Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Life Processes
Hochgeladen von
Himanshu TalwarOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Life Processes
Hochgeladen von
Himanshu TalwarCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
6.
Life Processes
Life processes Continuously perform the functions of maintenance in living organisms Examples- digestion, respiration, circulation etc. Nutrition Process of obtaining nutrients from the environment Two types - autotrophic and heterotrophic Autotrophic nutrition Synthesis of food by photosynthesis Sunlight Photosynthesis equation- 6CO2 + 6H 2O C6 H12O6 + 6O2 chlorophyll Events of photosynthesis Absorption of light energy Splitting of water in hydrogen and oxygen Synthesis of ATP and NADPH2 Reduction of CO2 to carbohydrates Heterotrophic nutrition Generally derive energy from plants and animal sources Mainly of three typesholozoic, parasitic, and saprophytic Digestion- mechanical and chemical reduction of ingested nutrients Human digestive system- consists of the long alimentary canal Alimentary canal includes- mouth, pharynx, oesophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine Accessory organs- pancreas, liver Nutrition in humans
Saliva is secreted by salivary glands located under the tongue. It contains a digestive enzyme salivary amylase, which breaks down starch into sugar. Tongue helps in chewing and swallowing of food. The food from mouth passes down the oesophagus to the stomach, through the movement of walls of oesophagus (peristalsis) Stomach mixes the food received from oesophagus with digestive juices. Inner lining of stomach secretes: Mucus protects the lining of stomach Hydrochloric acid creates an acidic medium and dissolves bits of food. Digestive juices break down protein into simple substance The food from stomach moves into the small intestine. Digestion in small intestine It is the longest part (about 7.5 m long) of alimentary canal. It is the site where complete digestion of carbohydrate, proteins, and fats takes place. It receives intestinal juice from two glands liver and pancreas that help in further digestion of food. Liver - It is the largest gland of the body and secretes bile juice. Bile juice is stored in gall bladder and it plays an important role in the digestion of fats. Pancreas - Pancreas contains enzymes that help in complete digestion of all food components. The digestive tract and associated glands together constitute the digestive system. Respiration
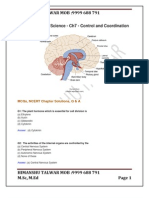
Enzymatically- controlled energy released from the breakdown of organic substances Two types- aerobic and anaerobic Aerobic respiration Oxidation of food materials with the help of oxygen Yields 36 ATP Steps in cellular respiration First step- breakdown of glucose (6C) into pyruvates (3C); takes place in the cytoplasm Second step- pyruvate is broken down to CO2 and water; takes place in mitochondria, energy produced in the form of ATP. Anaerobic respiration Oxidation of nutrients without utilizing molecular oxygen Yields 2 ATP First step- glycolysis (occurs in the cytoplasm), 2 pyruvate produced Second step- break down of pyruvic acid into ethanol and water and energy (in yeast) and lactic acid and energy (in muscle cells) Human respiration Includes the nose, pharynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles and alveoli
Bronchioles divide to form many alveoli Alveoli are sites of gas exchange O2 present in alveolar blood vessels transported to body cells
Hemoglobin pigment present in blood is mainly responsible for the transport of carbon dioxide and oxygen. Transportation
A liquid medium is required
Transportation in humans In human there occurs double circulation i.e. the blood goes through the heart twice during each cardiac cycle. Blood, lymph- involved in transportation Components of blood- RBCs, WBCs, platelets, and plasma Three types of blood vessels- arteries, veins and capillaries Arteries carry oxygenated blood, except pulmonary artery Veins carry deoxygenated blood, except pulmonary vein Human heart is divided into four chambers right auricle, right ventricle, left auricle, and left ventricle
Right side of the heart receives deoxygenated blood from all cells of the body Left side of the heart receives oxygenated blood from lungs. Transportation in plants Transport of water-xylem Transport of water occurs due to transpiration pull, root pressure and difference in pressure gradient. Transport of food (translocation) through phloem; it requires energy. Excretion Involves removal of harmful metabolic wastes from the body
Excretion in humans
