Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Cell Organelles Functions
Hochgeladen von
Seiji MingOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Cell Organelles Functions
Hochgeladen von
Seiji MingCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Name ____________________________ Period _____ Date _____________
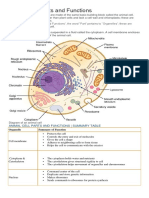
Cells and Their Organelles Cell Boundary Organelles
The cell is the basic unit of life. The following is a glossary of animal cell terms. All cells are surrounded by a cell membrane. The cell membrane is semipermeable, allowing some substances to pass into the cell and blocking others. It is composed of a double layer of phospholipids and embedded proteins. Color and
label the cell membrane black. Plant cells have an additional layer surrounding
them called the cell wall. The cell wall is made of nonliving material called cellulose. Color and label the cell wall light green.
Cell Control Center Organelles
The nucleus in the center of a cell is a spherical body containing the nucleolus that makes ribosomes. The nucleus controls many of the functions of the cell (by controlling protein synthesis). It also contains DNA assembled into chromosomes. The nucleus is surrounded by the nuclear membrane. Color and label the nucleolus gray, the nuclear membrane black, and the nucleoplasm yellow. Materials can move from the nucleus to the cytoplasm through nuclear pores in the membrane around the nucleus. Label the nuclear pores. Cytoplasm is the jellylike material outside the cell nucleus in which the organelles are located. Color and
label the cytoplasm white (blank). All cells, even prokaryotes contain small bodies
called ribosomes. Label the ribosomes. Proteins are made here by a process called protein synthesis. The centrosome (also called the "microtubule organizing center") is a small body located near the nucleus. The centrosome is where microtubules are made. During cell division (mitosis), the centrosome divides and the two parts move to opposite sides of the dividing cell. The centriole is the dense center of the centrosome. Only animal cells have centrosomes. Microtubules are shaped like soda straws and give the nucleus and cell its shape.
Label the microtubules inside the nucleus.
Cell Transport Organelles
Rough endoplasmic reticulum (rough ER) is a vast system of interconnected, membranous, infolded and convoluted sacks that are located in the cell's cytoplasm. The ER is continuous with the outer nuclear membrane. Rough ER is covered with ribosomes that give it a rough appearance. Color and label the rough ER orange. Rough ER transports materials through the cell and produces proteins in sacks which are sent to the Golgi body, or inserted into the cell membrane. The Golgi apparatus or Golgi complex is a flattened, layered, sac-like organelle that looks like a stack of pancakes. The Golgi body modifies & packages proteins and carbohydrates into membrane-bound vesicles for "export" from the cell. Color and label the Golgi export vesicles light blue. Smooth ER does NOT have ribosomes on its surface. It makes proteins and lipids that will be exported by the cell. It also controls the calcium level in muscles and detoxifies poisons, alcohol, and drugs. Color and label the smooth ER violet.
Cell Energy Organelles
Chloroplasts are elongated or disc-shaped organelles containing chlorophyll that trap sunlight for energy. Photosynthesis (in which energy from sunlight is converted into chemical energy - food) takes place in the chloroplasts. Only plant cells, not animal cells, can make their own food. Color and label the chloroplasts dark green. Cells also contain fluid-filled sacs called vacuoles. The vacuole fills with food being digested and waste material that is on its way out of the cell. In plant cells, a large central vacuole takes up most of the space in the cell. Color
and label the vacuoles pink. Mitochondria are spherical to rod-shaped organelles
with a double membrane. The inner membrane is infolded many times, forming a series of projections called cristae. The mitochondrion converts the energy stored in glucose into ATP (adenosine triphosphate) for the cell. Color and label the mitochondria red. Both mitochondria and chloroplasts have double membranes and their own DNA. Cells also contain spherical organelles called lysosomes that contain digestive enzymes. Nutrients are digested by the cell here, as well as, old cell organelles that are going to be recycled. Color and label the lysosomes pink.
1. Give the function of the nucleus.
2. What makes up the cell (plasma) membrane?
3. Where does cellular respiration take place?
4. Where does protein synthesis take place?
5. Where are ribosomes made?
6. Give two ways that an animal cell differs from a plant cell.
7. Do plant cells contain mitochondria? Explain.
8. How can you tell rough ER from smooth ER?
9. Where are cell products modified and packaged in vesicles for transport?
10. Where is DNA found in a cell?
11. Where would old cell organelles get broken down (digested) to be recycled in the cell?
Figure 2 Animal Cell
Color and label the organelles of the animal cell.
