Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Modern Algebra Final
Hochgeladen von
Vholts Villa VitugOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Modern Algebra Final
Hochgeladen von
Vholts Villa VitugCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
PLUMBING ARITHMETIC
CENTER FOR Philippines
TECHNICAL PROFESSIONS
A. NUMBER SYSTEM
A number is an item that describes a magnitude
or position. Numbers are classified into two
types, namely cardinal numbers and ordinal
numbers.
Cardinal numbers are numbers which allow us
to count the objects or ideas in a given
collection (i.e. 1, 2, 3,... 1000, 100000. Ordinal
numbers state the position of individual objects
in a sequence (i.e. first, second, third,...)
The number system is divided into two
categories, namely, real numbers and
imaginary numbers.
Real numbers are classified as follows:
Natural numbers considered as the counting
numbers. Ex. 1, 2, 3, ...
Integers the natural numbers, the negative numbers
and zero. Ex. -4, -1, 0, 3, 8
Rational numbers numbers which can be expressed
as a quotient (ratio) of two integers. Ex. 0.5, , -3,
0.333...
As a rule, a non-terminating but repeating (or
periodic) decimal is always a rational number. Also,
all integers are rational numbers.
Irrational numbers numbers which cannot be
expressed as a quotient of two integers. Ex. , , e, ...
They are in fact, non-terminating numbers with
non-repeating decimals.
Past Board Exam:
The number 7 + 0i is a/an ________ number.
a. Irrational c. Real
b. Imaginary d. Complex
Past Board Exam:
The number 0.123123123... is a _______
number.
a. Irrational c. Rational
b. Imaginary d. Complex
A complex number is an expression of both
real and imaginary number combined. It
takes the form of a +bi, where a and b
are real numbers.
If a = 0, then pure imaginary number is
produced while real number is obtained
when b = 0.
An imaginary number is denoted as i
which is equal to the square root of negative
one. In some other areas in mathematical
computation, especially in electronics and
electrical engineering it is denoted as j.
Imaginary number and its equivalent:
Past Board Exam:
Find the value of
1 i =
2
1 i =
3
i i =
4
i i =
5
(1 ) . i +
B. SIGNIFICANT DIGITS
Significant figures or digits define the
numerical value of a number. A digit is
considered significant unless it is used
to place a decimal point.
The significant digit of a number begins
with the first non-zero digit and ends
with the final digit, whether zero or non-
zero.
Past Board Exam:
The number 0.004212 has how many
significant digits?
Past Board Exam:
Round off 0.00432500 to 3 significant figures.
a. 0.00432000 c. 0.00433
b. 0.00433000 d. 0.00432
C. LEAST COMMON
MULTIPLE
A common multiple is a number that two
other numbers will divide into evenly. The
least common multiple (LCM) is the lowest
multiple of two numbers.
Past Board Exam:
What is the least common multiple of 15 and
18?
D. GREATEST COMMON
FACTOR
A factor is a number that divides into a
larger number evenly. The greatest
common factor (GCF) is the largest
number that divides into two or more
numbers evenly. Greatest common
factor is the same as greatest common
divisor (GCD).
Past ECE Board Exam:
What is the GCF of 70 and 112?
E. EXPONENTS
An exponent is a number that gives the
power to which a base is raised. For
example, in 3
2
, the base is 3 and the
exponent is 2.
The exponential notation states that if a is a
real number, variable or algebraic
expression and n is a positive number,
then:
n
a a a a a =
Properties of Exponents
Past Board Exam:
Solve for x in the given equation
a. 2 c. 4
b. 3 d. 5
Past Board Exam:
Find the value of x in the equation (3
5
)(9
6
) = 3
2x
.
a. 8.5 c. 9.5
b. 9 d. 8
Past Board Exam:
Solve for x if
a. 0.723 c. 0.852
b. 0.618 d. 0.453
4 3
8 2 8 2. x =
1 1 1 ... x =
F. LOGARITHMS
The logarithm of a number or variable x to
base b, is the exponent of b needed to give x.
i.e. may be written as
The term logarithm comes from Greek
words, logus meaning ratio and arithmus
meaning number. John Napier (1550-1617)
invented logarithm in 1614 using e = 2.718...
for its base. In 1616, through the suggestion of
John Napier, Henry Briggs improved the
logarithm using 10 as the base. The logarithm
with base 10 is known as common logarithm
or the Briggsian logarithm.
