Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Verb Tenses Revision 1st BAT
Hochgeladen von
Jov EjdOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Verb Tenses Revision 1st BAT
Hochgeladen von
Jov EjdCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
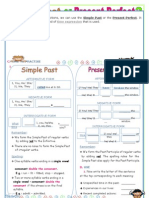
Verb tenses revision: Present Simple vs. Present Continuous.
Look at the following sentences: - Where's Ann? - She's in the living room. She's watching TV. - Matthew's jokes are so funny! I think he's absolutely nuts. - She often has a toast for breakfast. - They go to the theatre twice a month. - Where does your brother live? - He lives in Minnesota, but currently he's spending a school year in Paris. - What are you doing this evening? - I'm watching the football match. Some friends are coming over and we are going to order some pizzas.
Present Simple vs. Present Continuous.
Present simple:
- Structure: Subj.+ verb (s)+ obj. She's in the living room. Use the Present simple to talk about: - Permanent situations: I live in a flat. - Frequent actions or habits: They go out twice a week.
In combination with adverbs or frequency (always, usually, never, hardly ever...) or expressions of frequency (every day, once a month..)
Adverbs of frequency go before the main verb but after be: Frequency expressions (once a week, etc...) usually go at the
Present Simple vs. Present Continuous.
Present Continuous:
- Structure: Subj+ am/is/are + obj. - She's playing the guitar at the moment.
Use the Present Continuous to talk about:
- Actions happening now (with now, at the moment, this week).
- It's raining. We're listening to Classical music.
- Future arrangements (with expressions like this evening, tomorrow night).
- What are you doing this evening?
Past Simple vs Past Continuous.
Look at the following sentences:
- I met John six weeks ago. Now we're great friends! - I came, I saw, I conquered, said Julius Caesar.
- Last summer we went to Rome. It was a wonderful holiday!
- What were you doing yesterday at six o'clock?, asked the detective.
- It was a wonderful spring morning. The sun was shining and the birds were singing. He closed the door of his flat, and went down the street for a walk.
- The dogs were barking fiercely and running towards the postman, so he started to run as fast as he could. - The baby was taking a nap when the doorbell rang, so he started to cry.
Past Simple vs. Past Continuous.
Past Simple:
- Structure: Subj+ verb+ed/ 2nd column (irr.)+ obj. - Use the Past Simple to talk about completed actions in a specified time of the past. Yesterday evening, I saw an amazing show on TV.
Past simple vs. Past Continuous.
Past Continuous:
- Structure: Subj.+ was/were+ verb+ing+ obj. - Use the Past Continuous to talk about actions in progress at a specified time of the past, or actions that were interrupted (unfinished) by another action, or two incomplete actions in progress at the same time in the past.
In combination with the Past Continuous, the Past Simple is a simple tense, not a progressive tense. This means in the Past Continuous the action was still in progress and in the Past Simple, it was finished.
Going to and Will futures.
This evening I'm watching the match on TV, but next week I'm going to watch it at the stadium. I'm so excited about it! Next Saturday we are going to go to the beach for the first time this year. I hope the weather will be nice. You don't have to carry those heavy bags by yourself. I'll help you. The plane will take off at 7 o'clock in the evening. When I grow up, I'm going to be a hotel manager. Watch it! You're going to break the glass.
The soothsayer said that we will have at least three children. Can you imagine?
Going to and Will futures.
Going to future.
-Structure: Subj.+ am/is/are +going to+ inf+ obj. I'm going to work for my father.
Use the Going to future to talk about something that you have already decided to do. Future arrangements: A planned appointment, a meeting, something in the future that you have already arranged (Present continuous is also possible). I'm going to see the doctor on Monday. Predictions about an inmediate future, or based on observing a sequence of events:Look at those clouds. It's going to rain in a minute.
Going to and Will futures.
Will future:
- Structure: Subj.+ will+ inf. + obj. - She will be eighteen in November.
Use Will to make predictions (guessing, soothsaying, facts not depending on you).
I think they will win the race. The bus will leave at four. Don't be late!
To talk about unplanned decisions (making a decision or an offer at the moment of speaking). First person I/We.. will or shall. We shall overcome.
- It's windy, isn't it? I'll close the window.
Present Perfect vs. Past Simple.
- I heard that you had an accident last week. Are you alright? - You're late. The teacher has just told us what he will ask for the exam.
- Have you ever seen any film by the Coen brothers?
- Yes, they're great. About a month ago I saw The Big Lebowski.
- In any case, I didn't like No country for all men.
- Oh, I haven't seen that one. - Joe has recently started dating a girl. I think he's got a crush on her.
Present Perfect vs. Past Simple.
