTS Overview 20
Codes
(Orthogonal)
Max Power
Power
kbps*
3840
1920
960
480
240
120
15
Gross bitrate.
Effective bitrate is less
due to channel overhead
SF
1
2
4
8
16
32
256
Code 1
Code 2
Code 3
WCDMA Shared Resources
August - 2006
UMTS Overview 21
UMTS Overview
WCDMA Air Interface Principles
August - 2006
UMTS Overview 22
Multi-path propagation Time dispersion
h(t)
t
t
0
t
1
t
2
t
3
t
0
t
1
t
2
t
3
The Radio Channel
August - 2006
UMTS Overview 23
Fast (Rayleigh) Fading
time (mSec)
Composite
Received
Signal
Strength
Time between fades is related to
RF frequency
Geometry of multipath vectors
Vehicle speed:
Up to 2 fades/sec per kilometer/hour
Deep fade caused by destructive summation
of two or more multipath reflections
msec
Multipath Fading
August - 2006
UMTS Overview 24
CDMA Mobile Station RAKE Receiver Architecture
Each finger tracks a single multipath reflection
Also be used to track other base stations signal during soft handover
One finger used as a Searcher to identify other base stations
Finger #1
Finger #2
Finger #N
Searcher Finger
Combiner
Sum of
individual
multipath
components
Power measurement
of Neighboring
Base Stations
The RAKE Receiver
August - 2006
UMTS Overview 25
TX power
TX power
RX power RX power
t
t
t
t
Without power control With power control
Power Control Combats fast fading
August - 2006
UMTS Overview 26
BLER = Block Error Rate
SIR = Signal to Interference Ratio
TPC = Transmit Power Control
P(Startvalue)
Open loop
P(SIR-Target,UL)
P(SIR-Target, DL)
Inner loop
DL-TPC
UL-TPC
SIR-Target,DL
BLER-Measured,DL
DL-Outer loop
RNC
SIR-Target,UL
SIR-Error,UL
UL-Outer loop
CDMA Power Control
August - 2006
UMTS Overview 27
Inter-System Handover
Handover from a CDMA system to an Analog or TDMA system
Traffic and Control Channels are Disconnected and must be Reconnected
Hard Handover
When the MS must change CDMA carrier frequency during the Handover
Traffic and Control Channels are Disconnected and must be Reconnected
Soft Handover
Unique to CDMA
During Handover, the MS has concurrent traffic connections with two BSs
Handover should be less noticeable
Softer Handover
Similar to Soft Handover, but between two sectors of the same cell
Handover is simplified since sectors have identical timing
Handover
August - 2006
UMTS Overview 28
One finger of the RAKE receiver is constantly scanning neighboring
Pilot Channels.
When a neighboring Pilot Channel reaches the t_add threshold, the new
BS is added to the active set
When the original Base Station reaches the t_drop threshold, originating
Base Station is dropped from the active set
Monitor Neighbor BS Pilots Add Destination BS Drop Originating BS
CDMA Soft Handover
August - 2006
UMTS Overview 29
UMTS Overview
Coverage and Capacity Principles
August - 2006
UMTS Overview 30
GSM voice
WCDMA voice and low bit rate
64/128 kbps
WCDMA medium bit rates
128/384 kbps
The power requirement determines the service coverage in WCDMA
users will require different amount of power depending on environment, service, system load
System load or rather intereference will depend on:
- Number of users in other/own cells, i.e. other/own average cell power usage
- distribution of users and their service usage
WCDMA high bit rate
384 kbps
Service Coverage
August - 2006
UMTS Overview 31
The service coverage shrinks with increasing traffic in the cell
Max power
High bit rate
Medium bit rates
Low bit rate
Cell Breathing
August - 2006
UMTS Overview 32
Case B: Low power usage and high capacity
Case A
Case B
Case B
Case A
Node-B Power
Case A: High power usage and low capacity
Subscriber distribution impact capacity / coverage
August - 2006
UMTS Overview 33
Time
interference
Load In Neighbouring Cell Impact Capacity / Coverage
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Making Telecoms Work: From Technical Innovation to Commercial SuccessVon EverandMaking Telecoms Work: From Technical Innovation to Commercial SuccessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mobile Terminal Receiver Design: LTE and LTE-AdvancedVon EverandMobile Terminal Receiver Design: LTE and LTE-AdvancedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Network Planning and Optimisation 2G/3G/4G: Evolution to 5GVon EverandFundamentals of Network Planning and Optimisation 2G/3G/4G: Evolution to 5GNoch keine Bewertungen