2
log 16 4 =
4
2 16. =
The natural logarithm can be converted into
a common logarithm and vice versa. To
obtain this, a factor known as the modulus
of logarithm is necessary, such as:
The coefficients 0.4343 and 2.3026 are the
referred to as the modulus of logarithm.
log 0.4343ln x x = ln 2.3026log x x =
Properties of Logarithm
Past Board Exam:
Which of the following logarithmic
equations is equivalent to
a. c.
b. d.
Past Board Exam:
If , what is the value of
Past Board Exam:
Solve for x.
0
3 1? =
3
log 0 1 =
1
log 3 0 =
3
log 1 0 =
3
log 1 1 =
2
3
729 a =
1
2
. a
log 27 log 3 2
x x
+ =
G. REMAINDER THEOREM
Remainder Theorem states that if a
polynomial in an unknown quantity x is
divided by a first degree expression in
the same variable, (x-k), where k may
be any real number or complex number,
the remainder to be expected will be
equal to the sum obtained when the
numerical value of k is substituted for x
in the polynomial.
Past Board Exam:
What is the remainder if the polynomial
is divided by (x 5)?
a. 281 c. 218
b. 812 d. 182
Past Board Exam:
Given: f(x) = (x + 3)(x 4) + 4 when divided
by (x k), the remainder is k. Find k.
a. 2 c. 4
b. 3 d. -3
3 2
4 3 8 x x x + +
H. FACTOR THEOREM
Factor theorem states that if a
polynomial is divided by (x k) will result
to a remainder of zero, then the value
(x k) is a factor of the polynomial.
Past Board Exam:
What is the value of k if (x + 4) is a
factor of
3 2
2 7 ? x x x k + +
I. QUADRATIC EQUATION
Quadratic is an expression or an equation
that contains the variable squared, but not
raised to any higher power. A quadratic
equation in x is also known as a second-
degree polynomial equation.
The general quadratic equation is
expressed as:
Ax
2
+ Bx +C = 0
where A, B and C are real numbers and
with A 0.
The quadratic formula:
The quantity B
2
4AC in the above equation
is known as the discriminant. It determines
the nature of the roots of the quadratic
equation.
B
2
4AC Nature of roots
0 Only one root
(real and equal)
>0 Real and unequal
<0 Imaginary and unequal
2
4
2
B B AC
x
A
=
Sum of roots
Product of roots
Past Board Exam:
Two reviewees are solving a problem leading to a
quadratic equation. One student made a mistake in
the coefficient of the first degree term, got roots of 2
and -3. The other made a mistake in the coefficient of
the constant term and got roots of -1 and 4. What is
the correct equation?
Past Board Exam:
From the equation
determine the value of k so that the sum and product of
the roots are equal.
1 2
B
r r
A
+ =
1 2
C
r r
A
=
2
7 (2 1) 3 2 0 x k x k + + =
J. BINOMIAL THEOREM
Binomial is an expression containing two
terms joined by either + or -.
Binomial theorem gives the result of raising
a binomial expression to a certain power.
The expansion and the series it leads to are
called the binomial expansion and the
binomial series, respectively. The binomial
theorem is expressed as follows:
( )
( )
2 2 1
1
......
2!
n
n n y n n n
n n
x y x nx y x y nxy y
+ = + + + + +
Properties of Binomial expansion of (x + y)
n
:
The number of terms in the resulting expansion
is equal to n + 1.
The exponent of x decreases by 1 in succeeding
terms, while that exponent of y increases by 1 in
succeeding terms.
The sum of the exponents of each term is equal
to n.
The first term is x
n
and the last term is y
n
and
each of the terms has a coefficient of 1.
The coefficient increases and then decreases in
a symmetric pattern.
The Pascals Triangle:
Each number in the triangle is equal to the
sum of the two numbers immediately above it.
Another way to determine the coefficient of any
term in the binomial expansion is to use the
following formula:
where C is the coefficient of any term and PT is
the preceding term
The r
th
term of the binomial expansion of (x + y)
n
may be calculated using the following formulas:
( ) ( )
.
1
Coeff ofPT ExponentofxofPT
C
ExponentofyofPT
=
+
( ) ( )
( )
( )
1
1
1
1
1
( 1) 2 ... 2
( 1)!
n r
th r
n r
th r
n r
n n n n r
r x y
r
r C x y
+
+
+
=
=
A term involving a variable with a specific
exponent is obtained by using the following
formula:
Sum of the coefficients of the expansion of
(x + y)
n
: Sum = (Coeff. of x + coeff. of y)
n
Sum of exponents of the expansion of
(x + y)
n
: Sum = n (n + 1)
( )( ) ( )
1 2 ... 1
'
!
n r
r
n n n n r
y x y
r
+
=
Past Board Exam:
Find the 6
th
term of the expansion of (3x + 4y)
8
.