Consists of- a pair of kidneys, a pair of ureters, a urinary bladder, and a urethra Nitrogenous wastes such as urea and uric acid are removed Nephron- basic filtration unit Main components of the nephron - glomerulus, Bowmans capsule, renal tube Removal of nitrogenous wastes through artificial kidney is called dialysis **
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Cost Benefit Analysis - Basic ExampleDokument1 SeiteCost Benefit Analysis - Basic ExampleHimanshu TalwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Arithmetic ProgressionDokument8 SeitenArithmetic ProgressionHimanshu TalwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- New+Terms+Important+for+PMP+Exam+-+Drag+Drop Fill+In ScenariosDokument6 SeitenNew+Terms+Important+for+PMP+Exam+-+Drag+Drop Fill+In ScenariosHimanshu TalwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Risk Project ExperienceDokument11 SeitenRisk Project ExperienceHimanshu TalwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Making of The Global WorldDokument79 SeitenThe Making of The Global WorldHimanshu TalwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Coordinate GeometryDokument6 SeitenCoordinate GeometryHimanshu TalwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Grade 8 - Subject Enrichment ActivitiesDokument5 SeitenGrade 8 - Subject Enrichment ActivitiesHimanshu Talwar100% (1)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- 10 Gender, Religion & Catse Solu.-1Dokument3 Seiten10 Gender, Religion & Catse Solu.-1Himanshu TalwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- CLASS 8 SOCIAL SCIENCE Booklet 2021-2022 LatestDokument68 SeitenCLASS 8 SOCIAL SCIENCE Booklet 2021-2022 LatestHimanshu TalwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Class 8 Computer Science Booklet 2021-2022Dokument83 SeitenClass 8 Computer Science Booklet 2021-2022Himanshu TalwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CLASS 8 ENGLISH Booklet 2021-2022 PDFDokument86 SeitenCLASS 8 ENGLISH Booklet 2021-2022 PDFHimanshu TalwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- 10th TrigoDokument3 Seiten10th TrigoHimanshu TalwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Delhi Public School, Bangalore SouthDokument41 SeitenDelhi Public School, Bangalore SouthHimanshu TalwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Class 8 Science BookletDokument66 SeitenClass 8 Science BookletHimanshu TalwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- USA CMA Part 2 2021 Syllabus in DetailDokument4 SeitenUSA CMA Part 2 2021 Syllabus in DetailHimanshu TalwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Fill The Following Information:-: Full Name: Date of Birth: Permanent AddressDokument1 SeiteFill The Following Information:-: Full Name: Date of Birth: Permanent AddressHimanshu TalwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chart of AccountsDokument8 SeitenChart of AccountsHimanshu TalwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 and 9 CompatibilitiesDokument1 Seite6 and 9 CompatibilitiesHimanshu TalwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- What Is SAP COPA?: Key Components in SAP CO-PADokument2 SeitenWhat Is SAP COPA?: Key Components in SAP CO-PAHimanshu TalwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- USA CMA Part 1 2021 Syllabus in DetailDokument4 SeitenUSA CMA Part 1 2021 Syllabus in DetailHimanshu TalwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control and Coordination IIDokument12 SeitenControl and Coordination IIHimanshu TalwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Course Notes Part IDokument61 SeitenCourse Notes Part IWayne TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Light NotesiiiDokument6 SeitenLight NotesiiiHimanshu TalwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indirect Direct SpeechDokument1 SeiteIndirect Direct SpeechHimanshu TalwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- The TributeDokument1 SeiteThe TributeHimanshu TalwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignments For First Term Class - IX BiologyDokument3 SeitenAssignments For First Term Class - IX BiologyHimanshu TalwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Correctly Spelt Word Practice - 1 For SSC CGL 2012 MainsDokument1 SeiteCorrectly Spelt Word Practice - 1 For SSC CGL 2012 MainsHimanshu TalwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 12 English Core Exam Paper 2011 Set 1Dokument11 SeitenCBSE Class 12 English Core Exam Paper 2011 Set 1Himanshu TalwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Indigo by Louis Fischer Question BankDokument2 SeitenIndigo by Louis Fischer Question BankHimanshu TalwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deleciones Multiexon en COL1A2Dokument7 SeitenDeleciones Multiexon en COL1A2Alejandra ObandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Project The Walking DeadDokument11 SeitenBiology Project The Walking Deadapi-276956420Noch keine Bewertungen
