Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Cash Flow Statement Wit Sum
Hochgeladen von
Sunay KhaireOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Cash Flow Statement Wit Sum
Hochgeladen von
Sunay KhaireCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
By: Sunay Khaire Shilpi Jajodia
Meaning Classification
Objectives
Limitations Difference
& Uses
between Cash Flow & Fund Flow Statements
Cash comprises cash in hand and on demand deposits with banks.
Cash equivalents are short term, highly liquid investments that are readily convertible into known amounts of cash and which are subject to an insignificant risk of changes in value.
Cash flows are inflows and outflows of cash and cash equivalents. Operating activities are the principal revenue-producing activities of the enterprise and other activities that are not investing or financing activities. Investing activities are the acquisition and disposal of long-term assets and other investments not included in cash equivalents. Financing activities are activities that result in changes in the size and composition of the owners capital (including preference share capital in the case of a company) and borrowings of the enterprise.
Cash flow statement is additional information to user of financial statement. This statement exhibits the flow of incoming and outgoing cash.
This statement assesses the ability of the enterprise to generate cash and cash equivalents.
It also assesses the needs of the enterprise to utilize the cash and cash equivalents generated. It also assesses the liquidity and solvency of the enterprise.
Cash: It means all cash + cash equitable + marketable securities + bank balance . Flow: Flow means flow of cash from business to economy & economy to business i.e. cash inflows and cash outflows. Statement : Statement is a Performa Act,1948. prescribed by Charted Accountant
Thus,
Cash Flow Statement is a statement o f inflows (sources) and outflows (uses) of cash and cash equivalents in an enterprise during a specified period of time.
The cash flow statement should report cash flows during the period classified by :
Operating
It summarizes the causes of changes in cash position of a business enterprise between dates of two balance sheets.
Investing
Financing activities
Sum of these three types of cash flow reflect net increase or decrease of cash and cash equivalents.
It also reveals the movements of cash of a business enterprise for the given accounting period indicating specifically how the cash was generated.
And, it is required for short range financial planning.
As
per Accounting Standard-3 (revised) the changes resulting in cash inflows and cash outflows arise on account of three types of activities :
Cash Flow form Operating Activities: Operating activities are the principle revenue producing activities of the enterprise and other activities that are not investing and financing activities. Hence, these are the results of those transactions and events that determines the net profit or loss.
Cash receipts from the sale of goods and the rendering of services Cash receipts from royalties, fees, commissions and other revenues Cash payments to suppliers of goods and services Cash payments to and on behalf of employees Cash receipts and cash payments of an insurance enterprise for premiums and claims, annuities and other policy benefits
Cash payments or refunds of income taxes unless they can be specifically identified with financing and investing activities
Cash receipts and payments relating to future contracts, forward contracts, option contracts and swap contracts when the contracts are held for dealing or trading purposes.
Cash
Flow from Investing Activities:
Investing
activities include the acquisition and disposal of long-term assets and other investments not included in cash equivalents. The separate disclosure of cash flows arising from investing activities is important.
Cash payments to acquire fixed assets (including intangibles) Cash receipts from disposal of fixed assets (including intangibles) Cash payments to acquire and cash receipts from disposal of shares, warrants or debt instruments of other enterprises and interests in joint ventures. Cash advances and loans made to 3rd parties
Cash payments and receipts for future contracts, forward contracts, option contracts and swap contracts except when the contracts are held for dealing or trading purposes, or the payments are classified as financing activities
Cash
Flow from Financing Activities:
The separate
disclosure of cash flows arising from financing activities is important because it is useful in predicting claims of future cash flows by providers of funds (both capital and loan)to the enterprise. Financing activities are activities that result in changes in the size and composition of the owners capital (including preference share capital in the case of a company) and borrowings of the enterprise.
Cash proceeds from issuing shares or other similar instruments.
Cash proceeds from issuing debentures, loans, notes, bonds and other short or long term borrowings, and Cash repayments of amounts borrowed such as redemption of dentures, bonds, preference shares.
ABC Limited For the year ending.
(A) Cash Flows from Operating Activities: Net Profit before tax & extraordinary items Adjustment 1: Depreciation & Amortization Provision for Doubtful Debts Foreign Exchange gain/loss Dividend Interest XX XX XX XX XX Rs. Rs.