- BSS Radio Parameters Laboratory Exercise 3Dokument41 SeitenBSS Radio Parameters Laboratory Exercise 3Oni Ayodeji100% (1)
- Um InterfaceDokument6 SeitenUm InterfaceSuneth MendisNoch keine Bewertungen
- MSC and BSC Parameter DescriptionDokument25 SeitenMSC and BSC Parameter DescriptionsaabiaanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Layer 3 - Umts PDFDokument49 SeitenLayer 3 - Umts PDFSukrit Chaudhary100% (6)
- WCDMA Resource Congestion Introduction N703483 Apr-2013Dokument27 SeitenWCDMA Resource Congestion Introduction N703483 Apr-2013Quy HoangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To QoSConceptsDokument48 SeitenIntroduction To QoSConceptsIvica PutrićNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vodafone Call Log AnalysisDokument605 SeitenVodafone Call Log AnalysisMoon MalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phantom or Dummy RACHDokument18 SeitenPhantom or Dummy RACHproudpunk100% (1)
- RAN Capacity Monitoring BSC6910 R15 29042014Dokument42 SeitenRAN Capacity Monitoring BSC6910 R15 29042014Dzultanzania Roi VenuNoch keine Bewertungen
- GB - BT01 - E1 - 0 GSM Basics: Course ObjectivesDokument35 SeitenGB - BT01 - E1 - 0 GSM Basics: Course Objectiveskshitiz05Noch keine Bewertungen
- HSDPA Technology: ZTE University TD&W&PCS BSS Course TeamDokument51 SeitenHSDPA Technology: ZTE University TD&W&PCS BSS Course Teamcheviet100% (2)
- RF Optimization and PlanningDokument12 SeitenRF Optimization and PlanningVikash JhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Para List For GSMDokument5.544 SeitenPara List For GSMNeelesh Kumar MareleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fast WCDMA Reselection at 2G CS Call Release Feature Delivery GuideDokument17 SeitenFast WCDMA Reselection at 2G CS Call Release Feature Delivery GuideabojablNoch keine Bewertungen
- WCDMA Network Workshop OverviewDokument135 SeitenWCDMA Network Workshop OverviewMuhammad HarisNoch keine Bewertungen
- LTE R9 Technology IntroductionDokument44 SeitenLTE R9 Technology IntroductionJokercardz100% (1)
- RNPO Tutorial Engr SystemsDokument161 SeitenRNPO Tutorial Engr SystemsOmokuru NicholasNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM-To-UMTS Training Series 02 - WCDMA Radio Network Coverage Planning - V1.0Dokument86 SeitenGSM-To-UMTS Training Series 02 - WCDMA Radio Network Coverage Planning - V1.0AliKaiserNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 OMO115180 BSC6900 GSM V9R14R15 Radio Channel Management AlDokument82 Seiten5 OMO115180 BSC6900 GSM V9R14R15 Radio Channel Management AlEast AmmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM Features LicensesDokument4 SeitenGSM Features LicensesNino BongoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- SDCCH Half Rate ConfigurationDokument4 SeitenSDCCH Half Rate Configurationsmpillai11Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Complaint Is a Gift: How to Optimize Mobile NetworksDokument24 SeitenA Complaint Is a Gift: How to Optimize Mobile NetworksMohammedKhalifaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1x3 Against 1x1 Reuse in Real Frequency Hopping NetworksDokument5 Seiten1x3 Against 1x1 Reuse in Real Frequency Hopping NetworksKrispi FruttiNoch keine Bewertungen
- RF Network Planning and Optimization Service UMTS Performance Analysis For Multi-Carrier Capacity Expansion 01-EnDokument20 SeitenRF Network Planning and Optimization Service UMTS Performance Analysis For Multi-Carrier Capacity Expansion 01-EnMohammed El Hammaoui100% (1)
- 02-WCDMA Radio Interface Physical LayerDokument52 Seiten02-WCDMA Radio Interface Physical Layermehta.tarunNoch keine Bewertungen
- TEMS Investigation 15.0 Release NoteDokument22 SeitenTEMS Investigation 15.0 Release NotelahyouhNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2G Huawei Performance MonitoringDokument64 Seiten2G Huawei Performance Monitoringamirfiroozi87Noch keine Bewertungen
- Interfaces and Their Protocol Stacks - LTE and BEYOND - Tech-Blog On 4G - LTE and Beyond.Dokument9 SeitenInterfaces and Their Protocol Stacks - LTE and BEYOND - Tech-Blog On 4G - LTE and Beyond.Ivica PutrićNoch keine Bewertungen
