Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Measuring Attitudes with Scales
Hochgeladen von
Akanksha AgarwalOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Measuring Attitudes with Scales
Hochgeladen von
Akanksha AgarwalCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Measurement Using Scales
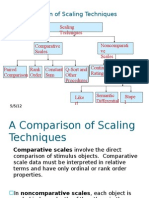
Scales for measuring attitude
Definition Procedures for attempting to determine quantitative measures of subjective and sometimes abstract concepts Scaling is a measurement tool
Assigns numbers or symbols to properties of an object
May be either unidimensional or multidimensional
Important Scales
Graphic Rating Scales (uncommon): Respondents select a point on a graphic continuum anchored at the extremes
Itemized Rating Scales (common): Similar to graphic rating scales, except that respondents must select from a limited number of ordered categories rather than placing a check mark on a continuous scale
Semantic Differential Scale
Begins by determining the concept to be rated. Then select dichotomous pairs of words or phrases that could be used to describe the concept Respondents then rate the concept on a scale Finally, compute the mean of these responses for each pair of adjectives and plotted as a profile or image
Semantic Differential Scale Example
Service is discourteous Location is convenient 1234567 1234567 Service is courteous Location is inconvenient Hours are convenient Loan interest rates
Hours are inconvenient 1234567 Loan interest rates 1234567
are high
are low
Profile Analysis (Snake Diagram) - Example
Service is discourteous Location is convenient 1234567
Bank A
Service is courteous Location is inconvenient Hours are convenient Loan interest rates
1234567
Bank B
Hours are inconvenient 1234567 Loan interest rates 1234567
are high
are low
Rank-Order Scale
Description - respondent is asked to judge one item against another. Example - Rank the following brands of cereal according to your preference (1=most preferred).
__ __ __ __ Kelloggs Corn Flakes Rice Krispies Wheaties Kelloggs Raisin Bran ...
Paired Comparisons
Description - Paired comparison scales ask a respondent to pick one of two objects from a set based upon a given criterion
Example - Which brand do you prefer? ___ Coca-Cola ___ Pepsi ___ Dr. Pepper ___ Pepsi ___ Coca-Cola ___ Seven-Up ___ Dr. Pepper ___ Seven-Up
Constant Sum Scales
This technique requires the respondent to divide a given number of points, typically 100, among two or more attributes based on their importance Constant sum scales are used more often than paired comparisons because the long list of paired items is avoided
Purchase or Behavioral Intent Scales
Scale designed to measure the likelihood that a potential customer will purchase a product or service or behave in a certain way. Example: If a season ticket were offered for the Dallas Stars (hockey) games for $240, how likely are you to buy it? __ Definitely will buy __ Probably will buy __ Probably will not buy __ Definitely will not buy
Multiple Item Scales
Measurement of several aspects of an individuals attitude towards an object Two or more single-item rating scales combined in specific ways
Using a Likert (Summated) Scale (very common) Allows the respondent to express intensity of feeling Construction: Subjects are asked to indicate their degree of agreement or disagreement with each and every statement in a series by checking the appropriate cell Use: Sum the scores across items -- an indicator of overall attitude
Likert Scale (Multi Item) - Example
1. Nordstroms is an attractive store.
Strongly Agree Agree Neither Agree Nor Disagree Disagree Strongly Disagree
2. The service at Nordstroms is slow.
Strongly Agree Agree Neither Agree Nor Disagree Disagree Strongly Disagree
3. Nordstroms has attractive prices.
Strongly Agree Agree Neither Agree Nor Disagree Disagree Strongly Disagree
Considerations When Constructing Itemized Rating Scales
Nature of Verbal Description
Number of Categories
Odd or Even Number of Scale Categories
Forced Versus Non-Forced Choice
Balanced Versus Nonbalanced Alternatives
Examples Of Category (Itemized) Rating Scales
1. Balanced, forced-choice, odd-interval scale focusing on an attitude toward a specific attribute (1) How do you like the taste of Classic Coke? ___ ___ ___ ___ ___
Like It Very Much Like it Neither Like Nor Dislike It Dislike It Strongly Dislike It
2. Balanced, forced-choice, even-interval scale focusing on an overall attitude (2) Overall, how would you rate Ultra Brite Toothpaste? ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___
Extremely Good Very Good Somewhat Good Somewhat Bad Very Bad Extremely Bad
Examples Of Category (Itemized) Rating Scales
3. Unbalanced, forced-choice, odd-interval scale focusing on an overall attitude (3) What is your reaction to this advertisement? ___ ___ ___ ___ ___
Enthusiastic Very Favorable Favorable Neutral Unfavorable
4. Balanced, non-forced, odd-interval scale focusing on a specific attribute (4) How would you rate the friendliness of the sales personnel at Sears downtown store? __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
Very Moderately Slightly Neither Slightly Moderately Very Dont Friendly Friendly Friendly Friendly Unfriendly Unfriendly Unfriendly Know Nor UnFriendly
Other Scales
There are numerous other scales. Examples:
Stapel
Scale Q-Sort Scale Thermometer Scale Happy Face Scale Fishbein weighted sum scale
Choosing an Attitude Scale
Choice is complicated by two problems:
Many
scales, each with its own advantages/ disadvantages Virtually any technique can be adapted to the measurement of attitude.
