Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Integrated Marketing Communication Strategy
Hochgeladen von
Sujoy SarkarOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Integrated Marketing Communication Strategy
Hochgeladen von
Sujoy SarkarCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Integrated Marketing Communication Strategy
Definition
A concept of marketing communications planning that recognizes the added value of a comprehensive plan that evaluates the strategic roles of a variety of communication disciplines generel advertising, direct responce, sales promotion, public relations and combines these disciplines to provide clarity, consistency, and maximum communication impact.
14- 1
Integrated Marketing Communications
The Marketing Communications Environment is Changing:
Mass markets have fragmented, causing marketers to shift away from mass marketing
Media fragmentation is increasing
Improvements in information technology are facilitating segmentation
14- 2
Integrated Marketing Communications
The Need for Integrated Marketing Communications
Conflicting messages from different sources or promotional approaches can confuse company or brand images
The problem is particularly prevalent when functional specialists handle individual forms of marketing communications independently
14- 3
Integrated Marketing Communications
14- 4
Integrated Marketing Communications
Integrated Marketing Communications
The concept under which a company carefully integrates and coordinates its many communications channels to deliver a clear, consistent, and compelling message about the organization and its products. IMC implementation often requires the hiring of a MarCom manager
14- 5
Elements in the Communication Process
14- 6
Developing Effective Communication
Step 1: Identifying the Target Audience
Affects decisions related to what, how, when, and where message will be said, as well as who will say it
14- 7
Developing Effective Communication
Step 2: Determining Communication Objectives
Objectives may be set to move buyers through the six readiness stages
14- 8
Developing Effective Communication
Step 3: Designing a Message
AIDA framework guides message design Message content
Rational Emotional
appeals: fear, humor, guilt, shame, love Moral appeals
14- 9
Developing Effective Communication
Step 3: Designing a Message
Message structure
Draw a conclusion? One-sided or two-sided? Strongest arguments presented first or last? Novelty, contrast, and more
14- 10
Message format
Developing Effective Communication
Step 4: Choosing Media
Personal vs. nonpersonal communication channels
14- 11
Developing Effective Communication
Step 4: Choosing Media
Personal communication channels
Includes face-to-face, phone, mail, and Internet chat communications Word-of-mouth influence is often critical Buzz marketing cultivates opinion leaders Includes media, atmosphere, and events
14- 12
Nonpersonal communication channels
Developing Effective Communication
Step 5: Selecting the Message Source
Highly credible sources are more persuasive A poor choice of spokesperson can tarnish a brand
14- 13
Developing Effective Communication
Step 6: Collecting Feedback
Recognition, recall, and behavioral measures are assessed May suggest changes in product/promotion
14- 14
Setting the Promotional Budget and Mix
Setting the Total Promotional Budget
Affordability Method Budget is set at a level that a company can afford Percentage-of-Sales Method Past or forecasted sales may be used Competitive-Parity Method Budget matches competitors outlays
14- 15
Setting the Promotional Budget and Mix
Setting the Total Promotional Budget
Objective-and-Task Method
Specific objectives are defined Tasks required to achieve objectives are determined Costs of performing tasks are estimated, then summed to create the promotional budget
14- 16
Setting the Promotional Budget and Mix
Setting the Overall Promotion Mix
Determined by the nature of each promotional tool and the selected promotion mix strategy
Revlon emphasizes advertising while Avon emphasizes personal selling
14- 17
Setting the Promotional Budget and Mix
Nature of Each Promotional Tool
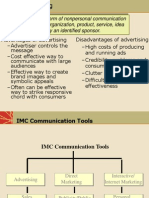
Advertising Personal Selling Sales Promotion Public Relations Direct Marketing
