Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Antiemetics
Hochgeladen von
Ahmad Ariff Azmer MunshiOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Antiemetics
Hochgeladen von
Ahmad Ariff Azmer MunshiCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
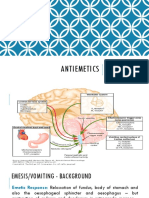
Antiemetics (Source: Dr Mohanty Lectures) Basic Physiology About Vomitting Nausea : The feeling that one about to vomit.
Vomitting : Forceful expulsion of the contents of the stomach and upper intestinal tract through the mouth.
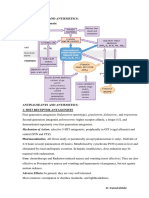
Higher cortical centres
Sensory input (pain, smell, sight)
Memory, fear, anticipation
Histamine antagonists Muscarinic antagonists Dopamine antagonists Cannabinoids Chemotherapy Anaesthetics Opioids
Benzodiazepines
Chemoreceptor Trigger Zone (area prostrema, 4th ventricle)
5HT3 antagonists
Vomiting Centre (medulla)
Vomiting Reflex
Histamine antagonists Muscarinic antagonists
Sphincter modulators
Chemotherapy Surgery Radiotherapy Gastroprokinetic agents
Stomach Small intestine
Labyrinths
Surgery Neuronal pathways Factors which can cause nausea & vomiting Sites of action of drugs
Vomiting is a complex reflex coordinated by a region in the brainstem medulla oblongata, known as vomitting centre. Neural input/Impulses from receptors in many region of the body can initiate the vomiting reflex.
The region include:
1. 2. 3. 4.
Chemoreceptor trigger zone (CTZ) outside BBB (area postrema) Higher cortical centres refer to cerebral cortex Peripheral tissues (GIT) stomach, intestine Vestibular apparatus/ labyrinths A system of interconnecting canals or channels in the inner ear. (motion sickness)
* cerebral cortex is responsible for sensing and interpreting input from various sources and maintaining
cognitive function. Sensory functions interpreted by the cerebral cortex include hearing, touch, and vision. Cognitive functions include thinking, perceiving, and understanding language.
Antiemetics agent Antiemetics agent : Drug that prevents vomiting. Class 5-HT3 R antagonists Dopamine antagonists Antimuscarinics Anti-histamines Cannabinoids Antacids H2 receptor antagonist Miscellaneous Drug Ondansetron, Granisetron Metoclopramide, Domperidone Scopolamine (l-hyoscine) Cyclizine, Promethazine, Doxylamine Nabilone, Dronabinol Magnesium hydroxide and aluminium hydroxide Ranitinidine, famotidine etc. Dexamethasone, Diazepam, antipsychotic (droperidol)
5-HT3 R antagonists (Oral, IV) MOA - Block serotonergic (5-HT3) receptors in the centre & periphery - gut. Uses - For prevention & treatment of vomiting due to anticancer agents, radiation & postoperative vomiting. *** ADR: well tolerated but can cause headache, constipation & in some patients QT prolongation Dopamine antagonists MOA - Block DA2 receptors in CTZ Uses - Anti-emetics (not for motion sickness), gastro-esophageal reflux disorder (GERD) ***ADR: Hyperprolactinemia, Extra pyramidal syndrome (EPS) only with metoclopramide.