Past Board Exam:
What is the sum of the numerical coefficients of the
expansion of (x + 4y)
12
?
Past Board Exam:
Find the sum of the coefficient of the variables in
the expansion of (3x 5)
6
.
Past Board Exam:
Find the term involving x
3
in the expansion of
(x 3x
-1
)
9
.
K. WORD PROBLEMS
Most word problems in algebra are
expressed in sentences rather than pure
mathematical expressions or equations.
To solve a word problem, one must first
interpret the sentences into its accurate
mathematical expression and then apply
algebraic operations to the expression
obtained.
AGE PROBLEMS
One of the most common problems in
Algebra is the age problem. This type of
problems must be solved meticulously by
giving emphasis to the tenses (i.e. past,
present or future) of the statement.
Past Board Exam:
Anna is 3 times as old as Mae. In 3 years,
she will be 2 years more than twice the age
of Mae will be then. What are their ages?
Past Board Exam:
Mary is 24 years old. She is twice as old as
Ann was when she was as old as Ann is now.
How old is Ann?
Past Board Exam:
The sum of the parents ages is twice the sum
of their childrens ages. Five years ago, the
sum of the parents ages is four times the sum
of their childrens ages. In fifteen years, the
sum of the parents ages will be equal to the
sum of their childrens ages. How many
children were in the family?
WORK PROBLEMS
Work done = rate of work x time
For a complete job.
Rate x time = 1
When there is a specific work and specific
time and manpower, the rate of doing the
work may be computed using the number of
man-hours.
Past Board Exam:
A tank is fitted with an intake pipe that can
fill it in 4 hours and an outlet pipe that can
empty it in 9 hours. If both pipes are
opened, how long will it take to fill the empty
tank?
Past Board Exam:
If 20 bakers can bake 40 pizzas in 8 hours,
how many bakers can bake 10 pizzas in 2
hours?
Past Board Exam:
A father can do a job in 9 days and his
son can do same job in 16 days. They
worked together. After 4 days, the son
leave and the father finished the job
alone. How many more days did it take
for the father to finish the job alone?
MIXTURE PROBLEMS
A basic idea in solving mixture problems is the
fact that the amount of the substances in the
mixture components is equal to the amount of
the final mixture.
Past Board Exam:
A 100 liter solution is 75% alcohol and 25%
gasoline. How much gasoline must be added to
produce a 50-50 mixture?
Digit Problems
Let h, t and u be the hundreds, tens, and
units digit, respectively. A three-digit
number must be represented in the
following manner.
Number = (h)(100) + (t)(10) + (u)
A two-digit number is represented by;
Number = (t)(10) + (u)
Past Board Exam:
The sum of the digits of a two-digit numbers
is 11. If the digits are reversed, the resulting
number is seven more than twice the
original number. What is the original
number?
Past Board Exam:
The sum of the digits of a 2-digit number is
10. If the number is divided by the units
digit, the quotient is 3 and the remainder is
4. Find the number.
Past Board Exam:
The denominator of a certain fraction is
three more than twice the numerator. If 7 is
added to both terms of the fraction, the
resulting fraction is 3/5. Find the original
fraction.
Motion Problems
In Algebra, the problems pertaining to
motion deals only with a uniform velocity,
i.e., no acceleration or deceleration in the
process. The following is the relationship
between the distance, time and velocity.
D = Vt V = D/t t = D/V
Past Board Exam:
A man rows downstream at the rate of 5
mph and upstream at the rate of 2 mph.
How far downstream should he go if he is
to return in 7/4 hours after leaving?
Past Board Exam:
An airplane travels from point A to point B
with a distance of 1500 km and a wind
along its flight line. If it takes the airplane 2
hours from A to B with the tailwind and 2.5
hours from B to A with the headwind, what
is the velocity of the plane?
Past Board Exam
Pedro started running at a speed of 10 kph.
Five minutes later, Mario started running in
the same direction and catches up with
Pedro in 20 minutes. What is the speed of
Mario?
Coin Problems
In solving coin problems, take note of the
denominations of the currency being used.
For US dollar currency, the following are the
equivalent value for each coin.
Penny 1 cent
Nickel 5 cents
Dime 10 cents
Quarter 25 cents
Half 50 cents
Past Board Exam:
A purse contains $11.65 in quarters and
dimes. If the total number of coins is 70,
find how many dimes are there.