Reaches large, geographically dispersed audiences, often with high frequency Low cost per exposure, though overall costs are high Consumers perceive advertised goods as more legitimate Dramatizes company/brand Builds brand image; may stimulate short-term sales Impersonal; one-way communication
14- 18
Setting the Promotional Budget and Mix
Nature of Each Promotional Tool
Advertising Personal Selling Sales Promotion Public Relations Direct Marketing
Most effective tool for building buyers preferences, convictions, and actions Personal interaction allows for feedback and adjustments Relationship-oriented Buyers are more attentive Sales force represents a longterm commitment Most expensive of the promotional tools
14- 19
Setting the Promotional Budget and Mix
Nature of Each Promotional Tool
Advertising Personal Selling Sales Promotion Public Relations Direct Marketing
May be targeted at the trade or ultimate consumer Makes use of a variety of formats: premiums, coupons, contests, etc. Attracts attention, offers strong purchase incentives, dramatizes offers, boosts sagging sales Stimulates quick response Short-lived Not effective at building longterm brand preferences
14- 20
Setting the Promotional Budget and Mix
Nature of Each Promotional Tool
Advertising Personal Selling Sales Promotion Public Relations Direct Marketing
Highly credible Many forms: news stories, news features, events and sponsorships, etc. Reaches many prospects missed via other forms of promotion Dramatizes company or benefits Often the most underused element in the promotional mix
14- 21
Setting the Promotional Budget and Mix
Nature of Each Promotional Tool
Advertising Personal Selling Sales Promotion Public Relations Direct Marketing
Many forms: Telephone marketing, direct mail, online marketing, etc. Four characteristics:
Nonpublic Immediate Customized Interactive
Well-suited to highly targeted marketing efforts
14- 22
Push vs. Pull Promotion Strategy
14- 23
Setting the Promotional Budget and Mix
Promotion Mix Strategies
Push strategy: trade promotions and personal selling efforts push the product through the distribution channels. Pull strategy: producers use advertising and consumer sales promotions to generate strong consumer demand for products.
14- 24
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Mastering Social Media Marketing: A Comprehensive Guide for Success.Von EverandMastering Social Media Marketing: A Comprehensive Guide for Success.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Integrated Marketing Communication: KavitaDokument25 SeitenIntegrated Marketing Communication: KavitaKavita KumariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing Interview Questions and Answers: Marketing Interview MasteryVon EverandMarketing Interview Questions and Answers: Marketing Interview MasteryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effective CommunicationDokument29 SeitenEffective CommunicationMalini MajumdarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integrated Marketing Communication StrategyDokument25 SeitenIntegrated Marketing Communication StrategySaket KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integrated Marketing Communication StrategyDokument7 SeitenIntegrated Marketing Communication StrategyRaman MaharanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter - 06c IMC StrategyDokument40 SeitenChapter - 06c IMC StrategyKJ VillNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 5 Integrated Marketing Communication StrategyDokument55 SeitenModule 5 Integrated Marketing Communication StrategyZavier Zay HodgesNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Global Perspective: Communicating Customer Value: Integrated Marketing Communications StrategyDokument38 SeitenA Global Perspective: Communicating Customer Value: Integrated Marketing Communications StrategyAmy ArNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of Marketing: Communicating Customer Value: Integrated Marketing Communications StrategyDokument55 SeitenPrinciples of Marketing: Communicating Customer Value: Integrated Marketing Communications Strategyසුමු ලියනාරච්චිNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 13Dokument47 SeitenChapter 13Roma OberoiNoch keine Bewertungen
- L Chapter-14-Imc SPR 2016Dokument51 SeitenL Chapter-14-Imc SPR 2016Irfan Qadir 2035029660Noch keine Bewertungen