- BSS COnfigurationDokument178 SeitenBSS COnfigurationMohamed GhuneimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Huawei High Performance HSPA Solution V1 0 20090625 1Dokument61 SeitenHuawei High Performance HSPA Solution V1 0 20090625 1drbiloukosNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4) OFDMA and SCFDMA PDFDokument49 Seiten4) OFDMA and SCFDMA PDFJAGDAMBAPALNoch keine Bewertungen
- First Steps & 1G: Archaic Mobile Communication" Electronic Communications: Fixed Networks"Dokument16 SeitenFirst Steps & 1G: Archaic Mobile Communication" Electronic Communications: Fixed Networks"Bassem AbouamerNoch keine Bewertungen
- WCDMA RNO Access Problem Analysis Guidance-20040716-A-2.0Dokument39 SeitenWCDMA RNO Access Problem Analysis Guidance-20040716-A-2.0adhi_123scribdNoch keine Bewertungen
- ZTE 2G Handover Algorithm: Why Do We Need Handover ?Dokument37 SeitenZTE 2G Handover Algorithm: Why Do We Need Handover ?syrish2622Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - WCDMA RAN FundamentalDokument65 Seiten1 - WCDMA RAN FundamentalJulia JuliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report FinalDokument55 SeitenReport Finalkacel marzoukNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wrong LAC PlanningDokument1 SeiteWrong LAC Planningprosenjeet_singhNoch keine Bewertungen
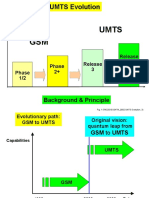
- 03 Tm2201eu04tm 0002 Umts EvolutionDokument5 Seiten03 Tm2201eu04tm 0002 Umts EvolutionBassem AbouamerNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3G Call FlowDokument5 Seiten3G Call FlownjgregNoch keine Bewertungen
- 05-Dimensioning of The LTE S1 Interface (X. Li)Dokument6 Seiten05-Dimensioning of The LTE S1 Interface (X. Li)kotafi_atefNoch keine Bewertungen
- OWO300050 WCDMA Abnormal Interference Problem Analysis ISSUE 1.00Dokument71 SeitenOWO300050 WCDMA Abnormal Interference Problem Analysis ISSUE 1.00riamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GPRS Dimensioning and Performance WorkshopDokument46 SeitenGPRS Dimensioning and Performance WorkshopBassem AbouamerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Radio Um InterfaceDokument24 SeitenRadio Um InterfaceVarun SainiNoch keine Bewertungen
- VoLTE and ViLTE: Voice and Conversational Video Services over the 4G Mobile NetworkVon EverandVoLTE and ViLTE: Voice and Conversational Video Services over the 4G Mobile NetworkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cross-Layer Resource Allocation in Wireless Communications: Techniques and Models from PHY and MAC Layer InteractionVon EverandCross-Layer Resource Allocation in Wireless Communications: Techniques and Models from PHY and MAC Layer InteractionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding UMTS Radio Network Modelling, Planning and Automated Optimisation: Theory and PracticeVon EverandUnderstanding UMTS Radio Network Modelling, Planning and Automated Optimisation: Theory and PracticeMaciej NawrockiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Cellular Network Planning and Optimisation: 2G/2.5G/3G... Evolution to 4GVon EverandFundamentals of Cellular Network Planning and Optimisation: 2G/2.5G/3G... Evolution to 4GNoch keine Bewertungen
- TCLTK HowtoDokument22 SeitenTCLTK HowtoMahamed SerwatNoch keine Bewertungen
- RF Drive Test From A To Z - ArabicDokument65 SeitenRF Drive Test From A To Z - Arabiceng Mahmoud Abdel-Aziz100% (1)
- Air Interface V2Dokument29 SeitenAir Interface V2Mahamed SerwatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rectangular Wave GuidesDokument44 SeitenRectangular Wave GuidesArshadahcNoch keine Bewertungen
- UMTS Physical LayerDokument31 SeitenUMTS Physical LayerMahamed SerwatNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10733-LTM902630 - 3ENA - Troubleshoot Wiring DiagramDokument1 Seite10733-LTM902630 - 3ENA - Troubleshoot Wiring DiagramRaimundo MouraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Police Radio 10-CodesDokument4 SeitenPolice Radio 10-Codeszab04148114Noch keine Bewertungen
- Auto Ref/Keratometer: User ManualDokument78 SeitenAuto Ref/Keratometer: User Manualjuanja83Noch keine Bewertungen
- 11 - Protection of Transmission Lines PDFDokument107 Seiten11 - Protection of Transmission Lines PDFWahed Imtiaz100% (2)
- Triple-Band Log-Periodic Dipole Antenna Design for Mobile CommunicationsDokument4 SeitenTriple-Band Log-Periodic Dipole Antenna Design for Mobile CommunicationsLuis Ariel EscaleraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soal Tes Akademik Bahasa Inggris Bintara Polri: Questions 1 To 2 Refer To The Following MonologueDokument4 SeitenSoal Tes Akademik Bahasa Inggris Bintara Polri: Questions 1 To 2 Refer To The Following MonologueDidik0% (1)
