Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Cranium
Hochgeladen von
Difa ZafiraOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Cranium
Hochgeladen von
Difa ZafiraCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Akademi Tekhnik Radiodiagnostik dan Radioterapi Depkes
Skull
The human cranium and the facial bones are the foundation for the soft tissues of the face and head. The cranium is that part of the skull that holds and protects the brain in a large cavity, called the cranial vault.
Skull
Eight plate-like bones form the human cranium by fitting together at joints called sutures. The most important of these cranial bones for the appearance of the face is the frontal bone, which underlies the top of the face above the eyeballs. The human skull also includes 14 facial bones that form the lower front of the skull and provide the framework for most of the face that is important to psychological research.
Skull
These 22 skull bones form other, smaller cavities besides the cranial vault, including those for the eyes, the internal ear, the nose, and the mouth. The important facial bones include the jaw bone or mandible, the maxilla or upper jaw, the zygomatic or cheek bone, and the nasal bone.
Skull ( AP )
Skull ( Lateral )
Skull
Soft tissue
: skin galeal muscles
Bones Meninges Brain Cerebro-spinal Liquid (CSF) Ventricular system Vascular
Skull
The skull bones are associated with many other features. Processes are areas where the bones have extra tissue to hold muscles and ligaments; lines are grooves in the bone from other developmental processes; foramina are holes in the bones through which nerves and blood vessels pass; sinuses are empty spaces in the bones that make the skull lighter. Some of these features affect the physiognomy of the face due to variations in thickness, size, location, and shape.
Organs
Eye Ear Nose Mouth Glands
: bulb, nerve, muscles : outer, middle, inner : sinuses : tongue, teeth, pharynx : Pineal, Hypophysis
BONES
Frontal Parietal Temporal Occipital Ethmoid
Frontal Bone
Temporal Bone
Occipital Bone
Ethmoid Bone
BONES
Sphenoid
Face
: Major wing Minor wing Sella turcica : Maxilla Mandibule Zygomatic Nasal
Sphenoid Bone
Sphenoid bone from the rear, with Parietal (3) and Temporal bones (4, mastoid process) attached. The sphenoid consists of the body of the sphenoid (1), its greater wings (2), the external pterygoid plate (5), and the internal pterygoid place (6). The frontal bone fits on the upper front part of this assembly (distant in the image) and the occipital bone fits on the rear (near in the image). The Ethmoid bone attaches to the front (distant) part of the Sphenoid.
Sphenoid Bone
BONES
: Ovale Carotid Spinosum Lacerum Outer and inner table Diploic
Foramen
SUTURES
Coronary Sagital Lamboid Temporo-Parietal
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The-Skull by Dr. Phan SandethDokument65 SeitenThe-Skull by Dr. Phan SandethTith Sunny100% (2)
- Respiratory SystemDokument54 SeitenRespiratory SystemHannah YsaBelle LeguroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pulmonary CirculationDokument16 SeitenPulmonary Circulationsajid_saiyad0% (1)
- Orbit - AnatomyDokument41 SeitenOrbit - Anatomysamuelpnrj25100% (2)
- Classification of JointsDokument25 SeitenClassification of JointsAida ZabidinNoch keine Bewertungen
- BB FM2102 L1 Vertebral Column & JointsDokument15 SeitenBB FM2102 L1 Vertebral Column & JointsSamJosephNoch keine Bewertungen
- Joints Anatomy PresentationDokument41 SeitenJoints Anatomy Presentationahmadnaveed99Noch keine Bewertungen
- Blood VesselsDokument7 SeitenBlood VesselsRohee TariqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Musculoskeletal SystemDokument2 SeitenMusculoskeletal SystemJames Wilstar Delicano SandovalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy & Physiology Unit 1Dokument29 SeitenAnatomy & Physiology Unit 1Priyanjali SainiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Supply of The BrainDokument32 SeitenBlood Supply of The BrainShimmering MoonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4) Mammary Gland 220413 Upnm2Dokument22 Seiten4) Mammary Gland 220413 Upnm2AaronMaroonFive100% (1)
- Triangles of NeckDokument6 SeitenTriangles of NeckDr santoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Joints of Lower Limb 2017Dokument77 SeitenJoints of Lower Limb 2017yasrul izadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Splints and Tractions in OrthopaedicsDokument56 SeitenSplints and Tractions in OrthopaedicsNinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2013 - Lower Limb-Fascial Compartments of Thigh - Student VersionDokument28 Seiten2013 - Lower Limb-Fascial Compartments of Thigh - Student Versionmarina_shawkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 MusclesDokument9 Seiten11 MusclesElaine Loreen Villanueva100% (1)
