Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Earthing
Hochgeladen von
rajeshreni1Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Earthing
Hochgeladen von
rajeshreni1Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Three-Phase AC machines
Resource 3
Three-phase Cage Rotor Starters and Control Gear
Three-Phase AC Machines Resource 3
3 Phase Cage Rotor Starters and Control Gear
Aims
To understand the control gear requirements of a cage rotor induction motor starter
To understand the operation of various types of motor starters
Three-Phase AC Machines Resource 3
3 Phase Cage Rotor Starters and Control Gear
Objectives
At the end of this lesson you should be able to:
To To To To To To be be be be be be able able able able able able to to to to to to
describe the control gear components of a DOL starter describe the operation of a DOL starter explain how a three-phase motor can be reversed describe the operation of a reversing DOL starter explain the starting problems with an induction motor describe the operation of a STAR-DELTA starter
Three-Phase AC Machines Resource 3
3 Phase Cage Rotor Starters and Control Gear
Components of a DOL Starter
DOL = Direct On Line = Direct connection of stator phases to the 3 phase supply
FUSES
MCB
Designed to operate very quickly Protect against short circuit currents to earth or between phases
Three-Phase AC Machines Resource 3
3 Phase Cage Rotor Starters and Control Gear
Components of a DOL Starter Isolator Isolator with integral fuses
Makes circuit dead allowing for maintenance Should be door interlocked and lockable for safety
Three-Phase AC Machines Resource 3 Contactor Coil terminals A1 & A2 Main pole terminals 1, 3&5
3 Phase Cage Rotor Starters and Control Gear
Auxiliary contact terminal 13
Coil
Coil
Main poles
Auxiliary contact
Main pole terminals 2, 4 & 6
Auxiliary contact terminal 14
Three-Phase AC Machines Resource 3
3 Phase Cage Rotor Starters and Control Gear
Components of a DOL Starter
Contactor Coil terminals A1 & A2 Main pole terminals 1, 3&5 Auxiliary contact terminal 13
When coil is energised it becomes a magnet Coil Pole contacts closes Auxiliary contact also closes
Main pole terminals 2, 4 & 6
Auxiliary contact terminal 14
Three-Phase AC Machines Resource 3 Components of a DOL Starter Overload Unit (Thermal type) Main pole terminals 1, 3 & 5 Reset button
3 Phase Cage Rotor Starters and Control Gear
When motor overheats due to overload conditions, main poles latch open
N/C Auxiliary contacts 95 & 96
N/O Auxiliary contacts 97 & 98
Auxiliary contacts also latch open and when interlocked within control circuit prevents motor restarting by itself when cool.
Main pole terminals 2, 4 & 6
Red pushbutton can be used to reset
Three-Phase AC Machines Resource 3
3 Phase Cage Rotor Starters and Control Gear
Components of a DOL Starter
Start and Stop pushbuttons Start button is green and flush mounted Stop button is red and protruding Emergency Stop button has a red mushroom head which latches in and must be turned to release
Contacts at the back of switches can be either N/O or N/C
N/O contact
N/C contact
Three-Phase AC Machines Resource 3
3 Phase Cage Rotor Starters and Control Gear
DOL Starter
Power Schematic
3-phase supply
Fuses
Isolator
Contactor C1 Overload Unit OL1 Safety earth
Auxiliary contact (retainer) Auxiliary contact (interlock)
Induction Motor
Three-Phase AC Machines Resource 3 DOL Starter Control Circuit
3 Phase Cage Rotor Starters and Control Gear
Starting Press S2 C1 coil energises Contact C1 retains S2 can be released
Stopping
Press S1 breaks circuit C1 coil de-energises C1 retaining contact drops out
Faults
Overload causes OL1 to open C1 coil de-energises C1 retaining contact drops out
Three-Phase AC Machines Resource 3
3-phase supply
3 Phase Cage Rotor Starters and Control Gear
Fuses
Power Schematic
Isolator Forward Contacto r C2 Overload Unit OL2
Mechanical interlock Revers e Contact or C3
Phases swapped here by C3 Induction Motor
Safety earth
Three-Phase AC Machines Resource 3 Control Circuit
3 Phase Cage Rotor Starters and Control Gear
Reversing Starting - Forward DOL Starter Press S2
C2 coil energises Contact C2 retains S2 can be released Electrical interlock with C3
Starting - Reverse Press S3 C3 coil energises Contact C3 retains S3 can be released Electrical interlock with C2
Stopping
Faults
Press S1 breaks circuit C2 or C3 coil de-energises C2 or C3 retaining contact drops out
As for DOL
Three-Phase AC Machines Resource 3 High Starting Current
3 Phase Cage Rotor Starters and Control Gear
Induction Motor Starting Problems
Starting current = 7 x full load current
As speed increases, stator current reduces
Three-Phase AC Machines Resource 3 Solution:- Start off in STAR, then run in DELTA
3 Phase Cage Rotor Starters and Control Gear
Induction Motor Starting Problems
Motor current follows STAR curve. Change over to DELTA curve after motor reaches 80% of full synchronous speed
Change over can be done using a timer or centrifugal switch
Three-Phase AC Machines Resource 3 Solution:- Start off in STAR, then run in DELTA
3 Phase Cage Rotor Starters and Control Gear
Induction Motor Starting Problems
Motor torque follows STAR curve. Change over to DELTA curve after motor reaches 80% of full synchronous speed
Lower starting torque in STAR means that load must be checked to ensure it can be turned in STAR.
