Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Darcy-Law (Rock)
Hochgeladen von
Maqsood IqbalCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Darcy-Law (Rock)
Hochgeladen von
Maqsood IqbalCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Flow in Porous Media
Porous rocks are fluid-permeated, containing oil, gas, or water as a standing point of reservoir engineering aspects. Gravitational and capillary forces largely control the distribution of these fluids in petroleum accumulations. The porous mediums storage capacity is denoted by porosity, i.e., the void fraction of the volume available for the fluids. The ability of the porous medium to transmit the fluid pass through its pore spaces is specified by the quantity of permeability. The concept of conductivity that is known as permeability was introduced by Darcy (1856). The dimension of permeability is the square of length.
PERMEABILITY & DARCYS LAW
Permeability is a property of the porous medium that measures the capacity and ability of the formation to transmit fluids. The rock permeability, k, is a very important rock property because it controls the directional movement and the flow rate of the reservoir fluids in the formation. In fact, the equation that defines permeability in terms of measurable quantities is called Darcys Law. Darcy developed a fluid flow equation that has since become one of the standard mathematical tools of the petroleum engineer. If a horizontal linear flow of an incompressible fluid is established through a core sample of length L and a cross-section of area A, then the governing fluid flow equation is defined as
where n = apparent fluid flowing velocity, cm/sec k = proportionality constant, or permeability, Darcys m = viscosity of the flowing fluid, cp dp/dL = pressure drop per unit length, atm/cm The apparent velocity determined by dividing the flow rate by the cross-sectional area across which fluid is flowing. Substituting the relationship, q/A, in place of n in Equation 321 and solving for q results in
where q = flow rate through the porous medium, cm3/sec A = cross-sectional area across which flow occurs, cm2
4
One Darcy is a relatively high permeability as the permeabilities of most reservoir rocks are less than one Darcy. In order to avoid the use of fractions in describing permeabilities, the term millidarcy is used. The negative sign in Equation is necessary as the pressure increases in one direction while the length increases in the opposite direction.
Integrate the above equation
Linear flow model
where L = length of core, cm A = cross-sectional area, cm2 Assumptions; Laminar (viscous) flow No reaction between fluid and rock Only single phase present at 100% pore space saturation This measured permeability at 100% saturation of a single phase is called the absolute permeability of the rock.
For a radial flow, Darcys equation in a differential form can be written as:
Intergrating Darcys equation gives:
The term dL has been replaced by dr as the length term has now become a radius term.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 2-Fluid Flow in Porous MediaDokument46 Seiten2-Fluid Flow in Porous Mediafatma belkacemiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10.1007 s11242 009 9432 Z Effective Correlation of Apparent Gas Permeability in Tight Porous MediaDokument10 Seiten10.1007 s11242 009 9432 Z Effective Correlation of Apparent Gas Permeability in Tight Porous MediaSina ForoudiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Masters Thesis: Groundwater Finite Element Model by Igiri Christiana Friday:university of CalabarDokument150 SeitenMasters Thesis: Groundwater Finite Element Model by Igiri Christiana Friday:university of CalabarChinyere IgiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 - Flow Through Porous MediaDokument33 SeitenChapter 6 - Flow Through Porous MediaSuta Vijaya100% (1)
- Dynamics of Fluid in Porous MediaDokument70 SeitenDynamics of Fluid in Porous MediaAnna Lucci de MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8-Flow in Pipes02Dokument76 SeitenChapter 8-Flow in Pipes02Julian RiverosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluids in Porous MediaDokument46 SeitenFluids in Porous MediablankballNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rock PermeabilityDokument43 SeitenRock PermeabilityShaho Abdulqader Mohamedali100% (1)
- Heat Transfer 1 PDFDokument72 SeitenHeat Transfer 1 PDFMerazka FaroukNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial - Flow in Porous MediaDokument1 SeiteTutorial - Flow in Porous MediaEzwan Zazi100% (1)
- Water Pollution - WikipediaDokument42 SeitenWater Pollution - WikipediaChandrakala ShivakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annular Condensation CFD Models For The Water-Steam in The Heat Pipe SystemsDokument9 SeitenAnnular Condensation CFD Models For The Water-Steam in The Heat Pipe SystemsRashed KaiserNoch keine Bewertungen
