Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Disorders of The Thyroid1
Hochgeladen von
Saddamix AL Omari0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
53 Ansichten22 SeitenHyperthyroidism is present when the thyroid gland is over secreting hormones. Females are more prone to developing Grave's disease along with hyperthyroid. A normal total T3 level is 80-230 ng / dL.
Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Disorders of the Thyroid1
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
PPT, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenHyperthyroidism is present when the thyroid gland is over secreting hormones. Females are more prone to developing Grave's disease along with hyperthyroid. A normal total T3 level is 80-230 ng / dL.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
53 Ansichten22 SeitenDisorders of The Thyroid1
Hochgeladen von
Saddamix AL OmariHyperthyroidism is present when the thyroid gland is over secreting hormones. Females are more prone to developing Grave's disease along with hyperthyroid. A normal total T3 level is 80-230 ng / dL.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 22
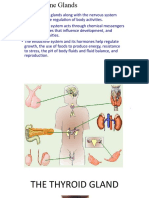
Disorders of the Thyroid
Actions of the thyroid
Controls body temperature
How body burns calories
Controls how fast food
moves through digestive
tract
Muscle strength
Thyroid hormones:
T3-thyroxine
T4-triiodothyronine
Calcitonin
Normal Thyroid Gland
Synthesis of thyroid hormone depends upon
sufficient quantities of iodine from dietary
source. The rate of extraction of iodine from
the blood stream and the rate at which T
3
and
T
4
and synthesized and released from storage
(as thyroglobulin) and secreted into the
bloodstream are regulated by pituitary TSH.
TSH is regulated by Thyrotropin-Releasing
hormone from hypothalamus. Serum T
3
and
T
4
are bound to albumin and thyroid-binding
globulin (TBG).
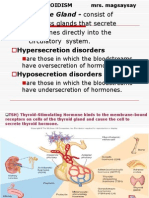
Hyperthyroidism is present when the thyroid
gland is over secreting hormones.
Thus, increasing the metabolic rate of the body
and speeding up the body.
Hyperthyroidism
Graves disease(autoimmune disorder ).
A benign nodule on the thyroid.
Thyroiditis.
Taking too much of the synthetic thyroid
hormone.
Causes of Hyperthyroidism
Diarrhea and weight loss
Eye problems
Enlarged thyroid gland
Hair and skin changes
Heat intolerance
Heart palpitations
Clubbing
Menstrual cycle changes
Muscle weakness
Easily bruised
Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism
Nervousness
Restlessness
Anxiety
Irritability
Sleeplessness or insomnia
Exhaustion
Emotional Symptoms of
Hyperthyroidism
How do we diagnosis these disorders??
Thyroid stimulation hormone (TSH) test
Normal levels of TSH are 0.4-4.5milliunits/L.
Thyroid hormone test
In adults, a normal total T3 level is 80-230 ng/dL. Total
T4 levels should be at 5-14 mcg/dL.
Diagnostics
Who is more prone to develop
Graves disease??
Female are more prone to
developing Graves disease along
with Hyperthyroidism. Due to a
genetic background of both
disorders, I have a greater risk.
With Graves Disease, the immune system begins
to attack the thyroid and produces antibodies
that mimic TSH.
Women are more likely to develop Graves
disease.
Hereditary and environmental influences.
Graves Disease
Goiter:
It is a general term for enlargement of thyroid
gland.It occurs whenever there is elevation of TSH or
TSI.
Goiter may occurs in hypothyroidism (as low thyroid
hormones in low iodine with increase TSH), and
hyperthyroidism (hyper-secretion of TSH caused by
hypothalamic or pituitary causes or Graves disease
with increase TSI).
It is caused by: OPhysiological enlargement: it is
seen mostly in puberty and pregnancyOIodine
deficiency: it occurs in geographic area where diet is
deficient in iodine O Hashimotos thyroiditis O
Goitrogens: they are foods or drugs that suppress
synthesis of thyroid hormone.
Radioactive iodine
Typical treatment is 3-12 millicuries.
However, this treatment can cause hypothyroidism.
It must also be followed by thyroid replacing
hormones.
Beta-Blockers
Antithyroid medication-Propylthiouracil (PTU) or
Tapazole
Treatments for Hyperthyroidism
Hypothyroidism is present when the thyroid
gland is producing little or no thyroid
hormones. Thus slowing things down....
Hypothyroidism
Thyroiditis
Treatment for hyperthyroidism
Congenital hypothyroidism
Radiation therapy given to the head and/or
neck
Causes of Hypothyroidism
Myxedema: it is more common
in women than men. It is
manifested in adult. CPuffiness of
face, eyelids and handsC Dry
skinCHair loss, coarse and brittle
hair, scant axillary and pubic hair,
thining of the lateral aspect of the
eyebrowC increase in relaxation
phase of deep tendon reflex.
