Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
The Finite Element Method
Hochgeladen von
Shaker Ullah ChowdhuryOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
The Finite Element Method
Hochgeladen von
Shaker Ullah ChowdhuryCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
The finite element method
Began in 1940s to help solve
problems in elasticity and structures
It has evolved to solve nonlinear,
thermal, structural, and
electromagnetic problems
Key commercial codes are ANSYS,
ABAQUS, Nastran, etc.
Well use ANSYS, but other codes are
as good or better (a religious
question)
The Process
Build a model
Geometry
Material Properties
Discretization/mesh
Boundary conditions
Load
Solve
Postprocessing
Structural Elements
Truss
Beam
s
Planar
3-D
Plate
Elements
Truss
Beam
Plana
r
Shell
Brick
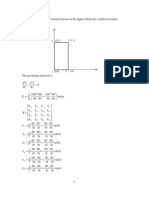
Finite Element Fundamentals
The building block of FEM is the
element stiffness matrix
1
3
2
a
a
(
(
(
(
+ + +
3
3
2
2
1
1
66 62 61
26 22 21
16 12 11
3
3
2
2
1
1
v
u
v
u
v
u
k k k
k k k
k k k
f
f
f
f
f
f
y
x
y
x
y
x
Now Put Several Together
4
5
1
2
3
6
9
8 7
{ } | |{ } U K F =
Global Stiffness
{ }
=
y
x
y
x
y
x
y
x
y
x
y
x
y
x
y
x
y
x
f
f
f
f
f
f
f
f
f
f
f
f
f
f
f
f
f
f
F
9
9
8
8
7
7
6
6
5
5
4
4
3
3
2
2
1
1
{ }
=
9
9
8
8
7
7
6
6
5
5
4
4
3
3
2
2
1
1
v
u
v
u
v
u
v
u
v
u
v
u
v
u
v
u
v
u
U
[K] is a composite of the
element stiffness elements
Once K is known, we can
choose forces and calculate
displacements, or choose
displacements and
calculate forces
Boundary conditions are
needed to allow solution
Element Stiffness
1
3
2
a
a
u
3
u
2
u
1
v
2
v
1
v
3
f
3x
f
1x
f
2x
f
2y
f
1y
f
3y
y
x
How Do We Get Element
Stiffness?
a c c v a c c u
a c c v a c c u
c v c u
a y x
y a x
y x
y c x c c y x v
y c x c c y x u
assume
6 4 3 3 1 3
5 4 2 2 1 2
4 1 1 1
3 3
2 2
1 1
6 5 4
3 2 1
;
;
;
; 0
0 ;
0 ; 0
) , (
) , (
+ = + =
+ = + =
= =
= =
= =
= =
+ + =
+ + =
{ } { }
{ } | | { }
| |
(
(
(
(
(
(
=
=
(
(
(
3
2
1
3
2
1
1
1
3
2
1
3
2
1
1 0 1
0 1 1
0 0
1
1 0 1
0 1 1
0 0
1
0 1
0 1
0 0 1
] [
u
u
u a
a
c
c
c
a
a
A
u A c
c
c
c
a
a
u
u
u
c A u
Coordinates
of element
corners
Substitute
coordinates
into assumed
functions
Rewrite as
matrix
equation
Continued
{ } | |
{ } | |
(
(
(
(
(
(
3
2
1
3
2
1
3
2
1
3
2
1
1 0 1
0 1 1
0 0
1
1
1
1 0 1
0 1 1
0 0
1
u
u
u a
y x
a
u
c
c
c
y x u
u
u
u a
a
c
c
c
{ } | | ( )
( )
( ) ( )y u u x u u au
a
y x u
u u
u u
au
y x
a
u
3 1 2 1 1
3 1
2 1
1
1
) , (
1
1
+ + + + =
+
+ =
Rewrite
assumed
functions
Substitute
Multiply
Continued
( )
3 3 2 2 1 1
3
2
1
3 3 2 2 1 1
3 2 1
) , (
1
) , (
1
) , (
v N v N v N y x v
Similarly
a
y
N
a
x
N
a
y
a
x
N
u N u N u N y x u
yu xu u y x a
a
y x u
+ + =
=
=
=
+ + =
+ + =
Collect terms
Stress-Strain
3 3 2 2 1 1
3 3 2 2 1 1
3
2
1
