Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
CH 02 Student PPT Slides
Hochgeladen von
Izzah Zabidi Danial ShaufiOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
CH 02 Student PPT Slides
Hochgeladen von
Izzah Zabidi Danial ShaufiCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
2
Analyzing the External Environment of the Firm
McGraw-Hill/Irwin Strategic Management: Text and Cases, 4e Copyright 2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
2-3
Learning Objectives
After reading this chapter, you should have a good understanding of:
-
The importance of developing forecasts of the business environment. Why environmental scanning, environmental monitoring, and collecting competitive intelligence are critical inputs to forecasting. Why scenario planning is a useful technique for firms competing in industries characterized by unpredictability and change. The impact of the general environment on a firms strategies and performance.
2-4
Learning Objectives
After reading this chapter, you should have a good understanding of:
How forces in the competitive environment can affect profitability and how a firm can improve its competitive position by increasing its power vis--vis these forces. How trends and events in the general environment and forces in the competitive environment are interrelated and affect performance. How the intranet and digitally based compatibilities are affecting the five competitive forces and industry profitability. The concept of strategic groups and their strategy and performance implications.
2-5
Creating the Environmentally Aware Organization
2-6
Environmental Scanning & Monitoring
External Scanning
- Surveillance of a firms external environment:
Predict environmental changes to come Detect changes already under way Proactive mode
External Monitoring
- Track evolution of:
Environmental trends Sequence of events Streams of activities
2-7
Competitive Intelligence
Define and understand a firms industry Identify rivals strengths and weaknesses
- Intelligence gathering (data) - Interpretation of intelligence data
Helps a firm avoid surprises
2-8
Environmental Forecasting
Plausible projections about
Direction of environmental change Scope of environmental change Speed of environmental change Intensity of environmental change
Scenario analysis
2-9
SWOT Analysis
Managers need to analyze
- The general environment - The firms industry and competitive advantage
SWOT analysis
Strengths Weaknesses Opportunities Threats Basic technique for analyzing firm and industry condition
2 - 10
The General Environment
Segments of the general environment include:
Demographic Sociocultural Legal/Political Technological Economic Global
General Environmen t
General environmental trends and events:
- Little ability to predict them - Even less ability to control them - Can vary across industries
2 - 11
The Competitive Environment
Segments of the competitive environment include:
- Competitors - Customers - Suppliers
Competitive Environment
Sometimes called the task or industry environment Porters five forces model
2 - 12
Porters Five Forces Model of Industry Competition
2 - 13
How the Internet and Digital Technologies Influences Industry
2 - 14
Using Industry Analyses: A Few Caveats
Five Forces analysis implicitly assumes a zero-sum game Five Forces analysis is essentially a static analysis
- Value net
Suppliers and customers (the vertical net) Substitutes and complements (the horizontal net)
2 - 15
The Value Net
2 - 16
Strategic Groups within Industries
Two unassailable assumptions in industry analysis
- No two firms are totally different - No two firms are exactly the same
Strategic groups Cluster of firms that share similar strategies
Breadth of product and geographic scope Price/quality Degree of vertical integration Type of distribution system
2 - 17
Strategic Groups within Industries
Value of strategic groups as an analytical tool
- Identify barriers to mobility that protect a group from attacks by other groups - Identify groups whose competitive position may be marginal or tenuous - Chart the future direction of firms strategies - Thinking through the implications of each industry trend for the strategic group as a whole
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 2nd Week - Strategic ManagementDokument26 Seiten2nd Week - Strategic ManagementHari Camel IINoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of The External EnvironmentDokument40 SeitenAnalysis of The External EnvironmentJoseyyyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Environmental AnalysisDokument43 SeitenEnvironmental AnalysisShivangi Dhamija100% (1)
- Module 2Dokument32 SeitenModule 2Brian Daniel BayotNoch keine Bewertungen
