Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
7cost Sheet 7
Hochgeladen von
Jyoti GuptaOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
7cost Sheet 7
Hochgeladen von
Jyoti GuptaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Cost sheet
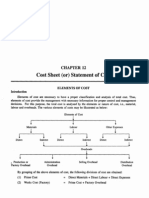
Cost sheet is a statement, which shows various components of total cost of a product. It classifies and analyses the components of cost of a product. It is a statement which shows per unit cost in addition to total cost. Selling price is ascertained with the help of cost sheet. Cost sheet is prepared on the basis of historical cost and estimated cost. Historical Cost sheet is prepared on the basis of actual cost incurred. Estimated cost sheet is prepared on the basis of estimated cost. The statement prepared before the commencement of production is called estimated cost sheet. Such cost sheet is useful in quoting the tender price of a job or a contract. Importance of Cost Sheet The importance of cost sheet is as follows: 1) Cost ascertainment The main objective of the cost sheet is to ascertain the cost of a product. Cost sheet helps in ascertainment of cost for the purpose of determining cost after they are incurred. It also helps to ascertain the actual cost or estimated cost of a Job. 2) Fixation of selling price To fix the selling price of a product or service, it is essential to prepare the cost sheet. It helps in fixing selling price of a product or service by providing detailed information of the cost. 3) Help in cost control For controlling the cost of a product it is necessary for every manufacturing unit to prepare a cost sheet. Estimated cost sheet helps in the control of material cost, labour cost and overheads cost at every point of production. 4) Facilitates managerial decisions It helps in taking important decisions by the management such as: whether to produce or buy a component, what prices of goods are to be quoted in the tender, whether to retain or replace an existing machine etc. Components of total cost Components of total cost are as follows: 1) Prime Cost
It consists of direct material, direct wages and direct expenses. In other words Prime cost represents the aggregate of cost of material consumed, productive wages, and direct expenses. It is also known as basic, first, flat or direct cost of a product. Prime Cost = Direct material + Direct Wages + Direct expenses 2) Factory Cost In addition to prime cost it includes works or factory overheads. Factory overheads consist of cost of indirect material, indirect wages, and indirect expenses incurred in the factory. Factory cost is also known as works cost, production or manufacturing cost. Factory Cost = Prime cost + Factory overheads 3) Cost of goods sold It is not necessary, that all the goods produced in a period are sold in the same period. There is stock of finished goods in the opening and at the end of the period. The cost of opening stock of finished goods is added in the total cost of production in the current period and cost of closing stock of finished goods is deducted. The cost of goods sold is calculated as: Cost of goods sold = Total cost of production + Opening stock of Finished goods Closing stock of finished goods 4) Total Cost/ Cost of Sales If selling and distribution overheads are added to the total cost of production, total cost is arrived at. This cost is also termed as cost of Sales. Hence the total cost is calculated as: Total Cost = Cost of Goods sold + Selling and distribution overheads
Items excluded from cost accounts
There are certain items which are excluded from cost accounting. These may be the following. 1) Profit or losses arising on sale of fixed assets: Any profit or loss arising on sale or transfer of fixed assets are purely financial in nature and excluded from cost accounting.