Ultimately choice is shaped by:
Specific
information required Adaptability of scale to method of administration Compatibility of scale with the structure of the respondents attitude
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Business Research Methods: Attitude MeasurementDokument37 SeitenBusiness Research Methods: Attitude MeasurementShantanu DubeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1attitudescaling 0903Dokument37 Seiten1attitudescaling 0903Sandip ChaudhariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Research Methods Attitude MeasurementDokument40 SeitenBusiness Research Methods Attitude MeasurementAbdul BasitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Session 10Dokument37 SeitenSession 10Kshitij SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research Methods GuideDokument92 SeitenResearch Methods GuideFahad AhsanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Research Methods: Attitude MeasurementDokument67 SeitenBusiness Research Methods: Attitude Measurementعنبر رضا حسنNoch keine Bewertungen
- Attitude Measurement: Jonali SarmaDokument36 SeitenAttitude Measurement: Jonali SarmaArindam DeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measurement and ScaleDokument25 SeitenMeasurement and Scalepkumarjothi6433Noch keine Bewertungen
- Attitude Scaling: Ravi Shankar RaiDokument54 SeitenAttitude Scaling: Ravi Shankar RaiRobinvarshneyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measuring AttitudeDokument37 SeitenMeasuring AttitudeDev KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Attitude Measurementfinal1Dokument45 SeitenAttitude Measurementfinal1rahulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measurement and Scaling ConceptsDokument57 SeitenMeasurement and Scaling ConceptsSadia Easmin MunnyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scaling Methods for Business ResearchDokument23 SeitenScaling Methods for Business ResearchNijatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Attitude ScalesDokument11 SeitenAttitude Scaleslifeis1enjoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measurement Scale SelectionDokument40 SeitenMeasurement Scale Selectionginish12Noch keine Bewertungen
- Business Research Methods 3 Unit: Iv Sem Bba by Premalatha K PDokument40 SeitenBusiness Research Methods 3 Unit: Iv Sem Bba by Premalatha K PPremalatha KPNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rating Scales - Attitude MeasurementDokument10 SeitenRating Scales - Attitude MeasurementacidreignNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit V Attitude Measurement ScaleDokument26 SeitenUnit V Attitude Measurement ScaleNayan MorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measure Attitudes Using ScalesDokument34 SeitenMeasure Attitudes Using ScalesMurthy GrandhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measurement Scales: Selection of Measurement ScaleDokument5 SeitenMeasurement Scales: Selection of Measurement Scalefas4106Noch keine Bewertungen
- Market Research - MBA Lecture Notes Presentation - 4Dokument28 SeitenMarket Research - MBA Lecture Notes Presentation - 4Alper Orhun KilicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Attitude Measurement TechniquesDokument48 SeitenAttitude Measurement Techniquesshashank reddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Attitude Measurement: Shalini V.Das Shilpi ThukralDokument24 SeitenAttitude Measurement: Shalini V.Das Shilpi ThukralAnil Singh ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Attitude:: Attitudes Compromises of Three ComponentsDokument20 SeitenAttitude:: Attitudes Compromises of Three Componentsmonica rajuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.2 Attitude MeasurementDokument33 Seiten4.2 Attitude MeasurementLakshmi SaraswathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- RM - 07 - Measurement and Scaling TechniquesDokument22 SeitenRM - 07 - Measurement and Scaling TechniquesBCom HonsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit II ScalingDokument57 SeitenUnit II ScalingGopal KrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research Methodology - Unit 5 - Attitude MeasurementDokument29 SeitenResearch Methodology - Unit 5 - Attitude MeasurementFrancisca RebelloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 6 Questionnaire Notes 11-4-22Dokument11 SeitenLecture 6 Questionnaire Notes 11-4-22Vishal PaithankarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scaling Technique Research MethodologyDokument13 SeitenScaling Technique Research MethodologyVikas Tirmale100% (1)