Gain/ Loss on sale of fixed assets/investments
XX
XXX
ABC Limited For the year ending.
(A) Cash Flows from Operating Activities: Rs. Rs.
Operating Profit before Working Capital Changes
Adjustment 2: for changes in working capital Bills Receivables Debtors XX XX
Inventories
Prepaid Expenses Bills Payable Creditors
XX
XX XX XX XXX XXX XXX XXX
Cash Generated from Operations
Income Tax Paid Cash before extraordinary items Extraordinary Items
XXX
Net Cash from (used in) Operating Activities
XXX
ABC Limited For the year ending.
(B) Cash Flows from Investing Activities: Purchase of Fixed Assets Proceeds from Sale of fixed assets Purchase of Investments Rs. XX XX XX Rs.
Proceeds from Sale of investments
Interests received Dividend received Net Cash from (used in) Investing Activities
XX
XX XX XXX
ABC Limited For the year ending.
(C) Cash Flows from Financing Activities: Rs. XX XX XX Rs.
Proceeds from Issue of Shares/ Debentures Proceeds from Long-term debts Repayment of Long-term Debts
Redemption of Debentures
Redemption of Preference Shares Dividend paid Interest paid
XX
XX XX XX
Net Cash from (used in) Financing Activities
Net increase/decrease in cash and Cash Equivalents (A+B+C)
XXX
XXX XXX XXX
Cash and Cash Equivalents at the beginning of the year Cash and Cash Equivalents at the end of the year
You are required to prepare a Cash Flow Statement of the company for the period ended 31st March 2008 in accordance with AS-3 (Revised) by direct method.
Particulars Balance on 01-04-2007 Issue of Shares
Amt (RS.) 1000 6000
Particulars Payments to Suppliers Payments for Fixed Assets Payments for Overheads Wages & Salaries Taxation
Amt (RS.) 40000 4000 4000 2000 5000
Receipts from customers
Sale of Fixed Assets
56000
2000
Dividends
Repayment of Bank Loan Balance c/d 65000
1000
6000 3000 65000
In the Books of Long Ltd. Cash Flow Statement for the year ending 31st March 2008 Particulars (A) Cash Flow from Operating Activities: Cash receipts from customers Cash paid to Suppliers Cash paid to employees (Wages & Salaries) Cash paid for expenses (overheads) 56000 -40000 -2000 -4000 Amt (RS.) Amt (RS.)
Cash generated from operation Income-tax paid Net Cash flow from Operating Activities (i)
10000 -5000 5000
In the Books of Long Ltd. Cash Flow Statement for the year ending 31st March 2008 Particulars Amt (RS.) Amt (RS.)
(B) Cash Flow from Investing Activities : Cash reciepts on sale of fixed assets Cash paid for purchase of fixed assets 2000 -4000
Net Cash flow from Investing Activities (ii)
-2000
In the Books of Long Ltd. Cash Flow Statement for the year ending 31st March 2008 Particulars (C) Cash Flow from Financing Activities: Cash reciepts on issue of shares 6000 Amt (RS.) Amt (RS.)
Cash paid for dividend
Cash paid on repayment of bank loan Net Cash flow from Financing Activities (iii) Net increase in Cash and Cash Equivalents Cash and Cash Equivalents at the beginning of the period Cash and Cash Equivalents at the end of the period
-1000
-6000 -1000 2000
1000
3000
The primary objective of CFS is to provide information regarding the cash receipts and payments of an enterprise for an accounting period. The secondary objective is to disclose information about the operating, investing and financing activities of an enterprise during an accounting period. According to AS-3 (Revised), the objective of cash flow statement is to provide information about the cash flows of an enterprise to the users of financial statements with a basis to assess the ability of the enterprise to generate cash and cash equivalents and the needs of the enterprise to utilize those cash flows so that they may know about the historical changes in cash and cash equivalents.
In brief, the cash flow statement serves the following purposes:
Helpful
in planning and Co-ordination
Helpful
Useful
in Control
in Internal Financial Management of changes in Cash position
Knowledge Helpful
in Short-term financial decisions
The cash flow statement has the following limitations:
Misleading Influenced
Comparisons by changes in Management
Policies
Incomplete
Substitutes
CASH FLOW STATEMENT
FUND FLOW STATEMENT
Meaning of fund: Funds means only cash which is a component of net current assets. Objective: Its objective is to know about the changes occurred in cash position between two balance sheet dates. Basis of preparation: Increase in current liability or decrease in current asset (except cash) results in an increase in cash or vice-versa.