We use the Present Perfect to....
--> Talk about our experiences of the past.
--> Talk about an action that has recently happened or is expected to finish around this time. --> Talk about an action that took place at an unspecified time in the past and is still important.
With yet, ever, never, already, just, since, recently, lately. Structure: Subj + have/has + participle + obj.
Present Perfect vs. Past Simple.
We use the Past Simple:
--> To talk about finished actions that took place at a specified time of the past.
--> Often with phrases like: yesterday, last week, a month ago, in January, last Christmas...
Structure: Subj.+ main verb (ed)/ 2nd Column (irregular verb)+ object. In combination with the Present Perfect, the Present Perfect refers to an experience or an action that has developed around the time we are speaking.
Past Simple vs. Past Perfect.
- What did you do last night?
- Oh, not much. I spent the evening with my family.
- Before we met, I had heard about you. - They read the story after the child had brushed his teeth. - The robbers took all the jewels and money after they had tied up the shop assistant and the customers. - I was so tired. I had been working all day. - I have told you many times. Don't make me wait for so long. I've been waiting for you at least for an hour.
Past Simple vs. Past Perfect.
The Past Simple is often seen in combination with the Past Continuous, the Present Perfect or the Past Perfect.
- I saw Bob a week ago. He was walking in the street along with his sister. - I have already finisihed lunch. The meat was delicious! - I drunk some coffee last night. Afterwards, I couldn't sleep -> I couldn't sleep last night because I had drunk some coffee earlier.
In combination with the Past Perfect, the Past Perfect refers to an action that was previous to the time we are speaking about.
Past Simple vs. Past Perfect.
Past Perfect:
- Structure: Subj.+ had+ main verb (participle or 3rd column)+ obj.
We had had lunch before we met so we just drank a cup of tea.
Past Perfect Continuous:
- The Past Perfect Continuous is a progressive tense. It means that the action had been in progress before the time we refer to.
- We had had lunch before we met. I had been eating in the same restaurant where we met.
Future Continuous vs. Future Perfect.
I will be rich when I turn 35. Sally will be finishing her last year at University, when you start.
When you return from your holiday in the Canaries I will be still working at the office.
Tomorrow at this time I will be having coffee with my friends. She won't wait for you. By the time you get home she will have had dinner. It's quite late this evening. When we get home, Salvados will have finished.
Future Continuous vs. Future Perfect.
The Future (Will) is the Future Simple tense. Other future tenses are the Future Continuous and the Future Perfect.
- She will be reading her book when you phone her (Future Continuous). - She will have finished her book when you phone her (Future Perfect).
The Future Continuous refers to an action that will be in progress at a specific time in the future, often in connection with another action. Structure: Subj.+ will be+ verb (+ing)+ obj.
Future Continuous vs. Future Perfect.
The Future Perfect refers to an action that will have finished at a specific time of the Future, often in connection with another action.
- This time tomorrow I will have finished studying for my exam.
- When you get home, he will have cooked dinner.
Structure: Subj.+ have + main verb (Participle or 3rd column)+ obj.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- All Tenses - ExamplesDokument6 SeitenAll Tenses - ExamplesGisele FioroteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tenses CorrectionDokument29 SeitenTenses Correctionapi-271650264100% (1)
- Verb TensesDokument10 SeitenVerb TensesDarcy DeeaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TensesDokument6 SeitenTensesKunajomiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recuperación InglésDokument4 SeitenRecuperación InglésTania GascueñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 Performing: VocabularyDokument14 SeitenUnit 2 Performing: VocabularyLeandro FernándezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present Tenses: Present Simple Present Continuous Past Tense Past Continuous TenseDokument53 SeitenPresent Tenses: Present Simple Present Continuous Past Tense Past Continuous TenseIRzhaa Calser CuQinwaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tenses of The Verb (Compiled)Dokument5 SeitenTenses of The Verb (Compiled)Kwing KweenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tense Direct Speech Reported SpeechDokument9 SeitenTense Direct Speech Reported SpeechGeo KemoNoch keine Bewertungen