Cases of myxedema: OTherapy for
hyperthyroidism with surgery, irradiation, or
drugs is the most common cause of
myxedema in US.OUnknown cause (primary
idio-pathic myxedema) is secondary most
common form of myxedema, which may be
of auto-immune origin. OHashimotos
thyroiditisODrugs (as Lithium
carbonate)OIodine deficiency: is the most
important causes in some geographic area
(Himalayas, Andes and central Africa).
Clinical characteristics of myxedema:OGeneral:
Tiredness, somnolence, weight gain, and cold
intoleranceOCVS: bradycardia, hypertension, angina,
cardiac failureOCNS: delay relaxation of tendon,
depression,mental and physical slowness, muscle
stiffness ODermatology: Dry skin, alopecia, Puffiness
of face, eyelid, and handsOReproduction: Menorrhagia,
impotanceOGIT: constipation.
Cretinism: It is manifested in children. It is
characterized by: OSever mental
retardationOimpairment of physical growth with
retardate bone development and dwarfismOlarge
tongueOprotuberant abdomen.
Cold intolerance
Slow digestion
Weight gain
Fatigue
Thin, coarse hair
Brittle fingernails
Muscle aches
Dizziness
Ringing in ears
Numbness
Carpal tunnel
Poor memory
Skin changes
Voice changes
Milky discharge from
breasts
Symptoms of Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism can be linked to psychiatric
depression.
Roughly 15% of all patients suffering from
depression are found to be hypothyroid.
Some symptoms found are:
Paranoia
Aural and Visual hallucinations
Emotional Symptoms of
Hypothyroidism
How do we diagnosis these disorders??
Thyroid stimulation hormone (TSH) test
Normal levels of TSH are 0.4-4.5milliunits/L.
Thyroid hormone test
In adults, a normal total T3 level is 80-230 ng/dL. Total
T4 levels should be at 5-14 mcg/dL.
Diagnostics
Thyroid replacement pills-most common
Some medicines can cause hypothyroidism.
Stop the medication and symptoms should cease.
Treatment of Hypothyroidism
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Thyroid Diet: How to Improve Thyroid Disorders, Manage Thyroid Symptoms, Lose Weight, and Improve Your Metabolism through Diet!Von EverandThyroid Diet: How to Improve Thyroid Disorders, Manage Thyroid Symptoms, Lose Weight, and Improve Your Metabolism through Diet!Noch keine Bewertungen
- Thyroid DiseaseDokument30 SeitenThyroid Diseasemy Lord JesusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypo Thyroids MDokument26 SeitenHypo Thyroids MBridget NjambiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thyroid and Adrenal MedullaDokument32 SeitenThyroid and Adrenal MedullaDipika RawatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypothyroidism Diagnosis and TreatmentDokument23 SeitenHypothyroidism Diagnosis and TreatmentShafern TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- HPERTHYROIDISMDokument4 SeitenHPERTHYROIDISMSalwa KaramanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 4 - Alteration of Hormonal RegulationDokument17 SeitenGroup 4 - Alteration of Hormonal RegulationMarcus KaglNoch keine Bewertungen
- ThyroidDokument18 SeitenThyroidLhojhi MathaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thyroid DisordersDokument55 SeitenThyroid DisordersNsubuga Ivan100% (1)
- Thyroid DisordersDokument66 SeitenThyroid DisordersJOY SANDHYA JOSEPH (RA2123003011002)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hyperthyroidism and HypothyroidismDokument59 SeitenHyperthyroidism and HypothyroidismJun AmaroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of EndocrinologyDokument25 SeitenPathophysiology of EndocrinologyISRAELNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functions of The Thyroid GlandDokument3 SeitenFunctions of The Thyroid Glandred888342193Noch keine Bewertungen
- Thyroid Gland Dont Erase Ate KatDokument24 SeitenThyroid Gland Dont Erase Ate KatThess Tecla Zerauc AzodnemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thyrotoxicosi S: Dr.P.Viswakumar M.S Assistant Professor, Dept of General Surgery, PsgimsrDokument57 SeitenThyrotoxicosi S: Dr.P.Viswakumar M.S Assistant Professor, Dept of General Surgery, PsgimsrpurnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 4Dokument36 SeitenLecture 4tamtamtamtama0Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of Endocrine SystemDokument64 SeitenPathophysiology of Endocrine SystemTess MohamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypo Thyroid Is MDokument27 SeitenHypo Thyroid Is Mdhiraj parmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thiroid DisordersDokument11 SeitenThiroid Disordersرعد النميريNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypothyroidism (Underactive)Dokument3 SeitenHypothyroidism (Underactive)jhNoch keine Bewertungen
- ThyrotoxicosisDokument105 SeitenThyrotoxicosisAli Murtaza Abbas100% (1)
