Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Amity Business School: MBA Class of 2013, Semester II
Hochgeladen von
chitra1490Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Amity Business School: MBA Class of 2013, Semester II
Hochgeladen von
chitra1490Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Amity Business School
Amity Business School
MBA Class of 2013, Semester II
FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
Module I
BHAVNA RANJAN
1
Amity Business School
COURSE OBJECTIVE
To develop an understanding of short-term and long-term
financial decisions of a firm and various financial tools used in
taking these decisions.
To develop the understanding of the financial environment in
which a company operates and how it copes with it.
Credit Units 04
Syllabus
2
Amity Business School
Evaluation Plan
Components %age Marks
External Evaluation 70
Attendance 05
Mid Sem Test 10
Term paper 10
Class test 05 (2.5+2.5)
Total 100
3
Amity Business School
FINANCE - CONCEPT
Finance may be defined as the art and science of
managing money.
Financial Management is that managerial activity which is
concerned with the planning and controlling of the firms
financial resources.
It encompasses the procurement of the funds in the most
economic and prudent manner and employment of these
funds in the most optimum way to maximize the return to the
owner.
4
Amity Business School
FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
According to Van Horne and Wachowicz
Financial Management is concerned with the acquisition,
financing and management of assets with some overall goal in
mind
5
Amity Business School
EVOLUTION OF FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
Modern phase
Transitional phase
Traditional phase
Amity Business School
OVERVIEW OF FINANCIAL
MANAGEMENT
Amity Business School
FINANCIAL DECISION MAKING / FUNCTIONS OF
FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
Financial
Decisions
Investment
Decision
Financing
Decision
Dividend
Decision
Amity Business School
a) Investment Decision
The investment decision relates to the selection of assets in
which funds will be invested by a firm.
The assets which can be acquired fall into two broad groups:
(a) Long-term assets (Capital Budgeting)
(b) Short-term or current assets (Working Capital
Management)
9
Amity Business School
Investment Decision
Selection of assets in which funds will be invested by a firm
Fixed Assets
Current Assets
Capital Budgeting
Decisions
Working Capital
Management
Amity Business School
b) Financing Decision
The concern of the financing decision is with the financing-mix
or capital structure or leverage. There are two aspects of the
financing decision.
a) Capital Structure decisions
b) Cost of capital
11
Amity Business School
Financing Decision
Decisions relating to the debt-equity mix of the firm.
Borrowed Funds
Debentures
Long term Loans
Shareholders Funds
Equity share Capital
Preference share Capital
Amity Business School
c) Dividend Policy Decision
The dividend decision should be analyzed in relation to the
financing decision of a firm. Two alternatives are available in
dealing with the profits of a firm:
(i) they can be distributed to the shareholders in the form of
dividends or
(ii) they can be retained in the business itself.
13
Amity Business School
Dividend Decision
Decisions relating to the payout and reinvestment
of the Profit After Tax(PAT)
Deciding the Dividend
Payout
Ratio
Deciding the proportion of
profits to be retained
in the business
Amity Business School
KEY ACTIVITIES OF FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
Financial Analysis, Planning and Control
Management of
firms financial
structure
Balance Sheet
Management of
firm s asset
structure
Long Term
Financing
Long Term assets
Short Term
Financing
Short Term assets
Amity Business School
OBJECTIVES OF FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
Objectives of
financial
management
Profit
Maximization
Approach
Wealth
Maximization
Approach
Amity Business School
a) Profit Maximization Approach
The term Profit in the Profit maximization concept can be used
in two senses
- Owner oriented concept
- Operational concept
Technical Flaws of the concept
- Ambiguity
- Timing of benefits
- It ignores risk
17
Amity Business School
( ) ( ) ( )
)
`
+
+
+
+
+
n
n
k
A
k
A
k
A
1
___
1 1
2
2
1
1
W = V C
Where W = Value of the firm/ Net Present Worth
V = Gross Present worth
C = Investment
V =
b) Wealth Maximization Approach
Amity Business School
ORGANISATION OF FINANCE FUNCTION
In small firms, the finance functions are generally performed by
the accounting departments.
In large firms, there is a separate department of finance headed
by a specialist known by different designations such as vice-
president, director of finance, chief finance officer and so on.