) , (
) , (
1
v N v N v N y x v
u N u N u N y x u
a
y
N
a
x
N
a
y
a
x
N
+ + =
+ + =
=
=
=
a
v
a
v
a
u
a
u
x
v
y
u
a
v
a
v
y
v
a
u
a
u
x
u
u
x
N
u
x
N
u
x
N
x
u
xy
y
x
x
2 1 3 1
3 1
2 1
3
3
2
2
1
1
+ + =
c
c
+
c
c
=
+ =
c
c
=
+ =
c
c
=
c
c
+
c
c
+
c
c
=
c
c
=
c
c
c
Stress-Strain
| |
| |
| | | | | || | | | | || | B D B tA dV B D B k
a
B
v
u
v
u
v
u
B
T
T
V
xy
y
x
= =
(
(
(
}}}
0 1 1 0 1 1
1 0 0 0 1 0
0 0 0 1 0 1
1
3
3
2
2
1
1
c
c
Comes from
minimizing total
potential energy
(variational
principles)
Material Properties
[D] comes from
the stress-strain
equations
For a linear,
elastic, isotropic
material
{ } | |{ }dV D U
E
D
D
T
V
xy
y
x
xy
y
x
c c
v
v
v
v
c
c
t
o
o
}}}
=
(
(
(
(
2
1
2
1
0 0
0 1
0 1
1
] [
] [
2
Strain Energy
Final Result for Our Case
( )
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
( )
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
(
(
(
(
(
(
(
(
+
+
=
=
(
(
(
(
(
(
(
(
+
+
=
2 0 0 2 2 2
0 1 1 0 1 1
0 1 1 0 1 1
2 0 0 2 2 2
2 1 1 2 3 1
2 1 1 2 1 3
1 4
] [
2
1
2 0 0 2 2 2
0 1 1 0 1 1
0 1 1 0 1 1
2 0 0 2 2 2
2 1 1 2 3 1
2 1 1 2 1 3
1 2
] [
2
2
2 2
v v
v v v v
v v v v
v v
v v v v v
v v v v v
v
v v
v v v v
v v v v
v v
v v v v v
v v v v v
v
Et
k
a A
a
AEt
k
or
( )
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
(
(
(
(
(
(
(
(
+
+
3
3
2
2
1
1
2
3
3
2
2
1
1
2 0 0 2 2 2
0 1 1 0 1 1
0 1 1 0 1 1
2 0 0 2 2 2
2 1 1 2 3 1
2 1 1 2 1 3
1 4
v
u
v
u
v
u
Et
f
f
f
f
f
f
y
x
y
x
y
x
v v
v v v v
v v v v
v v
v v v v v
v v v v v
v
Examples
( ) ( )
( )
1
2
3
3
2
2
1
1
2
1
1
2
1
3
1 4
u
Et
f
f
f
f
f
f
y
x
y
x
y
x
v
v
v
v
v
v
u
1
Examples
v
1
( ) ( )
( )
1
2
3
3
2
2
1
1
2
1
1
2
3
1
1 4
v
Et
f
f
f
f
f
f
y
x
y
x
y
x
v
v
v
v
v
v
Prescribe forces
F
Process
What do we know? v
1
=v
2
=0; f
3y
=F; all
horizontal forces are 0
Remove rigid body motion arbitrarily
set u
1
=0 to remove horizontal translation;
hence, f
1x
is a reaction
Reduce matrix to essential elements for
calculating unknown displacements
cross out rows with unknown reactions
and columns with displacements that are
0
Solve for displacements
Back-solve for reaction forces
Equations
( )
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
( )
)
(
(
(
(
(
(
(
(
(
(
(
+
+
3
3
2
2
3
3
2
2
2
1
1
2 0 2
0 1 0
2 0 2
1 4
0
0
0
0
0
2 0 0 2 2 2
0 1 1 0 1 1
0 1 1 0 1 1
2 0 0 2 2 2
2 1 1 2 3 1
2 1 1 2 1 3
1 4
0
0
v
u
u
Et
F
or
v
u
u
Et
F
f
f
f
y
y
x
v
v
v
v
v v
v v v v
v v v v
v v
v v v v v
v v v v v
v
Solution
(
(
(
1
0
2
3
3
2
v
Et
F
v
u
u
Putting 2 Together
a
a
1
2
1 2
3 4
Element 2 Stiffness Matrix
1
3
2
1 (4)
3 (2)
2
(3)
Rotate 180
o
c s 0 0 0 0
-s c 0 0 0 0
0 0 c s 0 0
0 0 -s c 0 0
0 0 0 0 c s
0 0 0 0 -s c
T =
K = T
T
KT
For 180
o
rotation
K=K
Just rearrange the rows and columns top correspond
to global numbering scheme (in red).