- Hypothyroidism: Erbil Polytechnic University Erbil Health Technical College MLT Department Third Stage Group: CDokument5 SeitenHypothyroidism: Erbil Polytechnic University Erbil Health Technical College MLT Department Third Stage Group: CRayan JabbarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thyroid Disorders: Medical Surgical NursingDokument20 SeitenThyroid Disorders: Medical Surgical Nursingthanuja mathewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypothyroidism: Regulation of Thyroid HormoneDokument4 SeitenHypothyroidism: Regulation of Thyroid HormoneAmer Abdulla SachitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gabriel Chacón - ULA (VE) - Pharmacy - 1041 Physiopathology - Subject 4 - Endocrine DisordersDokument8 SeitenGabriel Chacón - ULA (VE) - Pharmacy - 1041 Physiopathology - Subject 4 - Endocrine DisordersGabriel ChacónNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thyroid Gland Diseases in ChildrenDokument29 SeitenThyroid Gland Diseases in ChildrenadinayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study of Hypothroidism SAHIL GUNJALDokument27 SeitenCase Study of Hypothroidism SAHIL GUNJALDarling DadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hyperthyroidism 2011Dokument30 SeitenHyperthyroidism 2011Elyza MagsaysayNoch keine Bewertungen
- ThyroidDokument20 SeitenThyroidako798918Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hyperthyroidism Vs Hypothyroidism: Ngmontecillo SSLC 1ST SEM 2021-2022Dokument76 SeitenHyperthyroidism Vs Hypothyroidism: Ngmontecillo SSLC 1ST SEM 2021-2022Giovanne BuendiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HypothyroidismDokument7 SeitenHypothyroidismavinash dhameriyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GoiterDokument48 SeitenGoiterRizki NurNoch keine Bewertungen
- 35thyroid DisordersDokument21 Seiten35thyroid DisordersDurga VoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- HYPOTHYROIDISM (Underactive Thyroid)Dokument16 SeitenHYPOTHYROIDISM (Underactive Thyroid)Jerika Shane MañosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Goiter: Prepared By: Felix Kevin M. Villa Iv, RNDokument47 SeitenGoiter: Prepared By: Felix Kevin M. Villa Iv, RNFelix Kevin VillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hperthyroidism 1Dokument4 SeitenHperthyroidism 1Salwa KaramanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thyroid and ParathyroidDokument29 SeitenThyroid and Parathyroidpranutan739Noch keine Bewertungen
- HipothiroidDokument27 SeitenHipothiroidYuji AdityaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Archivo en Ingles-Patologias TiroideasDokument4 SeitenArchivo en Ingles-Patologias Tiroideasesther avilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thyroid Gland An Diseases of Thyroid D Gland: Omc LectureDokument59 SeitenThyroid Gland An Diseases of Thyroid D Gland: Omc LectureEdward MakemboNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is HyperthyroidismDokument7 SeitenWhat Is HyperthyroidismGelo LeañoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hyperthyroidism & HypothyroidismDokument109 SeitenHyperthyroidism & Hypothyroidismmadelynmas75% (4)
- Hypothyroidism (Underactive Thyroid)_ Symptoms, Causes, Tests, TreatmentsDokument9 SeitenHypothyroidism (Underactive Thyroid)_ Symptoms, Causes, Tests, TreatmentsHannah Denise BatallangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypothyroidism: ClassificationDokument9 SeitenHypothyroidism: Classificationpali_sakshamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Main Thyroid DiseasesDokument25 SeitenMain Thyroid DiseasesPurnima ChoudhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of HyperthyroidismDokument97 SeitenPathophysiology of HyperthyroidismMarie Joyce SablanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypothyroidism: Practice EssentialsDokument32 SeitenHypothyroidism: Practice EssentialsEdinson Cabrera MenesesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thyroid Disorders in ChildrenDokument30 SeitenThyroid Disorders in ChildrenZm100% (1)
- Thyroid DisorderDokument16 SeitenThyroid DisorderfahadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diagnosis and Evaluation of Thyroid DisordersDokument21 SeitenDiagnosis and Evaluation of Thyroid DisordersIvan AditamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dr.Rihab Pediatrics 04.HypothyroidismDokument7 SeitenDr.Rihab Pediatrics 04.HypothyroidismMujtaba JawadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sahil Gunjal HypothyroidismDokument30 SeitenSahil Gunjal HypothyroidismSahil ShaikhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wo Week 4 (Hyperthyroidism)Dokument12 SeitenWo Week 4 (Hyperthyroidism)Theddyon BhenlieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thyrotoxicosis Seb 4Dokument35 SeitenThyrotoxicosis Seb 4Bersisa chalchisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thyroid Disorders Guide: Causes, Symptoms & TreatmentsDokument81 SeitenThyroid Disorders Guide: Causes, Symptoms & Treatmentschetankumarbhumireddy50% (2)