19
Amity Business School
ORGANISATION OF FINANCE FUNCTION
Board of Directors
Managing Director/Chairman
Vice-President/Director (Finance)/Chief Finance Officer (CFO)
Treasurer
Controller
Financial
planning and
fund-raising
manager
Cash
Manager
Credit
Manager
Foreign
exchange
manager
Tax
manager
Cost
accounting
manager
Capital
expenditure
manager
Pension
fund
manager
Corporate
accounting
manager
Financial
accounting
manager
Organisation of Financial Management Function
Amity Business School
Role of The Financial Manager
Financial
manager
Firm's
operations
Financial
markets
(1) Cash raised from investors
(1)
(2) Cash invested in firm
(2)
(3) Cash generated by operations
(3)
(4a) Cash reinvested
(4a)
(4b) Cash returned to investors
(4b)
Amity Business School
22
1. Investment analysis
2. Working capital management
3. Sources and cost of funds
4. Determination of capital structure
5. Dividend policy
6. Analysis of risks and returns
Primary Disciplines
Accounting
Macroeconomics
Microeconomics
Other Related Disciplines
Marketing
Production
Quantitative methods
Shareholder wealth maximization
Financial Decision Areas
Support
Support
Resulting in
Figure 1: Impact of Other Disciplines on Financial Management
FINANCE AND RELATED DISCIPLINES
Amity Business School
EMERGING ROLE OF FINANCE MANAGERS
IN INDIA
Reflecting the emerging economic and financial environment
in the post-liberalization era since the early nineties, the
role/job of finance managers in India has become more
important, complex and demanding. The key challenges are in
the areas of
(1) financial structure,
(2) foreign exchange management,
(3) treasury operations,
(4) investor communication,
(5) management control and
(6) investment planning. 23
Amity Business School
AGENCY PROBLEM
There is a Principal Agent relationship between managers and
shareholders.
In theory, Managers should act in the best interests of
shareholders.
In practice, managers may maximise their own wealth (in the
form of high salaries and perks) at the cost of shareholders.
This conflict is known as Agency problem and it results into
Agency costs.
24
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- SFM-chapter 1Dokument24 SeitenSFM-chapter 1animut silesheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Corporate FinanceDokument22 SeitenIntroduction To Corporate FinanceTushar GargNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACC 312 - Financial Management Lecture NotesDokument239 SeitenACC 312 - Financial Management Lecture NotesAmber MomentNoch keine Bewertungen
- P. Financial Management 2020Dokument99 SeitenP. Financial Management 2020hayenje rebeccaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Finance and Corporate Finance.Dokument22 SeitenFinance and Corporate Finance.SHIVA THAVANINoch keine Bewertungen
- CH - 01 - Financial Management An OverviewDokument37 SeitenCH - 01 - Financial Management An OverviewSanchit AroraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial ManagementDokument97 SeitenFinancial ManagementGuruKPO100% (17)
- SLM-19617-B Com-Financial ManagementDokument148 SeitenSLM-19617-B Com-Financial ManagementMohammed RasiqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Corporate FinanceDokument22 SeitenIntroduction To Corporate FinancebusebeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Objectives and Scope of Financial ManagementDokument62 SeitenObjectives and Scope of Financial ManagementCharles MateoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bba3b05 Financial ManagementDokument164 SeitenBba3b05 Financial ManagementMohammed MubeenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ajit Das - 18133008 (A-1)Dokument13 SeitenAjit Das - 18133008 (A-1)Ajit DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financialmanagementpondicherry 140323121153 Phpapp01Dokument70 SeitenFinancialmanagementpondicherry 140323121153 Phpapp01Nguyen Dac ThichNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Financial ManagementDokument24 SeitenIntroduction To Financial ManagementPasa YanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MFL - AE19-FM - Module 11Dokument35 SeitenMFL - AE19-FM - Module 11Jemalyn PiliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 2 To 4Dokument33 SeitenLecture 2 To 4Nakul GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- FinMan AE 19 Module 1 Intro To FinManDokument8 SeitenFinMan AE 19 Module 1 Intro To FinManMILLARE, Teddy Glo B.