Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Design of Roadways, Railways & Guideways - Sections & Intersections Presentation - Part 2
Hochgeladen von
John Kervin RodriguezCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Design of Roadways, Railways & Guideways - Sections & Intersections Presentation - Part 2
Hochgeladen von
John Kervin RodriguezCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
PRESS ENTER TO START!
QUOTABLE QUOTES
"I have often regretted my speech, never my silence." - Xenocrates
(396-314 B.C.)
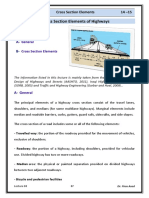
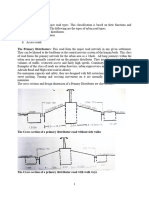
Shoulders should be provided continuously along all highways. Well-maintained, smooth, firm shoulders increase the effective width of the traffic lane to as much as 2ft since vehicle officers tend to drive closer to the edge. Shoulders should be wide enough to permit & encourage vehicles to leave the pavement when stopping. A shoulder width is to be at least 10ft & preferably 12ft clear of all obstructions. In mountainous areas where extra cost in providing shoulders is prohibitive, a minimum of 4ft shoulders can be used with 6ft-8ft preferable. In terrain with guard rails/retaining walls are used, additional 2ft of shoulder must be provided. The slope of shoulders is greater than that of the pavement. High-type surfacing must have a slope of 3/8 in/ft. Sodded shoulders slope is as high as 1in/ft to carry water away from the pavement.
The downward slope from the edge of the shoulder toward the ditch is called the side slope. The slope from the edge of the ditch upward is called the back slope.
Side slopes of 6:1 or flatter can be negotiated safely & must be provided whenever practical. This is also called the barn house design.
An alternative is to provide a 4:1 slope downward from the shoulder.
Much steeper slopes, as steep as 1.5:1, are often used along high fill sections for economical reasons. For this, roadside barriers must be placed along the edge of the fill.
Since majority of crashes involve vehicles that run off the roadway, the roadside area(including shoulders) should be designed so as to give errant motorists as much as chance to regain control. Research shows a 30ft width should permit recovery of out-ofcontrol cars by 85%. Where feasible, a 30-ft-wide, obstacle-free zone adjacent to the roadway should be provided.
Generally speaking, guardrail barriers are warranted in fills more than 8ft in height with slopes steeper than 3:1.
Guardrails may also be required along the edges of deep roadside ditches with steep banks & in area of limited right-of-way.
Various types of guardrail systems are used at the present. There are three general classifications of guardrail, namely; Flexible(Box Beam) Semi-Rigid(Blocked-out W-Beam) Rigid(Concrete)
Use of curbs is generally confined to urban to suburban roadways. Curbs adjacent to the road, where there is no sidewalks, should be low and very flat. The face must not be steeper than 45o so that vehicles can mount them easily. Curbs in parking lots and adjacent to sidewalks must be at least 6in-8in in height, with faces nearly vertical. Drainage ditches, in their relation to the highway cross-section, should be located within or beyond the limits of the shoulder and under normal conditions be low enough to drain water from under the pavement. Round ditch section has been found out to be safer than V-type ditch. Ditch maintenance is also less on rounded ditch sections.
Pro Deo, Familia et Patria
The End
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Stair-Building and the Steel Square: A Manual of Practical Instruction in the Art of Stair-Building and Hand-Railing, and the Manifold Uses of the Steel SquareVon EverandStair-Building and the Steel Square: A Manual of Practical Instruction in the Art of Stair-Building and Hand-Railing, and the Manifold Uses of the Steel SquareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transpo ReportingDokument28 SeitenTranspo ReportingAbegail Jane BanguisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geometric Design of HighwaysDokument41 SeitenGeometric Design of HighwaysTafaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transportation Engineeirng: Prepared By: Engr Shujaat Abbas Delivered To: BS CivilDokument20 SeitenTransportation Engineeirng: Prepared By: Engr Shujaat Abbas Delivered To: BS CivilAdnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cross Sectional Elements PDFDokument23 SeitenCross Sectional Elements PDFmuzamilNoch keine Bewertungen
- IHS standardsDokument3 SeitenIHS standardsGeovanni Collantes DumpasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transportation Engineering-part 2 (1)Dokument151 SeitenTransportation Engineering-part 2 (1)Bayan AmmoriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Highway Engineering Group 1 BSCE-4CDokument30 SeitenHighway Engineering Group 1 BSCE-4CMark RipaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Section 6: Cross Sectional ElementsDokument17 SeitenSection 6: Cross Sectional ElementsKrishhKrishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit IvDokument38 SeitenUnit IvAmith SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cross Slopes and Pavement PeakDokument13 SeitenCross Slopes and Pavement PeakNurul Atiqa100% (1)