Past ECE Board Exam:
In a box there are 25 coins consisting of
quarters, nickels and dimes with a total
amount of $2.75. If the nickels were dimes,
the dimes were quarters and the quarters
were nickels, the total amount would be
$3.75. How many quarters are there?
Clock Problems
Clock problems focus on the relationship of
the movements of the hands (hour hand,
minute hand, second hand) of the clock.
The longest hand is the second hand while
the shortest hand is the hour hand. By
principle, the second hand (SH) always
moves faster than the minute hand (MH)
and the minute hand always moves faster
than the (HH).
The relation between the three hands of the
clock are as follows:
Past Board Exam:
In how many minutes after 2 oclock will the
hands of the clock extends opposite
direction for the first time?
12
MH
HH =
720
SH
HH =
60
SH
MH =
Past Board Exam:
At how many minutes after 3pm will the
minute hand coincide with the hour hand?
Past Board Exam;
At what time after 12 noon will the hour
hand and minute hand of the clock forms an
angle of 120
o
?
Variation Problems
Variation problems are problems in algebra
which show the relationship between the
variables in terms of expressions such as
directly proportional or inversely proportion
or simply proportional.
The expression x varies directly as y is
expressed as follows: x y
The symbol varies () is replaced by an
equality symbol and a constant of
proportionality, k, hence: x = ky
The expression x varies inversely as the
square of y is expressed as follows:
Past ECE Board Exam:
If x varies directly as y and inversely as z,
and x = 14 when y = 7 and z = 2, find the
value of x when y = 16 and z = 4.
2
1
x k
y
=
Past ECE Board Exam:
The resistance of a wire varies directly with
its length and inversely with its area. If a
certain piece of wire 10m long and 0.10cm
in diameter has a resistance of 100 ohms,
what will its resistance be if it is uniformly
stretched so that its length becomes 12m?
L. PROGRESSION
A sequence is a set or collection of
numbers arranged in an orderly manner
such that the preceding and the following
numbers are completely specified.
An infinite sequence is a function whose
domain is the set of positive integer. If the
domain of the function consists of the first n
positive integers only, then it is said to be a
finite sequence.
Elements are the term used to describe the
numbers in a given sequence. An element
is sometimes called a term.
Series is the sum of the terms in a
sequence. An alternating series has
positive and negative terms arranged
alternately.
If an infinite series has a finite sum, it is
referred to as convergent series and
divergent series if it has no sum at all.
A progression is simply another term for a
sequence.
Arithmetic Progression
A sequence is said to be in arithmetic
progression if its succeeding terms have a
common difference.
The corresponding sum of all the terms in
arithmetic progression is called as
arithmetic series.
Last term (n
th
term):
Sum of all terms:
or
Where:
= first term
= last term (n
th
term)
n = number of terms
d = common difference
d = a
2
a
1
= a
3
a
2
= ...
( )
1
1
n
a a n d = +
( )
1
2
n
n
S a a = +
( )
1
2 1
2
n
S a n d = + (
1
a
n
a
Geometric Progression
A sequence is said to be a geometric
progression if its succeeding terms have a
common ratio.
The corresponding sum of all the terms in
geometric progression is called as
geometric series.
Last term (n
th
term): a
n
= a
1
r
n-1
Sum of all terms:
or
Where:
= first term
= last term (n
th
term)
n = number of terms
r = common ratio =
1
a
n
a
( )
1
1
1
n
a r
S
r
=
( )
1
1
1
n
a r
S
r
3 2
1 2
a a
a a
=
Infinite Geometric Progression
This type of progression is a geometric
progression only that the number of terms
(n) is extremely large or infinity.
If r>1, sum of all terms is infinite
If r<1, the sum of all terms is
Where: a
1
= first term
r = common ratio
1
1
a
S
r
=
Harmonic Progression
A sequence of numbers whose reciprocals
form an arithmetic progression is known as
harmonic progression. In solving a
problem, it would be wise to convert all
given terms into arithmetic sequence by
getting its reciprocals. Use the formulas in
arithmetic sequence and take the reciprocal
of resulting value to obtain the equivalent
harmonic term for an answer.
Past Board Exam:
How many terms of the sequence -9, -6, -3,
must be taken so that the sum is 66?