- Integrated Marketing Communications StrategyDokument31 SeitenIntegrated Marketing Communications Strategyazwan ayop0% (1)
- Communicating Customer Value: Integrated Marketing Communications StrategyDokument54 SeitenCommunicating Customer Value: Integrated Marketing Communications StrategyIssac020Noch keine Bewertungen
- Integrated Marketing CommunicationDokument26 SeitenIntegrated Marketing Communicationanamikasharma1970Noch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing - Chapter 15Dokument4 SeitenMarketing - Chapter 15Fabian NonesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of Marketing: Communicating Customer Value: Integrated Marketing Communications StrategyDokument55 SeitenPrinciples of Marketing: Communicating Customer Value: Integrated Marketing Communications StrategyAdilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Session 9: Communicating Customer Value: Integrated Marketing Communications StrategyDokument27 SeitenSession 9: Communicating Customer Value: Integrated Marketing Communications StrategyAmenyo GodknowsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communicating Customer Value Integrated Marketing670 PDFDokument31 SeitenCommunicating Customer Value Integrated Marketing670 PDFHafiz ShoaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Introduction To Integrated Marketing CommunicationsDokument37 SeitenAn Introduction To Integrated Marketing Communicationsazam49Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 5Dokument25 SeitenUnit 5Pallavi SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IMC Chapter 15Dokument26 SeitenIMC Chapter 15Pooja SheoranNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9 - Integrated Marketing CommunicationsDokument34 Seiten9 - Integrated Marketing CommunicationsBheesham KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Designing and Managing ImcDokument31 SeitenDesigning and Managing ImcRavi Verma100% (1)
- Chapter 14 Communicating Customer ValueDokument7 SeitenChapter 14 Communicating Customer ValueTaylor Kalinowski100% (4)
- Chapter Nine: Communicating Customer Value: Integrated Marketing Communications StrategyDokument35 SeitenChapter Nine: Communicating Customer Value: Integrated Marketing Communications StrategyTarikul Islam TomalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Promotional Mix Presentation Imc - FinalDokument50 SeitenPromotional Mix Presentation Imc - FinalArnab ChatterjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- MbaDokument70 SeitenMbakarthiyayini_kmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Promotional MixDokument54 SeitenPromotional MixSugandha DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integrating Marketing Communications To Build Brand EquityDokument4 SeitenIntegrating Marketing Communications To Build Brand EquityTahir Amin KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- IMC Communication Tools: Advertising Direct Marketing Interactive/ Internet MarketingDokument27 SeitenIMC Communication Tools: Advertising Direct Marketing Interactive/ Internet MarketingMeena GogriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Any Paid Form of Nonpersonal Communication About An Organization, Product, Service, Idea or Cause by An Identified SponsorDokument28 SeitenAny Paid Form of Nonpersonal Communication About An Organization, Product, Service, Idea or Cause by An Identified SponsorAbdul Rehman KalvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PromotionDokument21 SeitenPromotionMd Omar KhoiyamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name:-Attia Tul Wadood Reg No: - BBA07183046 Subject: - Marketing Managment Submited: - MR Wasif BilalDokument5 SeitenName:-Attia Tul Wadood Reg No: - BBA07183046 Subject: - Marketing Managment Submited: - MR Wasif BilalAlizy khanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12.integrated MKT ComDokument20 Seiten12.integrated MKT Computranto nurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Designing and Managing Integrated Marketing CommunicationsDokument6 SeitenDesigning and Managing Integrated Marketing CommunicationsHenry PK ZEeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit IV: Marketing Communication: Sandeep Kumar Singh, Assistant Professor, Dept. of Commerce, CHRIST UniversityDokument32 SeitenUnit IV: Marketing Communication: Sandeep Kumar Singh, Assistant Professor, Dept. of Commerce, CHRIST