Three-Phase AC Machines Resource 3
MAIN Contactor C1
3 Phase Cage Rotor Starters and Control Gear
STAR-DELTA Starter Power Schematic U1
Overload Unit OL1
3-phase supply, fuses, isolator and motor earth not shown
STAR
W2
U2 V2
Mechanical interlock
W1
V1
Induction Motor
DELTA Contactor C3 DELTA Contactor connects U1 to W2 V1 to U2 W1 to V2
DELTA
W1
W2 U1
V2
U2 V1
STAR Contact or C2
STAR Contactor connects U2 to V2 to W2
Three-Phase AC Machines Resource 3
3 Phase Cage Rotor Starters and Control Gear
STAR-DELTA Starter
Control Circuit Starting Press S2 C1 coil energises Contact C1 retains S2 can be released Auxiliary contact C1 closes CR timer starts timing C2 coil energises - STAR CR timer finishes timing C2 coil de-energises C3 coil energises - DELTA Stopping & Faults As for DOL
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- 2020 Commencement ProgramDokument113 Seiten2020 Commencement ProgramÉrika DLNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Concrete Mix DesignDokument12 SeitenConcrete Mix DesignWilliam ProvidoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASHRAE/IESNA Standard 90.1-1999Dokument69 SeitenASHRAE/IESNA Standard 90.1-1999Jônatas SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Non Destructive Testing Seminar ReportDokument22 SeitenNon Destructive Testing Seminar ReportMonu LodhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Masonry DesignDokument21 SeitenMasonry DesignkevinblacheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Substructure Taking OffDokument4 SeitenSubstructure Taking Offlutos2100% (5)
- Local Case Study Arba Minch University D PDFDokument16 SeitenLocal Case Study Arba Minch University D PDFKayfi Akram Mawlan100% (1)
- February2009-Errata - Hiner Seismic BookDokument16 SeitenFebruary2009-Errata - Hiner Seismic BookfdafaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shallow Foundation Safety FactorDokument7 SeitenShallow Foundation Safety FactorZafira EdinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Buckling Restrained Braced FrameDokument24 SeitenBuckling Restrained Braced Framedanish khanNoch keine Bewertungen
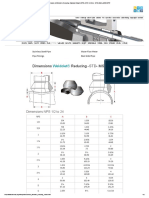
- Dimensions of Weldolets Reducing, Standard Weight (STD), NPS 1 - 2 (3 - 4) - NPS (20) 24, MSS-SP97Dokument2 SeitenDimensions of Weldolets Reducing, Standard Weight (STD), NPS 1 - 2 (3 - 4) - NPS (20) 24, MSS-SP97Qiuniu100% (1)
- Chance Reichel Templ TaskID WBS 05 12 00Dokument12 SeitenChance Reichel Templ TaskID WBS 05 12 00smshaidrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agile ModelingDokument4 SeitenAgile Modelingvedavith ravulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ce 3010 Honors Project 3d Printing and Construction IndustryDokument18 SeitenCe 3010 Honors Project 3d Printing and Construction Industryapi-297914209Noch keine Bewertungen
- Phx2018UC MDAO Northrop-Grumman HodgeDokument32 SeitenPhx2018UC MDAO Northrop-Grumman HodgeMohan Babu ANoch keine Bewertungen
- MQ SP e 6001Dokument41 SeitenMQ SP e 6001jaseel kNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 14 Security Engineering 1Dokument48 SeitenChapter 14 Security Engineering 1Fattah MuhyiddeenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crusher Equipment ListDokument12 SeitenCrusher Equipment ListTommy AndriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indian Navy Short Service ComissionDokument3 SeitenIndian Navy Short Service ComissionMI BOX 4KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engg. Graphics CAD Lab MEP-117 SyllabusDokument3 SeitenEngg. Graphics CAD Lab MEP-117 SyllabusMukul RathoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- CV For Prof. Charles Manasseh Mokua Ondieki-012016Dokument6 SeitenCV For Prof. Charles Manasseh Mokua Ondieki-012016Charles OndiekiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Page0036 PDFDokument1 SeitePage0036 PDFkapereshemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Training Catalogue: QRA and CFD Simulation Phast, Safeti and KFXDokument16 SeitenTraining Catalogue: QRA and CFD Simulation Phast, Safeti and KFXKrishna KusumaNoch keine Bewertungen
- European CV Format-1Dokument2 SeitenEuropean CV Format-1BayisaGebre100% (1)
- Stress Analysis of Mast Structure For Water-Well Drilling MachineDokument8 SeitenStress Analysis of Mast Structure For Water-Well Drilling MachineBruno Santos100% (1)
- 83 Kashif NaveedDokument2 Seiten83 Kashif NaveedSajid HanifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mir Titiles About PDFDokument20 SeitenMir Titiles About PDFgauriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Avoiding Plagiarism Through ParaphrasingDokument36 SeitenAvoiding Plagiarism Through ParaphrasingJan Iriesh EspinosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TDS - Masterflow 928 TDokument4 SeitenTDS - Masterflow 928 TVenkata RaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Drives Boldea I and Nasar SA 2006 Book ReDokument2 SeitenElectric Drives Boldea I and Nasar SA 2006 Book ReMahir DžafićNoch keine Bewertungen