Past Board Exam:
There are seven arithmetic means between 3 and
35. Find the sum of all the terms.
Past Board Exam:
Determine the sum of the infinite geometric series
of 1, -1/5, 1/25,
Past Board Exam:
Find the sum of the first 10 terms of the GP 2, 4,
8, 16,
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Pre-Algebra and AlgebraDokument66 SeitenPre-Algebra and Algebramiccass100% (20)
- Integer OperationsDokument14 SeitenInteger Operationsnatashkan100% (1)
- 1.basic Mathematics - Theory & Exercise PartDokument32 Seiten1.basic Mathematics - Theory & Exercise PartLikhith UsurupatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculator Techniques For Solving Progression ProblemsDokument8 SeitenCalculator Techniques For Solving Progression ProblemsDash SmthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical ProblemsDokument9 SeitenPractical Problemscesardako100% (2)
- EcomomicsDokument30 SeitenEcomomicsJayvee BalagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final S-CurveDokument30 SeitenFinal S-CurveErwin Macapinlac MabutiNoch keine Bewertungen
- REB-Basic Principles of EcologyDokument8 SeitenREB-Basic Principles of EcologyVholts Villa Vitug100% (4)
- MC 54 PDFDokument6 SeitenMC 54 PDFMarvis Garcia DellosaNoch keine Bewertungen
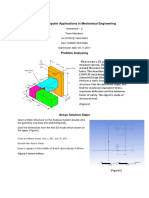
- ME 472 Computer Applications in Mechanical Engineering (Şarmutah)Dokument4 SeitenME 472 Computer Applications in Mechanical Engineering (Şarmutah)Isa Gumus100% (1)
- Sanitary Engineer Board Exam January-February 2022 ProgramDokument4 SeitenSanitary Engineer Board Exam January-February 2022 ProgramPRC BoardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Milestones Studyguide Algebra1 11-16 CompressedDokument276 SeitenMilestones Studyguide Algebra1 11-16 Compressedapi-268582979100% (1)
- Formworks (Lecture & Sample Problems) : Quantity Surveying Professor: Engr. Shane Francis B. GarciaDokument28 SeitenFormworks (Lecture & Sample Problems) : Quantity Surveying Professor: Engr. Shane Francis B. GarciaJohn AbandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- LimitsDokument1 SeiteLimitsJogor SinagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Builders: Demolition Excavation Hauling Design PaintingDokument2 SeitenBuilders: Demolition Excavation Hauling Design PaintingVholts Villa VitugNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plumbing Final Pre-BoradDokument12 SeitenPlumbing Final Pre-BoradVholts Villa Vitug71% (7)
- Building System Design Quizzes 2Dokument4 SeitenBuilding System Design Quizzes 2Edmar TabinasNoch keine Bewertungen
- USA Harvard MIT Mathematics Tournament 2013 139Dokument11 SeitenUSA Harvard MIT Mathematics Tournament 2013 139Ml PhilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Estimate Guide-Dry WallsDokument1 SeiteEstimate Guide-Dry WallsVholts Villa Vitug100% (5)
- Engineering Economy Problem1Dokument11 SeitenEngineering Economy Problem1frankRACENoch keine Bewertungen
- PD 1216 - Open SpaceDokument2 SeitenPD 1216 - Open SpaceVholts Villa VitugNoch keine Bewertungen
- OW Building SpecificationsDokument20 SeitenOW Building SpecificationsVholts Villa Vitug0% (1)
- + 18y + 8y - 4 Is Divided byDokument27 Seiten+ 18y + 8y - 4 Is Divided byAndrea Sochayseng Solijon100% (1)
- Module 1 Lesson 2 Basic Concepts For Construction DatabaseDokument23 SeitenModule 1 Lesson 2 Basic Concepts For Construction DatabaseErza LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topology Without Tears PDFDokument277 SeitenTopology Without Tears PDFPranshu Gupta100% (2)
- Clock ProblemsDokument2 SeitenClock ProblemskennethNoch keine Bewertungen
- Excel Review: A: Large B: Highest C: Most D: MaximumDokument4 SeitenExcel Review: A: Large B: Highest C: Most D: MaximumkbfalknerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lotech Welding Can Purchase A Machine For 175000 and Depreciate It As 5 Year Macrs PropertyDokument1 SeiteLotech Welding Can Purchase A Machine For 175000 and Depreciate It As 5 Year Macrs PropertyDoreenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vectors and MatricesDokument8 SeitenVectors and MatricesdorathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Partial DiffDokument25 SeitenPartial DiffNitin GroverNoch keine Bewertungen