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Financial Management: Unit IDokument37 SeitenIntroduction To Financial Management: Unit IkunalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial ManagementDokument48 SeitenFinancial ManagementAishu SathyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 Introduction - Chapter 2 Industrial ProfileDokument74 SeitenChapter 1 Introduction - Chapter 2 Industrial Profilebalki123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 - Introduction To Financial ManagementDokument27 SeitenUnit 1 - Introduction To Financial Managementharsh gawliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial ManagementDokument107 SeitenFinancial ManagementFarshan SulaimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit - 3 - Acma CMC 653Dokument192 SeitenUnit - 3 - Acma CMC 653sakshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-I FMDokument31 SeitenUnit-I FMAishvarya PujarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 Scope and Objectives of Financial Management 2Dokument19 SeitenChapter 1 Scope and Objectives of Financial Management 2Pandit Niraj Dilip SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FM1.1 2017Dokument67 SeitenFM1.1 2017Mridul PantNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corporte Finance Financial Management - : CMA Ramesh RajagopalanDokument93 SeitenCorporte Finance Financial Management - : CMA Ramesh RajagopalanRU ShenoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Management & Its Area of ActivitiesDokument13 SeitenFinancial Management & Its Area of ActivitiesAjit DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Management - Meaning, Objectives and FunctionsDokument5 SeitenFinancial Management - Meaning, Objectives and FunctionsRuchi ChhabraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Management: Chapter - IDokument26 SeitenFinancial Management: Chapter - IAryan GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial ManagementDokument8 SeitenFinancial ManagementAfifaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Management: Unit IDokument72 SeitenFinancial Management: Unit IE-sabat RizviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Management: Unit IDokument72 SeitenFinancial Management: Unit Isubhash_92Noch keine Bewertungen
- Winter Semester 2023-24 - MGT2006 - TH - AP2023246000029 - 2024-01-18 - Reference-Material-IDokument19 SeitenWinter Semester 2023-24 - MGT2006 - TH - AP2023246000029 - 2024-01-18 - Reference-Material-Isujithsai2004Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Financial Management 2024Dokument27 SeitenIntroduction To Financial Management 2024rezerracerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial ManagementDokument60 SeitenFinancial ManagementDEAN TENDEKAI CHIKOWONoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial ManagementDokument17 SeitenFinancial Managementnivedita singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nature and Scope of Financial Management MINI 1 - 1Dokument22 SeitenNature and Scope of Financial Management MINI 1 - 1Prakash KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Managment m1-2010Dokument29 SeitenFinancial Managment m1-2010pavithragowtham100% (1)
- Financial ManagementDokument6 SeitenFinancial Managementarchana_anuragiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intro I M PandeyDokument29 SeitenIntro I M PandeySandeep SaraswatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Basic Elements of Financial ManagementDokument27 SeitenIntroduction To Basic Elements of Financial Managementvansh.s3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 Introduction To Financial ManagementDokument12 SeitenUnit 1 Introduction To Financial ManagementPRIYA KUMARINoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 - Financial Policy and Corporate StrategyDokument12 SeitenChapter 1 - Financial Policy and Corporate Strategysungate007100% (8)
- Chapter 1Dokument24 SeitenChapter 1fentawmelaku1993Noch keine Bewertungen
- ABM 104 Financial ManagementDokument20 SeitenABM 104 Financial ManagementGenner RazNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACCN09B Strategic Cost Management 1: For Use As Instructional Materials OnlyDokument3 SeitenACCN09B Strategic Cost Management 1: For Use As Instructional Materials OnlyAdrienne Nicole MercadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Financial ManagementDokument18 SeitenIntroduction To Financial ManagementAahaanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Management - NotesDokument39 SeitenFinancial Management - NotesdollyguptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Financial ManagementDokument23 SeitenIntroduction To Financial ManagementLifeatsiem Rajpur100% (6)
- Financial Management - NotesDokument49 SeitenFinancial Management - NotesSoniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial ManagementDokument17 SeitenFinancial ManagementSmita PriyadarshiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wel Come To Ambo UniversityDokument52 SeitenWel Come To Ambo Universityalex266Noch keine Bewertungen