- FHWA Green Book-A Policy On Geometric Design of Highways & StreetsDokument2 SeitenFHWA Green Book-A Policy On Geometric Design of Highways & StreetsHarpreet SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Highway Design Manual Vol 1Dokument268 SeitenHighway Design Manual Vol 1Rajan Patel100% (26)
- Design of Roadways, Railways & Guideways - Sections & Intersections PresentationDokument23 SeitenDesign of Roadways, Railways & Guideways - Sections & Intersections PresentationJohn Kervin RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3-Ce103-1 Design Criteria For Highway and RailwaysDokument50 Seiten3-Ce103-1 Design Criteria For Highway and RailwaysUnesca TeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crossection of A RoadDokument27 SeitenCrossection of A RoadFatima KamranNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4565chapter 4 (1), Hoghway Geometric DesignDokument66 Seiten4565chapter 4 (1), Hoghway Geometric DesignKarim AljawhariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 08 Highway Engineering - Cross Section ElementsDokument15 SeitenLec 08 Highway Engineering - Cross Section ElementsDr Firas Asad81% (16)
- Module in Highway & Transportation Engineering Topic 4 V 4Dokument35 SeitenModule in Highway & Transportation Engineering Topic 4 V 4Radie ArnaldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aashto Lane Width PDFDokument1 SeiteAashto Lane Width PDFnywd806033Noch keine Bewertungen
- Designing The Highway: Calvin Paul P. DapitanonDokument6 SeitenDesigning The Highway: Calvin Paul P. DapitanonPaul SuicoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Davidson John F 193208 Ms 120757Dokument141 SeitenDavidson John F 193208 Ms 120757Usman HaiderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cross Sectional Elements of A RoadDokument4 SeitenCross Sectional Elements of A RoadAbdur RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Road Interchange Student ResearchDokument12 SeitenRoad Interchange Student ResearchKookie BTS100% (1)
- TransportationDokument107 SeitenTransportationHalf EngrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 4Dokument51 SeitenGroup 4ahmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 2 - Designing The HighwayDokument10 SeitenTopic 2 - Designing The Highwaygreg100% (2)
- CLE 2005 - TRANSPORTATION ENGINEERING CLASSIFICATIONDokument21 SeitenCLE 2005 - TRANSPORTATION ENGINEERING CLASSIFICATIONAnjali KumariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elements of A Typical Cross-Section of Road: Transportation Engineering - IDokument40 SeitenElements of A Typical Cross-Section of Road: Transportation Engineering - INasirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Movement SystemDokument71 SeitenMovement SystemSophia Manila Silla100% (4)
- Highway Cross Sectional Elements and Pavement TypesDokument10 SeitenHighway Cross Sectional Elements and Pavement TypesChidi HenryNoch keine Bewertungen
- BHS advice dimensions width area heightDokument6 SeitenBHS advice dimensions width area heightrodantetorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geometric Design of Roadways Is Separated Into Three LevelsDokument21 SeitenGeometric Design of Roadways Is Separated Into Three LevelsChris AdaminovicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 3 Cross Section ElementsDokument19 SeitenLecture 3 Cross Section ElementsNdanu MercyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cross Section of RoadsDokument41 SeitenCross Section of RoadsHow to code HtcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Designing The HighwayDokument44 SeitenDesigning The HighwayAl-Fahme Sajiran100% (1)
- Chapter 13-14Dokument14 SeitenChapter 13-14markjoseph.lomedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Highway - Chapter 2Dokument63 SeitenHighway - Chapter 2Jandel kier TriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Batas Pambansa BLG 344Dokument20 SeitenBatas Pambansa BLG 344Aira Joy Rivera100% (1)
- Designing Highways: Consistency and Defining TermsDokument34 SeitenDesigning Highways: Consistency and Defining TermsLovely Mae Cruza GawinganNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Lane Widening With Paved ShouldersDokument147 Seiten2 Lane Widening With Paved ShouldersyedidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture No 3Dokument85 SeitenLecture No 3Arman AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- LRFD bridge design standards for cross slopes, medians, sidewalks and bikewaysDokument1 SeiteLRFD bridge design standards for cross slopes, medians, sidewalks and bikewaysLINoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 6 Elements of A Highway SectionDokument4 SeitenLec 6 Elements of A Highway Sectionimran ullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- I, I P F: BranchDokument4 SeitenI, I P F: BranchCris John Parisan JocsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urban Road Types 25.01.2022Dokument5 SeitenUrban Road Types 25.01.2022Balogun IbrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cross-Section and SuperelevationDokument14 SeitenCross-Section and SuperelevationMarilu' CrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Designing The Highwayv2Dokument24 SeitenDesigning The Highwayv2jess21602Noch keine Bewertungen
