Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Pentavalent Vaccine
Hochgeladen von
Sabita PaudelOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Pentavalent Vaccine
Hochgeladen von
Sabita PaudelCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
The
pentavalent vaccine which was introduced in Nepal from April 2009 is a combination of five vaccines in one against the diseases: diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough, hepatitis B and Haemophilus influenza type b (the bacteria that causes meningitis, pneumonia and otitis). has also led to a reduction in cases of immuno-preventive illnesses, especially meningitis caused by Haemophilus influenza type b.
It
The
National Immunization Programme (at the time known as the Expanded Programme on Immunization - EPI) was initiated in 1979 in three districts with only two antigens (BCG and DPT) and was rapidly expanded to include all 75 districts with all six recommended antigens (BCG, DTP, OPV, and measles) by 1988. In 2003, with the support of Alliance, monovalent Hepatitis vaccine was introduced, which administered as a single tetravalent injection. the GAVI B (HepB) was later (DPT-HepB)
In2009,vaccinationagainst
Haemophilus influen zae type b was introduced through out the nation in a phase wise manner starting in Far Western (FWDR) and Western (WDR) Development Regions.
Also in 2009, Japanese encephalitis (JE) vaccine was introduced into the routine immunizationprogramme in 16 JE endemic districts following JE mass vaccination campaigns
Pentavalent
is a conjugate adsorbed vaccine containing five antigens Diphtheria , Pertussis , Tetanus , Hepatitis B and Hib (Haemophilus influenzae type b).
is a homogenous liquid containing purified diphtheria and tetanus toxoids, inactivated whooping cough (pertussis) organisms, highly purified, non-infectious particles of Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) and Hib component as a bacterial subunit vaccine containing highly purified, noninfectious Haemophilus Influenza type b (Hib) capsular polysaccharide chemically conjugated to a protein (Tetanus Toxoid)
It
It
shouldnot be frozen. It should be stored in a refrigerator between 4 to 8 degree celsius. The vaccine should be used before the date of expiry indicated on vial. When issued to a subcentre,the vaccine should be used within a week. The vaccine will lose potency if kept at room temperature over a longer period of time.
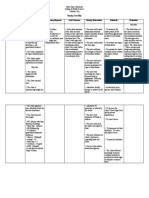
Pentavalent can be used in future immunization session for up to a maximum of 4 weeks, provided that all of the following conditions are met1. The expiry date has not passed. 2. The vaccines are stored under appropriate cold chain conditions. 3. The vaccine vial septum has not been submerged in water. 4. Aseptic technique has been used to withdraw all doses 5. The vaccine vial monitor (VVM), if attached, has not reached the discard point (see figure).
The vaccine should be visually inspected for any foreign particulate matter and/or variation of physical aspect prior to administration. In event of either being observed discard the vaccine.
Vaccine
vial monitors (VVMs) are part of the
label. The color dot which appears on the label of the vial is a VVM. This is a time temperature sensitive dot that provides an indication of the cumulative heat to which the vial has been exposed. It warns the end user when the exposure to heat is likely to have degraded the vaccine beyond an acceptable level.
The
interpretation of the VVM is simple. Focus on the central square. Its colour will change progressively. As long as the color of this square is lighter than the colour of the ring, then the vaccine can be used. As soon as the colour of the central square is the same colour as the ring or of a darker colour than the ring, then the vial should be discarded.
For
active immunization of infants and preschool children, it is recommended that three deep intra muscular injection of 0.5 ml be administered with an interval of four weeks between doses. (i.e.6,10,14 weeks)
of the priciple recommendation of 1984,Global Advisory Group is that for child under one year of age it should be administered in lateral aspect of thigh.
One
booster dose of Diphtheria, Tetanus, Pertussis, Hepatitis B and Haemophilus Influenza type b Conjugate Vaccine Adsorbed can be given at the age of 15-18 months.