Fund means net working capital (i.e. current assets minus current liabilities).
Its objective is to know about the changes occurred in net working capital between two balance dates. Increase in current liability and decrease in current asset results in a decrease in net working capital or vice-versa.
CASH FLOW STATEMENT
FUND FLOW STATEMENT
Effect of transaction: Effect of a transaction on cash is considered. Utility: Cash flow statement is useful for short-term analysis. Statement of changes in Working Capital: No such statement is prepared separately in cash flow statement. Cash Balances: Opening and closing balances of cash are shown in cash flow statement.
Effect of a transaction on net working capital is considered. Fund flow statement is useful for long-term analysis. A separate statement for changes in working capital is prepared in fund flow statement or analysis. Such balances of cash are shown in statement of changes in working capital.
HAVE A GREAT DAY !!
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Cash Flow Accounts Final Project (2Dokument21 SeitenCash Flow Accounts Final Project (2KandaroliNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Study On Financial Statement Analysis in HDFC Bank LTD 2013Dokument85 SeitenA Study On Financial Statement Analysis in HDFC Bank LTD 2013Abhirup Ubale100% (1)
- Viva On Project and CfsDokument7 SeitenViva On Project and CfsCrazy GamerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Valuation GoodwilllDokument22 SeitenValuation GoodwilllShubashPoojariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economic ReformsDokument30 SeitenEconomic ReformssaritaNoch keine Bewertungen
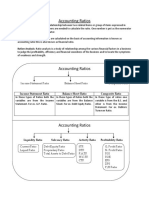
- Accounting Ratios NewDokument3 SeitenAccounting Ratios NewAnkit RoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ascertainment of ProfitDokument18 SeitenAscertainment of ProfitsureshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Long-Term Financial Planning and Growth Chap4Dokument39 SeitenLong-Term Financial Planning and Growth Chap4spectrum_48Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ratio Analysis - Tata and M Amp MDokument38 SeitenRatio Analysis - Tata and M Amp MNani BhupalamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cash Flow Statement AnalysisDokument36 SeitenCash Flow Statement Analysisthilaganadar100% (5)
- A Project Report ON Ratio Analysis of TCS: Submitted to:SUBMITTED BY Prof. Anil TilakDokument32 SeitenA Project Report ON Ratio Analysis of TCS: Submitted to:SUBMITTED BY Prof. Anil TilakSurbhi LodhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Financial System Refers To A System Which Enables The Transfer of Money Between Investors and BorrowersDokument8 SeitenA Financial System Refers To A System Which Enables The Transfer of Money Between Investors and BorrowersAnu SingalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 Capital StructureDokument27 SeitenUnit 2 Capital StructureNeha RastogiNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Sharpe Index ModelDokument3 SeitenThe Sharpe Index ModelSohini Mo BanerjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk Return RelationshipDokument10 SeitenRisk Return RelationshipJunaid PantheeranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wipro - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokument6 SeitenWipro - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaSasidhar ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- AFM Question Bank For 16MBA13 SchemeDokument10 SeitenAFM Question Bank For 16MBA13 SchemeChandan Dn Gowda100% (1)
- Final Accounts Illustration ProblemsDokument11 SeitenFinal Accounts Illustration ProblemsSarath kumar CNoch keine Bewertungen
- Predicting Financial Distress of Pharmaceutical Companies in India Using Altman Z Score ModelDokument4 SeitenPredicting Financial Distress of Pharmaceutical Companies in India Using Altman Z Score ModelInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Capital Budgeting Management Accounting Sem V T.y.bafDokument6 SeitenCapital Budgeting Management Accounting Sem V T.y.bafShravan BaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Capital Budgeting SHARIBDokument103 SeitenCapital Budgeting SHARIBfarzijii4Noch keine Bewertungen