- Porous Media PDFDokument9 SeitenPorous Media PDFcezar_iasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drag of A SphereDokument4 SeitenDrag of A SphereJean-Franz Baschube100% (1)
- Vi. Fluid Friction in Steady One Dimensional FlowDokument38 SeitenVi. Fluid Friction in Steady One Dimensional FlowAlna LiviaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chte3 Fluidproperties Examples 1Dokument4 SeitenChte3 Fluidproperties Examples 1Sphe DlomoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Convection: Heat and Mass Transfer: Fundamentals & ApplicationsDokument58 SeitenFundamentals of Convection: Heat and Mass Transfer: Fundamentals & ApplicationsWalter Nuas100% (2)
- Enhancement Porformence of Heat Exchanger 2018-19Dokument44 SeitenEnhancement Porformence of Heat Exchanger 2018-19Srinivasa bnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Dynamics Past Exam SolutionDokument4 SeitenFluid Dynamics Past Exam SolutionPaulo PolloNoch keine Bewertungen
- PE 543 - Spring 2012/2013 Gas Condensate Assignment # 5 April 22, 2013 Problem # 1Dokument3 SeitenPE 543 - Spring 2012/2013 Gas Condensate Assignment # 5 April 22, 2013 Problem # 1Maqsood IqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Changes of Ow Patterns in A Horizontal Subsurface Ow Constructed Wetland Treating Domestic Wastewater in Tropical RegionsDokument7 SeitenChanges of Ow Patterns in A Horizontal Subsurface Ow Constructed Wetland Treating Domestic Wastewater in Tropical RegionssholichinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Mechanics QtnsDokument3 SeitenFluid Mechanics QtnsAnonymous NV1AeWXEo100% (1)
- Fluid Flow in Porous MediumDokument20 SeitenFluid Flow in Porous MediumTARIQNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 4 Gas Permeability MeasurementDokument6 SeitenLab 4 Gas Permeability MeasurementRichard OwusuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uebs C0 o QDokument11 SeitenUebs C0 o Qmaribo2005Noch keine Bewertungen
- Multiphase Flow in Porous MediaDokument70 SeitenMultiphase Flow in Porous MediaBulatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Permeability NMRDokument5 SeitenPermeability NMRFarid Hendra Pradana100% (1)
- Wu Gas Flow in Porous Media With Klinkenberg EffectsDokument21 SeitenWu Gas Flow in Porous Media With Klinkenberg Effectssahand_neko64Noch keine Bewertungen
- Oil Spill Detection With Remote SensorsDokument7 SeitenOil Spill Detection With Remote SensorsFikri Adji Wiranto100% (1)
- Permeability of Reservoir Rocks: by DR Anil KumarDokument96 SeitenPermeability of Reservoir Rocks: by DR Anil KumarJassieNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Specific Problems of Water and Gas Coning Are Listed BelowDokument30 SeitenThe Specific Problems of Water and Gas Coning Are Listed BelowUthman MohammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dissolution of Benzoic AcidDokument2 SeitenDissolution of Benzoic AcidAngela Calatayud100% (1)
- Part 4 Diffusivity Equation Line Source Radial Flow Radius Invest PDFDokument34 SeitenPart 4 Diffusivity Equation Line Source Radial Flow Radius Invest PDFrasyal iyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch8791 Transport PhenomenaDokument150 SeitenCh8791 Transport PhenomenarathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Open-Source Toolbox For Multiphase Flow in Porous MediaDokument26 SeitenAn Open-Source Toolbox For Multiphase Flow in Porous MediaAndrés SalazarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7a-Reservoir Rock Properties-Interfacial Tension and WettabilityDokument61 Seiten7a-Reservoir Rock Properties-Interfacial Tension and WettabilityMohammed Amer100% (2)
- Mass Transfer Coefficient and Interphase Mass TransferDokument33 SeitenMass Transfer Coefficient and Interphase Mass TransferpandianvijaybharathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brinkman EquationDokument5 SeitenBrinkman EquationAdegbite Jamiu OyekanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study and Analysis of Siltation at Nahre Ghasr Fishery PortDokument11 SeitenStudy and Analysis of Siltation at Nahre Ghasr Fishery PortkayeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dedan Kimathi University of TechnologyDokument11 SeitenDedan Kimathi University of TechnologyDuncoh Dun100% (1)
- Environmental Impact of Geothermal Energy SynthesisDokument10 SeitenEnvironmental Impact of Geothermal Energy SynthesisKyle Vince Miñano AnchetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Turbulent Buoyant Jets and Plumes: HMT: The Science & Applications of Heat and Mass Transfer. Reports, Reviews & Computer ProgramsVon EverandTurbulent Buoyant Jets and Plumes: HMT: The Science & Applications of Heat and Mass Transfer. Reports, Reviews & Computer ProgramsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical ThermodynamicsDokument33 SeitenChemical ThermodynamicsAkash Ghosh0% (1)
