Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Fatigue Crack Propagation
Hochgeladen von
djsouravCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Fatigue Crack Propagation
Hochgeladen von
djsouravCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Fatigue Crack Propagation
Fatigue Crack Growth
Once a crack is present in a material, it will
tend to grow under the influence of cyclic
loading.
The crack may be initiated by fatigue, or
may be pre-existing from manufacture, or
may be caused by an impact, or similar
event (e.g., a thermal shock.)
The crack will grow to a critical length then
fracture of the component will occur.
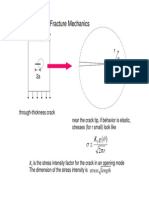
Driving Force for Crack Growth
The driving force for crack growth is the
range in the stress intensity factor during
cycling.
0 R for
0 R for
a (a/W) K
< =
> =
=
max
min max
f
o o A
o o o A
t o A A
Cyclic Loading
o
mean
=
o
max
+o
min
2
o
range
= o
max
o
min
o
amplitude
=
o
max
o
min
2
StressRatio, R =
o
min
o
max
Rotating Machinery
Airframes, Bridges, Tanks, etc,
Crack Growth Rate, da/dN
X
X
C
r
a
c
k
L
e
n
g
t
h
,
a
Cycles, N
a
o
a
c2
Ao
2
Ao
1
Ao
1
<
Ao
2
a
c1
da/dN
2
da/dN
1
Paris Law
Paris Region
Stable Growth
T
h
r
e
s
h
o
l
d
R
e
g
i
o
n
S
l
o
w
G
r
o
w
t
h
F
a
s
t
F
r
a
c
t
u
r
e
R
e
g
i
o
n
R
a
p
i
d
-
u
n
s
t
a
b
l
e
G
r
o
w
t
h
log(AK)
l
o
g
(
d
a
/
d
N
)
da
dN
= A(AK)
m
A
m
Crack Growth Rates and
Microstructural Features
Fractographic Evidence of Crack Growth
fatigue
striations
10 m
Fatigue Striations in Al-alloy:
5 small cycles between overloads
Crack Growth
direction
No Load
Loaded
Max Load
Load reduced
No Load
Loaded again
Slip
Crack Growth Mechanisms
Model for
Crack Growth
4
1
2
5
6
7
Crack Propagation Life, N
p
Total fatigue life is the sum of the crack initiation life and the
crack propagation (growth) life.
p i f
N N N + =
For some components, where stress levels are high and/or the critical
crack size is small, the crack propagation life is neglected in design.
For other structures, including pressure vessels, ship structures,
transport aircraft, etc. the crack growth life may be a substantial
component of total life.
N
p
=
da
A(AK)
m
a
o
a
c
}
Limits of Integration
The initial crack length, a
o
, is usually either
found by inspection or a reasonable minimum
size of crack is assumed for the analysis.
The critical crack size is found from:
Where o
max
is the maximum stress.
(its not the stress range)
2
c
c
(a/W)
K 1
a
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
max
f o t
Procedure for Constant Amplitude
Crack Growth life Calculation
Obtain appropriate crack growth rate data
for material, environment and stress ratio
Determine starting crack size, a
o
Determine critical crack size, a
c
Determine AK for starting crack size, a
o
. If
AK< AK
th
then crack will not grow
If
AK> AK
th
then integrate to get crack
growth life. (Can conservatively use Paris
Law, if appropriate)
General Paris Law Solution for N
p
c
o
a
a
m
p
a (a/W) A
da
N
) f t o A
(
(
=
c o
3 3 2 3
p
a
1
a
1
Y A
2
N
) (
/
o A t
Special Case: m=3; f(a/W) constant=Y
General Solution:
A more general solution will include the
actual growth rate data in the threshold and
near-threshold region.
If the starting crack size is relatively small,
this will represent a major portion of growth
life, so it may be un-economical to neglect it.
The life in the fast fracture region is
generally neglected. Use this data carefully.
Try it!
