Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Important Quetsions
Hochgeladen von
api-78343547Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Important Quetsions
Hochgeladen von
api-78343547Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
EC396 COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
Unit 1 1. 2. State the linear property of Fourier Transform. An FM signal with 90 MHz carrier having a modulation index of 7.25 when modulated with a 10 kHz audio signal. Find the maximum frequency deviation. 3. If the power of unmodulated carrier of an AM transmitter is 10 kW. The power of the transmitter is found to be 11.8 kW when modulated. Find the modulation index. 4. 5. State the Carsons rule for determination of the bandwidth of FM signal. What is Image Frequency?
6.
Draw the waveform and the spectrum if a 80 kHz carrier is amplitude modulated by a 10 kHz sine wave using DSB Full-carrier AM with modulation index of 0.5
7.
Explain with neat sketch of the waveforms, the relation between Frequency Modulation and Phase Modulation.
8.
A 90 MHz carrier is frequency modulated by an audio signal of maximum frequency 16 kHz. If the modulation index of the FM wave is 3, find the bandwidth of the FM signal using Carsons rule.
9.
State the expression for Phase Modulated and Frequency Modulated signal with carrier frequency fc, modulated with a sinusoidal message signal m(t) = sin(2fmt). Draw a neat sketch of the both the signals along with the message signal.
Unit 2 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Define critical frequency. What is the characteristic impedance of a transmission line? Define reflection coefficient. For a 27 MHz transmitter of power 10 Watts, find the path loss for a distance of 900m. What is a White Gaussian Noise?
6.
A coaxial transmission line with a distributed impedance of 100 nH/m and capacitance of 150 pF/m. If the line is terminated by a load of impedance 50, find the reflection coefficient and SWR.
7.
Explain the concept of a distributed and lumped parameter model and hence derive an expression of the characteristic impedance for a transmission line.
8.
Write short notes on the following; (i) Ground wave propagation, (ii) Space wave propagation, (iii) Sky wave propagation, (iv) Maximum Usable Frequency.
9.
A transmitter and a receiver stations are located 300 km apart. The virtual height of the ionosphere is 200 km and its critical frequency fCR is 12 MHz. Neglecting the curvature of the earth, find the Maximum Usable Frequency between the stations.
Unit 3 1. 2. 3. State Nyquists Theorem. What is aliasing? If an analog signal is quantized to 512 levels, find the number of bits required to represent each sample.
1|Page
4. 5.
Differentiate FSK and PSK. Define BER.
6. 7.
Define quantization noise. Derive an expression for the quantization noise power for a digital signal. A channel with AWG Noise of 2 W is used to transmit a digital data of 5 Mbps. If the available bandwidth is 500 kHz, find the minimum signal power required for error free communication using Shannons theorem.
8.
Derive an expression for ASK and deduce the frequency spectrum of it. Estimate the minimum bandwidth required for an ASK.
9.
Write short notes on TDM.
Unit 4 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. State the difference between LAN and WAN. Differentiate even parity and odd parity codes. What is ASCII codes? An 8 bit parallel interface of 1200 words/s is converted into a serial interface. find the bit rate. What is ISDN?
6. 7.
Draw and explain the functionalities provided by each layers in the OSI 7 layer architecture. Explain serial and parallel interface, with examples for each. Discuss the advantages and disadvantages for both.
8. 9.
Explain how error detection and correction could be achieved in a digital transmission. Draw the logical circuit for generating the even-parity bit for a 5 bit word. How many errors in a word could be detected?
Unit 5 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Define look angles. Define path loss. What is a geostationary orbit? Define multipath dispersion. What are its effects? Define numerical aperture.
6.
A fiber with a propagation loss of 2 dB/km, is run from a city to another on a 300 km path. There are 30 connectors on the path connecting the fiber sections. Each of the connectors introduces a loss of 3 dB. If the required optical power output at the receiver is 3 W, find the power of the LASER source that should be used at the transmitter. (Ignore any other losses)
7. 8. 9.