(Domperidone does not cross BBB & hence, no EPS)
Antimuscarinics MOA - Block muscarinic (M1) R in vestibular apparatus Uses - for prevention and treatment of motion sickness, sea sickness ***ADR : drowsiness, dryness of mouth, blurred vision & other atropine like side effects
Anti-histamines MOA : Block H1 & M1 (atropine like action) receptors Uses : similar to hyoscine ***ADR : similar to hyoscine Cannabinoids MOA - prevents stimulation of CTZ Uses - Reserved drug for anticancer drug induced vomiting and radiation sickness ***ADR: Mood changes, drowsiness, psychotic reactions,& drug dependence Antacids MOA : from first to last gastric acid neutralization Uses : 15 to 30ml doses of single or multiple agents may provide relief from simple nausea and vomiting associated H2 receptor antagonist May be used in low doses to manage simple nausea and vomiting associated with heartburn or gastroesophageal reflux. Miscellaneous a. Corticosteroids : Dexamethasone Mechanism not known. May inhibit prostaglandin synthesis. Uses: synergistic with other antiemetics in anticancer drug induced vomiting b. Diazepam, Lorazepam May control anticipatory vomiting by sedative & antianxiety action. Uses: synergistic with other antiemetics in anticancer drug induced vomiting
Other uses Vomiting in pregnancy - Reassurance. Pyridoxine alone or Promethazine + Pyridoxine or pyridoxine + doxylamine only if absolutely necessary Vomiting in children - pediatric gastroenteritis - rehydration measures. Children receiving chemotherapy a corticosteroid plus 5-HT 3 receptor antagonist may be preferred.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Basic Pharmacology And Drug Calculations [Practice Questions And Answers]Von EverandBasic Pharmacology And Drug Calculations [Practice Questions And Answers]Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Antiemetics and ProkineticsDokument29 SeitenAntiemetics and ProkineticsGilbert Girising100% (1)
- Medicinal Chemistry of Drugs Affecting the Nervous SystemVon EverandMedicinal Chemistry of Drugs Affecting the Nervous SystemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antiemetic Drugs: Presented By: Professor Dr. Imad A-J ThanoonDokument32 SeitenAntiemetic Drugs: Presented By: Professor Dr. Imad A-J ThanoonAnisa Karamina WardaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Anti Emetics II BDS 3 June 2020 AdobeDokument28 Seiten1 Anti Emetics II BDS 3 June 2020 AdobeBishal ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antiemetics: Prof. Dr. Fatima Rizvi Department of PharmacologyDokument44 SeitenAntiemetics: Prof. Dr. Fatima Rizvi Department of PharmacologydrfatimarizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antiemetic Drugs PDFDokument12 SeitenAntiemetic Drugs PDFDanisha Laila100% (2)
- Mpharm P'col 1y 2s 201t Adv.p'CologyDokument56 SeitenMpharm P'col 1y 2s 201t Adv.p'CologyNasrollah TalibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antinauseants and AntiemeticsDokument8 SeitenAntinauseants and AntiemeticsHamad AlshabiNoch keine Bewertungen
- AntiemeticsDokument30 SeitenAntiemeticsDustyNoch keine Bewertungen
- AntiemeticsDokument25 SeitenAntiemeticsPridho GaziansyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument44 SeitenUntitledTani BirlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AntiemeticsDokument33 SeitenAntiemeticsSaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANTIEMETICSDokument21 SeitenANTIEMETICSanaya khan StudentNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gastric and Doudenal Peptic Ulcer: DR - Rania Khalil MostafaDokument44 SeitenGastric and Doudenal Peptic Ulcer: DR - Rania Khalil MostafaMai OssamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NAUSEA AND VOMITING - ObatDokument8 SeitenNAUSEA AND VOMITING - ObatSri Ayu NingsihNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anti EmeticsDokument29 SeitenAnti EmeticsBezawit TsigeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antiemetics: Dr. Bikram TewariDokument31 SeitenAntiemetics: Dr. Bikram TewariRajkamal SarmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antiemetic DrugsDokument18 SeitenAntiemetic DrugsSuraj VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anti Emetic DrugsDokument3 SeitenAnti Emetic DrugsFaria Islam JuhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANTIEMETIKDokument23 SeitenANTIEMETIKshabrinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antiemetic Drugs: PHR Sangita ShakyaDokument26 SeitenAntiemetic Drugs: PHR Sangita ShakyaCurex QANoch keine Bewertungen
- AutacoidsDokument8 SeitenAutacoidsDeity CelleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs Used in The Treatment of Gastrointestinal DiseasesDokument20 SeitenDrugs Used in The Treatment of Gastrointestinal DiseasesPooja KumariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antiemetic DrugsDokument8 SeitenAntiemetic DrugsAyesha LiaqatNoch keine Bewertungen