A fatigue crack 1.5 mm long has been discovered in a
main wing spar of a CC-130 Hercules undergoing
structural tear down and inspection. Given the loading,
material and geometry shown, estimate the number of
flying hours to fracture, and comment on the results.
7075-T73511 al alloy
K
c
(6mm) = 40 MPa\m
S
y
= 455 MPa
A = 1.3x10
-10
m/cycle
m = 3
Y = 1.27 (assume constant)
AS
Section A-A Through Spar (inches)
Crack
a
Loading
time
100 cycles=1 flying hour
75
10
S
t
r
e
s
s
(
M
P
a
)
0
133 0
75
10
. R = =
OK...
a
o
= 1.5 mm, find a
o
(56.1mm) 0.0561m
75 27 1
40 1
YS
K 1
a
2
2
c
c
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
) ( .
max
t t
=
c
o
a
a
m
p
a Y A
da
N
) ( t o A
Stress Range, Ao = o
max
-o
min
= (75 - 10) MPa = 65 MPa
For m=3, Y constant:
hrs flight 1060
cycles 100
hr 1
cycles 106000
cycles 106000
1 056 0
1
0015 0
1
27 1 65 10 x 3 1
2
N
a
1
a
1
Y A
2
N
3 3 2 3 10
p
c o
3 3 2 3
p
= =
=
(
=
(
(
. .
) . ( ) ( .
) (
/
/
t
o A t
Crack Growth Curve
5 mm at half life!
a/ac =15%
95000 cycles
at half length!
N/Np =89%
Comments & Observations
There is a substantial period of crack
growth for this component. The fatigue
crack can be monitored, inspected, and the
component can be replaced or repaired after
500 more hours of operation.
Half-life (factor of safety on life) is a safer
criterion than length, because cracks grow
too rapidly as they become longer.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Fracture and FatigueDokument15 SeitenFracture and FatigueZou JiaweiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advances in Engineering Plasticity and its ApplicationsVon EverandAdvances in Engineering Plasticity and its ApplicationsW.B. LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- D Mec Frac Fatigue Part IIDokument38 SeitenD Mec Frac Fatigue Part IIsure516vNoch keine Bewertungen
- LCF HCFDokument85 SeitenLCF HCFnotonectalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Creep Test Guide for Lead SpecimensDokument4 SeitenCreep Test Guide for Lead SpecimensFerry Ferdiansyah50% (2)
- Von MisesDokument8 SeitenVon MisesAlex OliveiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fatigue Failure MATERIALSDokument37 SeitenFatigue Failure MATERIALSfadjar sophianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz & Test QuestionsDokument4 SeitenQuiz & Test QuestionsdadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strain Energy Part 1Dokument20 SeitenStrain Energy Part 1aalijanaabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stress Intensity Factor and Fracture Toughness TestingDokument31 SeitenStress Intensity Factor and Fracture Toughness TestingShahrul Azmin0% (1)
- Chapter 2 - General Fracture MechanicsDokument45 SeitenChapter 2 - General Fracture Mechanicsviv010275% (4)
- Chapter 4 - Axial LoadingDokument50 SeitenChapter 4 - Axial LoadingAbdullrahman Ahmed100% (1)
- Design For Fatigue and Simulation of Glass Fibre Epoxy Composite Automobile Leaf SpringDokument22 SeitenDesign For Fatigue and Simulation of Glass Fibre Epoxy Composite Automobile Leaf SpringjonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 13 Creep and Stress RuptureDokument25 Seiten13 Creep and Stress RuptureZdravko IvancicNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4102 - Chap 9 Creep Notes PDFDokument19 Seiten4102 - Chap 9 Creep Notes PDFjonthemesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab7 Fatigue Testing MachineDokument13 SeitenLab7 Fatigue Testing MachineHosam0% (1)
- Fracture Mechanics NotesDokument16 SeitenFracture Mechanics NotesHossam M ALrohilyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fracture Mechanics Stress Intensity Factor</TITLEDokument5 SeitenFracture Mechanics Stress Intensity Factor</TITLEGopinath ChakrabortyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Failure Mechanisms FatigueDokument12 SeitenFailure Mechanisms Fatigueaap1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Crack growth mechanisms in metalsDokument5 SeitenCrack growth mechanisms in metalsjonthemes100% (1)