2) Amortization of fictitious assets: Intangible and fictitious assets are only charged in financial accounting and find no place in cost accounting. Goodwill, patent, copy right, advertisement, preliminary expenses etc. 3) Appropriation of Profits: Certain portion of profits is appropriated for specific purposes. These are called appropriation of profits. It is not considered in cost accounts. These may be the following: donation and charities, income tax paid, dividend paid, transfer to general Reserve, transfer to capital reserve etc. 4) Financial incomes: There are certain incomes which are purely financial in nature and not included in cost accounting. Examples are rent receivable, share transfer fee received, interest received on bank deposits, dividend received, brokerage received, discount & commission received etc. Illustration From the following information, prepare a cost sheet for period ended on 31st March 2006. Opening stock of raw material 12,500 Purchases of raw material 1,36,000 Closing stock of raw material 8,500 Direct wages 54,000 Direct expenses 12,000 Factory overheads 100% of direct wages Office and administrative overheads 20% of works cost Selling and distribution overheads 26,000 Cost of opening stock of finished goods 12,000 Cost of Closing stock of finished goods 15,000 Profit on cost 20% Solution Direct Material : Material consumed Opening stock of raw material Add: Purchases 12500 136000 148500
Less: Closing stock of raw material COMC Direct wages Direct expenses Prime cost Factory overheads: 100% of direct wages Works cost Office and administrative overheads 20% of works cost Total cost of production Add : opening stock of finished goods Cost of Goods available for sale Less : Closing stock of finished goods Cost of goods sold Selling and distribution overheads Total Cost = cost of sales Profit (20% On Cost i.e. 3,35,00 20/100) Sales
8500 1,40,000 54,000 12,000 2,06,000 54,000 2,60,000 52,000 3,12 000 12,000 3,24,000 15,000 3,09,000 26,000 3,35,000 67,000 4,02,000
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Chapter 12 Cost Sheet or Statement of CostDokument16 SeitenChapter 12 Cost Sheet or Statement of CostNeelesh MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes On Cost AccountingDokument86 SeitenNotes On Cost AccountingZeUs100% (2)
- Cost and Management AccountingDokument84 SeitenCost and Management AccountingKumar SwamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 Costing Formulae Topic WiseDokument86 Seiten7 Costing Formulae Topic WiseHimanshu Shukla100% (1)
- Cost Sheet PDFDokument17 SeitenCost Sheet PDFRajuSharmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Costing Sheet - Easiest WayDokument11 SeitenCosting Sheet - Easiest Waypankajkuma981100% (1)
- Final Exam - 2020Dokument10 SeitenFinal Exam - 2020mshan lee100% (1)
- Final Accounts: Manufacturing, Trading and P&L A/cDokument51 SeitenFinal Accounts: Manufacturing, Trading and P&L A/cAnit Jacob Philip100% (1)
- Capital Vs Revenue Exp..... Point PresentationDokument16 SeitenCapital Vs Revenue Exp..... Point PresentationVinay Kumar100% (1)
- Cost AccountingDokument59 SeitenCost AccountingDitto SabuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contract CostingDokument11 SeitenContract CostingCOMEDSCENTRENoch keine Bewertungen
- Cost Accounting 2013Dokument3 SeitenCost Accounting 2013GuruKPO0% (1)
- Cost AccountingDokument21 SeitenCost Accountingabdullah_0o0Noch keine Bewertungen
- 14 Contract CostingDokument7 Seiten14 Contract CostingSumon Kumar DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT 5 - Relevant Costing Lecture 2 2018 - PDFDokument44 SeitenUNIT 5 - Relevant Costing Lecture 2 2018 - PDFMzimasi MjanyelwaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 4 Lecture Notes 2011Dokument27 SeitenLecture 4 Lecture Notes 2011Misu NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Cost Accounting: Prof. Chandrakala.M Department of Commerce Kristu Jayanti College BengaluruDokument11 SeitenIntroduction To Cost Accounting: Prof. Chandrakala.M Department of Commerce Kristu Jayanti College BengaluruChandrakala 10Noch keine Bewertungen
- Job, Batch, ContractDokument25 SeitenJob, Batch, ContractParminder Bajaj100% (1)
- SEM II Cost-Accounting Unit 1Dokument23 SeitenSEM II Cost-Accounting Unit 1mahendrabpatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adjusting Journal EntriesDokument3 SeitenAdjusting Journal Entriessudershan9Noch keine Bewertungen