- EkoTek Capitalized CostDokument10 SeitenEkoTek Capitalized CostLoharvik TNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overview+Soil Quiz 1Dokument241 SeitenOverview+Soil Quiz 1Elmer Cabulisan JrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 1Dokument10 SeitenProblem 1BeverlyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ugrd-Nsci6100-2016s Calculus-Based Physics 1 Prefinal ExamDokument22 SeitenUgrd-Nsci6100-2016s Calculus-Based Physics 1 Prefinal ExamLeo Jade AbiertasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final ExamDokument5 SeitenFinal ExamNarcisa RudnicNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Engineer and The Four P's of MarketingDokument4 SeitenThe Engineer and The Four P's of MarketingJunatan DinglasaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eqe Reviewer With AnswerDokument16 SeitenEqe Reviewer With AnswerKirstie Alley San JoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- MIT Math Correl 2nd Term AY 2014 2015 RetakeDokument9 SeitenMIT Math Correl 2nd Term AY 2014 2015 RetakeJhera Ku100% (1)
- Numerical Methods On Finding The RootsDokument26 SeitenNumerical Methods On Finding The RootsRobby Andre ChingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Profile Leveling 2Dokument20 SeitenProfile Leveling 2Arslan AnjumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ce Laws, Contracts and SpecificationsDokument20 SeitenCe Laws, Contracts and SpecificationsMIKE ARTHUR DAVIDNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2017.04.07 - Nicholaus Building - Structural Assessment LetterDokument2 Seiten2017.04.07 - Nicholaus Building - Structural Assessment LetterAnonymous Pg7RtdU8uHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weekly Progress Report: Republic of The Philippines Philippine Rural Development Project (PRDP)Dokument73 SeitenWeekly Progress Report: Republic of The Philippines Philippine Rural Development Project (PRDP)stella marizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Timber Design Module 1Dokument4 SeitenTimber Design Module 1mark jefferson castroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problems On StrainDokument16 SeitenProblems On StrainRalph Evidente33% (3)
- Research Work 3Dokument11 SeitenResearch Work 3Fer MaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- DAY-3-LONG-QUIZ-1 (Recovered 1)Dokument4 SeitenDAY-3-LONG-QUIZ-1 (Recovered 1)Benedick Jayson MartiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 5Dokument7 SeitenProblem 5Michael Huaccha100% (1)
- Year Book Value at The Beginning of The Year (P) Depreciation (P) Book Value at The End of The Year (P) 1 2 3 4 5Dokument9 SeitenYear Book Value at The Beginning of The Year (P) Depreciation (P) Book Value at The End of The Year (P) 1 2 3 4 5Kevin SimonsNoch keine Bewertungen
- MEC 257 - Chapter-02 Shawkut SirDokument126 SeitenMEC 257 - Chapter-02 Shawkut SirOlger Garcia100% (1)
- Ce 137 - Structural Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering: AnswerDokument2 SeitenCe 137 - Structural Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering: Answerbonnie5230% (1)
- Wind Load Design NSCP 2015Dokument6 SeitenWind Load Design NSCP 2015MARKCHRISTMASNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Mechanics MidtermDokument5 SeitenEngineering Mechanics MidtermConnorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Midterm Quiz 1 Solution Manual Pce414Dokument13 SeitenMidterm Quiz 1 Solution Manual Pce414manalorommel77Noch keine Bewertungen
- RA544Dokument30 SeitenRA544Antonio Z MancheteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math Set 1 Refresher PDFDokument2 SeitenMath Set 1 Refresher PDFLester John PrecillasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Local Media5124777314878222530Dokument6 SeitenLocal Media5124777314878222530Joforce Karl MalanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gauss Seidel Examples CompDokument3 SeitenGauss Seidel Examples CompvimabaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Algebra SolutionsDokument59 SeitenAlgebra SolutionsRandy Viola100% (1)
- Design of One Way Slab: Reference: NSCP 2001 Volume 1 Design of Reinforced Concrete by J.C. MccormacDokument25 SeitenDesign of One Way Slab: Reference: NSCP 2001 Volume 1 Design of Reinforced Concrete by J.C. Mccormacamantz91Noch keine Bewertungen
- Analytic and Solid Mensuration FINALSDokument6 SeitenAnalytic and Solid Mensuration FINALSJacky Boy Endencio Atienza100% (4)