- محاضرة 1 Cross SectDokument16 Seitenمحاضرة 1 Cross Sectasphalt labNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Guides For Elderly Drivers, Liability inDokument62 SeitenDesign Guides For Elderly Drivers, Liability inAlshenly Gallano AbadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Launching Eastern Shipbuilding Group's Nelson Street FacilityDokument12 SeitenLaunching Eastern Shipbuilding Group's Nelson Street Facilitykebrooks100% (1)
- Vulnerable Road UsersDokument6 SeitenVulnerable Road Usersabdikarim_omarNoch keine Bewertungen
- STIG Design Feutures Traffic Signal Controlled IntersectionDokument4 SeitenSTIG Design Feutures Traffic Signal Controlled IntersectionBillie Ian. Salamante JrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Traffic Design and Visual AidsDokument40 SeitenTraffic Design and Visual AidsPrakash SamshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- SANRAL Geometric Design GuideDokument304 SeitenSANRAL Geometric Design GuideDANIELVISSER86% (22)
- How To Drive On A Motorway: Including Highway Code rules for the motorwayVon EverandHow To Drive On A Motorway: Including Highway Code rules for the motorwayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Special Shoeing: Polo Horses, Hunters, Jumpers and Draft Animals - A Historical Article on the Art of the FarrierVon EverandSpecial Shoeing: Polo Horses, Hunters, Jumpers and Draft Animals - A Historical Article on the Art of the FarrierNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Unless Otherwise Specified, Dimensions Are in Inches.) 1.: Autocad Tutorial: 2D Fundamentals Add-1Dokument10 Seiten(Unless Otherwise Specified, Dimensions Are in Inches.) 1.: Autocad Tutorial: 2D Fundamentals Add-1shaikhaziz84Noch keine Bewertungen
- NSCP Design LoadsDokument10 SeitenNSCP Design LoadsShem Barro88% (33)
- Slope Deflection MethodDokument87 SeitenSlope Deflection MethodFian ArdiyanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Design Questions and AnswersDokument24 SeitenStructural Design Questions and AnswersJohn Kervin Rodriguez100% (1)
- (Unless Otherwise Specified, Dimensions Are in Inches.) 1.: Autocad Tutorial: 2D Fundamentals Add-1Dokument10 Seiten(Unless Otherwise Specified, Dimensions Are in Inches.) 1.: Autocad Tutorial: 2D Fundamentals Add-1shaikhaziz84Noch keine Bewertungen
- RCC13 Punching ShearDokument10 SeitenRCC13 Punching ShearJohn Kervin RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gates HydrauDokument5 SeitenGates HydrauJohn Kervin RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Retaining Wall DesignDokument10 SeitenRetaining Wall DesignklynchelleNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04 MomentDistribution PDFDokument88 Seiten04 MomentDistribution PDFSimran Radheshyam SoniNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE Board Exam 1998Dokument17 SeitenCE Board Exam 1998AaRichard Manalo100% (1)
- Retaining Wall DesignDokument10 SeitenRetaining Wall DesignklynchelleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Retaining Wall: S.No W, LB X, FT M W XDokument1 SeiteDesign of Retaining Wall: S.No W, LB X, FT M W XYOSEMITEROCKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Steel I-Section (BS5950)Dokument6 SeitenDesign of Steel I-Section (BS5950)Rachelle C. Abanes50% (4)
- Steel IntroductionDokument36 SeitenSteel IntroductionSeifeldin Ali MarzoukNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water Transportation PresentationDokument28 SeitenWater Transportation PresentationJohn Kervin RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- HCM 2010 Intersection AnalysisDokument111 SeitenHCM 2010 Intersection AnalysisJohn Kervin RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- CELAW5Dokument25 SeitenCELAW5John Kervin RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- CDC OJT report: Training at Clark Development CorporationDokument5 SeitenCDC OJT report: Training at Clark Development CorporationJohn Kervin RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Climate in The PhilippinesDokument20 SeitenClimate in The PhilippinesJohn Kervin RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering FunctionsDokument25 SeitenEngineering FunctionsJohn Kervin RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measurement of Precipitation (Sattelite)Dokument25 SeitenMeasurement of Precipitation (Sattelite)John Kervin RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formation of PrecipitationDokument24 SeitenFormation of PrecipitationJohn Kervin RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transportation ModelingDokument15 SeitenTransportation ModelingJohn Kervin RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functions