- Case Study of Hypothroidism NEWDokument27 SeitenCase Study of Hypothroidism NEWDarling DadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Thyroid Gland PathologyDokument138 SeitenUnderstanding Thyroid Gland PathologyRizky anandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypothyroidism: By: Judhaimah Mardhiah BT Mat Tari 0810544Dokument23 SeitenHypothyroidism: By: Judhaimah Mardhiah BT Mat Tari 0810544Jujue MardhiahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypothyroidism, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsVon EverandHypothyroidism, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Renal Structure and FunctionDokument35 SeitenRenal Structure and FunctionSaddamix AL OmariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antifungals 2011Dokument38 SeitenAntifungals 2011Saddamix AL OmariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Renal PathologyDokument31 SeitenRenal PathologySaddamix AL OmariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Peptic Ulcer Disease: Mashehabat@just - Edu.joDokument46 SeitenPeptic Ulcer Disease: Mashehabat@just - Edu.joSaddamix AL Omari100% (1)
- Blood Pressure RegulationDokument35 SeitenBlood Pressure RegulationSaddamix AL OmariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thyroid Drugs Student VersionDokument36 SeitenThyroid Drugs Student VersionSaddamix AL OmariNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Gonadal Hormones & InhibitorsDokument41 SeitenThe Gonadal Hormones & InhibitorsSaddamix AL OmariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine SystemDokument39 SeitenEndocrine SystemSaddamix AL OmariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adrenal Cortex: - Divided Into Three Zones - Zona Glomerulosa (Outer Layer) ProducesDokument25 SeitenAdrenal Cortex: - Divided Into Three Zones - Zona Glomerulosa (Outer Layer) ProducesSaddamix AL OmariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine SystemDokument39 SeitenEndocrine SystemSaddamix AL OmariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adrenocorticosteroids & Adrenocortical AntagonistsDokument34 SeitenAdrenocorticosteroids & Adrenocortical AntagonistsSaddamix AL OmariNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPR LectureDokument25 SeitenCPR LectureSaddamix AL OmariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pancreatic Hormones & Antidiabetic DrugsDokument41 SeitenPancreatic Hormones & Antidiabetic DrugsSaddamix AL OmariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pancreatic Hormones & Antidiabetic DrugsDokument41 SeitenPancreatic Hormones & Antidiabetic DrugsSaddamix AL OmariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antivirals UpdatedDokument42 SeitenAntivirals UpdatedSaddamix AL OmariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antiparasitic Medications: Dr. Meera Ababneh, Pharm.D, PHDDokument39 SeitenAntiparasitic Medications: Dr. Meera Ababneh, Pharm.D, PHDSaddamix AL OmariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Congestive Heart Failurebody SystemDokument48 SeitenCongestive Heart Failurebody SystemSaddamix AL OmariNoch keine Bewertungen
- ArrhythmiaDokument30 SeitenArrhythmiaSaddamix AL OmariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs Affecting The Cardiovascular System: Mashehabat@just - Edu.joDokument24 SeitenDrugs Affecting The Cardiovascular System: Mashehabat@just - Edu.joSaddamix AL OmariNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1) Review For The Cardiovascular SystemDokument84 Seiten1) Review For The Cardiovascular SystemSaddamix AL OmariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shock 1Dokument33 SeitenShock 1Saddamix AL OmariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypertension: Prepared by DR - Mustafa AlshehabatDokument25 SeitenHypertension: Prepared by DR - Mustafa AlshehabatSaddamix AL OmariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pneumonia+ TB 24-3Dokument20 SeitenPneumonia+ TB 24-3Saddamix AL OmariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pulmonary PathoPhysiologyDokument45 SeitenPulmonary PathoPhysiologySuliman Garalleh100% (1)