- 740SELECT - User ManualDokument183 Seiten740SELECT - User Manualcallmenuandagmail.comNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kartu MinatDokument43 SeitenKartu MinatDian OctavianiNoch keine Bewertungen
- High Voltage AC/DC Precision Dividers for Measurements up to 150kV & 300kVDokument1 SeiteHigh Voltage AC/DC Precision Dividers for Measurements up to 150kV & 300kVAnonymous HFIQgANMQNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grey Boat Code A Code of Practice For The Safety Assurance of Small Boats in Government ServiceDokument160 SeitenGrey Boat Code A Code of Practice For The Safety Assurance of Small Boats in Government Servicecell bboyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 07 NB-IoT C&P Impact SummaryDokument81 Seiten07 NB-IoT C&P Impact SummaryTarek GARANoch keine Bewertungen
- Lap-E01 Features and Specs: Lorawan Voice TransceiverDokument2 SeitenLap-E01 Features and Specs: Lorawan Voice TransceiverBill CheimarasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Audio Technology: Toaxyz - Raphaellee - T1923161 (Omit D/O, S/O)Dokument7 SeitenAudio Technology: Toaxyz - Raphaellee - T1923161 (Omit D/O, S/O)Luna ANoch keine Bewertungen
- RFS Waveguides and Accessories: A Comprehensive Selection GuideDokument24 SeitenRFS Waveguides and Accessories: A Comprehensive Selection GuideEhsan RohaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cellular System Design Fundamentals: Chapter 3, Wireless Communications, 2/e, T. S. RappaportDokument58 SeitenCellular System Design Fundamentals: Chapter 3, Wireless Communications, 2/e, T. S. RappaportSriram NarendranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tunable Wideband HF Monopole: 1 - 30 MHZ Product Code: Mono-A0092Dokument3 SeitenTunable Wideband HF Monopole: 1 - 30 MHZ Product Code: Mono-A0092Marco PoloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ericsson Radio Dot System: Redefining In-Building Small CellsDokument8 SeitenEricsson Radio Dot System: Redefining In-Building Small CellsKarim MahdyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antenna SpecificationsDokument4 SeitenAntenna SpecificationsRobertNoch keine Bewertungen
- Results From Watson Magitenna Installed in Loft - Essex HamDokument5 SeitenResults From Watson Magitenna Installed in Loft - Essex HamDomenico BufalinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Artex Elt 345 Emergency Locator TransmitterDokument60 SeitenArtex Elt 345 Emergency Locator TransmitterAlston SamuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module - 1: Drawbacks of IGDokument53 SeitenModule - 1: Drawbacks of IGgokulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electron direction in electrostatic field reactionDokument5 SeitenElectron direction in electrostatic field reactionJHOEMEL TANGONoch keine Bewertungen
- Frecuencias ItinerantesDokument7 SeitenFrecuencias ItinerantesFabián ZuluagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2001 - Thesis - Speckle Noise Reduction in SAR ImagesDokument116 Seiten2001 - Thesis - Speckle Noise Reduction in SAR Imagesjoelquintanilla79_84Noch keine Bewertungen
- Basudeb Bhatta - Global Navigation Satellite Systems - New Technologies and Applications (2021)Dokument387 SeitenBasudeb Bhatta - Global Navigation Satellite Systems - New Technologies and Applications (2021)Dipro SarkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mykenwood Car Stereomanual kdc135 PDFDokument56 SeitenMykenwood Car Stereomanual kdc135 PDFjm evansNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wi-Fi Network Report Floor PlanDokument21 SeitenWi-Fi Network Report Floor PlanRodolfo RibeiroNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Insiders Guide To Working With RFID - atlasRFIDstoreDokument184 SeitenThe Insiders Guide To Working With RFID - atlasRFIDstoreNew LearnerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ant ChapDokument8 SeitenAnt ChapJon BondNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of Modern Radar - Volume 1Dokument103 SeitenPrinciples of Modern Radar - Volume 1Pongsathorn36% (25)