- AutacoidsDokument38 SeitenAutacoidsdrmayangNoch keine Bewertungen
- AntiemeticDokument36 SeitenAntiemeticravannofanizza100% (1)
- AntiemeticsDokument37 SeitenAntiemeticsAriel OlshevskyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anti-Emetics: B. Dian Novita, DR., MkedDokument9 SeitenAnti-Emetics: B. Dian Novita, DR., MkedwdqqqdwNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacology of The GITDokument83 SeitenPharmacology of The GITJohn Wesley OmbogoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gastrointestinal System .Dokument6 SeitenGastrointestinal System .Jayward BucayuNoch keine Bewertungen
- AnesthesiaDokument12 SeitenAnesthesiaعلي الاسديNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anti Emetics DrugsDokument18 SeitenAnti Emetics Drugsvani reddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antiemitics & AntacidDokument22 SeitenAntiemitics & AntacidMohammad HayajnehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digestive System Diseases and Therapy NotesDokument19 SeitenDigestive System Diseases and Therapy NotesMbah GapinbissiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Muscarinic (M) Receptor Blockers (Antagonists) Anti Muscarinic Drugs Anti Cholinergic DrugsDokument4 SeitenMuscarinic (M) Receptor Blockers (Antagonists) Anti Muscarinic Drugs Anti Cholinergic Drugsfiena92Noch keine Bewertungen
- Medicinal Chemistry III Gi System: Emetics & Anti-Emetics: Pharm. Chem. PH.DDokument5 SeitenMedicinal Chemistry III Gi System: Emetics & Anti-Emetics: Pharm. Chem. PH.DAhmed BajahNoch keine Bewertungen
- L-3 GIT Diseases and DrugsDokument20 SeitenL-3 GIT Diseases and DrugsRafi AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Autonomic Nervous System-2Dokument8 SeitenAutonomic Nervous System-2محمد علي حميدNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anti Emetik: Emesis / MuntahDokument25 SeitenAnti Emetik: Emesis / MuntahT Z BenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gastrointestinal DrugsDokument49 SeitenGastrointestinal DrugsMae Antonette OrlinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AntiemeticsDokument16 SeitenAntiemeticswalt65Noch keine Bewertungen
- Emetics & AntiemeticsDokument7 SeitenEmetics & Antiemetics찬열박Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nausea Movement DisorderDokument5 SeitenNausea Movement DisorderoladapoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Moderator: Dr. Usha Suwalka Presenter: Dr. Suchismita NaikDokument44 SeitenModerator: Dr. Usha Suwalka Presenter: Dr. Suchismita NaikHarish KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- METOCLOPRAMIDE Drug StudyDokument2 SeitenMETOCLOPRAMIDE Drug Studygersalia.christiennikkiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANTIEMETICSDokument26 SeitenANTIEMETICSkhurshidghorihumaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs Acting On Gastro Intestinal TractDokument20 SeitenDrugs Acting On Gastro Intestinal TractManikanta GupthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antiemetics PDFDokument2 SeitenAntiemetics PDFLiezel CauilanNoch keine Bewertungen
- DR Theresa John Pharmacology Lecture Notes Drugs Used To Treat Gastrointestinal Diseases Feb 2022Dokument16 SeitenDR Theresa John Pharmacology Lecture Notes Drugs Used To Treat Gastrointestinal Diseases Feb 2022officialdanieladejumoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Histamines AntagonistDokument36 SeitenHistamines AntagonistBriana NdayisabaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GIT Drugs I. Drugs That Promote Upper Gastrointestinal MotilityDokument5 SeitenGIT Drugs I. Drugs That Promote Upper Gastrointestinal MotilityEli Ezer SimangunsongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs Acting On The Gastrointestinal TractDokument27 SeitenDrugs Acting On The Gastrointestinal TractJames PerianayagamNoch keine Bewertungen
- GastrointestinaldrugsDokument30 SeitenGastrointestinaldrugsmayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Important GIT DrugsDokument3 SeitenImportant GIT DrugsAndleeb ImranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Histamine, Serotonin and Ergot AlkaloidsDokument36 SeitenHistamine, Serotonin and Ergot AlkaloidsSteph Taylor Reyes RadanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emesis and AntimemeticsDokument17 SeitenEmesis and Antimemeticssunday danielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Preanesthetic Medication PDFDokument5 SeitenPreanesthetic Medication PDFSayan NagNoch keine Bewertungen