- Structure and Function of The Pulmonary SystemDokument30 SeitenStructure and Function of The Pulmonary SystemSuliman GarallehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Headache 1Dokument23 SeitenHeadache 1Saddamix AL OmariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Epilepsy in Adults A Basic IntroductionDokument40 SeitenEpilepsy in Adults A Basic IntroductionSaddamix AL OmariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diabetes Mellitus: Dr. Othman Al-Shboul Department of PhysiologyDokument28 SeitenDiabetes Mellitus: Dr. Othman Al-Shboul Department of PhysiologySaddamix AL OmariNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Basal Ganglia Mashehabat@just - Edu.joDokument62 SeitenThe Basal Ganglia Mashehabat@just - Edu.joSaddamix AL OmariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thyroid Disease in PregnancyDokument53 SeitenThyroid Disease in PregnancyTee Wei SianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hyperthyroidism Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and TreatmentDokument40 SeitenHyperthyroidism Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and TreatmentEmmanuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced thyroid exam: Inspecting, palpating gland & lymph nodesDokument44 SeitenAdvanced thyroid exam: Inspecting, palpating gland & lymph nodesAbdurehman AyeleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Preboards 2 - NP3 (Printable)Dokument10 SeitenPreboards 2 - NP3 (Printable)Joana Marie DomingoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Graves Disease - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDokument8 SeitenGraves Disease - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDr.Pradip PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diagnosis of Hyperthyroidism - UpToDateDokument24 SeitenDiagnosis of Hyperthyroidism - UpToDateEfrain Coral PantojaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BNS 2nd YEAR 2023 ReviseDokument20 SeitenBNS 2nd YEAR 2023 ReviseshadabkhanskNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subclinical Hyperthyroidism: To Treat or Not To Treat?: Best PracticeDokument5 SeitenSubclinical Hyperthyroidism: To Treat or Not To Treat?: Best PracticeRaka MahasaduNoch keine Bewertungen
- MRCS Clinical 3 1Dokument47 SeitenMRCS Clinical 3 1Alexandros Megas100% (1)
- Calculating drug dosages and conversionsDokument3 SeitenCalculating drug dosages and conversionsNina CasasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10clinical VignettespdfDokument71 Seiten10clinical VignettespdfKerin Ardy100% (1)
- Portafolio IcpnaDokument8 SeitenPortafolio IcpnaAngélicaAntuanetteVargasNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Child With Endocrine/Metabolic Dysfunction: Thyroid Gland DisordersDokument17 SeitenThe Child With Endocrine/Metabolic Dysfunction: Thyroid Gland DisordersMeccanazaren Susvilla BojorqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine Tess 1-7Dokument41 SeitenEndocrine Tess 1-7필리우크Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2020 NeoPREP Syllabus Book 1 - Fri-Sat PDFDokument383 Seiten2020 NeoPREP Syllabus Book 1 - Fri-Sat PDFPaty Juárez100% (2)
- Usmle Woreld MedicineDokument108 SeitenUsmle Woreld MedicineSaeed HasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neoplastic Thyroid Disease - Thyroid Nodules Goiter and Thyroid CancerDokument57 SeitenNeoplastic Thyroid Disease - Thyroid Nodules Goiter and Thyroid CancerNavya SreeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thyroid Profile: Test Report Mr. Jogi Reddy N 50 Years / Male 230120006631Dokument1 SeiteThyroid Profile: Test Report Mr. Jogi Reddy N 50 Years / Male 230120006631NALLA SUDEEP REDDYNoch keine Bewertungen
- 72 Endo AnnotatedDokument9 Seiten72 Endo AnnotatedErika ArceoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thyroid PathologyDokument9 SeitenThyroid PathologyNada MuchNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan HyperthyroidismDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan HyperthyroidismAbdallah Alasal0% (1)
- Cobalamin in Companion AnimalsDokument8 SeitenCobalamin in Companion AnimalsFlávia UchôaNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Pha) Le 5Dokument19 Seiten(Pha) Le 5Gabby TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thyroid Hormones: Thyroid Gland - Structure and FunctionDokument11 SeitenThyroid Hormones: Thyroid Gland - Structure and FunctionWaleed W Al-AzharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- THYROID FUNCTION TESTS DSL PACKAGEDokument7 SeitenTHYROID FUNCTION TESTS DSL PACKAGEUmar AzlanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thyroid DisorderDokument16 SeitenThyroid DisorderKen TokkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surgery & Pediatrics SurgeryDokument111 SeitenSurgery & Pediatrics SurgeryHIMANSHU GUPTANoch keine Bewertungen
- ОВБ-2 Ответы фулDokument70 SeitenОВБ-2 Ответы фулMoldir AkynbayNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANTERIOR PITUITARY DISORDERS AND THYROID CONDITIONSDokument4 SeitenANTERIOR PITUITARY DISORDERS AND THYROID CONDITIONSJe LynNoch keine Bewertungen