- Immunology Paper 1 Past PapersDokument15 SeitenImmunology Paper 1 Past PapersRehab KhaledNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment-1 Genetics 341Dokument4 SeitenAssignment-1 Genetics 341damionsimmons10Noch keine Bewertungen
- Plant Tissue Culture (PDFDrive)Dokument223 SeitenPlant Tissue Culture (PDFDrive)MdNasirHaiderNooriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Watermelon Seedless ColchicineDokument12 SeitenWatermelon Seedless ColchicineCatalina BanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Supra SobDokument34 SeitenSupra SobZakaria NersNoch keine Bewertungen
- PPSC Lecturer Zoology Mcqs DAtaDokument9 SeitenPPSC Lecturer Zoology Mcqs DAtaEjaz KazmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Methods of Bacterial Isolation and Culture and Preservation Microbial Isolation Techniques NotesDokument4 SeitenMethods of Bacterial Isolation and Culture and Preservation Microbial Isolation Techniques Notesmervyn balbuenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SolutionDokument3 SeitenSolutionSiddhant DwivediNoch keine Bewertungen
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Karyotype Analysis of Lablab PurpureusDokument1 SeiteKaryotype Analysis of Lablab PurpureusZain JawadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Materi Dr. MayaDokument33 SeitenMateri Dr. MayaNishi RuciNoch keine Bewertungen
- ArticuloDokument11 SeitenArticuloalvarogascareinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 23 Anatomy Physiology TermsDokument30 Seiten23 Anatomy Physiology TermsAlyssa Gwyneth GalubaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GM Food (IB MYP Essay)Dokument10 SeitenGM Food (IB MYP Essay)Trippin OnAcidNoch keine Bewertungen
- COVID-19 Alvin RinaldoDokument21 SeitenCOVID-19 Alvin RinaldoAlvin RinaldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gel Electrophoresis IDokument6 SeitenGel Electrophoresis ISalvador MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Molecular Mechanisms and Physiological Importance of Circadian RhythmsDokument18 SeitenMolecular Mechanisms and Physiological Importance of Circadian Rhythmsngthathu.taNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stem Cell TherapyDokument64 SeitenStem Cell Therapyjeyacharles88% (26)
- Merzenich,.+changing+brains +applying+brain+plasticity+to+advance+and+recover+human+abilityDokument465 SeitenMerzenich,.+changing+brains +applying+brain+plasticity+to+advance+and+recover+human+abilityYasmin S Fonseca100% (1)
- 3 16 I Quit Sugar 7 Successful Secrets For Healing Your Microbiome With FoodDokument3 Seiten3 16 I Quit Sugar 7 Successful Secrets For Healing Your Microbiome With FoodClaudia100% (1)
- Reproduction SystemDokument38 SeitenReproduction SystemNurfatin AdilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genetics and Genomics in Nursing Health Care 2nd EditionDokument61 SeitenGenetics and Genomics in Nursing Health Care 2nd Editionjulia.swanson282100% (44)
- HistotechniquesDokument47 SeitenHistotechniquesJean VipinosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digestive SystemDokument143 SeitenDigestive SystemCarlos Enrique Pijo PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Rice Research Notes Vol.19 No.3Dokument64 SeitenInternational Rice Research Notes Vol.19 No.3ccquintosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biomarker Guide Refreshed 2Dokument18 SeitenBiomarker Guide Refreshed 2Rezi KirvalidzeNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Artigo) KYALANGALILWA Et Al 2013 Phylogenetic Classification Acacia Vachellia SenegaliaDokument24 Seiten(Artigo) KYALANGALILWA Et Al 2013 Phylogenetic Classification Acacia Vachellia SenegaliaRafael GuimarãesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microbiological and Phytochemical Analyses of Some Selected Herbal Mixtures Sold in NigeriaDokument5 SeitenMicrobiological and Phytochemical Analyses of Some Selected Herbal Mixtures Sold in NigeriaIJAR JOURNALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Local Media3371875718567533646Dokument2 SeitenLocal Media3371875718567533646Rufa NarioNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossVon EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (6)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityVon EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (28)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsVon EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeVon EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeBewertung: 2 von 5 Sternen2/5 (1)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDVon EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionVon EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (404)