- AutacoidsDokument34 SeitenAutacoidsBrîndușa PetruțescuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cholinoceptor Blocking Drugs: She Believed She Could Save The World So She Became A PharmacistDokument23 SeitenCholinoceptor Blocking Drugs: She Believed She Could Save The World So She Became A PharmacistJing Lomboy AcostaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conservative: Prophylaxis Expectant TDokument1 SeiteConservative: Prophylaxis Expectant TAhmad Ariff Azmer MunshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Septic Arthritis: Most Common - Knee (50%), HipDokument5 SeitenSeptic Arthritis: Most Common - Knee (50%), HipAhmad Ariff Azmer MunshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Protein C & S DeficiencyDokument20 SeitenProtein C & S DeficiencyAhmad Ariff Azmer MunshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- SGT 2Dokument98 SeitenSGT 2Ahmad Ariff Azmer MunshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Describe Brain TumorDokument1 SeiteDescribe Brain TumorAhmad Ariff Azmer MunshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conservative: Prophylaxis Expectant TDokument1 SeiteConservative: Prophylaxis Expectant TAhmad Ariff Azmer MunshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- BelchingDokument3 SeitenBelchingAhmad Ariff Azmer MunshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Checklist Spec 1Dokument2 SeitenChecklist Spec 1Ahmad Ariff Azmer MunshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learn 1 Word English Every DayDokument1 SeiteLearn 1 Word English Every DayAhmad Ariff Azmer MunshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- PCGDokument3 SeitenPCGAhmad Ariff Azmer MunshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Year 4 - Calendar YearDokument1 SeiteYear 4 - Calendar YearAhmad Ariff Azmer MunshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Expertise COVER PAGEDokument1 SeiteExpertise COVER PAGEAhmad Ariff Azmer MunshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abd PainlDokument2 SeitenAbd PainlAhmad Ariff Azmer MunshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impact of Social Media On Students Academic PerformanceDokument67 SeitenImpact of Social Media On Students Academic PerformanceAhmad Ariff Azmer Munshi100% (14)
- Content ExpertiseDokument1 SeiteContent ExpertiseAhmad Ariff Azmer MunshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPG Diabetic NephropathyDokument23 SeitenCPG Diabetic NephropathyapalaginihNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ila 4 Tuberculosis Final CompilationDokument24 SeitenIla 4 Tuberculosis Final CompilationAhmad Ariff Azmer MunshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Difference Acute and ChronicDokument3 SeitenDifference Acute and ChronicAhmad Ariff Azmer MunshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Davars LOM Vol 2Dokument163 SeitenDavars LOM Vol 2Sridhar SriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 5 - Experiment No.9 - Preparation of Bacterial Smear and Gram StainingDokument10 SeitenGroup 5 - Experiment No.9 - Preparation of Bacterial Smear and Gram StainingPMG BrightNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teleradiologi: Cross Reporting & Smart AssignDokument17 SeitenTeleradiologi: Cross Reporting & Smart Assignrafael100% (1)
- Chemical Peel Guidelines PDFDokument1 SeiteChemical Peel Guidelines PDFHasan MurdimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Funda Lab - Prelim ReviewerDokument16 SeitenFunda Lab - Prelim ReviewerNikoruNoch keine Bewertungen
- BSA Creat Clearance Calculation OriginalDokument2 SeitenBSA Creat Clearance Calculation Originalstrider_sdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diphenhydramine AHFSDokument18 SeitenDiphenhydramine AHFSDymas PrayogaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toprank Midterms Post TestDokument79 SeitenToprank Midterms Post TestTony ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kidney StonesDokument11 SeitenKidney StonesNader Smadi100% (1)
- IDSP BelgaumDokument36 SeitenIDSP BelgaumJ Nuchin100% (1)
- Use of Chlorhexidine Varnishes in Preventing and Treating Periodontal DiseaseDokument4 SeitenUse of Chlorhexidine Varnishes in Preventing and Treating Periodontal Diseasetaher adelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diagnostic Diabetes: Diagnosing Maturity-Onset Diabetes of The Young (MODY)Dokument32 SeitenDiagnostic Diabetes: Diagnosing Maturity-Onset Diabetes of The Young (MODY)Christian SalimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit Historical Development OF Psychiatric: NursingDokument12 SeitenUnit Historical Development OF Psychiatric: NursingAmit TamboliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aplikasi Terapi Generalis Dalam Pemberian Asuhan Keperawatan Jiwa Pada Nn. R Dengan HalusinasiDokument13 SeitenAplikasi Terapi Generalis Dalam Pemberian Asuhan Keperawatan Jiwa Pada Nn. R Dengan Halusinasicindy veronikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 EL Husseinys Essentials of Cardiovascular System @eduwaves360Dokument236 Seiten4 EL Husseinys Essentials of Cardiovascular System @eduwaves360ahmed_abu_alrobNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alsayed Alrokh - Pharmacology Review PDFDokument90 SeitenAlsayed Alrokh - Pharmacology Review PDFAlan DafoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newborn Care: A Newborn Baby or Animal Is One That Has Just Been BornDokument26 SeitenNewborn Care: A Newborn Baby or Animal Is One That Has Just Been BornJenny-Vi Tegelan LandayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- HSG PresentationDokument18 SeitenHSG Presentationashikin92Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Sage Encyclopedia of Abnormal and Clinical Psychology - I36172Dokument5 SeitenThe Sage Encyclopedia of Abnormal and Clinical Psychology - I36172Rol AnimeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiology - Regulation of Body TemperatureDokument35 SeitenPhysiology - Regulation of Body TemperatureGhaidaa Sadeq100% (2)