of an EngineerDokument25 SeitenFunctions of an EngineerJohn Kervin RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- University of Southeastern PhilippinesDokument11 SeitenUniversity of Southeastern PhilippinesShin BusqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Letter To Request School TestingDokument1 SeiteSample Letter To Request School TestingJohn Kervin RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPM01Dokument11 SeitenCPM01John Kervin RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Moment DistributionDokument27 SeitenMoment DistributionJoanna Marie NunagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case 1: Middle Span Carry Minimum LoadDokument10 SeitenCase 1: Middle Span Carry Minimum Loadsam_cm100% (1)
- Structural Beam Calculator Beam With Load at Location Between Support and LoadDokument4 SeitenStructural Beam Calculator Beam With Load at Location Between Support and LoadSpreadsheetZONENoch keine Bewertungen
- AASHTO 07 - Minimum Designs For Truck and Bus TurnsDokument13 SeitenAASHTO 07 - Minimum Designs For Truck and Bus TurnsValentínNoch keine Bewertungen
- Government Polytechnic Achalpur: Highway EngineeringDokument24 SeitenGovernment Polytechnic Achalpur: Highway EngineeringGauri KarawaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary BOQ New Line Drain ProjectDokument14 SeitenSummary BOQ New Line Drain ProjectMasaya Salad PremiumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Options For The Intersection of U.S. 75 and Main Street in LuverneDokument18 SeitenOptions For The Intersection of U.S. 75 and Main Street in LuverneKari LucinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cross Sections: Lanes and ShouldersDokument29 SeitenCross Sections: Lanes and ShouldersAirvin John PalacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- BRIDGE DESIGN CONSIDERATIONSDokument32 SeitenBRIDGE DESIGN CONSIDERATIONSDammy Taiwo-AbdulNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04c - E70 Vertical Dynamics SystemsDokument76 Seiten04c - E70 Vertical Dynamics SystemsEngine Tuning UpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Section 4Dokument22 SeitenSection 4David BaltazaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Road Siganages & Road FurnitureDokument6 SeitenRoad Siganages & Road FurnitureHemant Gaikwad100% (1)
- Standard Details DrawingsDokument61 SeitenStandard Details DrawingsagilaliqqaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Verge Parking and Indented ParkingDokument17 SeitenVerge Parking and Indented ParkingSharmila ShikariNoch keine Bewertungen
- 064WPR - 10272018 (Final)Dokument524 Seiten064WPR - 10272018 (Final)bert cruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Standart Ulits VilnyusaDokument24 SeitenStandart Ulits VilnyusarockefsNoch keine Bewertungen
- K) Jeddah Road Design Manual - DRAFTDokument290 SeitenK) Jeddah Road Design Manual - DRAFTBahar VaeziNoch keine Bewertungen
- SECTION 02500 Paving and Roadway Appurtenances Restoration: GeneralDokument14 SeitenSECTION 02500 Paving and Roadway Appurtenances Restoration: GeneralDaniel KariukiNoch keine Bewertungen
- SGGP Reference No: P0116-TAK-P01-0071-02Dokument20 SeitenSGGP Reference No: P0116-TAK-P01-0071-02Jabel Oil Services Technical DPTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Standard Drawings For Public Works - San Diego 2012Dokument426 SeitenStandard Drawings For Public Works - San Diego 2012Alex Beldner100% (3)
- Matrix - PALC and DP RequirementsDokument25 SeitenMatrix - PALC and DP RequirementsTajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cement Based Construction Materials: Busineess Proposal OnDokument51 SeitenCement Based Construction Materials: Busineess Proposal OnTesfaye DegefaNoch keine Bewertungen
- B902 PDFDokument7 SeitenB902 PDFSafwat El RoubyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Standard Drawing Set for Infrastructure WorksDokument206 SeitenStandard Drawing Set for Infrastructure WorksHaytham Tantawy73% (15)
- TCS (DRAIN) - Model PDFDokument1 SeiteTCS (DRAIN) - Model PDFYAZERNoch keine Bewertungen
- Checklist Pre-Tender Civil ProjectsDokument8 SeitenChecklist Pre-Tender Civil Projectssarathirv6Noch keine Bewertungen
- App110 20210510Dokument7 SeitenApp110 20210510Luen HopNoch keine Bewertungen
- As 2876-2000 Concrete Kerbs and Channels (Gutters) - Manually or Machine PlacedDokument6 SeitenAs 2876-2000 Concrete Kerbs and Channels (Gutters) - Manually or Machine PlacedSAI Global - APACNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water SystemDokument612 SeitenWater SystemmohdnazirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Certificate Course On Road Safety Audit and Other Road Safety Related AspectsDokument99 SeitenCertificate Course On Road Safety Audit and Other Road Safety Related AspectsNilay Bhavsar100% (1)
- Volume 5 - Information To TendererDokument307 SeitenVolume 5 - Information To TendererFaseen ibnu Ameer AhasenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mxroad PDFDokument2 SeitenMxroad PDFParmar BhavinNoch keine Bewertungen