Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Presentation 1
Hochgeladen von
Thila SingamOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Presentation 1
Hochgeladen von
Thila SingamCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
A mobile phone (also known as a cellular phone, cell phone, and a hand phone) is a device that can make
and receive telephone calls over a radio link while moving around a wide geographic area. It does so by connecting to a cellular network provided by a mobile phone operator, allowing access to the public telephone network
Facsimile
A facsimile (from Latin fac simile ('make alike'), a spelling that remained in currency until the late 19th century) is a copy or reproduction of an old book, manuscript, map, art print, or other item of historical value that is as true to the original source as possible. It differs from other forms of reproduction by attempting to replicate the source as accurately as possible in terms of scale, color, condition, and other material qualities
Braille Writer
Braille is a tactile writing system used by the blind and the visually impaired, and found in books, on menus, signs, elevator buttons, and currency. Braille-users can read computer screens and other electronic supports thanks to refreshable braille displays. They can write braille with a slate and stylus or type it on a braille writer, such as a portable braille note-taker, or on a computer that prints with a braille embosser.
Ham Radio
Ham Radio, also known as Amateur Radio is a popular hobby and a service in which licensed participants operate communications equipment with a deep appreciation of the radio art. The unique hobby of Amateur Radio is a mix of fun, public service, and convenience.
Morse Code
Morse Code is named after Samuel F. B. Morse (1791-1872), a painter and founder of the National Academy of Design, who, along with Alfred Vail (1807-1859) a machinist and inventor, and the physicist Joseph Henry (1797-1878) developed the electromagnetic telegraph and the code that assigns a set of dots and dashes or short and long pulses to each letter of the English alphabet.
Notebook
A notebook (notepad, writing pad, drawing pad, legal pad) is a book or binder composed of pages, often ruled, made out of paper, used for purposes including recording notes or memoranda, writing, drawing, and scrapbooking
Radio
How radio communication works. Information such as sound is transformed into an electronic signal which is applied to a transmitter. The transmitter sends the information through space on a radio wave (electromagnetic wave). A receiver intercepts some of the radio wave and extracts the information-bearing electronic signal, which is converted back to its original form by a transducer such as a speaker.
Telephone
A telephone, or phone, is a telecommunications device that permits two or more users to conduct a conversation when they are not in the same vicinity of each other to be heard directly. A telephone converts sound, typically and most efficiently the human voice, into electronic signals suitable for transmission via cables or other transmission media over long distances, and replays such signals simultaneously in audible form to its user. The word telephone has been adapted into the vocabulary of many languages. It is derived from the Greek: , tle, far and , phn, voice, together meaning distant voice.
Television
Television (TV) is a telecommunication medium for transmitting and receiving moving images that can be monochrome (black-and-white) or colored, with or without accompanying sound. "Television" may also refer specifically to a television set, television programming, or television transmission.