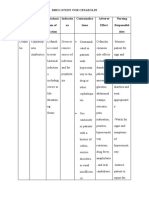
Fever
and mild local rxns are common. It is estimated that 2 to 6 % of vacinees develop fever of 39 degree celcius or higher. 5 to 10% experience swelling and induration or pain lasting more than 48 hrs. Most severe complications are neurological (encephalitis/encephalopathy, prolonged convulsions , infantile spasms and Reye syndrome) The type and rate of severe adverse reactions do not differ significantly from the DTP, HepB and Hib vaccine reactions described separately.
Individuals
infected with the human immunedeficiency virus (HIV), both asymptomatic and symptomatic, should be immunized with combined vaccine according to standard schedules.
Any
children who are seriously ill or need hospitalization. It should not be repeated if a severe rxn occur after a previous dose.(such rxns include collapse or shock like state,persistent screaming episodes,temperatur above 40 degree C, convulsions ,other neurological symptoms and anaphylactic reactions)
Known
hypersensitivity to any component of the vaccine, or a severe reaction to the previous dose of the combination vaccine or any of its constituents is an absolute contraindication to subsequent doses of the combination vaccine or the specific vaccine knows to have provoked an adverse reaction. In this case the vaccine should not be given as a combination vaccine but DT should be given instead of DPT and Hep B and Hib vaccines given separately.
ADRENALINE INJECTION (1:1000) MUST BE IMMEDIATELY AVAILABLE SHOULD AN ACUTE ANAPHYLACTIC REACTION OCCUR DUE TO ANY COMPONENT OF THE VACCINE. For treatment of severe anaphylaxis the initial dose of adrenaline is 0.1 0.5mg (0.1 0.5 ml of 1:1000 injection) given s/c or I/m. single dose should not exceed 1mg (1 ml) For infants and children the recommended dose of adrenaline is 0.01 mg/kg (0.01ml/kg of 1:1000 injection). Single pediatric dose should not exceed 0.5 mg (0.5ml). The mainstay in the treatment of severe anaphylaxis is the prompt use of adrenaline, which can be life saving.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Cefuroxime, Celecoxib, ChloridineDokument2 SeitenCefuroxime, Celecoxib, ChloridinekrizzywhizzyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pentabio PDFDokument7 SeitenPentabio PDFDicky KurniawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument21 SeitenDrug StudyShyla Garnace JavillonarNoch keine Bewertungen
- BerodualDokument1 SeiteBerodualAelysa PabloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument2 SeitenDrug Studydwyane0033Noch keine Bewertungen
- MSU-Iligan Institute of TechnologyDokument9 SeitenMSU-Iligan Institute of TechnologyNathanielle Keith PENASONoch keine Bewertungen
- Penta VaccineDokument4 SeitenPenta VaccineArlyn Barte AlboloteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study GuideDokument2 SeitenDrug Study GuideAubrey Sunga100% (1)
- NAHCO3Dokument2 SeitenNAHCO3Krizha Angela NicolasNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP & Drug Study (Tondo Med)Dokument5 SeitenNCP & Drug Study (Tondo Med)Kevin_Remollo_2431Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan 1: Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions RationaleDokument8 SeitenNursing Care Plan 1: Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions RationaleTrysna Ayu SukardiNoch keine Bewertungen
- RISK For INJURY Related To Regulatory Function (Sensory Difunction As Evidenced by Decrease Visual Acuity, Unable To Recognize Object 12-14 Inches Away, Not Wearing of Eyeglasses.Dokument2 SeitenRISK For INJURY Related To Regulatory Function (Sensory Difunction As Evidenced by Decrease Visual Acuity, Unable To Recognize Object 12-14 Inches Away, Not Wearing of Eyeglasses.Senyorita KHayeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Voluven InfusDokument19 SeitenVoluven InfusAji Darundriyo sNoch keine Bewertungen
- HydroxyzineDokument4 SeitenHydroxyzineGeorge Smith AbeledaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BaclofenDokument2 SeitenBaclofenamiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tissue PerfusionDokument2 SeitenTissue Perfusionnursezey100% (3)