( )
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
(
(
(
(
(
(
(
(
(
(
(
+
+
4
4
3
3
2
2
1
1
2
4
4
3
3
2
2
1
1
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 2 0 0 2 2 2
0 0 0 1 1 0 1 1
0 0 0 1 1 0 1 1
0 0 2 0 0 2 2 2
0 0 2 1 1 2 3 1
0 0 2 1 1 2 1 3
1 4
v
u
v
u
v
u
v
u
Et
f
f
f
f
f
f
f
f
y
x
y
x
y
x
y
x
v v
v v v v
v v v v
v v
v v v v v
v v v v v
v
( )
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
(
(
(
(
(
(
(
(
(
(
(
+
+
4
4
3
3
2
2
1
1
2
4
4
3
3
2
2
1
1
3 1 1 2 2 1 0 0
1 3 1 2 2 1 0 0
1 1 1 0 0 1 0 0
2 2 0 2 2 0 0 0
2 2 0 2 2 0 0 0
1 1 1 0 0 1 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 4
v
u
v
u
v
u
v
u
Et
f
f
f
f
f
f
f
f
y
x
y
x
y
x
y
x
v v v v v
v v v v v
v v v v
v v
v v
v v v v
v
Element Matrices
( )
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
(
(
(
(
(
(
(
(
(
(
(
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
4
4
3
3
2
2
1
1
2
4
4
3
3
2
2
1
1
3 1 1 2 2 1 0 0
1 3 1 2 2 1 0 0
1 1 3 0 0 1 2 2
2 2 0 3 1 0 1 1
2 2 0 1 3 0 1 1
1 1 1 0 0 3 2 2
0 0 2 1 1 2 3 1
0 0 2 1 1 2 1 3
1 4
v
u
v
u
v
u
v
u
Et
f
f
f
f
f
f
f
f
y
x
y
x
y
x
y
x
v v v v v
v v v v v
v v v v v
v v v v v
v v v v v
v v v v v
v v v v v
v v v v v
v
Add the element matrices
What if triangles have midside
nodes?
3
4
5
2
6
1
2
12 11
2
10 9 8 7
2
6 5
2
4 3 2 1
) , (
) , (
y c xy c x c y c x c c y x v
y c xy c x c y c x c c y x u
+ + + + + =
+ + + + + =
What about a quadrilateral element?
3
4
2
1
xy c y c x c c y x v
xy c y c x c c y x u
8 7 6 5
4 3 2 1
) , (
) , (
+ + + =
+ + + =
What about arbitrary shapes?
For most problems, the element
shapes are arbitrary, material
properties are more general, etc.