- Tutorial 3-Rigid Jointed Frame AnalysisDokument23 SeitenTutorial 3-Rigid Jointed Frame AnalysissagarNoch keine Bewertungen
- DENR AO 33 - Revised IRR of PD 856 Chapter 21 PDFDokument17 SeitenDENR AO 33 - Revised IRR of PD 856 Chapter 21 PDFSchuldich SchwarzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dy DX: Lny 5 X +LNCDokument12 SeitenDy DX: Lny 5 X +LNCWenaBacxNoch keine Bewertungen
- 15 Ciap Doc 102 Section 1-5 RobinDokument53 Seiten15 Ciap Doc 102 Section 1-5 RobinJoshua Ian Aban0% (1)
- Stera 3d Manual v.3.3Dokument42 SeitenStera 3d Manual v.3.3constantine2008Noch keine Bewertungen
- Report Math2.1Dokument15 SeitenReport Math2.1Anonymous qOUo59FCNoch keine Bewertungen
- MODULE 2-CHAPTER 7 R.A. 544-An Act To Regulate The Practice of Civil Engineering in The PhilippinesDokument10 SeitenMODULE 2-CHAPTER 7 R.A. 544-An Act To Regulate The Practice of Civil Engineering in The PhilippinesJerichoRoiEspirituTabangNoch keine Bewertungen
- A NoteDokument106 SeitenA NoteKenneth SantiagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week02 - Bracketing MethodsDokument24 SeitenWeek02 - Bracketing MethodsInunHazwaniKhairuddin100% (2)
- Compiled Questions For Quiz 3 Row 406 and Beyond WalaDokument10 SeitenCompiled Questions For Quiz 3 Row 406 and Beyond Wala2ne1 BlackjackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slope and Deflection of Beams Area-Moment Method Theorem 1: The Change in Slope Between Tangents Drawn ToDokument2 SeitenSlope and Deflection of Beams Area-Moment Method Theorem 1: The Change in Slope Between Tangents Drawn ToJuDeNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE 3132 Module 05 - Analysis of Statically Determinate Structures (Part 1)Dokument8 SeitenCE 3132 Module 05 - Analysis of Statically Determinate Structures (Part 1)FedieTabaquiraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 103 B.P.S. X Maths Chapter Notes 2014 15Dokument65 Seiten103 B.P.S. X Maths Chapter Notes 2014 15arpitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philgeps RegistrationDokument6 SeitenPhilgeps RegistrationVholts Villa VitugNoch keine Bewertungen
- Estimate Guide 2Dokument1 SeiteEstimate Guide 2Vholts Villa VitugNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alternative Transportation: Parking CapacityDokument24 SeitenAlternative Transportation: Parking CapacityBindu SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cost Estimating StagesDokument4 SeitenCost Estimating StagesVholts Villa VitugNoch keine Bewertungen
- TondoDokument47 SeitenTondoVholts Villa VitugNoch keine Bewertungen
- OW-Owner's Supplied ItemsDokument1 SeiteOW-Owner's Supplied ItemsVholts Villa VitugNoch keine Bewertungen
- Periodic PropertiesDokument50 SeitenPeriodic PropertiesVholts Villa Vitug100% (1)
- Company Name: 123 Anystreet Your City, USA 12345 Phone (123) 456-7890Dokument1 SeiteCompany Name: 123 Anystreet Your City, USA 12345 Phone (123) 456-7890Vholts Villa VitugNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bid Docs Cladding WorksDokument8 SeitenBid Docs Cladding WorksVholts Villa VitugNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plumbing 46Dokument1 SeitePlumbing 46Vholts Villa VitugNoch keine Bewertungen
- Filmographia v12.05.1Dokument326 SeitenFilmographia v12.05.1Vholts Villa VitugNoch keine Bewertungen
- R.D. Sablan Construction & Metal Works: Company ProfileDokument9 SeitenR.D. Sablan Construction & Metal Works: Company ProfileVholts Villa VitugNoch keine Bewertungen
- 25 August 2012 To: Mr. Melchor Ong General Manager LT Steel Center Subject: Proposal For Painting Works of External Canopies Glorietta 1Dokument1 Seite25 August 2012 To: Mr. Melchor Ong General Manager LT Steel Center Subject: Proposal For Painting Works of External Canopies Glorietta 1Vholts Villa VitugNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ra 7279Dokument23 SeitenRa 7279Vholts Villa VitugNoch keine Bewertungen
- RA 9856 - Real Estate Investment Trust of 2009 (Draft IRR)Dokument46 SeitenRA 9856 - Real Estate Investment Trust of 2009 (Draft IRR)Vholts Villa VitugNoch keine Bewertungen
- PEG Company ProfileDokument18 SeitenPEG Company ProfileVholts Villa VitugNoch keine Bewertungen
- RA 9856 - Real Estate Investment Trust of 2009 (Draft IRR)Dokument46 SeitenRA 9856 - Real Estate Investment Trust of 2009 (Draft IRR)Vholts Villa VitugNoch keine Bewertungen