- DioxelDokument1 SeiteDioxelJosselle Sempio CalientaNoch keine Bewertungen
- LevofloxacinDokument15 SeitenLevofloxacinsonal aranhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Veklury (Remdesivir) Dosing, Indications, Interactions, Adverse Effects, and MoreDokument4 SeitenVeklury (Remdesivir) Dosing, Indications, Interactions, Adverse Effects, and MoreRex ChanNoch keine Bewertungen
- DP Discharge Plan@@@@@@@@Dokument6 SeitenDP Discharge Plan@@@@@@@@Maemae SumalinogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study FinalDokument5 SeitenDrug Study FinalJackie Ann Marie DapatNoch keine Bewertungen
- DRUG StudyDokument4 SeitenDRUG StudyMaica LectanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study Peralta (Drug N NCP)Dokument10 SeitenCase Study Peralta (Drug N NCP)Trisha Cruise100% (1)
- Pathophysiology / Explanation of The ProblemDokument1 SeitePathophysiology / Explanation of The ProblemArian May MarcosNoch keine Bewertungen
- DrugStudy - CamaristaColeenMaeC (BSN III-G) (Prednisone)Dokument2 SeitenDrugStudy - CamaristaColeenMaeC (BSN III-G) (Prednisone)Coleen Mae CamaristaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study CHDCDokument1 SeiteDrug Study CHDCIannBlancoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan Human Response Pattern AMB/Manifestation Nursing Diagnosis Goal/ Outcome Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan Human Response Pattern AMB/Manifestation Nursing Diagnosis Goal/ Outcome Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationMarielle Chua100% (1)
- AzithromycinDokument1 SeiteAzithromycinGrape JuiceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument17 SeitenDrug StudyJam CorrosNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP KateDor NewDokument6 SeitenNCP KateDor NewSteffi GolezNoch keine Bewertungen
- College of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityDokument4 SeitenCollege of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityFaye Andrea FranciscoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oral Suspension: 125 mg/5 Powder For Injection: 750 Premixed Containers: 750Dokument1 SeiteOral Suspension: 125 mg/5 Powder For Injection: 750 Premixed Containers: 750Diane Grace PadillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug-Study Immunizations-And-Chemotherapy Jairah 4Dokument10 SeitenDrug-Study Immunizations-And-Chemotherapy Jairah 4Yasmien MarieNoch keine Bewertungen
- College of Nursing: Rifadin RifampinDokument4 SeitenCollege of Nursing: Rifadin RifampinAnika PleñosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sal But AmolDokument2 SeitenSal But AmolCalimlim KimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resource Unit On Common Drugs (LRDR Rotation)Dokument37 SeitenResource Unit On Common Drugs (LRDR Rotation)kiamoiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument14 SeitenDrug StudyJho Ocampo NungayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pneumonia Drug StudyDokument3 SeitenPneumonia Drug Studyatienza02Noch keine Bewertungen
- NCPDokument3 SeitenNCPTweenie DalumpinesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Docu - Tips Drug StudyDokument14 SeitenDocu - Tips Drug StudyArdel LabadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Siver SulfadiazineDokument3 SeitenSiver SulfadiazineFernanda PutriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study For Cefazolin Drug Data Classificat Ion Mechani SM of Action Indicatio Ns Contraindica Tions Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibil ItiesDokument2 SeitenDrug Study For Cefazolin Drug Data Classificat Ion Mechani SM of Action Indicatio Ns Contraindica Tions Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibil ItiesCarl J.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Discharge Instructions For Lap CholeyDokument1 SeiteDischarge Instructions For Lap CholeyAnne Marie Angelica BilonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study.Dokument9 SeitenDrug Study.Chelsea Therese GuevarraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vit K Drug StudyDokument2 SeitenVit K Drug StudyKrisha AristonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name of Drug SoludexideDokument2 SeitenName of Drug SoludexideSian AsadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- I.intrODUCTION Hypertension (High Blood Pressure) Is ADokument19 SeitenI.intrODUCTION Hypertension (High Blood Pressure) Is Aoril04Noch keine Bewertungen