Derive from the fundamentals, the necessary velocity to keep a satellite in a circular orbit. State and explain Keplers laws. A satellite is to be launched in a circular orbit such that it revolves around the
24
earth once for every 8
hours. Find the height of the required orbit if the mass of the earth M = 5.974x10 kg and mean radius is re= 6371 km. Assume the gravitational constant G = 6.673 x 10-11 Nm2/kg2
2|Page
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- EC 396 - Communication Engineering Questions For Test 3: Part ADokument2 SeitenEC 396 - Communication Engineering Questions For Test 3: Part Aapi-78343547Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rejinpaul ADCDokument9 SeitenRejinpaul ADCvarshinipadmanathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communication Theory Overall Question BankDokument7 SeitenCommunication Theory Overall Question BankECEOCETNoch keine Bewertungen
- EC 2305 Novl 2010 Solved TwoMarksDokument4 SeitenEC 2305 Novl 2010 Solved TwoMarksgurugovanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Bank ADCDokument2 SeitenQuestion Bank ADCHOD ECE SriGuru Institute of TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Any Fivefull Questions.: Lo, G 0dband F 900 MHZ, FindpDokument2 SeitenAnswer Any Fivefull Questions.: Lo, G 0dband F 900 MHZ, FindpRuturajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sardar Raja College of Engineering, Alangulam: Micro Lesson PlanDokument10 SeitenSardar Raja College of Engineering, Alangulam: Micro Lesson PlanramarajanenggNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Bank (I and II)Dokument4 SeitenQuestion Bank (I and II)Anonymous 4u5XkWGONoch keine Bewertungen
- Short Answer Questions: Unit - I: Amplitude ModulationDokument8 SeitenShort Answer Questions: Unit - I: Amplitude ModulationSrinivas PadalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Bank For Test 2Dokument3 SeitenQuestion Bank For Test 2api-194677273Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Analog CommunicationDokument6 SeitenFundamentals of Analog CommunicationThiru DaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part-A: Analog and Digital Communication-Ec1291Dokument3 SeitenPart-A: Analog and Digital Communication-Ec1291Hema VathyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modulation Techniques For Mobile RadioDokument3 SeitenModulation Techniques For Mobile RadioAbhinav0% (1)
- CT 2 Marks QBDokument7 SeitenCT 2 Marks QB6060 Lisha priya.CNoch keine Bewertungen
- EC2311 University QuestionDokument9 SeitenEC2311 University QuestionSandhya VpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ec8651 TLRF Msajce QN BankDokument12 SeitenEc8651 TLRF Msajce QN BankPriyadharshini S VenkateshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analog Communications Question BankDokument10 SeitenAnalog Communications Question BankSsgn Srinivasarao100% (1)
- EC8395Dokument1 SeiteEC8395Wearablemems PVTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Important Questions For First Assessment. EC396 - Communication Engineering Short AnswersDokument2 SeitenImportant Questions For First Assessment. EC396 - Communication Engineering Short Answersapi-78343547Noch keine Bewertungen
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Dokument3 SeitenQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.ManimegalaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- EC6503-Transmission Lines and WaveguidesDokument15 SeitenEC6503-Transmission Lines and WaveguidesAnonymous lt2LFZH100% (1)
- 10mt665csm QBDokument6 Seiten10mt665csm QBPrince PavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- EC2305Dokument5 SeitenEC2305Elumalai RathakrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 Mobile Radio PropagationDokument3 SeitenChapter 4 Mobile Radio PropagationenyoyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AdcqbDokument13 SeitenAdcqbprakash_vitNoch keine Bewertungen