Figure 2 Plant Cell
Color and label the organelles of the plant cell.
12.
What process takes place inside chloroplasts?
13.
What is the energy for this process?
14.
What pigment traps the energy?
15.
Chloroplasts are found in what type of cell(s)?
16.
Both chloroplasts and mitochondria are like in that they both have _________________ membranes and their own _______.
17.
Food, water, and wastes are stored inside ______________.
18.
Digestion takes place inside _____________ containing _____________.
19.
The largest organelle in plants is the ____________ _____________.
20.
What organelle breaks down and recycles worn out cells?
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Cells and Organelles Coloring PagesDokument5 SeitenCells and Organelles Coloring Pagescarsontk421Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cells and Organelles Notes and Color SheetDokument7 SeitenCells and Organelles Notes and Color Sheetapi-236331206Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cells and Organelles Ws 2011Dokument8 SeitenCells and Organelles Ws 2011api-169639475Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dajana Lucaj - Cells & Their Organelles PDFDokument8 SeitenDajana Lucaj - Cells & Their Organelles PDFdajanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cells and OrganellesDokument8 SeitenCells and OrganellesWilliam RyandinataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Color and Label Color and Label .: Cells and Their OrganellesDokument4 SeitenColor and Label Color and Label .: Cells and Their OrganellesEllie GriffinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cells and Organelles - 1Dokument6 SeitenCells and Organelles - 1Izabayo philippeNoch keine Bewertungen
- The CellDokument14 SeitenThe CellDaniel NavarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Notes: Plant and Animal CellDokument4 SeitenScience Notes: Plant and Animal CellRosalinda LappayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksVon EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- Cell-The Fundamental Unit of Life: RibosomesDokument20 SeitenCell-The Fundamental Unit of Life: RibosomescbseiscNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hannah Belle Catharine M. Malinis Bsn1B: Assignment No. 1 - Cell OrganizationDokument5 SeitenHannah Belle Catharine M. Malinis Bsn1B: Assignment No. 1 - Cell OrganizationAngelo AbulenciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Biology:Cell Organalles For Class 9th Notes: 7th Maths 7th Science 8th Maths 8th Science 9th Maths CtetDokument10 SeitenCBSE Biology:Cell Organalles For Class 9th Notes: 7th Maths 7th Science 8th Maths 8th Science 9th Maths CtetWillSmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- PLB Plant Biology: Introduction To CellDokument9 SeitenPLB Plant Biology: Introduction To CellElle AdetounNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nucleoid: The Irregularly-Shaped Region Within A Prokaryote Cell Where The GeneticDokument5 SeitenNucleoid: The Irregularly-Shaped Region Within A Prokaryote Cell Where The GeneticHustler ZaydeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organelles Found in Both Animal and Plant CellsDokument3 SeitenOrganelles Found in Both Animal and Plant CellsDr.CharinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functions of A CellDokument4 SeitenFunctions of A CellyayayanizaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy of An Animal CellDokument4 SeitenAnatomy of An Animal CellYukiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Life Processes and Cells: Chapter 1:-Longman GCSE BiologyDokument16 SeitenLife Processes and Cells: Chapter 1:-Longman GCSE BiologynkllaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cells and Organelles New - Answer KEY - FinalDokument9 SeitenCells and Organelles New - Answer KEY - FinalMelyza Ann Pronebo50% (2)
- Cell NotesDokument10 SeitenCell Notesofwargod769Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gen BioCell TheoryDokument18 SeitenGen BioCell TheoryBernadeth CayaosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Coloring GuideDokument4 SeitenCell Coloring GuideCutie puppies 123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Structural and Functional Units of Living Organisms"Dokument12 SeitenBasic Structural and Functional Units of Living Organisms"cbseiscNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9th Class Notes Cell - The Fundamental Unit of LifeDokument6 Seiten9th Class Notes Cell - The Fundamental Unit of LifepralexprajapatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter - 5 Cell - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Class Ix Cbse - ScienceDokument34 SeitenChapter - 5 Cell - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Class Ix Cbse - ScienceMadhav DayareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animal Cell DefinitionDokument7 SeitenAnimal Cell DefinitionJoanne AlindayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animal Cell - The Definitive Guide Biology DictiDokument8 SeitenAnimal Cell - The Definitive Guide Biology DictiKolade YousuffNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Organelles - Notes Cell Theory Cells Are The Basic Unit of Life. The Cell Theory States ThatDokument7 SeitenCell Organelles - Notes Cell Theory Cells Are The Basic Unit of Life. The Cell Theory States ThatSpongie BobNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 7. Reading Materials - Cell Structure and Function 2021Dokument4 SeitenWeek 7. Reading Materials - Cell Structure and Function 2021yui kirigayayuukiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Organelles 2Dokument10 SeitenCell Organelles 2Hardik tyagiNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Basic Unit of Life: ObjectiveDokument4 SeitenThe Basic Unit of Life: ObjectiveHershell ContaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS RecapDokument17 SeitenCELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS RecapSonakshi Chavan100% (1)
- Nature of CellsDokument7 SeitenNature of CellsAdrian Lee VannorsdallNoch keine Bewertungen
- CellDokument7 SeitenCellPrashant PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animal and Plant CellsDokument14 SeitenAnimal and Plant Cellslea a delgadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology of The CELLDokument14 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology of The CELLlorelie asisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell and Cell Membrane: Patricia Caldani MSDokument51 SeitenCell and Cell Membrane: Patricia Caldani MSkittypattyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11a Revision Pack T1Dokument36 Seiten11a Revision Pack T1Najat BteichNoch keine Bewertungen
- The CellDokument6 SeitenThe CellshaniahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animal and Plant Cell Anatomy Detailed NotesDokument5 SeitenAnimal and Plant Cell Anatomy Detailed NotesMadeleine AgiusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant Cells Cristae Mitochondria Chloroplasts: The Following Is A Glossary of Plant Cell Anatomy TermsDokument15 SeitenPlant Cells Cristae Mitochondria Chloroplasts: The Following Is A Glossary of Plant Cell Anatomy TermsanyoyoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 2-Parts and Functions of The CellDokument45 SeitenTopic 2-Parts and Functions of The CellDe Guia, Yuan Loriene Nina100% (1)
- Lecture 2 CytoplasmmDokument46 SeitenLecture 2 Cytoplasmmdiyarberwari15Noch keine Bewertungen
- Structure and Nature of Living CellDokument11 SeitenStructure and Nature of Living CellKikiez PathanasriwongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animal and Plant CellsDokument3 SeitenAnimal and Plant CellsBeth AlcontinNoch keine Bewertungen
- cls9 cp5Dokument4 Seitencls9 cp5Pankaj PathakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Byjus Com Biology Cell OrganellesDokument26 SeitenByjus Com Biology Cell OrganellesᏗᏕᎥᎷ ᏗᏝᎥNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell and Its Function Class 8 NotesDokument4 SeitenCell and Its Function Class 8 NotesNavyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 - Cell Structure and Function - NotesDokument8 SeitenUnit 2 - Cell Structure and Function - Notesronel.jnmsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animal Cell Parts and Functions - Summary TableDokument16 SeitenAnimal Cell Parts and Functions - Summary TableAnnie Lyn Villamor100% (1)
- JetDokument14 SeitenJetAnnie Lyn VillamorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Organelles JigsawDokument10 SeitenCell Organelles JigsawSusan VictoriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Structure Function and PropertiesDokument10 SeitenCell Structure Function and PropertiesWanda JohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCB 203 EUKARYOTIC CELLDokument9 SeitenMCB 203 EUKARYOTIC CELLGabi taofeekatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamental Unit of LifeDokument5 SeitenFundamental Unit of Lifechabalalalulama5Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Classix Session3 Made by Purnima Sharma 1Dokument7 SeitenCell Classix Session3 Made by Purnima Sharma 1jeetjyoti787Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Following Is A Glossary of Plant Cell Anatomy Terms.: Plant Cells Cristae Mitochondria ChloroplastsDokument6 SeitenThe Following Is A Glossary of Plant Cell Anatomy Terms.: Plant Cells Cristae Mitochondria ChloroplastsHitesh MoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Animal Cell and Division Biology for Kids | Children's Biology BooksVon EverandThe Animal Cell and Division Biology for Kids | Children's Biology BooksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reviewer Midterm PathfitDokument2 SeitenReviewer Midterm PathfitMelendez, Abegail T.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Process of DigestionDokument4 SeitenProcess of DigestionKennard LIONGNoch keine Bewertungen