Typical solution is to integrate stiffness
solution numerically
Typically gaussian quadrature, 4 points
| | | | | || |dV B D B k
T
V
}}}
=
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Continuous and Discrete Time Signals and Systems (Mandal & Asif) Solutions - Chap05Dokument51 SeitenContinuous and Discrete Time Signals and Systems (Mandal & Asif) Solutions - Chap05mvalderm100% (2)
- 4 Node QuadDokument27 Seiten4 Node QuadMathiew EstephoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 7 Sex Limited InfluencedDokument19 SeitenWeek 7 Sex Limited InfluencedLorelyn VillamorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Origami Oso HormigueroDokument9 SeitenOrigami Oso HormigueroRogelio CerdaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Methods of Recording Retruded Contact Position in Dentate PatientsDokument15 SeitenMethods of Recording Retruded Contact Position in Dentate PatientsYossr MokhtarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageVon EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsVon EverandApplication of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- E Flight Journal Aero Special 2018 Small PDFDokument44 SeitenE Flight Journal Aero Special 2018 Small PDFMalburg100% (1)
- TCL LD24D50 - Chassis MS09A-LA - (TKLE2413D) - Manual de Servicio PDFDokument41 SeitenTCL LD24D50 - Chassis MS09A-LA - (TKLE2413D) - Manual de Servicio PDFFabian OrtuzarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jesus Prayer-JoinerDokument13 SeitenJesus Prayer-Joinersleepknot_maggotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solutions of Homework 7: (A) Pressure at x=0, x=l resulting in uniform stress σDokument6 SeitenSolutions of Homework 7: (A) Pressure at x=0, x=l resulting in uniform stress σArthur DingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Turn Around Coordinator Job DescriptionDokument2 SeitenTurn Around Coordinator Job DescriptionMikeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hey Friends B TBDokument152 SeitenHey Friends B TBTizianoCiro CarrizoNoch keine Bewertungen
- X X X X X X X X X X X X X: Sin Lim 4 1 3 1 2 1 3 Sin 3 1 2 2 Sin 2 1 Lim 3 Sin 1 2 Sin 1 Lim: 3 Sin 2 Sin Lim - 1Dokument5 SeitenX X X X X X X X X X X X X: Sin Lim 4 1 3 1 2 1 3 Sin 3 1 2 2 Sin 2 1 Lim 3 Sin 1 2 Sin 1 Lim: 3 Sin 2 Sin Lim - 1Albina ImamovicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mid IDokument11 SeitenMid IpassmefoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linear Algebra Assignment 8Dokument9 SeitenLinear Algebra Assignment 8Adnan Alam KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanics of Solids Week 13 LecturesDokument8 SeitenMechanics of Solids Week 13 LecturesFlynn GouldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discrete Random Variables and Probability DistributionsDokument36 SeitenDiscrete Random Variables and Probability DistributionskashishnagpalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Constant Strain Triangle (CST) : BY R.PONNUSAMY (2008528)Dokument33 SeitenConstant Strain Triangle (CST) : BY R.PONNUSAMY (2008528)hariharanveerannanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSTDokument33 SeitenCSTVasthadu Vasu KannahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tugas SMDokument6 SeitenTugas SMSrie UtariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Finite Element Method (CG NOTE 2)Dokument8 SeitenFinite Element Method (CG NOTE 2)Jon Bisu DebnathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homework 2 SolutionsDokument5 SeitenHomework 2 SolutionsbigevilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chpt05-FEM For 2D SolidsnewDokument56 SeitenChpt05-FEM For 2D SolidsnewKrishna MyakalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q. 1: For The Rectangular Element Shown in The Figure Obtain The Coefficient MatrixDokument6 SeitenQ. 1: For The Rectangular Element Shown in The Figure Obtain The Coefficient MatrixVivek HarrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matri Ni Ra Un: Kemal Halilović, Profesor Matematike Brčko 1Dokument14 SeitenMatri Ni Ra Un: Kemal Halilović, Profesor Matematike Brčko 1*mile*Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Overview of Numerical AnalysisDokument59 Seiten2 Overview of Numerical AnalysisVashish RamrechaNoch keine Bewertungen
- UsingB MatrixDokument8 SeitenUsingB MatrixcrooniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mech300H Introduction To Finite Element Methods: Finite Element Analysis (F.E.A.) of 1-D ProblemsDokument31 SeitenMech300H Introduction To Finite Element Methods: Finite Element Analysis (F.E.A.) of 1-D Problemsbadboys123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hallar Los Valores de Las Siguientes Expresiones:: Limite de Una FunciónDokument8 SeitenHallar Los Valores de Las Siguientes Expresiones:: Limite de Una FunciónValencia Navarrete Diego PaúlNoch keine Bewertungen