Typewriter
A typewriter is a mechanical or electromechanical machine for writing in characters similar to those produced by printer's type by means of keyboard-operated types striking a ribbon to transfer ink or carbon impressions onto the paper.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Thomas Calculus 11th (Textbook + Solutions)Dokument140 SeitenThomas Calculus 11th (Textbook + Solutions)Sendhilkumar Alalasundaram76% (33)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- HAARP InfoDokument7 SeitenHAARP InfoThomas BoncioNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Lecture 10 PiezoresistiveDokument13 SeitenLecture 10 Piezoresistives_hassan_167419100% (1)
- Surface Movement Radar 0Dokument6 SeitenSurface Movement Radar 0rainatkmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anagram Riddles 3Dokument2 SeitenAnagram Riddles 3Thila Singam100% (5)
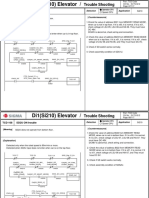
- TCD 114 RPD ON trouble detection and countermeasuresDokument7 SeitenTCD 114 RPD ON trouble detection and countermeasuresFERNSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Valleylab Force FX-C Service ManualDokument230 SeitenValleylab Force FX-C Service Manualbiomedico123100% (5)
- Family and Friends Daily ActivitiesDokument4 SeitenFamily and Friends Daily ActivitiesThila SingamNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Brave Little ParrotDokument4 SeitenThe Brave Little ParrotThila SingamNoch keine Bewertungen
- BAHASA INGGERIS 014 TAHUN 5 - Copy-DPETD01AMJADDokument4 SeitenBAHASA INGGERIS 014 TAHUN 5 - Copy-DPETD01AMJADThila SingamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Word CardsDokument16 SeitenWord CardsThila SingamNoch keine Bewertungen
- PBD Transit Form DailyDokument5 SeitenPBD Transit Form DailyThila SingamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rancangan Pelajaran Harian 2018: SK Sungai Kelamah (F)Dokument14 SeitenRancangan Pelajaran Harian 2018: SK Sungai Kelamah (F)Thila SingamNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Colour Is The SkyDokument6 SeitenWhat Colour Is The SkyThila SingamNoch keine Bewertungen
- PBD Transit Form DailyDokument5 SeitenPBD Transit Form DailyThila SingamNoch keine Bewertungen
- SK SUNGAI KELAMAH(F) MARCH 2018 MONTHLY TESTDokument4 SeitenSK SUNGAI KELAMAH(F) MARCH 2018 MONTHLY TESTThila SingamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Post Upsr ProgrammeDokument4 SeitenPost Upsr ProgrammeThila SingamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Words Ending With XDokument14 SeitenWords Ending With XThila SingamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sicka Picka PDFDokument2 SeitenSicka Picka PDFVladimirStijepovićNoch keine Bewertungen
- Consonant Dig Raph Game CardsDokument2 SeitenConsonant Dig Raph Game CardsThila SingamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alyaa Darwisyah Syahir Arif Danial Haikal Sakinah D. Akmar D. Rezza Danial Aiman Alif Najmi Ain Izzati Khairil Aidil AkhmalDokument6 SeitenAlyaa Darwisyah Syahir Arif Danial Haikal Sakinah D. Akmar D. Rezza Danial Aiman Alif Najmi Ain Izzati Khairil Aidil AkhmalThila SingamNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Year 3 Paper 2 140204012751 Phpapp01Dokument6 SeitenEnglish Year 3 Paper 2 140204012751 Phpapp01Zatul Izawati Ahmad IbrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rearrange The Words To Form Correct SentencesDokument1 SeiteRearrange The Words To Form Correct SentencesThila SingamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Story TellingDokument5 SeitenStory TellingThila SingamNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1Dokument2 Seiten1Thila SingamNoch keine Bewertungen
- SK SG Kelamah (F) September Monthly Test English Language Year 3 (1 HOUR) Name: ClassDokument7 SeitenSK SG Kelamah (F) September Monthly Test English Language Year 3 (1 HOUR) Name: ClassThila SingamNoch keine Bewertungen
- RPT Bi Yr 6 2017 by Teacher Fiza v1.0 v3Dokument19 SeitenRPT Bi Yr 6 2017 by Teacher Fiza v1.0 v3Thila SingamNoch keine Bewertungen
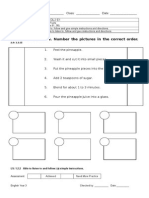