- Strength of Materials NotesDokument66 SeitenStrength of Materials NotesHimanshu MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiaxial Fatigue Life PredictionDokument10 SeitenMultiaxial Fatigue Life PredictionGooftilaaAniJiraachuunkooYesusiinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 Torsion TestDokument16 Seiten10 Torsion Testfrankjono75% (4)
- Digital Universal Hardness Tester BRV-187.5TDokument5 SeitenDigital Universal Hardness Tester BRV-187.5T周记伟Noch keine Bewertungen
- EM321 TOPIC 1 - Failure Theories and Fatigue Strength PDFDokument180 SeitenEM321 TOPIC 1 - Failure Theories and Fatigue Strength PDFJoshua RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab ManualDokument62 SeitenLab ManualKhalid M. Hafez100% (1)
- Impact IzodDokument6 SeitenImpact IzodTanu RdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Testing and Evaluation of Engineering MaterialsDokument5 SeitenTesting and Evaluation of Engineering MaterialsFAHED AYYAD100% (1)
- 2-Theories of Failure (MOS-2)Dokument28 Seiten2-Theories of Failure (MOS-2)Sohaib Zaib KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brittle Fracture and Impact TestingDokument20 SeitenBrittle Fracture and Impact TestingWaseeq AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Fracture Mechanics and Fatigue Analysis NotesDokument403 SeitenEngineering Fracture Mechanics and Fatigue Analysis NotesAtheena PaulsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical Properties of MetalsDokument258 SeitenMechanical Properties of MetalsIsza Marie N. SocorinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formula Sheet For Exam 1Dokument1 SeiteFormula Sheet For Exam 1chris ricaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vibration of Continuous SystemsDokument14 SeitenVibration of Continuous SystemsRidwan OlatunjiNoch keine Bewertungen
- PA-Solutions 4012 PDFDokument31 SeitenPA-Solutions 4012 PDFjonthemesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Numerical in Electrical, Mechanical, Electronic, Optical Materials From Different Books Along With Previous Year Papers of GATE, ES, CS and Other Exams.Dokument24 SeitenNumerical in Electrical, Mechanical, Electronic, Optical Materials From Different Books Along With Previous Year Papers of GATE, ES, CS and Other Exams.Rehan Sharma100% (1)
- Chapter 10: Failure: Issues To Address..Dokument31 SeitenChapter 10: Failure: Issues To Address..Jhei UploadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical VibrationsDokument45 SeitenMechanical VibrationsFauiqe YousafNoch keine Bewertungen
- ExergyDokument64 SeitenExergyAndree RosalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plastic Analysis 0809Dokument81 SeitenPlastic Analysis 0809GrootKoning Werner100% (1)
- 8.2 Final Fracture ToughnessDokument19 Seiten8.2 Final Fracture ToughnessHenry Theodore DaquinagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fatigue Ch12Dokument87 SeitenFatigue Ch12Bolaji Suberu100% (1)
- Phase DiagramsDokument48 SeitenPhase DiagramszanretNoch keine Bewertungen
- PPT On Fracture MechanicsDokument81 SeitenPPT On Fracture Mechanicskamel touilebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Torsional Vibrations of Rotor SystemsDokument104 SeitenTorsional Vibrations of Rotor SystemsSharath UpadhyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- r05320305 Design of Machine Members IIDokument9 Seitenr05320305 Design of Machine Members IISRINIVASA RAO GANTANoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 Low and High Cycle FatigueDokument14 Seiten10 Low and High Cycle FatiguePRASAD326100% (1)
- Whirling of ShaftDokument7 SeitenWhirling of Shaftadityaguptaa100% (1)
- Toughness TestDokument25 SeitenToughness TestNehaJainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pressure VesselsDokument63 SeitenPressure Vesselsكرار نعيمNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fracture MechanicsDokument187 SeitenFracture MechanicsLuis Alberto Ruiz PestañaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DTS-Short Questions and AnswerDokument7 SeitenDTS-Short Questions and AnswerAlfred Franklin V100% (1)