- TensorsDokument46 SeitenTensorsfoufou200350% (2)
- I. Newton-Raphson Method - 2 Dim Case: X X X X FDokument9 SeitenI. Newton-Raphson Method - 2 Dim Case: X X X X FsayedmhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Remiting For Clockperiod MinimizationDokument15 SeitenRemiting For Clockperiod MinimizationSameer NandagaveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Configuration Form : System Model RepresentationDokument2 SeitenConfiguration Form : System Model RepresentationTyler GriesingerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Four Node Iso-Parametric Quadrilateral ElementDokument15 SeitenFour Node Iso-Parametric Quadrilateral ElementBiao LiNoch keine Bewertungen
- MATLAB FormulasDokument3 SeitenMATLAB FormulasRoberto Alessandro IonescuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Num SheetDokument1 SeiteNum SheetedexcelpastpapersNoch keine Bewertungen
- PJC h2 Math p1 SolutionsDokument13 SeitenPJC h2 Math p1 SolutionsjimmytanlimlongNoch keine Bewertungen
- 004 - s02 - The Lorentz GroupDokument4 Seiten004 - s02 - The Lorentz GroupBradley NartowtNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE311 HomeworkIII NewsolutionDokument5 SeitenEE311 HomeworkIII Newsolutiondoubleagent93Noch keine Bewertungen
- Shape Function For 4 Noded ElementDokument2 SeitenShape Function For 4 Noded ElementAshish KandoiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Root Finding:: X X D D X X D X XDokument3 SeitenRoot Finding:: X X D D X X D X Xyana22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 14Dokument58 SeitenChap 14Vinayaga VigneshNoch keine Bewertungen
- High Voltage Engineering Lec2Dokument14 SeitenHigh Voltage Engineering Lec2nasirvivacNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics TrigonometryDokument4 SeitenMathematics TrigonometryVara Prasad VemulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linearna Algebra - Rjesenja, ETFDokument44 SeitenLinearna Algebra - Rjesenja, ETFmarkovukNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 5Dokument61 SeitenModule 5Saravanan Kumar PNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mi h2 Math Solutions p1Dokument10 SeitenMi h2 Math Solutions p1jimmytanlimlongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ship in Composite Materials: JL Mantari, PHDDokument15 SeitenShip in Composite Materials: JL Mantari, PHDJL MantariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam 2solutionDokument5 SeitenExam 2solutionJames Steven HaneyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answers For Chapter 13Dokument51 SeitenAnswers For Chapter 13karensheuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formulas14 PDFDokument1 SeiteFormulas14 PDFjuanmiguelgarcesNoch keine Bewertungen
- (PPT) ... Transforming Stress Tensor. Direction Cosines. ... A. Tx. Polar Coordinates. ... Procedure. Use Stress TransformationDokument143 Seiten(PPT) ... Transforming Stress Tensor. Direction Cosines. ... A. Tx. Polar Coordinates. ... Procedure. Use Stress TransformationSampath MummaneniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geometric Transformations 1Dokument26 SeitenGeometric Transformations 1familyumaNoch keine Bewertungen
- L11 Hermite Bicubic Surface PatchDokument15 SeitenL11 Hermite Bicubic Surface PatchAnonymous dGnj3bZNoch keine Bewertungen
- F C D I: Jesús Rubí MirandaDokument2 SeitenF C D I: Jesús Rubí Mirandalmarobesg94Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lista 1Dokument5 SeitenLista 1João Augusto Oliveira LuizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Orthogonality: A X A Sin A X ADokument7 SeitenOrthogonality: A X A Sin A X Ashimo1992Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Number of Paths of Length 4 From: Is2 Is2Dokument4 SeitenThe Number of Paths of Length 4 From: Is2 Is2Đặng Minh KhiêmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classwork Activity #11 With SolutionsDokument2 SeitenClasswork Activity #11 With SolutionsChala1989Noch keine Bewertungen
- (Hidayatul-'Ibaad ila makarim aklaq dawah wal-irshad هِدايةُ العبادِ إلى مكارمِ أخْلاقِ الدَّعوةِ والإرشادِVon Everand(Hidayatul-'Ibaad ila makarim aklaq dawah wal-irshad هِدايةُ العبادِ إلى مكارمِ أخْلاقِ الدَّعوةِ والإرشادِNoch keine Bewertungen