- Acounting Atve Summarised NotesDokument118 SeitenAcounting Atve Summarised NotesFolegwe FolegweNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter One Introdutoin: 1.1. What Is Cost Accounting?Dokument156 SeitenChapter One Introdutoin: 1.1. What Is Cost Accounting?NatnaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 NotesDokument6 SeitenChapter 5 NotesXenia MusteataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cost Accounting Notes Fall 19-1Dokument11 SeitenCost Accounting Notes Fall 19-1AnoshiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes - Contract CostingDokument13 SeitenNotes - Contract CostingBlessMarcKupiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gbagada General HospitalDokument1 SeiteGbagada General HospitalChijioke PaschalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cost Accounting IIDokument62 SeitenCost Accounting IIShakti S SarvadeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Standard (I Unit Produced) ParticularsDokument11 SeitenStandard (I Unit Produced) ParticularsForam Raval100% (1)
- Edu-Care Professional Academy:, 243, Sundaram Coplex, Bhanwerkuan Main Road, IndoreDokument10 SeitenEdu-Care Professional Academy:, 243, Sundaram Coplex, Bhanwerkuan Main Road, IndoreCA Gourav Jashnani100% (1)
- Statement of Comprehensive IncomeDokument18 SeitenStatement of Comprehensive IncomeCharies Dingal100% (1)
- UNit Costing Study MaterialDokument42 SeitenUNit Costing Study MaterialChetana SoniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cost Sheet: Solutions To Assignment ProblemsDokument3 SeitenCost Sheet: Solutions To Assignment ProblemsNidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cost Concepts & Classification ShailajaDokument30 SeitenCost Concepts & Classification ShailajaPankaj VyasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cost Accounting Notes PDFDokument55 SeitenCost Accounting Notes PDFadv suryakant jadhavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Costing in BriefDokument47 SeitenCosting in BriefRezaul Karim TutulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit - 1: Introduction To Cost AccountingDokument262 SeitenUnit - 1: Introduction To Cost AccountingSamuel AnthrayoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial RatiosDokument7 SeitenFinancial RatiosarungarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cost AccountingDokument28 SeitenCost Accountingrenjithrkn12Noch keine Bewertungen
- Manufacturing SolutionsDokument8 SeitenManufacturing SolutionsMothusi M NtsholeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.2 Cost Sheet ProblemsDokument7 Seiten2.2 Cost Sheet ProblemsApparao ChNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cost Accounting UNIT I Theroy (1) New PDFDokument18 SeitenCost Accounting UNIT I Theroy (1) New PDFyogeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accounting CostingDokument156 SeitenAccounting CostingMorning32100% (1)
- Cost Accounting, Job Costing & Batch CostingDokument10 SeitenCost Accounting, Job Costing & Batch Costing✬ SHANZA MALIK ✬Noch keine Bewertungen
- Job Costing: I) Specific Order or Job Costing II) Continuous Operation or Process CostingDokument11 SeitenJob Costing: I) Specific Order or Job Costing II) Continuous Operation or Process CostingPulak DebnathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contract CostingDokument22 SeitenContract Costingrikesh radheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sales Mix BreakDokument1 SeiteSales Mix Breaklaur33nNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cost Sheet: Learning OutcomesDokument15 SeitenCost Sheet: Learning OutcomesshubNoch keine Bewertungen
- Short-Run Decision Making and CVP AnalysisDokument43 SeitenShort-Run Decision Making and CVP AnalysisHy Tang100% (1)
- Cost Accounting - Aunja MamDokument51 SeitenCost Accounting - Aunja MamRavi Kumar PariharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cost SheetDokument13 SeitenCost SheetShr3yasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cost SheetDokument15 SeitenCost Sheetnagesh dashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cost Sheet GarmentDokument9 SeitenCost Sheet GarmentAnonymous uHT7dDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 2 Cost ClassificationDokument7 SeitenLecture 2 Cost ClassificationNanda MaharajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cost SheetDokument15 SeitenCost SheetDikshit Kothari100% (2)
- Cost Analysis of Any Product or ServiceDokument27 SeitenCost Analysis of Any Product or ServiceAayushiNoch keine Bewertungen
- In Production, Research, Retail, and Accounting, A Cost Is The Value of Money That Has Been Used Up To Produce Something or Deliver A ServiceDokument20 SeitenIn Production, Research, Retail, and Accounting, A Cost Is The Value of Money That Has Been Used Up To Produce Something or Deliver A ServiceBHUSHAN PATILNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manufacturing AccountsDokument6 SeitenManufacturing Accountsdhanyasugukumar100% (2)
- Cost SheetDokument17 SeitenCost Sheet9986212378Noch keine Bewertungen