- Special Senses - II: DR Muhammad Ressam NazirDokument26 SeitenSpecial Senses - II: DR Muhammad Ressam NazirRessam NazirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bone Joint Cartilage PowerpointDokument81 SeitenBone Joint Cartilage PowerpointChevie WisemanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Joints and Ligaments of The Skull and Neck-2Dokument79 SeitenJoints and Ligaments of The Skull and Neck-2armanious64Noch keine Bewertungen
- Popliteal Fossa and LegDokument40 SeitenPopliteal Fossa and LegRaj Shekhar SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genital ProlapseDokument9 SeitenGenital Prolapsesher singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Anterior and Posterior Triangles of The NeckDokument10 SeitenThe Anterior and Posterior Triangles of The NeckClair TomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subclavius Pectoralis Minor: Axial Skeleton To Shoulder Girdles (Ventral Side)Dokument6 SeitenSubclavius Pectoralis Minor: Axial Skeleton To Shoulder Girdles (Ventral Side)馮素琴Noch keine Bewertungen
- How Many Bones Are in The BodyDokument3 SeitenHow Many Bones Are in The BodycanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spinal Cord: DR Ganesh Khemnar Assistant Professor Dept. of Anatomy BVDUMC, PuneDokument43 SeitenSpinal Cord: DR Ganesh Khemnar Assistant Professor Dept. of Anatomy BVDUMC, PunePraneetha NouduriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Obturator NerveDokument3 SeitenObturator NerveDr santoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Pelvic Girdle: By/Dr - Abdisamad Omar AliDokument30 SeitenThe Pelvic Girdle: By/Dr - Abdisamad Omar AliSAKARIYE MAXAMEDNoch keine Bewertungen
- ORBITDokument46 SeitenORBITdr yati gothwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Anatomy,: First Edition Mckinley & O'LoughlinDokument40 SeitenHuman Anatomy,: First Edition Mckinley & O'LoughlinAgung PurmanaNoch keine Bewertungen
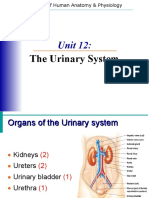
- Lecture 23 - The Urinary SystemDokument46 SeitenLecture 23 - The Urinary SystemIhab MoustafaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cerebral Artery RevisedDokument16 SeitenCerebral Artery RevisedbobirfansyahputraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1-Bones of The Upper Limb Final-2Dokument18 Seiten1-Bones of The Upper Limb Final-2DrVasu Mudiraj100% (1)
- Nerve and Blood Supply - LEDokument53 SeitenNerve and Blood Supply - LEAlyanna Morales100% (1)
- Upper Limb 0809 PDFDokument59 SeitenUpper Limb 0809 PDFasdaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Female Pelvis and Fetal Skull PDFDokument9 SeitenThe Female Pelvis and Fetal Skull PDFMohammed AbdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cutaneous Circulation: DR Pushpa Lata Sachan Associate Professor CIMS&H, LucknowDokument19 SeitenCutaneous Circulation: DR Pushpa Lata Sachan Associate Professor CIMS&H, LucknowNishankumar JhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiology of RespirationDokument2 SeitenPhysiology of RespirationIOSRjournalNoch keine Bewertungen
- AneurysmDokument37 SeitenAneurysmbilal safiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chest and Abdominal Injuries: Forensic Medicine by Yazan AbueidehDokument54 SeitenChest and Abdominal Injuries: Forensic Medicine by Yazan AbueidehRayyan Alali100% (1)
- Ana Phisio Lab Report.Dokument4 SeitenAna Phisio Lab Report.Diana Amor100% (1)
- Thorax AllDokument174 SeitenThorax Allravindra sharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digestive System Power PointDokument17 SeitenDigestive System Power PointAlyssa Mae DapadapNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ocular InjuryDokument46 SeitenOcular InjurysnyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular System: More Than Just The HeartDokument34 SeitenCardiovascular System: More Than Just The HearteliseudesafateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Orbital Anatomy: JI Georgemar V. Arana JRDokument49 SeitenOrbital Anatomy: JI Georgemar V. Arana JRGeorgemar AranaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Knee InjuriesDokument6 SeitenTypes of Knee InjuriesSagarNoch keine Bewertungen
- JointsDokument28 SeitenJointsS.I. G.T.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Muscles of The Thorax That Assist in BreathingDokument6 SeitenMuscles of The Thorax That Assist in Breathinge jeighNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy / Physio of The EarDokument58 SeitenAnatomy / Physio of The EarRA100% (1)
- Hip JointDokument25 SeitenHip JointHashim OmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Splinting For Peripheral Nerve Injuries-PPT (2023)Dokument49 SeitenSplinting For Peripheral Nerve Injuries-PPT (2023)KarisiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Papilloedema and Optic AtrophyDokument27 SeitenPapilloedema and Optic AtrophyRobert MontgomeryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Brain: 1 Prepared by A.Devasena Asso - Prof./ECE, Dhanalakshmi College of EnggDokument17 SeitenHuman Brain: 1 Prepared by A.Devasena Asso - Prof./ECE, Dhanalakshmi College of EnggSebastin Suresh100% (1)