- SPE 89334 Analysis of The Effects of Major Drilling Parameters On Cuttings Transport Efficiency For High-Angle Wells in Coiled Tubing Drilling OperationsDokument8 SeitenSPE 89334 Analysis of The Effects of Major Drilling Parameters On Cuttings Transport Efficiency For High-Angle Wells in Coiled Tubing Drilling OperationsmsmsoftNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applications of Nanofluids: Electronic Cooling in Micro-ChannelsDokument29 SeitenApplications of Nanofluids: Electronic Cooling in Micro-ChannelsMohd Rashid SiddiquiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mass Transfer QuizzesDokument10 SeitenMass Transfer QuizzesNate JamesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2512 Practical 1 ReportDokument12 Seiten2512 Practical 1 ReportAaron Fraka Riches100% (1)
- AnswersDokument5 SeitenAnswersDivyam ShreevatsalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Flow in Porous MediaDokument19 SeitenFluid Flow in Porous MediaPaoLo AsequiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agitation and Mixing-H4 Class-TKMCEDokument111 SeitenAgitation and Mixing-H4 Class-TKMCERaghulal SethumadhavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Manual Fluid MechanicsDokument26 SeitenLab Manual Fluid MechanicsFarahSyazwaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boundary Layers Integral Approach 2Dokument29 SeitenBoundary Layers Integral Approach 2jacksonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid MechanicsDokument12 SeitenFluid MechanicsAditya NandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sheet 01 20-21 Properties of Fluid RevDokument2 SeitenSheet 01 20-21 Properties of Fluid RevBibaswan MukherjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Viscosity BwarDokument11 SeitenViscosity BwarMUHAMMAD AKRAM100% (1)
- NU - Lecture 12 (WATER HAMMER)Dokument1 SeiteNU - Lecture 12 (WATER HAMMER)Mr. Mark B.100% (1)
- Langelier Index Corrosion MineralizationDokument17 SeitenLangelier Index Corrosion MineralizationdeyprasenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp 1 Reynolds' NumberDokument7 SeitenExp 1 Reynolds' NumberDonna Mae Ramos GalaezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Confined Fluid Phase Behavior and CO2 Sequestration in Shale ReservoirsVon EverandConfined Fluid Phase Behavior and CO2 Sequestration in Shale ReservoirsNoch keine Bewertungen
- DCA DataDokument2 SeitenDCA DataMaqsood IqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Cash FlowDokument1 SeiteProject Cash FlowMaqsood IqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reading Intermediate Log Values From Log ScalesDokument1 SeiteReading Intermediate Log Values From Log ScalesMaqsood IqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fill in The Blanks With Suitable Answer.: Problem # 1: (30 Points)Dokument2 SeitenFill in The Blanks With Suitable Answer.: Problem # 1: (30 Points)Maqsood IqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geo StatisticsDokument5 SeitenGeo StatisticsMaqsood IqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
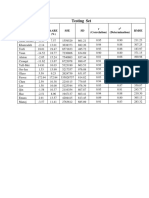
- Testing Set: Model ARE (%) Aare (%) SSE SD R (Correlation) R (Determination) RmseDokument1 SeiteTesting Set: Model ARE (%) Aare (%) SSE SD R (Correlation) R (Determination) RmseMaqsood IqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forptd M 0.813 N 0.588 Litho (Ls-52%, Silica-30% and Dolo-18%)Dokument1 SeiteForptd M 0.813 N 0.588 Litho (Ls-52%, Silica-30% and Dolo-18%)Maqsood IqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recovery Comparison Sio Al O: W1 W2 W1 W2Dokument1 SeiteRecovery Comparison Sio Al O: W1 W2 W1 W2Maqsood IqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pollutant Mean Air Quality Health Effect Index Status Sensitive Groups Health Effects Statements Cautionary StatementsDokument1 SeitePollutant Mean Air Quality Health Effect Index Status Sensitive Groups Health Effects Statements Cautionary StatementsMaqsood IqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nano RecDokument1 SeiteNano RecMaqsood IqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economic ModellingDokument1 SeiteEconomic ModellingMaqsood IqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Incremental Recovery Sio2 Al2O3Dokument2 SeitenIncremental Recovery Sio2 Al2O3Maqsood IqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- MMP Affected UnderDokument219 SeitenMMP Affected UnderMaqsood IqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rocks