Universitynishant haweliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integrated Marketing CommunicationsDokument24 SeitenIntegrated Marketing CommunicationsarunbvijayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Integrated Marketing CommunicationsDokument16 SeitenIntroduction To Integrated Marketing CommunicationsazazelaveyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Session 9 - Integrating Marketing Communications To Build Brand EquityDokument13 SeitenSession 9 - Integrating Marketing Communications To Build Brand Equityaditi kushwahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IMCDokument28 SeitenIMCChanchal Kansal0% (1)
- The World of AdvertisingDokument25 SeitenThe World of AdvertisingPankaj GiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- IMC NotesDokument11 SeitenIMC NotesAvinash GurjarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 5 NotesDokument20 SeitenModule 5 NotesHarshith AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presented By-Rakesh Kumar Rahul Kesarwani (II Semester)Dokument22 SeitenPresented By-Rakesh Kumar Rahul Kesarwani (II Semester)Smriti KhannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 017Dokument35 SeitenChap 017Ng. Minh ThảoNoch keine Bewertungen
- MM, Group No. 10 (Marketing Commu. Mix) in DetailDokument36 SeitenMM, Group No. 10 (Marketing Commu. Mix) in DetailJaimin VaghelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 14 SummaryDokument5 SeitenChapter 14 SummarygeneoeiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overview of Integrated Marketing CommunicationsDokument14 SeitenOverview of Integrated Marketing CommunicationsNadeem MustafaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dasar-Dasar Pemasaran: Pokok BahasanDokument12 SeitenDasar-Dasar Pemasaran: Pokok Bahasancuterika100% (1)
- 1 Rev IntroductionDokument28 Seiten1 Rev IntroductionVivek MandalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prasanna Kumar Chandrakar: ID. NO.-MU09MBA027 Mba - Iiird Sem. MSMSR, Mats University Raipur C.GDokument13 SeitenPrasanna Kumar Chandrakar: ID. NO.-MU09MBA027 Mba - Iiird Sem. MSMSR, Mats University Raipur C.GJijo JohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- AdvertisementDokument76 SeitenAdvertisementChinthuUnnikrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 13 NotesDokument5 SeitenChapter 13 Notesfauzi_aimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- University of Information Technology and Sciences: AssignmentDokument7 SeitenUniversity of Information Technology and Sciences: AssignmentMAMUN AlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 13: Promoting Products (Part 1)Dokument5 SeitenChapter 13: Promoting Products (Part 1)Jennie MuNoch keine Bewertungen
- The BABM Programme Unit 8 Marketing Strategy: MKT306 ModuleDokument51 SeitenThe BABM Programme Unit 8 Marketing Strategy: MKT306 ModuleSheryn LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- PRINCIPLES OF MARKETING - UNIT 5 Pormotion & Recent Developments2Dokument69 SeitenPRINCIPLES OF MARKETING - UNIT 5 Pormotion & Recent Developments2YoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing Managemen1esson 11bDokument6 SeitenMarketing Managemen1esson 11bnasayaobeladonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integrating Marketing Communications To Build Brand EquityDokument29 SeitenIntegrating Marketing Communications To Build Brand EquityMaryam KhaliqNoch keine Bewertungen
- SujoyDokument20 SeitenSujoySujoy SarkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Academic AchievementsDokument2 SeitenAcademic AchievementsSujoy SarkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cyber - LawDokument11 SeitenCyber - Lawvijayfs2Noch keine Bewertungen