- FatigueDokument32 SeitenFatigueMostaMostafaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fatigue of Materials ExplainedDokument40 SeitenFatigue of Materials ExplainednitinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Planning of Inspection and Repair For Ship Operation: SchallDokument8 SeitenPlanning of Inspection and Repair For Ship Operation: Schallchwinboss85Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 11 Fatigue 2Dokument8 SeitenLecture 11 Fatigue 2giovanniNoch keine Bewertungen
- FractureDokument16 SeitenFractureElvis Osorio SantanderNoch keine Bewertungen
- CFD hw1Dokument33 SeitenCFD hw1krittrin.pNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intro To MooringDokument55 SeitenIntro To MooringsojanvasudevanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transition Note – Master Plans for 4 Cities in RajasthanDokument4 SeitenTransition Note – Master Plans for 4 Cities in RajasthandjsouravNoch keine Bewertungen
- Do Anchor Tenants Make or Break Shopping MallsDokument3 SeitenDo Anchor Tenants Make or Break Shopping MallsdjsouravNoch keine Bewertungen
- ABCDokument13 SeitenABCdjsouravNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corrugated Box Plant Business PlanDokument14 SeitenCorrugated Box Plant Business PlanYojit BindlishNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP 2222Dokument17 SeitenNCP 2222djsouravNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nicmar - Sode: SsignmentDokument13 SeitenNicmar - Sode: SsignmentdjsouravNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCPDokument18 SeitenNCPdjsourav100% (1)
- NCP 30 - Site Organisationa FinalDokument17 SeitenNCP 30 - Site Organisationa Finaldjsourav100% (1)
- KHNKJH NCP 30 1Dokument31 SeitenKHNKJH NCP 30 1djsouravNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP 22Dokument13 SeitenNCP 22djsouravNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plan Equipment and Order Bitumen for New Airport ConstructionDokument15 SeitenPlan Equipment and Order Bitumen for New Airport ConstructiondjsouravNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course No.: PGPM 14/ NCP 23 Course Title: Construction Contracts and Contracting Assignment No.: OneDokument21 SeitenCourse No.: PGPM 14/ NCP 23 Course Title: Construction Contracts and Contracting Assignment No.: OnedjsouravNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP 23 - PGPPMDokument22 SeitenNCP 23 - PGPPMShelly Delhi100% (1)
- Course No.: PGPM 14/ NCP 23 Course Title: Construction Contracts and Contracting Assignment No.: OneDokument21 SeitenCourse No.: PGPM 14/ NCP 23 Course Title: Construction Contracts and Contracting Assignment No.: OnedjsouravNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP 22Dokument12 SeitenNCP 22Soumen DharaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamental Rights of An Indian Ciitizen: Meenakshi SharmaDokument14 SeitenFundamental Rights of An Indian Ciitizen: Meenakshi SharmadjsouravNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nicmar - Sode: SsignmentDokument13 SeitenNicmar - Sode: SsignmentdjsouravNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trade Union Act, 1926Dokument9 SeitenTrade Union Act, 1926djsourav100% (1)
- Managerial EconomicsDokument9 SeitenManagerial EconomicsdjsouravNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 Structure and DesignDokument27 SeitenChapter 5 Structure and DesigndjsouravNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manage Organizational Change & ConflictDokument28 SeitenManage Organizational Change & ConflictdjsouravNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diligent Sustainability Professional Seeks New OpportunitiesDokument2 SeitenDiligent Sustainability Professional Seeks New Opportunitiesch MuzammalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Omd 551 Basics of Biomedical InstrumentationDokument24 SeitenOmd 551 Basics of Biomedical Instrumentationkrithikgokul selvamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applied Welding Engineering Lab ReportDokument4 SeitenApplied Welding Engineering Lab ReportIdham DanialNoch keine Bewertungen