Minerals OilDokument3 SeitenRocks Minerals OilMaqsood IqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Year Jan Feb Mar Apr May: Monthly and Annually Inflation Rate History From 2000 To 2017Dokument3 SeitenYear Jan Feb Mar Apr May: Monthly and Annually Inflation Rate History From 2000 To 2017Maqsood IqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Student Name Marks Obtained Pass: James Jolly Robert Thomas Joy Lilly Denairo PachinoDokument3 SeitenStudent Name Marks Obtained Pass: James Jolly Robert Thomas Joy Lilly Denairo PachinoMaqsood IqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment of Ambient Air Quality in The State of Kuwait: Al-AhmadiDokument19 SeitenAssessment of Ambient Air Quality in The State of Kuwait: Al-AhmadiMaqsood IqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vehicle Dynamics HandbookDokument110 SeitenVehicle Dynamics HandbookFer SalazarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade XI SCIENCE - Holiday Homework & WorksheetsDokument19 SeitenGrade XI SCIENCE - Holiday Homework & WorksheetsReeja MathewNoch keine Bewertungen
- TD NotesDokument147 SeitenTD NotesThi KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- NX Nastran 8 Rotor Dynamics User's GuideDokument333 SeitenNX Nastran 8 Rotor Dynamics User's GuideMSC Nastran Beginner100% (1)
- Defect Types and Non-Destructive Testing Techniques For Composites and Bonded JointsDokument19 SeitenDefect Types and Non-Destructive Testing Techniques For Composites and Bonded JointsShanker PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
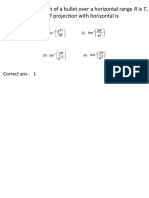
- 10.motion in A PlaneDokument60 Seiten10.motion in A PlaneMohd kaif AnsariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Placek To TyDokument7 SeitenPlacek To TyTymoteusz WowczukNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 8 - FrictionDokument17 SeitenModule 8 - FrictionMadelar, Arc Francis C.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Torsion of Circular ShaftsDokument26 SeitenTorsion of Circular ShaftsNaveen Kumar0% (1)
- 04 - Szyga PlutaDokument22 Seiten04 - Szyga PlutalukaszNoch keine Bewertungen
- L12 ChaosDokument39 SeitenL12 Chaoscotopaxi64.mopiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of AerodynamicsDokument39 SeitenFundamentals of AerodynamicsMarion Nori MarallagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trihedron TNB Frame PDFDokument43 SeitenTrihedron TNB Frame PDFAneelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exploring Gas Laws: Learning Goals: Once You Have Completed This Activity, You Should Understand The Concepts ofDokument5 SeitenExploring Gas Laws: Learning Goals: Once You Have Completed This Activity, You Should Understand The Concepts ofAdam CrabbNoch keine Bewertungen
- III Lattice VibrationDokument35 SeitenIII Lattice VibrationErya Warandita Bupuly TomaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deep BeamsDokument11 SeitenDeep BeamsArcon Solite BarbanidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simulationandmodelingofahydraulicsystem Fluidsim Oronjak PDFDokument5 SeitenSimulationandmodelingofahydraulicsystem Fluidsim Oronjak PDFHadi NurhidayatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid MechanicsDokument4 SeitenFluid MechanicsAmarjit KeneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrostatic ThrustDokument11 SeitenHydrostatic ThrustMicah Dianne DizonNoch keine Bewertungen
- MagnetismDokument11 SeitenMagnetismbaymaxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overview of Tuned Liquid Dampers and Possible Ways of Oscillation Damping Properties ImprovementDokument6 SeitenOverview of Tuned Liquid Dampers and Possible Ways of Oscillation Damping Properties Improvementmostafa shahrabiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermodynamics of Phase Transitions: 3.A. 3.B. 3.C. 3.D. 3.E. 3.F. 3.G. 3.HDokument49 SeitenThermodynamics of Phase Transitions: 3.A. 3.B. 3.C. 3.D. 3.E. 3.F. 3.G. 3.HAnonymous 4nyKDmNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.bernoulli's Equation Cannot Be Applied When The Flow IsDokument9 Seiten1.bernoulli's Equation Cannot Be Applied When The Flow IssureshkumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tension Piles C Phi SoilDokument12 SeitenTension Piles C Phi SoilAhmedKarimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 09 Rheology PDFDokument29 SeitenLecture 09 Rheology PDFsukebadorNoch keine Bewertungen
- High Mast Design Calculation PDFDokument24 SeitenHigh Mast Design Calculation PDFSandip Sengupta60% (5)
- Grassmann NumbersDokument4 SeitenGrassmann NumbershyriusenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Midterm Examination in Physics 101Dokument7 SeitenMidterm Examination in Physics 101Ires YuloNoch keine Bewertungen