- Maxillary Sinus Approaches-1Dokument23 SeitenMaxillary Sinus Approaches-1Ahmed KhattabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brief Intervention: Mhgap-Ig Base Course - Field Test Version 1.00 - May 2012 1Dokument16 SeitenBrief Intervention: Mhgap-Ig Base Course - Field Test Version 1.00 - May 2012 1TEOFILO PALSIMON JR.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Homeopathic Care, Don Hamilton DVM PDFDokument48 SeitenHomeopathic Care, Don Hamilton DVM PDFBibek Sutradhar0% (1)
- Dengue Infection During Pregnancy andDokument7 SeitenDengue Infection During Pregnancy andAlia SalviraNoch keine Bewertungen
- HBN 6 V2 DssaDokument80 SeitenHBN 6 V2 Dssaمحمد عبدالجبار حسن اليوسفيNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANZCOR Guideline 13.4 - Airway Management and Mask Ventilation of The NewbornDokument18 SeitenANZCOR Guideline 13.4 - Airway Management and Mask Ventilation of The NewbornEssam HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tumor Trofoblas GestasionalDokument14 SeitenTumor Trofoblas GestasionalTriyoga PramadanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Evaluation Report For Trilogy Evo Ventilator: Prepared For: Respironics, IncDokument79 SeitenClinical Evaluation Report For Trilogy Evo Ventilator: Prepared For: Respironics, Incdaphnestc0211Noch keine Bewertungen
- PEH 3 Lesson 2Dokument3 SeitenPEH 3 Lesson 2ShaineMaiko MarigocioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Literature Review 1Dokument5 SeitenLiterature Review 1api-550490262Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossVon EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsVon EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeVon EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeBewertung: 2 von 5 Sternen2/5 (1)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityVon EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (24)
- The Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearVon EverandThe Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (23)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisVon EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (42)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedVon EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (80)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDVon EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- 12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosVon Everand12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (207)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsVon EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsVon EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (169)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerVon EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (392)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsVon EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (3)
- Sleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningVon EverandSleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (3)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisVon EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryVon EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (44)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaVon EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityVon EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (3)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Von EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (110)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisVon EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2)
- Algorithms to Live By: The Computer Science of Human DecisionsVon EverandAlgorithms to Live By: The Computer Science of Human DecisionsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (722)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeVon EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (253)
- To Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceVon EverandTo Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (51)
![Basic Pharmacology And Drug Calculations [Practice Questions And Answers]](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/475660044/149x198/2c7fc45015/1691161640?v=1)