- Accounts 2023 AnsDokument42 SeitenAccounts 2023 AnsAshish YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ratio Analysis - HeroDokument25 SeitenRatio Analysis - HeroGOURAV SHRIVASTAVA Student, Jaipuria IndoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Funds Flow AnalysisDokument16 SeitenFunds Flow AnalysisPravin CumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lupin LimitedDokument12 SeitenLupin LimitedDJ Razz OfficialNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Statement of RaymondsDokument35 SeitenFinancial Statement of RaymondsKevin DoshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hul Ratio AnalysisDokument14 SeitenHul Ratio Analysisvviek100% (1)
- Finance ColgateDokument104 SeitenFinance ColgatecharvitrivediNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ratio Analysis Numerical QuestionsDokument9 SeitenRatio Analysis Numerical Questionsnsrivastav1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Repo Rate and Its Effect On GDP: An Empirical Indian ExperienceDokument11 SeitenRepo Rate and Its Effect On GDP: An Empirical Indian ExperienceAnonymous CwJeBCAXpNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3P - Finance With Other DisciplinesDokument2 Seiten3P - Finance With Other DisciplinesRaju RajendranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Financial AccountingDokument9 SeitenIntroduction To Financial AccountingThai Hoang AnhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infosys Ratio AnalysisDokument61 SeitenInfosys Ratio AnalysisGaurav Bhalgat0% (1)
- International Liquidity & International ReservesDokument17 SeitenInternational Liquidity & International ReservesPrabu ManoharanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Responsibility Accounting - Types, Features, Prerequisites & ExamplesDokument8 SeitenResponsibility Accounting - Types, Features, Prerequisites & Examplesprakashzodpe2013Noch keine Bewertungen
- Commerce Jayesh AgarwalDokument17 SeitenCommerce Jayesh Agarwaljayshree agarwal100% (1)
- Cash Flow StatementDokument11 SeitenCash Flow StatementDuke CyraxNoch keine Bewertungen
- 652oswaal Case-Based Questions Accountancy 12th (Issued by CBSE in April-2021)Dokument7 Seiten652oswaal Case-Based Questions Accountancy 12th (Issued by CBSE in April-2021)Nitesh kuraheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Law of DemandDokument20 SeitenLaw of Demandaman27jaiswalNoch keine Bewertungen
- CadburyDokument37 SeitenCadburyjdh_apsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 20 Difference Between Operating Leverage and Financial LeverageDokument2 Seiten20 Difference Between Operating Leverage and Financial LeverageVenkatsubramanian R IyerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7 CapitalisationDokument19 SeitenChapter 7 CapitalisationPooja SheoranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cash Flow Statement PDFDokument30 SeitenCash Flow Statement PDFDebashish GoraiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reserve Bank of IndiaDokument3 SeitenReserve Bank of IndiaRijo VargheseNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 12 Business Studies - Consumer ProtectionDokument8 SeitenCBSE Class 12 Business Studies - Consumer ProtectionPratham TomarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project On Book KeepingDokument23 SeitenProject On Book KeepingAkhil Narain BahadurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 Acceptance of Deposits by CompaniesDokument52 SeitenChapter 5 Acceptance of Deposits by CompaniesAbhay SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparative Statement Analysis: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleDokument24 SeitenComparative Statement Analysis: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleRahul RathoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ratio Analysis On Optcl, BBSRDokument47 SeitenRatio Analysis On Optcl, BBSRSusmita Nayak100% (1)
- LeverageDokument7 SeitenLeverageChiranjeev RoutrayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Larsen & ToubroDokument15 SeitenLarsen & ToubroAngel BrokingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Key Terminology in Clearing and Sattelment Process NSEDokument9 SeitenKey Terminology in Clearing and Sattelment Process NSETushali TrivediNoch keine Bewertungen
- Share CapitalDokument21 SeitenShare CapitalMehal Ur RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Four Walls: Live Like the Wind, Free, Without HindrancesVon EverandThe Four Walls: Live Like the Wind, Free, Without HindrancesBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- CFSDokument20 SeitenCFSDipak VakraniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ias 3Dokument21 SeitenIas 3JyotiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cash Flow Analysis PresentationDokument44 SeitenCash Flow Analysis Presentationkojo2kg100% (1)