- Torsional Irregularity Check ReportDokument1 SeiteTorsional Irregularity Check ReportAC Estructural ProyectosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strip Footing Design CalculationsDokument13 SeitenStrip Footing Design CalculationsSha Mas ShaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 06-2 QCS 2014Dokument25 Seiten06-2 QCS 2014Raja Ahmed Hassan100% (6)
- Transformer Tap Setting in Optimal Load FlowDokument7 SeitenTransformer Tap Setting in Optimal Load FlowjhongeralpeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Provisional List of Degree Engineering Institutes For Year 2020-21Dokument31 SeitenProvisional List of Degree Engineering Institutes For Year 2020-21Rajvi PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nice3000 Manual PDFDokument235 SeitenNice3000 Manual PDFChadwick Chehung100% (7)
- Proceedings CDTNDokument373 SeitenProceedings CDTNQT Trái Tim Của GióNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boiler Drum DesignDokument3 SeitenBoiler Drum Designtsrinivasan508350% (2)
- Value Analysis and Value Engineering: by - Ravishankar K SrescoeDokument31 SeitenValue Analysis and Value Engineering: by - Ravishankar K SrescoeThiru TrishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Support RingDokument13 SeitenSupport RingvamsiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arrancador Monfasico ATS01N106FT SchneiderDokument2 SeitenArrancador Monfasico ATS01N106FT SchneiderJulian Lopez LopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- DiagridsDokument34 SeitenDiagridsChristianFernando100% (1)
- Machinery 6190 Un SeDokument942 SeitenMachinery 6190 Un SeJohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review On Bore Well Pipe Lifting and Transportation Machine Ijariie8295Dokument4 SeitenReview On Bore Well Pipe Lifting and Transportation Machine Ijariie8295KADIRIPURAM ARJUNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Civil Engg Drawing Pract 1 & 2 Materials & FixturesDokument2 SeitenCivil Engg Drawing Pract 1 & 2 Materials & Fixturesmind_mac24302867% (6)
- Faculty List 1Dokument16 SeitenFaculty List 1Maruti LavateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wall Load Calculations - FinalDokument7 SeitenWall Load Calculations - FinalAbhilekh PrasaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ms 1934 Part 3 2007-Methods of Test For Masonry - Part 3 Determination of Initial Shear Strength-850492Dokument19 SeitenMs 1934 Part 3 2007-Methods of Test For Masonry - Part 3 Determination of Initial Shear Strength-850492Bryan EweNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Cover Letter For Internship Software EngineeringDokument8 SeitenSample Cover Letter For Internship Software Engineeringfetditwhf100% (1)
- Pour StripsDokument2 SeitenPour StripsChetan Tolia100% (1)
- Design of Tension MembersDokument30 SeitenDesign of Tension Memberssharer1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Modeling The Behavior of Load Bearing Concrete Walls Under Fire ExposureDokument11 SeitenModeling The Behavior of Load Bearing Concrete Walls Under Fire ExposureNasarKhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Austin ASHRAE Newsletter 2008 - 2011Dokument15 SeitenAustin ASHRAE Newsletter 2008 - 2011Pradeep SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Waterproofing101 GMXDokument27 SeitenWaterproofing101 GMXJatinder BhatiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- App8Dokument7 SeitenApp8César Rodriguez BNoch keine Bewertungen
- C192PF8-RPR 0Dokument75 SeitenC192PF8-RPR 0Rolando Henry Flores CamavilcaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Rubrics for ThermodynamicsDokument16 SeitenAssessment Rubrics for Thermodynamicstaufiqishak09Noch keine Bewertungen