- AC Previous PapersDokument4 SeitenAC Previous PapersranddconsultancyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adc QB 2020Dokument14 SeitenAdc QB 2020priyaroopaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Outline ICE-4103 Cellular and Mobile Communication 16-17Dokument4 SeitenQuestion Outline ICE-4103 Cellular and Mobile Communication 16-17MD RAHATUL RABBINoch keine Bewertungen
- Analog Comm. System Paper 03Dokument2 SeitenAnalog Comm. System Paper 03Gourav SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microwave Systems (10EC74) Assignment Set - 8Dokument3 SeitenMicrowave Systems (10EC74) Assignment Set - 8VivekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wireless Communication (ECE - 405)Dokument2 SeitenWireless Communication (ECE - 405)viswatejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bài Tập Thông Tin Di ĐộngDokument20 SeitenBài Tập Thông Tin Di ĐộngNguyễn Đình Duân100% (1)
- Amplitude ModulationDokument3 SeitenAmplitude ModulationArunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question BankDokument6 SeitenQuestion Banksweetkhushboo786_592Noch keine Bewertungen
- BlakeDokument19 SeitenBlakeDeanneLaylayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Explain The Power Efficiency of DSB-AM. Explain The Envelope Detection Method of Demodulation of AM WaveDokument1 SeiteExplain The Power Efficiency of DSB-AM. Explain The Envelope Detection Method of Demodulation of AM Wavednes9999Noch keine Bewertungen
- 14EC2044 - Fundamentals of Wireless Communication - Question BankDokument7 Seiten14EC2044 - Fundamentals of Wireless Communication - Question BankJenkin WInstonNoch keine Bewertungen
- EC8651 TLRF RejinpaulDokument2 SeitenEC8651 TLRF RejinpaulDeepa SushmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quetion Bank Ecom Week WiseDokument3 SeitenQuetion Bank Ecom Week WiseHet PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ec 6801-Wireless Communication-Anna University QuestionsDokument7 SeitenEc 6801-Wireless Communication-Anna University QuestionsPuveeyarasu VNoch keine Bewertungen
- WDC Question Bank 2018Dokument8 SeitenWDC Question Bank 2018Aadharsh HariharanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution Manual for 100 Genesys Design Examples: Second EditionVon EverandSolution Manual for 100 Genesys Design Examples: Second EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Bank - Cycle Test - 2Dokument2 SeitenQuestion Bank - Cycle Test - 2Apurva DesaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ADC Unitwise QBDokument11 SeitenADC Unitwise QBKumar ManiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Apc Assignment 1: F 100 KHZ A. B. C. D. R 10 1 A. B. C. D. E. 0.5Dokument2 SeitenApc Assignment 1: F 100 KHZ A. B. C. D. R 10 1 A. B. C. D. E. 0.5Priya AnandNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice SetDokument5 SeitenPractice Setrishavkumarsingh088Noch keine Bewertungen
- PT-I ADC Director FormatDokument11 SeitenPT-I ADC Director FormatEASACOLLEGENoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment PDFDokument2 SeitenAssignment PDFPrisha SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analog and Digital Communication: Question Bank Unit 1 A CDokument11 SeitenAnalog and Digital Communication: Question Bank Unit 1 A CJ.NishanthiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 7Dokument3 SeitenAssignment 7Akmal KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- All-Optical RegenerationDokument5 SeitenAll-Optical RegenerationNguyễn Hữu QuânNoch keine Bewertungen
- Questions OC Class Test CorrectedDokument1 SeiteQuestions OC Class Test CorrectedsrinivasNoch keine Bewertungen