- I'm Using: Present Simple and Present ContinuousDokument3 SeitenI'm Using: Present Simple and Present ContinuousMara R. VergaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1.b PRESENT TENSES AND CONTINUOS - BASICDokument3 SeitenUnit 1.b PRESENT TENSES AND CONTINUOS - BASICMichael Andres Rodriguez CabezasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Affirmative Negative Interrogative Form Uses: Conditional SimpleDokument5 SeitenAffirmative Negative Interrogative Form Uses: Conditional SimplePrinces Aliesa Bulanadi0% (1)
- Present Perfect TenseDokument23 SeitenPresent Perfect TenseAnthony CoaguilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present PerfectDokument9 SeitenPresent Perfectsherry0% (1)
- Tenses - Semester 1Dokument22 SeitenTenses - Semester 1nada.chbikiNoch keine Bewertungen
- English 2mothDokument78 SeitenEnglish 2mothMichaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary: The Verb TensesDokument1 SeiteSummary: The Verb TensesAnabela GuedesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grammatica IngleseDokument35 SeitenGrammatica IngleseGreta CassarriNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Past TenseDokument25 SeitenThe Past TenseFranck Nyaze EkoloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tenses and Reported Speech (Vremena I Upravni Govor)Dokument5 SeitenTenses and Reported Speech (Vremena I Upravni Govor)balkanskiratoviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Copia de Copia de TENSESDokument20 SeitenCopia de Copia de TENSESjazminNoch keine Bewertungen
- BTS CG1 - 2022.11.22 - Anglais - English Tenses TheoryDokument12 SeitenBTS CG1 - 2022.11.22 - Anglais - English Tenses TheoryDuong CamNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Cutting Edge IntermediateDokument25 SeitenNew Cutting Edge IntermediateMarek DvořákNoch keine Bewertungen
- Definition of The Present Perfect TenseDokument20 SeitenDefinition of The Present Perfect TenseSelebriti Rafiq ChikidotNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Past Perfect TenseDokument2 SeitenThe Past Perfect Tensepuvan esweranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pre-Evaluación InglésDokument4 SeitenPre-Evaluación InglésAnxela TaboadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present PerfectDokument9 SeitenPresent PerfectOmar AchirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Past Continuous TenseDokument12 SeitenPast Continuous TenseAlexandra DaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Past Continuous TenseDokument12 SeitenPast Continuous TensealvarousNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indirect Speech or Reported Speech 2Dokument21 SeitenIndirect Speech or Reported Speech 2Constanza Farfán100% (1)
- Units Grammar Review 5-6Dokument11 SeitenUnits Grammar Review 5-6Fernando LeonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present Simple: When, As Soon As, If, Even If, Unless, As Long AsDokument7 SeitenPresent Simple: When, As Soon As, If, Even If, Unless, As Long AsYanina ChaileNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grammar Reference: Verb TensesDokument9 SeitenGrammar Reference: Verb TensesBlaze ConsultoriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grammar NotebookDokument8 SeitenGrammar NotebookAlex BulseviculNoch keine Bewertungen
- Golden RulesDokument31 SeitenGolden RulesyasovilliNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Tenses CorectDokument30 SeitenThe Tenses CorectPopCătălinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Egzamin 8klasisty PodsumowanieDokument34 SeitenEgzamin 8klasisty PodsumowanieKasia SoltykiewiczNoch keine Bewertungen
- Past Tense and Past ContinousDokument4 SeitenPast Tense and Past ContinousDimas RifkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Future Tense1Dokument2 SeitenFuture Tense1api-258586418Noch keine Bewertungen
- Engleski CasoviDokument13 SeitenEngleski CasoviSonjaStojanovićNoch keine Bewertungen
- Look at These Sentences and Complete The Tables Below.: I've Lived Here For 8 YearsDokument16 SeitenLook at These Sentences and Complete The Tables Below.: I've Lived Here For 8 YearsJosi Llanes GonzálezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Talking About The PastDokument4 SeitenTalking About The Pastshahzeb khanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reported Speech - AdvancedDokument9 SeitenReported Speech - Advancedomla2024pcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cex - Tenses Review Plus Sequence of TensesDokument6 SeitenCex - Tenses Review Plus Sequence of TensesSilvia MihaelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A1 C2 USE-of-ENGDokument6 SeitenA1 C2 USE-of-ENGLaura BernabéNoch keine Bewertungen
- Future FormsDokument5 SeitenFuture FormsIulia OstafiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reported Speech 000000000Dokument5 SeitenReported Speech 000000000Алена ДимоваNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grammar LotteDokument8 SeitenGrammar LottezlottezNoch keine Bewertungen
