Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Yolanda Liceo
Hochgeladen von
Yolis ElizondoOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Yolanda Liceo
Hochgeladen von
Yolis ElizondoCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
1
Introduction What is electricity Static Electricity Moving Electricity History reference sources Conclucions
.. 3 4 . 5 . 6 7 . 8 . 9
Electricity is a form of energy. Electricity is the flow of electrons. All matter is made up of atoms, and an atom has a center, called a nucleus. The nucleus contains positively charged particles called protons and uncharged particles called neutrons. The nucleus of an atom is surrounded by negatively charged particles called electrons. The negative charge of an electron is equal to the positive charge of a proton, and the number of electrons in an atom is usually equal to the number of protons. When the balancing force between protons and electrons is upset by an outside force, an atom may gain or lose an electron. When electrons are "lost" from an atom, the free movement of these electrons constitutes an electric current.
Electricity is a type of activity arising from the existence of charge. The basic unit of charge is that on the proton or electron. The protons charge is called positive while the electron's is negative. A particle of matter usually has a charge. The charge is positive or negative. Two particles with the same charges, both positive or both negative, repel or drive away each other, while two particles with unlike charges are attracted. The negatively charged electrons in an atom are kept near the nucleus because of their attraction for the positively charged protons in the nucleus. Materials differ in their ability to allow electricity to flow through them. Conductors allow electricity to flow through them easily. Copper wire is a good example and makes up our housing and appliance wiring. Insulators are materials that don't allow electricity to pass through them easily. Materials such as rubber are good insulators and are used around appliance and house wires to keep the electricity from creating a short circuit. Semiconductors: conduct electricity under some conditions.
Static Electricity Electrostatics is the study of charges, or charged objectects that do not involve moving charges or current. When positive or negative charge builds up on objects, static electricity occurs. The charge can be built up by rubbing certain objects together. The friction between the objects causes electrons to be transferred from one object to the another. The object that has lost the electrons has a positive charge and the object act that has gained them has an equal negative charge. An electrically neutral object can be charged by bringing it in contact with a charged object: if the charged object is positive, the neutral object gains a positive charge when some of its electrons are attracted onto the positive object; if the charged object is negative, the neutral object gains a negative charge when some electrons are attracted onto it from the negative object. This may happen to a person when rubbing one's feet on a carpet and then touching an object and receiving an electrical shock.
Moving Electricity Electrodynamics is the study of charges in motion. A flow of electric charge makes up an electric current. There are several things needed to complete an electrical circuit. There must be an electromotive force from batteries or generators, conductors such as copper wire and an appliance such as a bulb to be lit. A device called a switch can be used to stop or open the circuit or close or create the circuit. When a circuit is not completed because the electricity is diverted to a path of least resistance it is a short circuit. In a simple circuit there are two types of wiring. One is a parallel circuit. This is when all the batteries and appliances such as bulbs are wired with the positive terminals of the batteries wired together and the negative terminals of the wired together so there are parallel pathways for the electricity to travel. In a parallel circuit, if one appliance such as a bulb goes out, the rest of the circuit remains on. The force from the batteries does not increase, however, if more batteries are added. In a series circuit, the positive terminal or end of a battery is wired to the negative terminal of the other battery and the positive end of one appliance to the negative or terminal of the other appliance such as a bulb. Thus if one bulb or appliance goes out, the whole flow of electricity is interrupted and the circuit goes out. However, if more batteries are added to the circuit, the bulb will get brighter as more force will go to that bulb.
In March 2003 the Department created two offices to provide focus in several critical areas: the Office of Electric Transmission and Distribution (TD), which advanced the technologies needed to ensure a reliable, robust and modern U.S. electricity grid, and the Office of Energy Assurance (EA).