- MBA 401 Strategic ManagementDokument74 SeitenMBA 401 Strategic ManagementAkhand PratapNoch keine Bewertungen
- Environmental Appraisal: 2 Year MBA Group 3Dokument37 SeitenEnvironmental Appraisal: 2 Year MBA Group 3Megha ThackerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Session 2 Environmental Appraisal and Organizational AppraisalDokument33 SeitenSession 2 Environmental Appraisal and Organizational AppraisalNarayana ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic Management: #2 - Environmental Scanning: ExternalDokument39 SeitenStrategic Management: #2 - Environmental Scanning: ExternalDeasy Dwi PratiwiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ch13 SDLCDokument45 Seitench13 SDLCCarmina Pangan100% (1)
- Analyzing A CompanyDokument10 SeitenAnalyzing A CompanyMars MaguenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Environmental Scanning and Industry Analysis: Unit IIDokument41 SeitenEnvironmental Scanning and Industry Analysis: Unit IIhimanshuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 External-Analysis 2019 NewDokument89 Seiten3 External-Analysis 2019 NewMd HimelNoch keine Bewertungen
- External Environment Analysis - 2021 - For StudentsDokument58 SeitenExternal Environment Analysis - 2021 - For StudentsLan Anh NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- The External Environment AnalysisDokument6 SeitenThe External Environment AnalysisThanh VânNoch keine Bewertungen
- External Environmental AnalysisDokument44 SeitenExternal Environmental AnalysisgoelgeetNoch keine Bewertungen
- External Environmental AnalysisDokument44 SeitenExternal Environmental AnalysisZakaria HaiderNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Strategic PositionDokument41 SeitenThe Strategic PositionMariaDotNoch keine Bewertungen
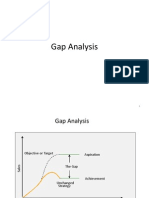
- Gap, ETOP Analyses, BSCDokument28 SeitenGap, ETOP Analyses, BSCniaz11788Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 13Dokument41 SeitenChapter 13PrashantNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 2Dokument23 SeitenCH 2Reema LaserNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic Management Chapter-2Dokument27 SeitenStrategic Management Chapter-2Towhidul HoqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 2 3 Op StrategyDokument11 SeitenLec 2 3 Op StrategyJEFF SHIKALINoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 The External Environment AnalysisDokument14 Seiten2 The External Environment Analysisltquang.raitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic Management Chap2Dokument3 SeitenStrategic Management Chap2leztly93Noch keine Bewertungen
- Formulation of Manufacturing StrategyDokument30 SeitenFormulation of Manufacturing StrategywaqasalitunioNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is External Analysis?Dokument6 SeitenWhat Is External Analysis?nanda tyasNoch keine Bewertungen
- The External Environment: by Prof. Pradip K. MukherjeeDokument33 SeitenThe External Environment: by Prof. Pradip K. MukherjeeDipesh TekchandaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3.1Dokument30 SeitenChapter 3.1Andrea EdejerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic Analysis: - Identify Issues in A Firm's External & Internal Environment Which Open Up Avenues ToDokument15 SeitenStrategic Analysis: - Identify Issues in A Firm's External & Internal Environment Which Open Up Avenues Toprabin ghimireNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sbaa1504 - Business Policy and Strategy - Unit Ii - PPT (3) 2Dokument55 SeitenSbaa1504 - Business Policy and Strategy - Unit Ii - PPT (3) 2abcdNoch keine Bewertungen
- The External Environment: Opportunities, Threats, Industry Competition, Competitive Dynamics and Competitor AnalysisDokument37 SeitenThe External Environment: Opportunities, Threats, Industry Competition, Competitive Dynamics and Competitor AnalysisShashank GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic EvaluationDokument54 SeitenStrategic EvaluationanviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Envrnmnt Scan TechDokument25 SeitenEnvrnmnt Scan TechVandana SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- External Environment AnalysisDokument16 SeitenExternal Environment Analysisshubhamagarwal63Noch keine Bewertungen