- VancomycinDokument2 SeitenVancomycinxoxo318Noch keine Bewertungen
- NCP of Difficulty of BreathingDokument2 SeitenNCP of Difficulty of BreathingMan GatuankoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument6 SeitenDrug StudyAisha LakibulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Famotidine: Maintenance Therapy For Duodenal Ulcer Patients at Reduced Dosage After Healing of An Active UlcerDokument2 SeitenFamotidine: Maintenance Therapy For Duodenal Ulcer Patients at Reduced Dosage After Healing of An Active Ulcerangeleigh viernesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Date Time Focus D-Ata A-Ction R-Esponse D - Patient Verbalized "Sakit Kaau Akong TotoyDokument1 SeiteDate Time Focus D-Ata A-Ction R-Esponse D - Patient Verbalized "Sakit Kaau Akong TotoyKim Glaidyl BontuyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanDokument6 SeitenChronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanRuva Oscass JimmyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emergency Drug StudyDokument3 SeitenEmergency Drug StudyGrace Santos MirandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nausea and Vomiting Nausea and VomitingDokument6 SeitenNausea and Vomiting Nausea and VomitingTHERESA CLAIRE ENCINARESNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrocortisone Inj. (IV)Dokument2 SeitenHydrocortisone Inj. (IV)zepoli_zepoly6232Noch keine Bewertungen
- NCPDokument4 SeitenNCPJoseph Dableo ParreñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rabi PurDokument3 SeitenRabi PurDiana Laura LeiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vaccination: Passive ImmunityDokument12 SeitenVaccination: Passive ImmunityuouoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Care of Child With IncubatorDokument26 SeitenCare of Child With IncubatorSabita Paudel100% (2)
- Text CompletionDokument26 SeitenText CompletionSabita PaudelNoch keine Bewertungen
- GRE Reading Comprehension Practice TestDokument22 SeitenGRE Reading Comprehension Practice TestLewis HarrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- GlobalizationDokument8 SeitenGlobalizationSana SiddiquiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Care During First Stage of LabourDokument6 SeitenCare During First Stage of LabourSabita PaudelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acid Base DisorderDokument26 SeitenAcid Base DisorderSabita PaudelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Female Reproductive OrganDokument31 SeitenFemale Reproductive OrganSabita PaudelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gyn TAH BSO PDFDokument1 SeiteGyn TAH BSO PDFSabita PaudelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura Case StudyDokument60 SeitenIdiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura Case StudySabita PaudelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asymptomatic BacteriuriaDokument23 SeitenAsymptomatic BacteriuriaSabita PaudelNoch keine Bewertungen
- National Health FoundationDokument33 SeitenNational Health FoundationSabita PaudelNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 N MalnutritionDokument35 Seiten6 N MalnutritionSabita Paudel75% (4)
- Child Guidance ClinicDokument14 SeitenChild Guidance ClinicSabita Paudel60% (5)
- Physilogy of ReproductionDokument6 SeitenPhysilogy of ReproductionSabita PaudelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antenatal ExerciseDokument10 SeitenAntenatal ExerciseSabita PaudelNoch keine Bewertungen