- 102 Lab Exam4 Reviewer - PartsDokument5 Seiten102 Lab Exam4 Reviewer - PartsJan Marvin Lichauco Mendoza100% (1)
- Introduction in Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument35 SeitenIntroduction in Human Anatomy and Physiologyraul nino MoranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Appendicitis: The Etiology, Hygenic and Dietetic TreatmentVon EverandAppendicitis: The Etiology, Hygenic and Dietetic TreatmentBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (2)
- Thyroglossal Duct Cysts, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsVon EverandThyroglossal Duct Cysts, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Cockroach (Periplaneta Americana, L.): An Introduction to Entomology for Students of Science and MedicineVon EverandThe Cockroach (Periplaneta Americana, L.): An Introduction to Entomology for Students of Science and MedicineBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (2)
- Pancreatic Pseudo Cyst Case - Rachel FlorendoDokument122 SeitenPancreatic Pseudo Cyst Case - Rachel FlorendoKM100% (2)
- Orbital Decompression, Optic N Decompression and EndoDCRDokument97 SeitenOrbital Decompression, Optic N Decompression and EndoDCRAlok RathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Specification: iUBT435 - Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument3 SeitenTest Specification: iUBT435 - Anatomy and PhysiologyVicki TseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Skin Grade 6Dokument15 SeitenHuman Skin Grade 6Irene AnastasiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thyroid PharmacologyDokument26 SeitenThyroid PharmacologyVikrant GholapNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oral Histology IDEDokument765 SeitenOral Histology IDEArwa ChekrouniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cerebrum MCQDokument5 SeitenCerebrum MCQSrinivasa Rao BollaNoch keine Bewertungen
- High-Yield Histopathology 2e PDFDokument346 SeitenHigh-Yield Histopathology 2e PDFmary100% (1)
- F3 3.2Dokument41 SeitenF3 3.2amalina rohaizanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sensory Play Activities Kids Will LoveDokument5 SeitenSensory Play Activities Kids Will LoveGoh KokMingNoch keine Bewertungen
- UB Human Physiology Syllabus 2012Dokument5 SeitenUB Human Physiology Syllabus 2012Anonymous MPdGkx87bNoch keine Bewertungen
- HydronephrosisDokument7 SeitenHydronephrosisNaqash NobleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oral Hygiene QuizDokument1 SeiteOral Hygiene Quizramzan aliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument4 SeitenAnatomy and PhysiologyAnn-Ann Sihiyon SiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Periodontal Literature ReviewDokument70 SeitenPeriodontal Literature ReviewSmitha Kapani gowdaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise 3 Internal Anatomy of The Lubber Grasshopper Romalea - CompressDokument15 SeitenExercise 3 Internal Anatomy of The Lubber Grasshopper Romalea - Compressahmed fouadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kebutuhsn Implan Urologi Desember 2021 - November 2022 - 3Dokument32 SeitenKebutuhsn Implan Urologi Desember 2021 - November 2022 - 3Ilham ApriansyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Necrosis and InfarctDokument4 SeitenTypes of Necrosis and InfarctTowhidulIslam75% (4)
- Terminologi Anatomi ManusiaDokument184 SeitenTerminologi Anatomi ManusiaWirdatul JannahNoch keine Bewertungen
- LABORATORY EXERCISE The Gastrointestinal System With Accessory GlandDokument5 SeitenLABORATORY EXERCISE The Gastrointestinal System With Accessory GlandGelo AlonzoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chart of Emotions and Reactions by Internal OrgansDokument1 SeiteChart of Emotions and Reactions by Internal Organsmcvelli40100% (2)
- Pregnancy Induced Hypertension Case StudyDokument77 SeitenPregnancy Induced Hypertension Case StudyATEHAN BORDS100% (1)
- EXCRETION (The Wastage Disposing System)Dokument2 SeitenEXCRETION (The Wastage Disposing System)Anonymous mbcs6W3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine System MatrixDokument1 SeiteEndocrine System MatrixJonnel GadinganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Questions and Their Ideal AnswersDokument17 SeitenQuestions and Their Ideal AnswersHamzaShabaka100% (2)
- Unit 20 Urinary System NotesDokument45 SeitenUnit 20 Urinary System NotesRyann SmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pages From GMP001 - Module01 - Course04Dokument10 SeitenPages From GMP001 - Module01 - Course04Mangesh RautNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jake C. Canapi, RN, MSN, Ph.D. Lily Ann C. Mallabo, RN, MSN Gail Ann Parel-Pascual, RMT Reymel B. Magora, RMTDokument48 SeitenJake C. Canapi, RN, MSN, Ph.D. Lily Ann C. Mallabo, RN, MSN Gail Ann Parel-Pascual, RMT Reymel B. Magora, RMTAngelo LacisteNoch keine Bewertungen
- INFERTILITYDokument20 SeitenINFERTILITYKathleen FrugalidadNoch keine Bewertungen