- Unit Ii Accounting PDFDokument11 SeitenUnit Ii Accounting PDFMo ToNoch keine Bewertungen
- Entrepreneurial Project Guideline StudentDokument7 SeitenEntrepreneurial Project Guideline StudentNurnazihaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fabm ExamDokument3 SeitenFabm ExamRonald AlmagroNoch keine Bewertungen
- IRAC Question Assessment Task 2 - Sem 1 2022Dokument1 SeiteIRAC Question Assessment Task 2 - Sem 1 2022Lương Nguyễn Khánh Bảo100% (1)
- A Summer Internship Project Report ON "Online Ordering Business"Dokument35 SeitenA Summer Internship Project Report ON "Online Ordering Business"Ankur Guglani50% (2)
- Microfridge 1for DTNDokument2 SeitenMicrofridge 1for DTNNimmi PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cox Communication 1999Dokument7 SeitenCox Communication 1999ABHAYA SHARMA MBA IB 2018-20 (KOL)Noch keine Bewertungen
- MARKET STUDY of A Feasibility StudyDokument19 SeitenMARKET STUDY of A Feasibility StudySheena Doria de VeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management MCQDokument6 SeitenManagement MCQsujalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Costing IPCCCDokument40 SeitenCosting IPCCCAmith KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Capturing Marketing Insights: 1. Collecting Information and Forecasting DemandDokument64 SeitenCapturing Marketing Insights: 1. Collecting Information and Forecasting DemandNandan Choudhary100% (1)
- Blackrock Special Report - Inflation-Linked Bonds PrimerDokument8 SeitenBlackrock Special Report - Inflation-Linked Bonds PrimerGreg JachnoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revised Application For Renewal FM-CDC-MD-02 As of 2017 Sept 15Dokument4 SeitenRevised Application For Renewal FM-CDC-MD-02 As of 2017 Sept 15Christy SanguyuNoch keine Bewertungen
- PERI Study On Minumum WageDokument33 SeitenPERI Study On Minumum WageJim KinneyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presented To: Dr. Luxmi Malodia Presented By: Navneet KaurDokument25 SeitenPresented To: Dr. Luxmi Malodia Presented By: Navneet KaurNavneet NandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oct 2011: Qualitative Evaluation To Determine The Necessity of Step 1 of The Goodwill Impairment TestDokument3 SeitenOct 2011: Qualitative Evaluation To Determine The Necessity of Step 1 of The Goodwill Impairment TestSingerLewakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Taxation of Partnerships and LlpsDokument5 SeitenTaxation of Partnerships and LlpskalinovskayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GDR Global Depository ReceiptsDokument28 SeitenGDR Global Depository Receiptssrk_pk_sunnyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 003Dokument43 SeitenChap 003sarakhan0622Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3Dokument4 SeitenChapter 3Jefferson BlanciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1 Outline SuggestedDokument4 SeitenAssignment 1 Outline SuggestedThùy TrangNoch keine Bewertungen
- SDLCDokument2 SeitenSDLCsofiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tractor Supply Company Case Study 2Dokument1 SeiteTractor Supply Company Case Study 2KAR WAI PHOONNoch keine Bewertungen
- TRE8X10 Road Transport Costing and Distribution Assignment - Aug 2021Dokument5 SeitenTRE8X10 Road Transport Costing and Distribution Assignment - Aug 2021percyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Creating A Functional Process Control Configuration in HFMDokument3 SeitenCreating A Functional Process Control Configuration in HFMDeva Raj0% (1)
- Do You Think You Have A Good Head For Business?Dokument4 SeitenDo You Think You Have A Good Head For Business?IsraEli 1410Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cost Management 2nd Edition Eldenburg Test BankDokument40 SeitenCost Management 2nd Edition Eldenburg Test Bankaperez1105Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lead Time and Backward N Forward Scheduling, BackflushDokument14 SeitenLead Time and Backward N Forward Scheduling, BackflushRahul pawade100% (1)
- Top 50 Management Consulting Firms Guide PDFDokument165 SeitenTop 50 Management Consulting Firms Guide PDFSunny Naresh ManchandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Centre For Innovation, Incubation and Entrepreneurship (CIIE)Dokument13 SeitenCentre For Innovation, Incubation and Entrepreneurship (CIIE)Manish Singh RathorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Commerce 1 GRD 12 ProjectDokument12 SeitenCommerce 1 GRD 12 ProjectNeriaNoch keine Bewertungen