- BoneDokument22 SeitenBoneSabita PaudelNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 Rights of Deug AdministrationDokument3 Seiten10 Rights of Deug AdministrationSabita PaudelNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 Postpartum CareDokument20 Seiten7 Postpartum CareVirgie GigiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nationally Notifiable Infectious Diseases and Conditions, United States: Annual TablesDokument5 SeitenNationally Notifiable Infectious Diseases and Conditions, United States: Annual TablesgrowlingtoyouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yellow FeverDokument4 SeitenYellow FeverNader SmadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mantoux TestDokument3 SeitenMantoux Testfarrukhhussain2006Noch keine Bewertungen
- HPVDokument3 SeitenHPVdsaroha1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Oral CandidiasisDokument18 SeitenOral CandidiasisRose DawoudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mr. Mohit Sharma SampleDokument3 SeitenMr. Mohit Sharma SamplePrateeksha SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Student Exploration: Disease SpreadDokument5 SeitenStudent Exploration: Disease SpreadAndreNoch keine Bewertungen
- DBQ 3Dokument6 SeitenDBQ 3api-448501859Noch keine Bewertungen
- SHEA Position Paper: I C H EDokument17 SeitenSHEA Position Paper: I C H EIFRS SimoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sexual Transmited DiseaseDokument74 SeitenSexual Transmited DiseaseAdi PeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grafik 10 Penyakit Terbanyak Ruang TindakanDokument7 SeitenGrafik 10 Penyakit Terbanyak Ruang TindakanEka SatriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health Declaration Form Dha1Dokument3 SeitenHealth Declaration Form Dha1Irram RanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solutions For All Your Gaseous Chlorine Dioxide Needs The Chlorine Dioxide PeopleDokument7 SeitenSolutions For All Your Gaseous Chlorine Dioxide Needs The Chlorine Dioxide PeopleJesús GINoch keine Bewertungen
- Nama: Riris Putri Marito Sinaga NIM: 04022722125001 Prodi: Ilmu Kesehatan Anak No Soal 35Dokument13 SeitenNama: Riris Putri Marito Sinaga NIM: 04022722125001 Prodi: Ilmu Kesehatan Anak No Soal 35Riris SinagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essay HivDokument2 SeitenEssay HivPopoo KyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- dm2022 0033Dokument7 Seitendm2022 0033barogregNoch keine Bewertungen
- All India Institute of Medical Sciences (Aiims) : Laboratory Observation ReportDokument2 SeitenAll India Institute of Medical Sciences (Aiims) : Laboratory Observation ReportPiyush TripathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Candida AurisDokument5 SeitenCandida Aurisarunkumar76Noch keine Bewertungen
- UTI - Internship PresentationDokument27 SeitenUTI - Internship PresentationPernel Jose Alam MicuboNoch keine Bewertungen
- STI Risk & CondomsDokument5 SeitenSTI Risk & CondomsAdams LoveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thelma ImmunizationDokument51 SeitenThelma Immunizationclement johnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Affw0Glk0Slde - Fz@Eftracyainetb.G .Io#Fa9Diwtrdf0Doxycydine: ..Mwge P Mcnn5Dokument2 SeitenAffw0Glk0Slde - Fz@Eftracyainetb.G .Io#Fa9Diwtrdf0Doxycydine: ..Mwge P Mcnn5Raluca PăunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chicken PoxDokument1 SeiteChicken PoxmarincewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant Disease Symptoms Signs and Effects 17.11.2014Dokument28 SeitenPlant Disease Symptoms Signs and Effects 17.11.2014DiahNoch keine Bewertungen
- MrASHISHDUBEY 29Y MaleDokument2 SeitenMrASHISHDUBEY 29Y MaleNisha DubeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3573 - VIDAS B.R.a.H.M.S PCT - Reference 30450 - New Claim LaunchDokument8 Seiten3573 - VIDAS B.R.a.H.M.S PCT - Reference 30450 - New Claim Launchluisoft88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Neonatal Sepsis: Progress Towards Improved Outcomes: Andi L. Shane, Barbara J. StollDokument9 SeitenNeonatal Sepsis: Progress Towards Improved Outcomes: Andi L. Shane, Barbara J. StollMarco Antonio Mendoza OjedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9 - Anti Fungal DrugsDokument73 Seiten9 - Anti Fungal Drugszynab123Noch keine Bewertungen
- HIV and PregnancyDokument18 SeitenHIV and PregnancyekimarlianiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pneumonia Pada Kasus PediatrikDokument41 SeitenPneumonia Pada Kasus PediatrikasriNoch keine Bewertungen