- Student's Name-WPS OfficeDokument11 SeitenStudent's Name-WPS Officesquarestationery23Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2financial Analysis 2Dokument2 Seiten2financial Analysis 2Jyoti GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Market MeasurementDokument3 SeitenMarket MeasurementJyoti GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1meaning and Origin of Cost Accounting 1Dokument3 Seiten1meaning and Origin of Cost Accounting 1Jyoti GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11material Control 3, 11Dokument4 Seiten11material Control 3, 11Jyoti GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8emerging Terms 8Dokument2 Seiten8emerging Terms 8Jyoti GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2importance of Cost Accounting 2Dokument3 Seiten2importance of Cost Accounting 2Jyoti GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1meaning and Origin of Cost Accounting 1Dokument3 Seiten1meaning and Origin of Cost Accounting 1Jyoti GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Home OfficeDokument4 SeitenHome OfficeVenessa Lei Tricia G. JimenezNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Brand Community Practices Create ValueDokument23 SeitenHow Brand Community Practices Create ValueOdnooMgmr0% (1)
- SWOT AnalysisDokument9 SeitenSWOT AnalysisAnjali SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Articles of Confederation EssayDokument2 SeitenArticles of Confederation Essayapi-251089957Noch keine Bewertungen
- Property Surveyor CVDokument2 SeitenProperty Surveyor CVMike KelleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Latest Form 6 Revised.1998Dokument6 SeitenLatest Form 6 Revised.1998Chrizlennin MutucNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Studies Chapter 19 NotesDokument2 SeitenBusiness Studies Chapter 19 NotesMuhammad Faizan RazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AC 506 Midterm ExamDokument10 SeitenAC 506 Midterm ExamJaniña NatividadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Definition of Distributation ChannelDokument11 SeitenDefinition of Distributation ChannelrituparnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Embarke CoFounder Equity Split Template 2016 01Dokument7 SeitenEmbarke CoFounder Equity Split Template 2016 01Prashant A UNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dish TVDokument8 SeitenDish TVLekh RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business English IDokument171 SeitenBusiness English ISofija100% (2)
- Chapter 1Dokument23 SeitenChapter 1Rajendra K.C.Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2009 04 Searchcrm SaasDokument18 Seiten2009 04 Searchcrm SaasShruti JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- DPR Financial Model Final 30.07.10Dokument194 SeitenDPR Financial Model Final 30.07.10deshmukhvaibhav2009Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cost Accounting: A Managerial EmphasisDokument19 SeitenCost Accounting: A Managerial EmphasisAaminah AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabus: Digital Media Economics at UNC School of Journalism and Mass CommunicationDokument9 SeitenSyllabus: Digital Media Economics at UNC School of Journalism and Mass CommunicationRyan Thornburg100% (1)
- Company ProfileDokument2 SeitenCompany ProfileMonika RockerNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2018 10 17 - Indicative Bond Prices Southey Capital Bond Illiquid and DistressedDokument5 Seiten2018 10 17 - Indicative Bond Prices Southey Capital Bond Illiquid and DistressedSouthey CapitalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report Format Baru Sept SafetyDokument12 SeitenReport Format Baru Sept SafetyDylanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organizational Learning Agility: in This Case StudyDokument28 SeitenOrganizational Learning Agility: in This Case StudyharshadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economic Agents and Economic OperationsDokument2 SeitenEconomic Agents and Economic OperationsAllyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wiley Module 6 Acconting and Review Serv PDFDokument6 SeitenWiley Module 6 Acconting and Review Serv PDFMary Clarence AlbosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analisis Permintaan Beras Di Provinsi kaLTENGDokument9 SeitenAnalisis Permintaan Beras Di Provinsi kaLTENGWahyu Al FatihNoch keine Bewertungen
- Excel 2013: Pivot TablesDokument18 SeitenExcel 2013: Pivot TablesKhuda BukshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tally ERP 9: Shortcut Key For TallyDokument21 SeitenTally ERP 9: Shortcut Key For TallyDhurba Bahadur BkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Knowledge Bank ORIGINAL 2Dokument18 SeitenKnowledge Bank ORIGINAL 2Prakarsh SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beginner Tutorials: Salesforce Coding Lessons For The 99%Dokument85 SeitenBeginner Tutorials: Salesforce Coding Lessons For The 99%Ram KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ez Payment 2 UDokument12 SeitenEz Payment 2 USophy Sufian SulaimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- GST Invoice: Cdho Jilla Panchayat JunagadhDokument1 SeiteGST Invoice: Cdho Jilla Panchayat JunagadhOmkar DaveNoch keine Bewertungen