- Babz 1Dokument31 SeitenBabz 1Tiana TillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACFrOgBPa6ArtFy7uoEv0R8uYuPS4FrwCChqn02 I8yWvdk48w1c4qFsnQCtzXxmP70f4suZ7x ZgdE WgFdScqLiKlU4HvMC5Y GHfZOZC7sons5UQ2RJlpLcKUQ9MiY WCavS5lsoE9I8wNCQDokument89 SeitenACFrOgBPa6ArtFy7uoEv0R8uYuPS4FrwCChqn02 I8yWvdk48w1c4qFsnQCtzXxmP70f4suZ7x ZgdE WgFdScqLiKlU4HvMC5Y GHfZOZC7sons5UQ2RJlpLcKUQ9MiY WCavS5lsoE9I8wNCQfahadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Two The Business EnvironmentDokument57 SeitenChapter Two The Business EnvironmentBinyam TesfamariamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 2 Lecture Slides PDFDokument38 SeitenWeek 2 Lecture Slides PDFlegolasckkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic Planning and ImplementationDokument13 SeitenStrategic Planning and ImplementationShiva LKLNoch keine Bewertungen
- BMGT Slides ExamDokument272 SeitenBMGT Slides ExamNhung NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business EnvironmentDokument30 SeitenBusiness EnvironmentDr. Khem ChandNoch keine Bewertungen
- IDC MarketScape IT Project and Portfolio Management 2009Dokument54 SeitenIDC MarketScape IT Project and Portfolio Management 2009Quarry CeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adv. Lean Conc. 6Dokument9 SeitenAdv. Lean Conc. 6AlexNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business EnviromentDokument40 SeitenBusiness EnviromentMalav NanavatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Harley Davidson Case Study - Strategic Framework: 1 Assignment 1.1 Guidelines Mentioned in ClassDokument9 SeitenHarley Davidson Case Study - Strategic Framework: 1 Assignment 1.1 Guidelines Mentioned in ClassillavdmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 2 Dess Strategic Management SlideDokument37 SeitenChap 2 Dess Strategic Management SlideTMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson IV. Analyzing The External Environment of The Firm & Lesson V Assessing The Internal Environment of The Firm 4252022 2Dokument68 SeitenLesson IV. Analyzing The External Environment of The Firm & Lesson V Assessing The Internal Environment of The Firm 4252022 2Neekah JoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACC311 Week 1 NotesDokument8 SeitenACC311 Week 1 NotesCynthia LautaruNoch keine Bewertungen
- MGT 657 Strategic Management: The External AssessmentDokument22 SeitenMGT 657 Strategic Management: The External AssessmentabdibaasidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 - Organizational Strategy & Project SelectionDokument27 SeitenChapter 2 - Organizational Strategy & Project SelectionAliImranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Three External and Internal Environment AnalysisDokument49 SeitenChapter Three External and Internal Environment AnalysisEndalkachew Abebe KassuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management, 8/E: Powerpoint Presentation To Accompany Chapter 9 ofDokument42 SeitenManagement, 8/E: Powerpoint Presentation To Accompany Chapter 9 ofgowthamjayamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 Strategic Management..Ppt (Compatibility Mode) (Repaired)Dokument95 SeitenUnit 2 Strategic Management..Ppt (Compatibility Mode) (Repaired)vasudevprasad100% (1)
- Driver Monitoring Systems Market To Escalate $7.74 Billion by 2020-IndustryARCDokument10 SeitenDriver Monitoring Systems Market To Escalate $7.74 Billion by 2020-IndustryARCAutomotiveIARCNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Two Environment and Resource AnalysisDokument47 SeitenChapter Two Environment and Resource AnalysisSehabom GeberhiwotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic ManagementDokument36 SeitenStrategic Managementpoojakyad4Noch keine Bewertungen
- As SBM - Strategic AnalysisDokument53 SeitenAs SBM - Strategic AnalysisMd.Shakhawath HossainNoch keine Bewertungen
- DSKP KSSR Semakan Year 1 2017Dokument45 SeitenDSKP KSSR Semakan Year 1 2017Izzah Zabidi Danial ShaufiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interactive WhiteboardsDokument3 SeitenInteractive WhiteboardsIzzah Zabidi Danial ShaufiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3rd AssignmentDokument4 Seiten3rd AssignmentIzzah Zabidi Danial ShaufiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3rd AssignmentDokument4 Seiten3rd AssignmentIzzah Zabidi Danial ShaufiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 02 Student PPT SlidesDokument17 SeitenCH 02 Student PPT SlidesIzzah Zabidi Danial ShaufiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ELT ArticleDokument14 SeitenELT ArticletieyafathiyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Informer 37 PDFDokument32 SeitenInformer 37 PDFthesmartsakthiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Proposal For Online Student ManagementDokument2 SeitenProject Proposal For Online Student ManagementEmrul Hasan70% (33)
- Sicam TM 1703 MicDokument6 SeitenSicam TM 1703 MicIbrar H MalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Auto MechanicDokument34 SeitenAuto MechanicRaisul Haque RahatNoch keine Bewertungen