- R.D. Sablan Construction & Metal Works: Company ProfileDokument9 SeitenR.D. Sablan Construction & Metal Works: Company ProfileVholts Villa VitugNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research OnDokument2 SeitenResearch OnVholts Villa VitugNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1: Introduction To The Project: Capacity Assessment of Level 3 and Level 4 Hospitals in LuzonDokument2 Seiten1: Introduction To The Project: Capacity Assessment of Level 3 and Level 4 Hospitals in LuzonVholts Villa VitugNoch keine Bewertungen
- Itemized CostingsDokument1 SeiteItemized CostingsVholts Villa VitugNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pintworld SMFVDokument8 SeitenPintworld SMFVVholts Villa VitugNoch keine Bewertungen
- MTH202 Quiz-3 by Vu Topper RMDokument16 SeitenMTH202 Quiz-3 by Vu Topper RMdanish3175040486Noch keine Bewertungen
- HeyDokument92 SeitenHeyalbert corbillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Duren - Geometric Function TheoryDokument40 SeitenDuren - Geometric Function Theoryudin-san100% (1)
- 1 Real-NumbersDokument8 Seiten1 Real-NumbersHh HhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slides On Algebra of Coding TheoryDokument62 SeitenSlides On Algebra of Coding Theoryanon_195268295Noch keine Bewertungen
- Name: Bienvenido D. Necesario, Iii Quarter Assigned: 1 Quarter Week Assigned: WEEK 1-6Dokument6 SeitenName: Bienvenido D. Necesario, Iii Quarter Assigned: 1 Quarter Week Assigned: WEEK 1-6Benjr Junjun NecesarioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics QM016 Topic 1: Number System - TutorialDokument4 SeitenMathematics QM016 Topic 1: Number System - TutorialMohd NuuranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Algebra PDFDokument12 SeitenBasic Algebra PDFlaxmi mahtoNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLP Mathematics Q1 G7Dokument4 SeitenDLP Mathematics Q1 G7Exo dusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elements Halmos PDFDokument15 SeitenElements Halmos PDFIgor PavlovNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 2 - Set of Real NumbersDokument21 SeitenChapter 1 2 - Set of Real Numbersapi-263209117Noch keine Bewertungen
- Qdoc - Tips Class 7 Maths EnglishmediumDokument248 SeitenQdoc - Tips Class 7 Maths EnglishmediumVihaan ThothaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DAY 06 Number System-01 (21 Days 21 Marathon)Dokument5 SeitenDAY 06 Number System-01 (21 Days 21 Marathon)Janaksinh ZalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Australian Curriculum - Maths RubricDokument8 SeitenAustralian Curriculum - Maths Rubricapi-264721797Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sim SDL Cafae Cee 100 Week 1 3 UloaDokument9 SeitenSim SDL Cafae Cee 100 Week 1 3 UloaLourd Justin DelicanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inequalities With Strange Equality Conditions - Brilliant Math & Science WikiDokument6 SeitenInequalities With Strange Equality Conditions - Brilliant Math & Science WikiRituraj TripathyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8 Data TypesDokument6 SeitenChapter 8 Data TypesP.S. Mithul SouravNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 7 Rational NumbersDokument15 SeitenClass 7 Rational NumbersSMKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Maths PDFDokument39 SeitenBasic Maths PDFvineetthesupermanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subsets of Real Numbers Final Corrected TGDokument13 SeitenSubsets of Real Numbers Final Corrected TGDeonisis VersolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISM Lab Practical FileDokument25 SeitenISM Lab Practical FileBHANUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Positive Rational NumberDokument4 SeitenPositive Rational Numbertutorciecle123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Full Download Test Bank For Discrete Mathematics With Applications 5th Edition Susanna S Epp PDF Full ChapterDokument36 SeitenFull Download Test Bank For Discrete Mathematics With Applications 5th Edition Susanna S Epp PDF Full Chapterreportermaterw8s84n100% (15)
- A Design Methodology For Distributed Control Systems To Optimize Performance in The Presence of Time DelaysDokument28 SeitenA Design Methodology For Distributed Control Systems To Optimize Performance in The Presence of Time Delaysrajayu20002724Noch keine Bewertungen