- New C.v.gan Datta More11!1!1Dokument2 SeitenNew C.v.gan Datta More11!1!1Sujoy SarkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prashant 1Dokument2 SeitenPrashant 1Sujoy SarkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prashant 1Dokument2 SeitenPrashant 1Sujoy SarkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resume 2Dokument5 SeitenResume 2Sujoy SarkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rajiv ResumeDokument2 SeitenRajiv ResumeSujoy SarkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resume 2Dokument5 SeitenResume 2Sujoy SarkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resume 2Dokument5 SeitenResume 2Sujoy SarkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resume 2Dokument5 SeitenResume 2Sujoy SarkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CV MahtabDokument2 SeitenCV MahtabSujoy SarkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- PR For Cont. Ext.-Karan-110113Dokument1 SeitePR For Cont. Ext.-Karan-110113Sujoy SarkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Costumer Buying Patterns Report: Blackwell ElectronicsDokument13 SeitenCostumer Buying Patterns Report: Blackwell ElectronicsIvanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing Management Module 7Dokument5 SeitenMarketing Management Module 7Sharon Cadampog MananguiteNoch keine Bewertungen
- GoodyearDokument10 SeitenGoodyearMiteshwar SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iman Buss ManagementDokument15 SeitenIman Buss Managementulzzang looNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notesmatic: Marketing Mix of DoveDokument4 SeitenNotesmatic: Marketing Mix of DoveRitika SinghalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2013 The American Mold Builder - SummerDokument48 Seiten2013 The American Mold Builder - SummerAMBANoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronic Word of Mouth and Purchase Intention On TravelokaDokument4 SeitenElectronic Word of Mouth and Purchase Intention On TravelokaTrang HuyềnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Initiation For Increasing Brand ValueDokument4 SeitenInitiation For Increasing Brand ValueKrishNoch keine Bewertungen
- BrandingDokument7 SeitenBrandingJaime Chavez M100% (1)
- TrappedTraders v1-0 PDFDokument36 SeitenTrappedTraders v1-0 PDFwanqi08Noch keine Bewertungen
- Innovation and Entrepreneurship PresentationDokument11 SeitenInnovation and Entrepreneurship PresentationGandhi AnugrahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hindustan Unilever LTD Case Study Individual AssignmentDokument5 SeitenHindustan Unilever LTD Case Study Individual AssignmentRajat GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final ProjectDokument27 SeitenFinal ProjectSidharth Raina0% (1)
- Lesson 10 - Beverage Control Systems (Revised)Dokument17 SeitenLesson 10 - Beverage Control Systems (Revised)Daniela FotaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Marketing Plan For Tofu ProductDokument11 SeitenSample Marketing Plan For Tofu Productbotolaik100% (1)
- Retail Management Information SystemDokument12 SeitenRetail Management Information Systemmittalsakshi020692Noch keine Bewertungen
- Architectural Lighting - September October 2016Dokument68 SeitenArchitectural Lighting - September October 2016Nadeem HassoonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Google Advertising Fully Solved TestDokument10 SeitenGoogle Advertising Fully Solved TestfanegarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brand History: Mountain Dew - Darr Ke Aage Jeet HaiDokument8 SeitenBrand History: Mountain Dew - Darr Ke Aage Jeet HaiAnkit JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- WanjikuDokument41 SeitenWanjikujohn mwangi100% (1)
- A Strategic Analysis of Ocean Park of Hong KongDokument18 SeitenA Strategic Analysis of Ocean Park of Hong Kongchunwing9612450% (2)
- Ral BrandingDokument26 SeitenRal BrandingkhushiYNoch keine Bewertungen
- 20 More Creative Product Packaging ExamplesDokument30 Seiten20 More Creative Product Packaging ExamplesBerenice Martínez FdzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Transformation For The Insurance Industry PDFDokument10 SeitenDigital Transformation For The Insurance Industry PDFAsser El-FoulyNoch keine Bewertungen
- PMG Benchmarking 08-SCPIDokument2 SeitenPMG Benchmarking 08-SCPIshikhar19Noch keine Bewertungen
- PT3 English Paper 1 Q1-Q8 (Set 1)Dokument5 SeitenPT3 English Paper 1 Q1-Q8 (Set 1)Hoo Chin Wen50% (2)
- GIO+Course 3 Email Marketing Tahir AshrafDokument17 SeitenGIO+Course 3 Email Marketing Tahir AshrafSayed tahir Ashraf100% (1)
- Jasper CustomerList PriyankaDokument10 SeitenJasper CustomerList PriyankaSailapathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indonesian Pulp and Paper IndustryDokument5 SeitenIndonesian Pulp and Paper IndustryMEDIA DATA RISET, PTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Failure ReasonsDokument2 SeitenFailure Reasonskaka100% (1)