- English TensesDokument31 SeitenEnglish TensesMuhammad TalhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seg CuatDokument5 SeitenSeg CuatVirgi ColomerNoch keine Bewertungen
- ESP I Verbs & TensesDokument16 SeitenESP I Verbs & TensesmurpicantikbangetNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 - VerbsDokument8 Seiten3 - VerbsCarles Safont RodrigoNoch keine Bewertungen
- FUTURE Tenses - PPTDokument37 SeitenFUTURE Tenses - PPTi.diana100% (1)
- MODULE 1 CuadernilloDokument22 SeitenMODULE 1 CuadernilloLuciNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uses of TensesDokument7 SeitenUses of TensesJagadishBabu ParriNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Do We Use The Present Perfect TenseDokument3 SeitenHow Do We Use The Present Perfect TenseAndrea Michelle LydzinskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Verb TensesDokument8 SeitenEnglish Verb TensesIsgn MaputoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grammar For FCEDokument8 SeitenGrammar For FCERafaelHidalgoSanchísNoch keine Bewertungen
- AK3 - Updated Syllabus 2023Dokument8 SeitenAK3 - Updated Syllabus 2023Gabriela Barbuto MoraitiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparison ExercisesDokument17 SeitenComparison ExercisesnguyenngocquynhchiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CÂU HỎI ÔN TẬP - LÝ THUYẾT DỊCHDokument7 SeitenCÂU HỎI ÔN TẬP - LÝ THUYẾT DỊCHChiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functions of Speech Communication (Jacobson)Dokument2 SeitenFunctions of Speech Communication (Jacobson)joycehaelcabanero100% (1)
- Ielts TipsDokument12 SeitenIelts TipsAlisha JonesNoch keine Bewertungen
- m0831 Design Features of LanguagesDokument2 Seitenm0831 Design Features of Languagesapi-383253228Noch keine Bewertungen
- Module 7 Introduction To SyntaxDokument2 SeitenModule 7 Introduction To SyntaxAsterio Ornopia Asa100% (1)
- Language Center: 1St EditionDokument136 SeitenLanguage Center: 1St EditionTu papá PitudoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q2 Eng3Dokument4 SeitenQ2 Eng3Yunilyn GallardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phrasal VerbsDokument2 SeitenPhrasal VerbsKamilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 872b3651264e6dc703b639a47cdc3891Dokument5 Seiten872b3651264e6dc703b639a47cdc3891Anju BalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tenses Using GoogleDokument7 SeitenTenses Using Googlenero daunaxilNoch keine Bewertungen
- APA+Paper+With+Formatting+Instructions Rev6Dokument6 SeitenAPA+Paper+With+Formatting+Instructions Rev6Pkgerald150Noch keine Bewertungen
- Spelling Errors & Wrong WordsDokument16 SeitenSpelling Errors & Wrong WordsJaviera Camila Sanchez ToledoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan: 60 Minutes World of KnowledgeDokument2 SeitenLesson Plan: 60 Minutes World of KnowledgelizziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mother TongueDokument10 SeitenMother TongueAinah LaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 4 Reading Comprehension Grammar WritingDokument2 SeitenUnit 4 Reading Comprehension Grammar WritingIsabel Cordero GutiérrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teaching English As A Foreign Language: Dr. Zuliati Rohmah, M.PDDokument93 SeitenTeaching English As A Foreign Language: Dr. Zuliati Rohmah, M.PDMega SitumorangNoch keine Bewertungen
- 雅思真题 剑9Test03 智课网Dokument25 Seiten雅思真题 剑9Test03 智课网Jianyu SunNoch keine Bewertungen
- All Ug Courses - Language (Ba/Bsc/Bca/Bba/Bbm/Bcom/Bcom (Ca), Bcom (Co-Op)Dokument136 SeitenAll Ug Courses - Language (Ba/Bsc/Bca/Bba/Bbm/Bcom/Bcom (Ca), Bcom (Co-Op)tfacultyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guide Number 2 Activities: Do LikeDokument2 SeitenGuide Number 2 Activities: Do LikeKarla Stephany VARGAS PRADANoch keine Bewertungen
- Greek Verbs: An Introduction For The LearnerDokument10 SeitenGreek Verbs: An Introduction For The LearnerMira Spasova100% (1)
- Causative VerbsDokument15 SeitenCausative VerbsNatalia Eki MulyaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study Plan For Master Programmes 2017Dokument33 SeitenStudy Plan For Master Programmes 2017shauqi92Noch keine Bewertungen
- This Is My House: Oral PresentationsDokument8 SeitenThis Is My House: Oral PresentationsElisabete FerradiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Are They Doing Practice 1Dokument1 SeiteWhat Are They Doing Practice 1Pepe Human ChavezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grammar IndexDokument41 SeitenGrammar IndexThiên TuyênNoch keine Bewertungen
- 45th Preli ST-3 - (English L) Set-2 - AnsDokument2 Seiten45th Preli ST-3 - (English L) Set-2 - AnsKazi RaselNoch keine Bewertungen
- 840 2768 2 PBDokument14 Seiten840 2768 2 PBnormanofianto poltekkesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phonology Assignment and Lesson PlanDokument45 SeitenPhonology Assignment and Lesson PlanGeroNimoNoch keine Bewertungen