- Secondary Scaling Techniques for Marketing ResearchDokument5 SeitenSecondary Scaling Techniques for Marketing ResearchSaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scaling: Business Research MethodsDokument23 SeitenScaling: Business Research MethodsSatyajit GhoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measurement and Scaling ConceptsDokument57 SeitenMeasurement and Scaling ConceptsAnirban SamaddarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Attitude Measurement: C.Satapathy AmityDokument32 SeitenAttitude Measurement: C.Satapathy AmitySoumya SahooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 3Dokument40 SeitenGroup 3AbdulAhadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Non ComparativeNon Comparative Scaling Techniques - PPT Scaling TechniquesDokument16 SeitenNon ComparativeNon Comparative Scaling Techniques - PPT Scaling TechniquesSAASDASDA9682Noch keine Bewertungen
- Attitude Scales - Rating Scales To Measure DataDokument23 SeitenAttitude Scales - Rating Scales To Measure Dataparikh_prateek063784Noch keine Bewertungen
- Module 3.1-Measurement ScalesDokument82 SeitenModule 3.1-Measurement ScalesDeepak BangwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- BRM chp07Dokument29 SeitenBRM chp07Brijesh BaghelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 3Dokument40 SeitenGroup 3AbdulAhadNoch keine Bewertungen
- BRM Attitude MeasurementDokument36 SeitenBRM Attitude MeasurementRiteshSinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measurement Scales: Types, Development and UsesDokument58 SeitenMeasurement Scales: Types, Development and Useszia uddin khattakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scales For Measurement Classification of Scaling TechniquesDokument25 SeitenScales For Measurement Classification of Scaling TechniquesGowri J BabuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measurement Scales and Attitude Scaling TechniquesDokument41 SeitenMeasurement Scales and Attitude Scaling TechniquesSarvar PathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Attitudinal ScalesDokument35 SeitenAttitudinal ScalesLei PronceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scaling TechniquesDokument36 SeitenScaling TechniquesSatya Sharma100% (1)
- Measuring AttitudesDokument39 SeitenMeasuring AttitudeseshaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 - Measurement of VariablesScallingReliabilityDokument49 Seiten7 - Measurement of VariablesScallingReliabilityRizaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7 Scaling, Reliability and Validity - DC181Dokument43 SeitenChapter 7 Scaling, Reliability and Validity - DC181Lydia HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Attitudes and ScalingDokument63 SeitenAttitudes and ScalingAmmi ArdiyantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measure Attitudes with Rating, Ranking and Sorting ScalesDokument3 SeitenMeasure Attitudes with Rating, Ranking and Sorting ScalesJunaid AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Attitude Measurement Business ResearchDokument5 SeitenAttitude Measurement Business ResearchDj-Kanaan AsifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measurement&Scaleingmba 1Dokument81 SeitenMeasurement&Scaleingmba 1jagatapsvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparative and Non-Comparative ScalesDokument27 SeitenComparative and Non-Comparative Scalessanjay reddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 7 RMTDokument26 SeitenTopic 7 RMTScorpian MouniehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of ScalesDokument5 SeitenTypes of Scalesnithyabeecharaju2023Noch keine Bewertungen
- Business Research Methods (BRM) DR Seema GargDokument51 SeitenBusiness Research Methods (BRM) DR Seema GargSakshi JunejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- RMRP - Measurement and ScalingDokument47 SeitenRMRP - Measurement and ScalingMayank TayalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scaling TechniquesDokument45 SeitenScaling Techniquespraveen_scribdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resiliency Availability The Ultimate Step-By-Step GuideVon EverandResiliency Availability The Ultimate Step-By-Step GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- ConceptsDokument21 SeitenConceptsSachin GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monetary ND Fiscal Policy1Dokument34 SeitenMonetary ND Fiscal Policy1Akanksha AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- PlanningDokument5 SeitenPlanningAkanksha AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Purpose of Organisations Purpose of Organisations Defining Organisations Defining OrganisationsDokument10 SeitenPurpose of Organisations Purpose of Organisations Defining Organisations Defining OrganisationsAkanksha AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sanoussi Bilal, "Trade Blocs", in R. Jones Ed., Routledge Encyclopedia of International Political Economy, Routledge, Forthcoming (2001)Dokument10 SeitenSanoussi Bilal, "Trade Blocs", in R. Jones Ed., Routledge Encyclopedia of International Political Economy, Routledge, Forthcoming (2001)IrenosNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Polo e BrochureDokument21 SeitenNew Polo e Brochurechethan_nNoch keine Bewertungen
- Avoid Marketing Shortsightedness by Focusing on Customer NeedsDokument13 SeitenAvoid Marketing Shortsightedness by Focusing on Customer NeedsAkanksha Agarwal100% (1)