- AC Tutorial QuestionsDokument3 SeitenAC Tutorial QuestionsranddconsultancyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anna University Chennai - 600 025Dokument2 SeitenAnna University Chennai - 600 025SriramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Bank: Department of Ece Subject Code:141304 Subject Name: Analog and Digital Communication Year/Sem:II/IIIDokument7 SeitenQuestion Bank: Department of Ece Subject Code:141304 Subject Name: Analog and Digital Communication Year/Sem:II/IIIShanmuga PriyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adc 1Dokument2 SeitenAdc 1nithyajothiNoch keine Bewertungen
- COMMUNICATION THEORY SemDokument14 SeitenCOMMUNICATION THEORY SemThenappan SNoch keine Bewertungen
- ADC ImpqnsDokument4 SeitenADC Impqnsss mNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microwave Engineering Assignment 1 To 5Dokument6 SeitenMicrowave Engineering Assignment 1 To 5Anonymous 4bUl7jzGqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wideband RF Technologies and Antennas in Microwave FrequenciesVon EverandWideband RF Technologies and Antennas in Microwave FrequenciesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marks2010 54Dokument4 SeitenMarks2010 54api-78343547Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cat II ConsolidatedDokument9 SeitenCat II Consolidatedapi-78343547Noch keine Bewertungen
- SubstituteDokument1 SeiteSubstituteapi-78343547Noch keine Bewertungen
- II Sem ResultDokument3 SeitenII Sem Resultapi-78343547Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cat II ConsolidatedDokument9 SeitenCat II Consolidatedapi-78343547Noch keine Bewertungen
- Full-Scan: Ad-Hoc Methods Design Rules Scan Register Scan Flip-Flops Scan Test Sequences Overheads Scan Design SystemDokument22 SeitenFull-Scan: Ad-Hoc Methods Design Rules Scan Register Scan Flip-Flops Scan Test Sequences Overheads Scan Design Systemapi-78343547Noch keine Bewertungen
- Design For Testability - 2Dokument20 SeitenDesign For Testability - 2api-78343547Noch keine Bewertungen
- Test Process and AteDokument43 SeitenTest Process and Ateapi-78343547Noch keine Bewertungen
- Motivation and Economics Definitions (BIST) Process Bist (PG) Bist (RC) ExampleDokument59 SeitenMotivation and Economics Definitions (BIST) Process Bist (PG) Bist (RC) Exampleapi-78343547Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bist - 2Dokument27 SeitenBist - 2api-78343547Noch keine Bewertungen
- Problem of Sequential Circuit ATPG Time-Frame ExpansionDokument22 SeitenProblem of Sequential Circuit ATPG Time-Frame Expansionapi-78343547Noch keine Bewertungen
- Simulation-Based Methods: Use of Fault Simulation For Test Generation ContestDokument25 SeitenSimulation-Based Methods: Use of Fault Simulation For Test Generation Contestapi-78343547Noch keine Bewertungen
- Jan. 19, 2001 VLSI Test: Bushnell-Agrawal/Lecture 1 1Dokument16 SeitenJan. 19, 2001 VLSI Test: Bushnell-Agrawal/Lecture 1 1api-78343547Noch keine Bewertungen
- Yield Analysis - Unit 1Dokument15 SeitenYield Analysis - Unit 1api-78343547Noch keine Bewertungen
- Major Combinational AtpgDokument68 SeitenMajor Combinational Atpgapi-78343547Noch keine Bewertungen
- Combinational Automatic Test-Pattern Generation (ATPG) BasicsDokument26 SeitenCombinational Automatic Test-Pattern Generation (ATPG) Basicsapi-78343547Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pindyck TestBank 7eDokument17 SeitenPindyck TestBank 7eVictor Firmana100% (5)
- Ludwig Van Beethoven: Für EliseDokument4 SeitenLudwig Van Beethoven: Für Eliseelio torrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aluminum 3003-H112: Metal Nonferrous Metal Aluminum Alloy 3000 Series Aluminum AlloyDokument2 SeitenAluminum 3003-H112: Metal Nonferrous Metal Aluminum Alloy 3000 Series Aluminum AlloyJoachim MausolfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Profile On Sheep and Goat FarmDokument14 SeitenProfile On Sheep and Goat FarmFikirie MogesNoch keine Bewertungen