- TrafficDokument9 SeitenTrafficMelanie LaginanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Histology Course OutlineDokument1 SeiteHistology Course Outlineakifuji913100% (1)
- Science9 TGDokument327 SeitenScience9 TGEmma rebellonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surgical Anatomy of The Biliary TractDokument5 SeitenSurgical Anatomy of The Biliary TracthoangducnamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Note Making and Note TakingDokument33 SeitenNote Making and Note TakingManisha SalikarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neuro Complete ReviewDokument138 SeitenNeuro Complete ReviewMohsin FarooqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Four Chambers of The HeartDokument7 SeitenFour Chambers of The HeartJohn TecsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual Nervous SystemDokument6 SeitenManual Nervous SystemVynz Morales CosepNoch keine Bewertungen
- NAME: Christan Y. Tabia SECTION: B1-G12-05-STEM STM 007: General Biology 1 2 Performance TaskDokument12 SeitenNAME: Christan Y. Tabia SECTION: B1-G12-05-STEM STM 007: General Biology 1 2 Performance TaskTan TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCTB 2010 Class IXX Secondary BiologyDokument268 SeitenNCTB 2010 Class IXX Secondary BiologySenku Ishigami67% (3)
- Tristianti Nur Khasanah 180205136 18a3Dokument3 SeitenTristianti Nur Khasanah 180205136 18a3Tristianti NurkhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- @teamfunnymewat: Rank Booster Test SeriesDokument33 Seiten@teamfunnymewat: Rank Booster Test SeriesKirtan shuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 29 Child With CancerDokument9 SeitenChapter 29 Child With CancerMARCERA JERALDINE ALESSA P.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Malignancies of The Female Reproductive SystemDokument61 SeitenMalignancies of The Female Reproductive SystemMakanjuola Osuolale John50% (2)
- Different Types of Eggs With Example PDFDokument8 SeitenDifferent Types of Eggs With Example PDFAniruddh JhanwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tortora Aus1e ch09Dokument44 SeitenTortora Aus1e ch09jonas hingcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lectures No 4 Introduction & Method of Tissue Preparation & Specimen Reception & FixationDokument27 SeitenLectures No 4 Introduction & Method of Tissue Preparation & Specimen Reception & FixationAbdallah AlasalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomic Therapy PDFDokument364 SeitenAnatomic Therapy PDFrahul_choubey_9Noch keine Bewertungen
- Thyroid Gland Embryology, Anatomy, and Physiology: Gerard V. Walls and Radu MihaiDokument13 SeitenThyroid Gland Embryology, Anatomy, and Physiology: Gerard V. Walls and Radu MihaiKiara VelasquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Suggestive Questions of Icse Biology 2022 - 2nd Sem - April 2022Dokument2 SeitenSuggestive Questions of Icse Biology 2022 - 2nd Sem - April 2022Akshit BindhaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thomas H. Huxley Lessons in Elementary PhysiologyDokument481 SeitenThomas H. Huxley Lessons in Elementary PhysiologyAMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immunology NotesDokument6 SeitenImmunology NotesJesse ChengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Histopathology of Some Diseased Fishes: M. Kabil Hossain, M. Delwar Hossain and M. Habibur RahmanDokument4 SeitenHistopathology of Some Diseased Fishes: M. Kabil Hossain, M. Delwar Hossain and M. Habibur RahmanSoni AndriawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec2 - Primary HemostasisDokument28 SeitenLec2 - Primary HemostasisClaire GonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATOTW 136 Major Haemorrhage Part 1 2009Dokument6 SeitenATOTW 136 Major Haemorrhage Part 1 2009viaereaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reproductive SystemDokument6 SeitenReproductive SystemanojanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vet Terminology 1Dokument125 SeitenVet Terminology 1cassandroskomplexNoch keine Bewertungen
- Head and Neck Cancer - Reconstruction: HistoryDokument6 SeitenHead and Neck Cancer - Reconstruction: HistorySri MahyantiNoch keine Bewertungen