- ABM 104 Financial Management Course PackDokument9 SeitenABM 104 Financial Management Course PackGenner RazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gikondo Rusizi - Ur - Cbe Managerial Finance Notes April 2023 April 2023Dokument324 SeitenGikondo Rusizi - Ur - Cbe Managerial Finance Notes April 2023 April 2023Cyiza Ben RubenNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 1Dokument41 SeitenCH 1bjr_shagyounNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Literacy for Entrepreneurs: Understanding the Numbers Behind Your BusinessVon EverandFinancial Literacy for Entrepreneurs: Understanding the Numbers Behind Your BusinessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accounting and Finance for Business Strategic PlanningVon EverandAccounting and Finance for Business Strategic PlanningNoch keine Bewertungen
- CMC Business PlanDokument32 SeitenCMC Business PlanRobert ShisokaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Roddy Lawsuit DismissedDokument66 SeitenRoddy Lawsuit DismissedThe Huntsville TimesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual Stiga VILLA 92 MDokument6 SeitenManual Stiga VILLA 92 MCzesław WierzchowskiNoch keine Bewertungen
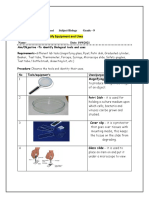
- Activity 1-Introduce Biological ToolsDokument3 SeitenActivity 1-Introduce Biological ToolsHaroldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sage Publications, LTDDokument25 SeitenSage Publications, LTDAntonio ScaliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory ShakerDokument2 SeitenLaboratory ShakeradhgachaswNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fields and Galois Theory: J.S. MilneDokument138 SeitenFields and Galois Theory: J.S. MilneUzoma Nnaemeka TeflondonNoch keine Bewertungen
- COMSATS University Islamabad, Lahore Campus: Assignment No. 01 - Spring 2019Dokument2 SeitenCOMSATS University Islamabad, Lahore Campus: Assignment No. 01 - Spring 2019waseem iftikharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Entrepreneurship in The PhilippinesDokument7 SeitenEntrepreneurship in The Philippinesjoanne rivera100% (1)
- 3.2 Server Maintenance Administration PlanDokument30 Seiten3.2 Server Maintenance Administration PlanAG Network ResourcesNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCQCDokument73 SeitenNCQCSaurabh Jaiswal JassiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 22 Hand Tool SafetyDokument8 Seiten22 Hand Tool SafetyAlma Tomas-CafeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Post Purchase Cognitive DissonanceDokument18 SeitenPost Purchase Cognitive DissonancePawan DihiyeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discuss The Nature and Extent of Slavery As An Institution in Greco-Roman SocietyDokument4 SeitenDiscuss The Nature and Extent of Slavery As An Institution in Greco-Roman SocietySouravNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lower LimbDokument53 SeitenLower LimbRupesh M DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Rating Summary 2010Dokument2 SeitenGas Rating Summary 2010ahmadhadraniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Commerce PDFDokument176 SeitenComputer Commerce PDFMallu TechNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 TH CSDokument2 Seiten7 TH CSkumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mock MU-BAAT Final Version Set 1Dokument8 SeitenMock MU-BAAT Final Version Set 1Priyanshu SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- CEP Presentation AOL 2023Dokument143 SeitenCEP Presentation AOL 2023Josh DezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kalish GI ProtocolsDokument5 SeitenKalish GI Protocolsgoosenl100% (1)
- The Atom: Cornell Doodle NotesDokument22 SeitenThe Atom: Cornell Doodle NotesSalina SalujaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summative Test Module 1.1 1.2Dokument2 SeitenSummative Test Module 1.1 1.2Jocelyn RoxasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Return To Sport After Surgical Management of Posterior Shoulder InstabilityDokument13 SeitenReturn To Sport After Surgical Management of Posterior Shoulder InstabilityAziz CupinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sita's RamayanaDokument2 SeitenSita's RamayanaAnonymous dSuPcxyn0% (1)
- The Sparrow: Srijani Bhowmick Class VDokument12 SeitenThe Sparrow: Srijani Bhowmick Class VsgphycoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tryout Un Bahasa Inggris SMKDokument9 SeitenTryout Un Bahasa Inggris SMKSMK Miftahul HikmahNoch keine Bewertungen
- First ContingencyDokument2 SeitenFirst Contingencymanju bhargavNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04 IMS Technical Differences (Nokia)Dokument4 Seiten04 IMS Technical Differences (Nokia)stern_uNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ionic EquilibriumDokument22 SeitenIonic EquilibriumbeherasubhammikunNoch keine Bewertungen