- AUTOSAR SWS DiagnosticEventManagerDokument511 SeitenAUTOSAR SWS DiagnosticEventManagerchinna0% (1)
- BYOD Case StudyDokument6 SeitenBYOD Case StudyBelner BelninhoNoch keine Bewertungen
- A High Gain Microstrip Patch Array For 5 GHZ Wlan ApplicationsDokument6 SeitenA High Gain Microstrip Patch Array For 5 GHZ Wlan ApplicationsYossef ARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ovhd Panel PDFDokument6 SeitenOvhd Panel PDFNickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Equipment Check ListDokument3 SeitenElectrical Equipment Check ListPuran Singh LabanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- May 2017 Monthly Disbursement ReportDokument186 SeitenMay 2017 Monthly Disbursement ReportPl PlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Guide LineDokument8 SeitenProject Guide LineAjay Adit J (RA1911018010031)Noch keine Bewertungen
- STS Module 7Dokument9 SeitenSTS Module 7Leshlengg LanwangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cimr-Vu2a0020faa SBDokument19 SeitenCimr-Vu2a0020faa SBعبد الكريم ملوحNoch keine Bewertungen
- Honda Common Service ManualDokument769 SeitenHonda Common Service ManualPradeep Kumar SukumaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power System Manager Mcu - 07-02Dokument8 SeitenPower System Manager Mcu - 07-02Hillary McgowanNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Model For The Lean IT Organization - Mark McDonaldDokument5 SeitenA Model For The Lean IT Organization - Mark McDonaldLucianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Java Terminology-3157Dokument5 SeitenJava Terminology-3157CEO OF BOLLYWOODNoch keine Bewertungen
- Apt Tanks For Fire Services: Volume One - Issued February 5, 2013Dokument8 SeitenApt Tanks For Fire Services: Volume One - Issued February 5, 2013kusmaryantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Company Overview: Private and ConfidentialDokument15 SeitenCompany Overview: Private and Confidentialkyne87Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 1 Sound EditingDokument8 SeitenLesson 1 Sound Editingyl04130Noch keine Bewertungen
- Avr 505 ManualDokument34 SeitenAvr 505 ManualaxxelloneNoch keine Bewertungen
- DevOps With Ansible, Chef and PowerVCDokument35 SeitenDevOps With Ansible, Chef and PowerVCAmit KaushikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Training Manual For National E-Government Procurement System of NepalDokument38 SeitenTraining Manual For National E-Government Procurement System of NepalRanjan Raj KoiralaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Programs Using 8051Dokument13 SeitenPrograms Using 8051Sasi BhushanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chiller IQ Checklist - 2021.05Dokument2 SeitenChiller IQ Checklist - 2021.05Yu-Chih PuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Id Ash Boards Turn Your Data Into InsightDokument10 SeitenId Ash Boards Turn Your Data Into InsightThiago LimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Role Based Home Pages R14.2Dokument148 SeitenRole Based Home Pages R14.2CHARLES TUMWESIGYENoch keine Bewertungen
- ABB Dry Type Transformer Safety, Reliability & Enviromental ImpactDokument41 SeitenABB Dry Type Transformer Safety, Reliability & Enviromental ImpactHari SantosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Main Report Nov 08 Final With Disclaimer June 09Dokument151 SeitenMain Report Nov 08 Final With Disclaimer June 09Arun KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary: The 5AM Club: Own Your Morning. Elevate Your Life. by Robin Sharma: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisVon EverandSummary: The 5AM Club: Own Your Morning. Elevate Your Life. by Robin Sharma: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (22)
- Summary of Noah Kagan's Million Dollar WeekendVon EverandSummary of Noah Kagan's Million Dollar WeekendBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- The Millionaire Fastlane: Crack the Code to Wealth and Live Rich for a LifetimeVon EverandThe Millionaire Fastlane: Crack the Code to Wealth and Live Rich for a LifetimeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (2)
- Leadership and Self-Deception: Getting out of the BoxVon EverandLeadership and Self-Deception: Getting out of the BoxBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (156)
- The Coaching Habit: Say Less, Ask More & Change the Way You Lead ForeverVon EverandThe Coaching Habit: Say Less, Ask More & Change the Way You Lead ForeverBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (186)
- The First Minute: How to start conversations that get resultsVon EverandThe First Minute: How to start conversations that get resultsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (57)