- IBM System 360 RPG Debugging Template and Keypunch CardVon EverandIBM System 360 RPG Debugging Template and Keypunch CardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Logical progression of twelve double binary tables of physical-mathematical elements correlated with scientific-philosophical as well as metaphysical key concepts evidencing the dually four-dimensional basic structure of the universeVon EverandLogical progression of twelve double binary tables of physical-mathematical elements correlated with scientific-philosophical as well as metaphysical key concepts evidencing the dually four-dimensional basic structure of the universeNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 4Dokument6 SeitenCH 4Shaker Ullah ChowdhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 22 Electric FieldsDokument3 SeitenChapter 22 Electric FieldsShaker Ullah Chowdhury100% (1)
- Linear Sorption Isotherm Freundlich Sorption Isotherm Langmuir Sorption Isotherm Linear Sorption IsothermDokument3 SeitenLinear Sorption Isotherm Freundlich Sorption Isotherm Langmuir Sorption Isotherm Linear Sorption IsothermShaker Ullah ChowdhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem BiologyDokument9 SeitenChem BiologyShaker Ullah ChowdhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Calculate Bricks in A WallDokument2 SeitenHow To Calculate Bricks in A WallShaker Ullah ChowdhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question-1: Answer:: Convergent, Divergent and Transform Continental Margins Can Provide Oil & Gas?Dokument6 SeitenQuestion-1: Answer:: Convergent, Divergent and Transform Continental Margins Can Provide Oil & Gas?Shaker Ullah ChowdhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluent For Catia V5Dokument4 SeitenFluent For Catia V5Shaker Ullah ChowdhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- LEIA Home Lifts Guide FNLDokument5 SeitenLEIA Home Lifts Guide FNLTejinder SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biological Beneficiation of Kaolin: A Review On Iron RemovalDokument8 SeitenBiological Beneficiation of Kaolin: A Review On Iron RemovalValentin GnoumouNoch keine Bewertungen
- All You Need To Know About Egg YolkDokument7 SeitenAll You Need To Know About Egg YolkGolden Era BookwormNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agnes de MilleDokument3 SeitenAgnes de MilleMarie-Maxence De RouckNoch keine Bewertungen
- Task 3 - LPDokument21 SeitenTask 3 - LPTan S YeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment of Students' Oral Communication in English ClassDokument10 SeitenAssessment of Students' Oral Communication in English ClassKeebeek S ArbasNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Mantel Colonized Nation Somalia 10 PDFDokument5 SeitenThe Mantel Colonized Nation Somalia 10 PDFAhmad AbrahamNoch keine Bewertungen
- HirePro Video Proctored Online-Instruction Sheet - Bain IndiaDokument1 SeiteHirePro Video Proctored Online-Instruction Sheet - Bain Indiaapoorv sharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Homework Song FunnyDokument5 SeitenThe Homework Song Funnyers57e8s100% (1)
- Vendor Information Sheet - LFPR-F-002b Rev. 04Dokument6 SeitenVendor Information Sheet - LFPR-F-002b Rev. 04Chelsea EsparagozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Online Extra: "Economists Suffer From Physics Envy"Dokument2 SeitenOnline Extra: "Economists Suffer From Physics Envy"Bisto MasiloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical Specification For 33KV VCB BoardDokument7 SeitenTechnical Specification For 33KV VCB BoardDipankar ChatterjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tetralogy of FallotDokument8 SeitenTetralogy of FallotHillary Faye FernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crown WF-3000 1.2Dokument5 SeitenCrown WF-3000 1.2Qirat KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agco Serie 800 PDFDokument24 SeitenAgco Serie 800 PDFJohnny VargasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Residual Power Series Method For Obstacle Boundary Value ProblemsDokument5 SeitenResidual Power Series Method For Obstacle Boundary Value ProblemsSayiqa JabeenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamics of Machinery PDFDokument18 SeitenDynamics of Machinery PDFThomas VictorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sam Media Recruitment QuestionnaireDokument17 SeitenSam Media Recruitment Questionnairechek taiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment#10 Global Strategy and The Multinational CorporationDokument1 SeiteAssignment#10 Global Strategy and The Multinational CorporationAnjaneth A. VillegasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Companyprofil E: Erfanconstructionsolut IonDokument14 SeitenCompanyprofil E: Erfanconstructionsolut IonNurin AleesyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aptitude Number System PDFDokument5 SeitenAptitude Number System PDFharieswaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Farmer Producer Companies in OdishaDokument34 SeitenFarmer Producer Companies in OdishaSuraj GantayatNoch keine Bewertungen