- Read The Sentences. Number The Pictures in The Correct OrderDokument1 SeiteRead The Sentences. Number The Pictures in The Correct Order4schoolyNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Year 3 Paper 2 140204012751 Phpapp01Dokument6 SeitenEnglish Year 3 Paper 2 140204012751 Phpapp01Zatul Izawati Ahmad IbrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1Dokument2 Seiten1Thila SingamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inovasi PBS Eng Y3 33Dokument1 SeiteInovasi PBS Eng Y3 33Thila SingamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Use prepositions correctly in sentencesDokument1 SeiteUse prepositions correctly in sentencesThila SingamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inovasi PBS Eng Y3 21Dokument1 SeiteInovasi PBS Eng Y3 21Thila SingamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test 2Dokument11 SeitenTest 2Thila SingamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effective Teaching StrategiesDokument3 SeitenEffective Teaching StrategiesThila Singam100% (1)
- Before You Cross The RoadDokument1 SeiteBefore You Cross The RoadThila SingamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infrared people counter counts entriesDokument3 SeitenInfrared people counter counts entriesthisissanjay100% (1)
- Chapter 8 - SynchronousDokument12 SeitenChapter 8 - SynchronousLin ChongNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9mm!ূຌዡገ๕ۉ࿋ഗ Rotary Potentiometers With Metal Shaft Series: WH9011A-1-18TDokument26 Seiten9mm!ূຌዡገ๕ۉ࿋ഗ Rotary Potentiometers With Metal Shaft Series: WH9011A-1-18TpeterfunNoch keine Bewertungen
- LAN Switch FundamentalsDokument24 SeitenLAN Switch Fundamentalssanky08Noch keine Bewertungen
- HPL - Solar All in One OfferingDokument2 SeitenHPL - Solar All in One OfferingShivamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Day 1 08 SE PDFDokument98 SeitenDay 1 08 SE PDFnova hilangNoch keine Bewertungen
- 34OJWN3gb Installation and OperatingDokument16 Seiten34OJWN3gb Installation and OperatingluanagueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nuclear Physics Multiple Choice QuestionsDokument5 SeitenNuclear Physics Multiple Choice QuestionssaleemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Velocity of Longitudinal WaveDokument12 SeitenVelocity of Longitudinal WaverenzoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monbat 12V200AhDokument1 SeiteMonbat 12V200AhMaria MuresanNoch keine Bewertungen
- SIVACON - The Versatile Low-Voltage Switchboard: Type-Tested Power Distribution Board 8PTDokument28 SeitenSIVACON - The Versatile Low-Voltage Switchboard: Type-Tested Power Distribution Board 8PTharianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Opencv User Guide: Release 2.4.9.0Dokument23 SeitenThe Opencv User Guide: Release 2.4.9.0osilatorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dialight LED Catalog UL StreetSense-StreetLight Americas EnglishDokument2 SeitenDialight LED Catalog UL StreetSense-StreetLight Americas EnglishDonalyn AdolfoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Efficiency Improvement of Wireless Charging SystemDokument9 SeitenEfficiency Improvement of Wireless Charging Systemgreeshmar967Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Notes On BJT & FETDokument10 SeitenLecture Notes On BJT & FETVamsi Krishna100% (3)
- Waveform Substitution Techniques For Recovering Missing Speech Segments in Packet Voice CommunicationsDokument9 SeitenWaveform Substitution Techniques For Recovering Missing Speech Segments in Packet Voice CommunicationsThuy Dieu NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- High Voltage EngineeringDokument38 SeitenHigh Voltage EngineeringsjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plc-5 Programmable Controllers Selection Guide 1785 and 1771Dokument60 SeitenPlc-5 Programmable Controllers Selection Guide 1785 and 1771diogo_kuster100% (1)
- tms320f28p559sj-q1Dokument268 Seitentms320f28p559sj-q1heliosentricNoch keine Bewertungen
- Short Overview of Perovskite Solar CellsDokument14 SeitenShort Overview of Perovskite Solar CellsFAISAL TAIMURINoch keine Bewertungen
- Real-Time Implementation of Hydroelectric Power Plant Using PLC and ScadaDokument4 SeitenReal-Time Implementation of Hydroelectric Power Plant Using PLC and ScadaJosephNoch keine Bewertungen
- Limit Fault Currents With FCL DeviceDokument1 SeiteLimit Fault Currents With FCL DeviceTrần Khắc ĐộNoch keine Bewertungen
- User's Manual: CNPS9700 / 9500A LEDDokument9 SeitenUser's Manual: CNPS9700 / 9500A LEDNelson CantoNoch keine Bewertungen