- 24 Assets: Create a digital, scalable, valuable and fun business that will thrive in a fast changing worldVon Everand24 Assets: Create a digital, scalable, valuable and fun business that will thrive in a fast changing worldBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (20)
- Brain Rules (Updated and Expanded): 12 Principles for Surviving and Thriving at Work, Home, and SchoolVon EverandBrain Rules (Updated and Expanded): 12 Principles for Surviving and Thriving at Work, Home, and SchoolBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (702)
- How to Talk to Anyone at Work: 72 Little Tricks for Big Success Communicating on the JobVon EverandHow to Talk to Anyone at Work: 72 Little Tricks for Big Success Communicating on the JobBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (37)
- Summary of Leaders Eat Last: Why Some Teams Pull Together and Others Don't by Simon SinekVon EverandSummary of Leaders Eat Last: Why Some Teams Pull Together and Others Don't by Simon SinekBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (142)
- Scaling Up: How a Few Companies Make It...and Why the Rest Don't, Rockefeller Habits 2.0Von EverandScaling Up: How a Few Companies Make It...and Why the Rest Don't, Rockefeller Habits 2.0Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Think Remarkable: 9 Paths to Transform Your Life and Make a DifferenceVon EverandThink Remarkable: 9 Paths to Transform Your Life and Make a DifferenceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary of Steven Bartlett's The Diary of a CEOVon EverandSummary of Steven Bartlett's The Diary of a CEOBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (4)
- Transformed: Moving to the Product Operating ModelVon EverandTransformed: Moving to the Product Operating ModelBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- The Catalyst: How to Change Anyone's MindVon EverandThe Catalyst: How to Change Anyone's MindBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (274)
- How to Win Friends and Influence People: Updated For the Next Generation of LeadersVon EverandHow to Win Friends and Influence People: Updated For the Next Generation of LeadersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (151)
- The 5 Languages of Appreciation in the Workplace: Empowering Organizations by Encouraging PeopleVon EverandThe 5 Languages of Appreciation in the Workplace: Empowering Organizations by Encouraging PeopleBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (46)
- TED Talks: The Official TED Guide to Public SpeakingVon EverandTED Talks: The Official TED Guide to Public SpeakingBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (210)
- Billion Dollar Lessons: What You Can Learn from the Most Inexcusable Business Failures of the Last Twenty-five YearsVon EverandBillion Dollar Lessons: What You Can Learn from the Most Inexcusable Business Failures of the Last Twenty-five YearsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (52)
- How to Lead: Wisdom from the World's Greatest CEOs, Founders, and Game ChangersVon EverandHow to Lead: Wisdom from the World's Greatest CEOs, Founders, and Game ChangersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (95)
- The Power of People Skills: How to Eliminate 90% of Your HR Problems and Dramatically Increase Team and Company Morale and PerformanceVon EverandThe Power of People Skills: How to Eliminate 90% of Your HR Problems and Dramatically Increase Team and Company Morale and PerformanceBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (22)
- Built to Serve: Find Your Purpose and Become the Leader You Were Born to BeVon EverandBuilt to Serve: Find Your Purpose and Become the Leader You Were Born to BeBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (24)
- Everyone Communicates, Few Connect: What the Most Effective People Do DifferentlyVon EverandEveryone Communicates, Few Connect: What the Most Effective People Do DifferentlyBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (347)
- Follow The Leader: A Collection Of The Best Lectures On LeadershipVon EverandFollow The Leader: A Collection Of The Best Lectures On LeadershipBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (122)
- Entreleadership: 20 Years of Practical Business Wisdom from the TrenchesVon EverandEntreleadership: 20 Years of Practical Business Wisdom from the TrenchesBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (186)
- How To Win Friends And Influence PeopleVon EverandHow To Win Friends And Influence PeopleBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (6518)
- Soundtracks: The Surprising Solution to OverthinkingVon EverandSoundtracks: The Surprising Solution to OverthinkingBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (19)