Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Abetsyllabusce 572 G
Hochgeladen von
rae2002Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Abetsyllabusce 572 G
Hochgeladen von
rae2002Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
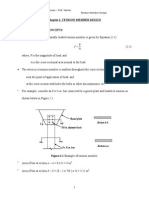
Civil Engineering 572: Design of Steel Structures Course Description: 3 cr. U/G.
Topics in design of steel structures; tension, compression, and beam members; combined axial and bending; connections; moment resisting frames; serviceability; composite construction, maintenance. Prereq: Jr St; Civ Eng 360(P), 372(P) Textbooks: J.C. McCormac, Structural Steel Design, LRFD Method, Harper Collins Publishers, 1995 Manual of Steel Construction, LRFD, Second Edition (Vol. 1 and Vol. 2), American Institute for Steel Construction, 1998 Prerequisites by Topics: Introduction to structural analysis Introduction to structural design
Course Objectives: Broad Objectives Provide background and training in basic and intermediate topics related to structural steel design in buildings using the LRFD method.
Learning Outcomes Basic understanding of design specifications for steel structures. Knowledge of the design of steel members including composite members and connections. Knowledge of serviceability issues in design.
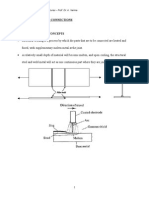
Topics Covered: AISC LRFD Specifications Tension, Compression Member Design (review) Beam Design (review) Use of Computer Program SAP2000 Serviceability Combined Axial Load and Bending Connections Composite Beams Framing Systems
Projects/Major Assignments Students do a semester-long project for the design of a multi-story steel building. Each project team consists of 2-3 students. They write a project report and make a presentation on the last day of classes.
Written Communications Project teams submit written reports.
Oral Communications Students make a presentation to the class describing their projects.
Class/Laboratory Schedule: Two 75-minute sessions per week. Contribution of Course to Meeting the Professional Component: This course is required for all structures students within Civil Engineering. This is the second undergraduate course that includes design of steel structures (the first course is Introduction to Structural Design, 372). Applicable codes and standards related to design of steel buildings are discussed in detail. Efficient and economical design of steel structures is emphasized through examples and the project. This course counts as three hours per week of design experience.
Relationship to Program Objectives: 1c 1d 2b 2d 2e 2f 2g 3b 3c 3f 4b Students apply basic mathematics, statics, and strength of materials concepts to the design of structural members. Students will learn how to formulate and solve a structural engineering design problem. Students will gain a broad understanding of structural engineering for steel buildings. Through semester-long design projects, students learn the basics of structural design of steel buildings. Students write a full report on their projects and present it to the entire class. This course prepares all structures majors with the basic understanding of structural steel design. Various building codes and standards applicable to steel design are discussed in detail. Design procedures include economic considerations and client expectations. Throughout the course, structural designers' professional and ethical responsibilities are discussed in different contexts. Instructors for this course are registered professional engineers. After completing this course, the students would be better positioned to participate in co-op programs by structural design consulting firms. This course utilizes an advanced computer program SAP2000 for the structural analysis and design of buildings. The web-based software package "Blackboard" is also used to streamline communications with students outside class and to facilitate transfer of text and graphical information.
Prepared by: Habib Tabatabai, September 27, 2001
Methods of Assessment: Course Evaluations by Students Graded Examinations Graded Project Feedback from Students During Lab Sessions Instructor Judgment PE Examination FE Examination
Resources Commonly Available: Instructor Computer program SAP2000 Computer projection system Small-scale physical models of structures "Blackboard" web-based software
Desirable Student Competencies: Ability to effectively utilize acquired knowledge in a number of different areas to the solution of a problem. Ability to synthesize and evaluate a relatively large data set to identify relevant information for the problem at hand.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- GRATING.xls Program Version 1.1Dokument2 SeitenGRATING.xls Program Version 1.1rae200250% (2)
- Properties of Section Described by Layers (From Top To Bottom)Dokument1 SeiteProperties of Section Described by Layers (From Top To Bottom)rae2002Noch keine Bewertungen
- User ManualDokument87 SeitenUser ManualebinjozerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Etabs Multistory SteelDokument78 SeitenEtabs Multistory SteelAjit ThoratNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical Unit LoadsDokument1 SeiteMechanical Unit Loadsrae2002Noch keine Bewertungen
- WD Passport Manual!Dokument87 SeitenWD Passport Manual!Ko NgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Checking Shear on BeamsDokument1 SeiteChecking Shear on BeamsAhmed MandorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Door Opening Bar LengthsDokument1 SeiteDoor Opening Bar Lengthsrae2002Noch keine Bewertungen
- Allowable Bearing Capacity CalculationDokument22 SeitenAllowable Bearing Capacity Calculationrae2002Noch keine Bewertungen
- CE470Chapter 2 - Tension MembersDokument38 SeitenCE470Chapter 2 - Tension Membersrae20020% (1)
- Axial Load Due To Wind Load On BracingsDokument3 SeitenAxial Load Due To Wind Load On Bracingsrae2002Noch keine Bewertungen
- Etabs Multistory SteelDokument78 SeitenEtabs Multistory SteelAjit ThoratNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE470 F07 Ch3b WeldsDokument11 SeitenCE470 F07 Ch3b Weldsrae2002Noch keine Bewertungen
- Limit States Design 8 E2 PDokument12 SeitenLimit States Design 8 E2 Prae2002Noch keine Bewertungen
- Letters About MonorailDokument2 SeitenLetters About Monorailrae2002Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial ETABSDokument60 SeitenTutorial ETABSValentin VrabieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Door Opening Bar LengthsDokument1 SeiteDoor Opening Bar Lengthsrae2002Noch keine Bewertungen
- CE470-Lab1 Solution Set 2012Dokument19 SeitenCE470-Lab1 Solution Set 2012rae2002Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Structural EngineeringDokument44 SeitenIntroduction To Structural Engineeringadian09Noch keine Bewertungen
- CE470-Lab1 Solution Set 2012Dokument19 SeitenCE470-Lab1 Solution Set 2012rae2002Noch keine Bewertungen
- CE470Chapter 2 - Tension MembersDokument38 SeitenCE470Chapter 2 - Tension Membersrae20020% (1)
- CE470-Lab1 Solution Set 2012Dokument19 SeitenCE470-Lab1 Solution Set 2012rae2002Noch keine Bewertungen
- CE470Ch3Bolts Part2Dokument6 SeitenCE470Ch3Bolts Part2rae2002Noch keine Bewertungen
- ©2008 Infinite Skills, Inc.: Terms & Conditions of UseDokument3 Seiten©2008 Infinite Skills, Inc.: Terms & Conditions of Usekaran976Noch keine Bewertungen
- CE470Ch3Bolts Part1Dokument16 SeitenCE470Ch3Bolts Part1rae2002Noch keine Bewertungen
- Elevator CoreDokument1 SeiteElevator Corerae2002Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Structural EngineeringDokument44 SeitenIntroduction To Structural Engineeringadian09Noch keine Bewertungen
- AbstractDokument1 SeiteAbstractrae2002Noch keine Bewertungen
- Clean Title, Intro, Load Summary PagesDokument6 SeitenClean Title, Intro, Load Summary Pagesrae2002Noch keine Bewertungen
- SyllabusDokument2 SeitenSyllabusrae2002Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)