http://www.mcwdn.org/Physics/Electricity.html http://inventors.about.com/library/inventors/blelectric1.htm http://www.k12.hi.us/~kealaint/projects/Spring09Projects/period2/kaElectricity.html http://www.bgfl.org/bgfl/custom/resources_ftp/client_ftp/ks3/science/elecricity_2/electricity.html
we depend more and more on machines to do important work for us, we must provide energy for electronic machines to work. Not only machines, but people need it to warm their homes in the winter, us it to power their forms of entertainment such as TV sets, or use the light electricity provides to move easily in the dark and do things when the sun has gone down.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Trabajo de CubaDokument5 SeitenTrabajo de CubaAmanda SaldivarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Use Them When You Need Them When Is Necessary. Create A Robot For Been in ChargeDokument4 SeitenUse Them When You Need Them When Is Necessary. Create A Robot For Been in ChargeYolis ElizondoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Libro RodolfoDokument1 SeiteLibro RodolfoYolis ElizondoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yolanda LiceoDokument9 SeitenYolanda LiceoYolis ElizondoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Libro RodolfoDokument1 SeiteLibro RodolfoYolis ElizondoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Participation Activities Homework Test Name: Average ScienceDokument3 SeitenParticipation Activities Homework Test Name: Average ScienceYolis ElizondoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ElectricityDokument1 SeiteElectricityYolis ElizondoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Participation Activities Homework Test Name: Average ScienceDokument3 SeitenParticipation Activities Homework Test Name: Average ScienceYolis ElizondoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Participation Activities Homework Test Name: Average ScienceDokument3 SeitenParticipation Activities Homework Test Name: Average ScienceYolis ElizondoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Participation Activities Homework Test Name: Average ScienceDokument3 SeitenParticipation Activities Homework Test Name: Average ScienceYolis ElizondoNoch keine Bewertungen
- What You Learned in The TechnologyDokument6 SeitenWhat You Learned in The TechnologyYolis ElizondoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Non Chip FormingDokument33 SeitenNon Chip FormingNur AmirahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 4 Cell Division and Cell Communication UnitDokument6 SeitenUnit 4 Cell Division and Cell Communication Unitapi-237676607Noch keine Bewertungen
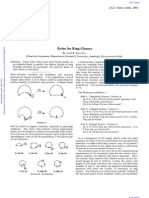
- Rules For Ring ClosureDokument3 SeitenRules For Ring ClosurecrazychemistryNoch keine Bewertungen
- CaseStudy2 WindmillDokument8 SeitenCaseStudy2 WindmillAnthony BergemannNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sasolwax SP30 TDSDokument2 SeitenSasolwax SP30 TDSLaboratorio Inkctech0% (1)
- Light in August EssayDokument7 SeitenLight in August Essayppggihnbf100% (2)
- Characterisation of Polymer With GCDokument104 SeitenCharacterisation of Polymer With GCAmit KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astm e 518Dokument5 SeitenAstm e 518Pao Dela Cruz100% (1)
- Stoichiometry Basics NotesDokument5 SeitenStoichiometry Basics NoteswardaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PRODUCT INFORMATIONDokument2 SeitenPRODUCT INFORMATIONAdriana GonçalvesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pressure Force and Area RAGDokument3 SeitenPressure Force and Area RAGruuki0% (2)
- Sachtleben Technology for Architectural and Decorative PaintsDokument16 SeitenSachtleben Technology for Architectural and Decorative PaintswinsonecNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stirling EngineDokument14 SeitenStirling EngineShivakumar Ainapur100% (1)
- Isolation and Characterization of Nucleic AcidsDokument25 SeitenIsolation and Characterization of Nucleic AcidsSophia GoNoch keine Bewertungen
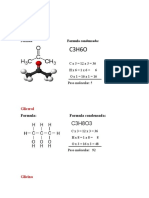
- Problemario 1 formulas químicasDokument11 SeitenProblemario 1 formulas químicasmata viejitosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Time of Setting of Hydraulic Cement by Vicat Needle: Standard Test Method ForDokument6 SeitenTime of Setting of Hydraulic Cement by Vicat Needle: Standard Test Method ForAhmed AbidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic StructureDokument2 SeitenAtomic Structureapi-350245383Noch keine Bewertungen
- SyllabusDokument4 SeitenSyllabusAlysson Vany ClochetteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Difference Between Sewing Method and Alternative Method4Dokument40 SeitenDifference Between Sewing Method and Alternative Method4sabberNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teleportation Via Wormhole-StargatesDokument34 SeitenTeleportation Via Wormhole-StargatesFranca GoiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Percentage ErrorDokument6 SeitenPercentage ErrormalakmounirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Statistical Physics Solution Manual: Kerson HuangDokument105 SeitenIntroduction To Statistical Physics Solution Manual: Kerson Huangsumivrindavan100% (7)
- 연습문제 SolutionDokument156 Seiten연습문제 Solution박민지Noch keine Bewertungen
- Junctions ExplainedDokument4 SeitenJunctions ExplainedJulio SaldanhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Squeezing Ground ConditionDokument16 SeitenSqueezing Ground ConditionMourad HosniNoch keine Bewertungen
- RHA ResumeDokument2 SeitenRHA ResumeJames McFarlaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cylinder Design Standards WSNZDokument5 SeitenCylinder Design Standards WSNZjamilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monitoring of BioprocessDokument41 SeitenMonitoring of BioprocessSandiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab - Properties of Carboxylic AcidsDokument2 SeitenLab - Properties of Carboxylic Acidsapi-209270909Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Cassini Ion and Neutral Mass Spectrometer (Inms) InvestigationDokument119 SeitenThe Cassini Ion and Neutral Mass Spectrometer (Inms) InvestigationDima FontaineNoch keine Bewertungen