- G.R. No. 185449, November 12, 2014 Del Castillo Digest By: DOLARDokument2 SeitenG.R. No. 185449, November 12, 2014 Del Castillo Digest By: DOLARTheodore DolarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ibbotson Sbbi: Stocks, Bonds, Bills, and Inflation 1926-2019Dokument2 SeitenIbbotson Sbbi: Stocks, Bonds, Bills, and Inflation 1926-2019Bastián EnrichNoch keine Bewertungen
- PCDokument4 SeitenPCHrithik AryaNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Field Definitions PlusDokument9 SeitenGeneral Field Definitions PlusOscar Alberto ZambranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wind Energy in MalaysiaDokument17 SeitenWind Energy in MalaysiaJia Le ChowNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduce Letter - CV IDS (Company Profile)Dokument13 SeitenIntroduce Letter - CV IDS (Company Profile)katnissNoch keine Bewertungen
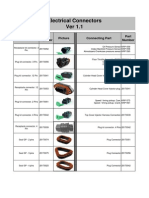
- Electrical ConnectorsDokument5 SeitenElectrical ConnectorsRodrigo SantibañezNoch keine Bewertungen
- United Nations Economic and Social CouncilDokument3 SeitenUnited Nations Economic and Social CouncilLuke SmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Online EarningsDokument3 SeitenOnline EarningsafzalalibahttiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abu Hamza Al Masri Wolf Notice of Compliance With SAMs AffirmationDokument27 SeitenAbu Hamza Al Masri Wolf Notice of Compliance With SAMs AffirmationPaulWolfNoch keine Bewertungen
- A. The Machine's Final Recorded Value Was P1,558,000Dokument7 SeitenA. The Machine's Final Recorded Value Was P1,558,000Tawan VihokratanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Government of West Bengal Finance (Audit) Department: NABANNA', HOWRAH-711102 No. Dated, The 13 May, 2020Dokument2 SeitenGovernment of West Bengal Finance (Audit) Department: NABANNA', HOWRAH-711102 No. Dated, The 13 May, 2020Satyaki Prasad MaitiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fidp ResearchDokument3 SeitenFidp ResearchIn SanityNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vinera Ewc1201Dokument16 SeitenVinera Ewc1201josue1965Noch keine Bewertungen
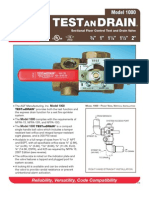
- Test & Drain Valve Model 1000Dokument2 SeitenTest & Drain Valve Model 1000saifahmed7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Multispan LC 2046 Length Counter PDFDokument2 SeitenMultispan LC 2046 Length Counter PDFvinod kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1934 PARIS AIRSHOW REPORT - Part1 PDFDokument11 Seiten1934 PARIS AIRSHOW REPORT - Part1 PDFstarsalingsoul8000Noch keine Bewertungen
- Star Link SafetyDokument2 SeitenStar Link SafetyJeronimo FernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- L1 L2 Highway and Railroad EngineeringDokument7 SeitenL1 L2 Highway and Railroad Engineeringeutikol69Noch keine Bewertungen
- Viceversa Tarot PDF 5Dokument1 SeiteViceversa Tarot PDF 5Kimberly Hill100% (1)
- Hexoskin - Information For Researchers - 01 February 2023Dokument48 SeitenHexoskin - Information For Researchers - 01 February 2023emrecan cincanNoch keine Bewertungen
- BST Candidate Registration FormDokument3 SeitenBST Candidate Registration FormshirazNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Review Paper On Improvement of Impeller Design A Centrifugal Pump Using FEM and CFDDokument3 SeitenA Review Paper On Improvement of Impeller Design A Centrifugal Pump Using FEM and CFDIJIRSTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brand Positioning of PepsiCoDokument9 SeitenBrand Positioning of PepsiCoAbhishek DhawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- NOP PortalDokument87 SeitenNOP PortalCarlos RicoNoch keine Bewertungen
- RevisionHistory APFIFF33 To V219Dokument12 SeitenRevisionHistory APFIFF33 To V219younesNoch keine Bewertungen