- Description: Session NoDokument5 SeitenDescription: Session NoAkanksha AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ep 03Dokument20 SeitenEp 03Sania ChaddaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Broken Bonds, Eternal TiesDokument15 SeitenBroken Bonds, Eternal TiesNINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Persuasive Writing BreakdownDokument25 SeitenPersuasive Writing Breakdownella100% (1)
- Research problem and questionsDokument8 SeitenResearch problem and questionsKurt TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gatsby EssayDokument2 SeitenGatsby EssayMatúš NeczliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prenatal Influences and Developmental MilestonesDokument5 SeitenPrenatal Influences and Developmental MilestonesKristal Jane RuedasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 2-Part 2 Technique in Professional Development Stage 1 - Communication SkillsDokument37 SeitenGroup 2-Part 2 Technique in Professional Development Stage 1 - Communication SkillsTRISHIA DELA CRUZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Famous Love QuotesDokument5 SeitenFamous Love QuotesEveryday shayriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oral Communication in Context Types of Communicative Strategy Learning Competency 1: Employs Various Communicative Strategies in Different SituationsDokument3 SeitenOral Communication in Context Types of Communicative Strategy Learning Competency 1: Employs Various Communicative Strategies in Different SituationsJaycel Ablir100% (1)
- Christiane Beerlandt - The Key To Self-LiberationDokument4 SeitenChristiane Beerlandt - The Key To Self-Liberationdpspc67% (3)
- Root Cause Analysis Training PresentationDokument40 SeitenRoot Cause Analysis Training PresentationGaby GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Z. J. Lipowski (Auth.), P. Pichot, P. Berner, R. Wolf, K. Thau (Eds.) - Biological Psychiatry, Higher Nervous Activity-Springer US (1985)Dokument928 SeitenZ. J. Lipowski (Auth.), P. Pichot, P. Berner, R. Wolf, K. Thau (Eds.) - Biological Psychiatry, Higher Nervous Activity-Springer US (1985)cc vereNoch keine Bewertungen
- TVL-HE (Caregiving) Activity Sheet - Quarter 4 - Week 2: Foster The Physical Development of ChildrenDokument7 SeitenTVL-HE (Caregiving) Activity Sheet - Quarter 4 - Week 2: Foster The Physical Development of ChildrenAsherah Jan Ambulo Varona100% (1)
- Reflection PaperDokument3 SeitenReflection Paperapi-532740777Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Course in MiraclesDokument8 SeitenA Course in MiraclesAmor em Movimento RJNoch keine Bewertungen
- Change Is MustDokument3 SeitenChange Is Mustgoytom gideyNoch keine Bewertungen
- National Library Catalogue of Educational & Psychological TestsDokument123 SeitenNational Library Catalogue of Educational & Psychological TestsPallab DattaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Character Analysis of Manuel E. Arguilla's Morning in NagrebcanDokument4 SeitenCharacter Analysis of Manuel E. Arguilla's Morning in NagrebcanMGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philo (Lesson 1 - 4)Dokument6 SeitenPhilo (Lesson 1 - 4)Alma Cecilia QuiaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comm 318 OutlineDokument6 SeitenComm 318 Outlineapi-657143147Noch keine Bewertungen
- UNIFICADO Bloco4 Ingles Portugues DiscDokument7 SeitenUNIFICADO Bloco4 Ingles Portugues DiscDuran BenettiNoch keine Bewertungen
- MOCK JOB INTERVIEW (Sample Questions & Answers)Dokument6 SeitenMOCK JOB INTERVIEW (Sample Questions & Answers)Cha Eun WooNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2022 - YLI National Program - Essay TopicDokument4 Seiten2022 - YLI National Program - Essay Topichappier everNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bi Y3 LP TS25 Module 10 (LP145-160)Dokument19 SeitenBi Y3 LP TS25 Module 10 (LP145-160)NORLILI BINTI HASHIM MoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Client Exit Policy: (Insert Organisation Name/logo)Dokument8 SeitenClient Exit Policy: (Insert Organisation Name/logo)DaivikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conclusion Credible - Evidence - Judgment - Relevance-Reliability - Source ValidityDokument4 SeitenConclusion Credible - Evidence - Judgment - Relevance-Reliability - Source ValidityArjon Bungay FranciscoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Poetry 1 My Mother at Sixty SixDokument5 SeitenPoetry 1 My Mother at Sixty Sixgitali kudnekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENGLISH - Elements-Of-Short-StoryDokument11 SeitenENGLISH - Elements-Of-Short-StoryElthea PascuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reflection Paper 5Dokument3 SeitenReflection Paper 5Adam Jordan ConcepcionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Green Lantern Arisia RrabDokument2 SeitenGreen Lantern Arisia RrabEnrique Fernandez TorreblancaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biophysiological MethodsDokument17 SeitenBiophysiological MethodsAnuja NairNoch keine Bewertungen