Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
129
Hochgeladen von
KURAKULA VIMAL KUMAROriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
129
Hochgeladen von
KURAKULA VIMAL KUMARCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Thesis Proposal
Reactive Power Market Clearing Scheme
By: Ting Zhang
Supervisor: Dr. B. Venkatesh
23 November 2006
Outline
Introduction
Objective
Problem Statement
Progress to date
Introduction
Reactive power supply plays an important role in the power
system.
In former deregulated power system: supply of real and reactive
power was charged in a composite fashion.
After deregulation of power systems, supply of real power and
ancillary services such as reactive power support have to be
unbundled & priced independently.
Composite
Power
Supply
Real Power Supply
Ancillary Services
including reactive power
supply
Reactive power market is established to trade reactive
power. In this market, there are vendors and customers.
Fig. 2 A schematic representation of a reactive power market
Introduction
Generation
Systems
Transmission
System
Distribution
Systems
Introduction
Elements of the power system that have to be
financially compensated for their participation in the
reactive market :
*Generators
*Shunt reactive elements
*Transformers
Objective
The main objective of reactive power market clearing
scheme in the deregulated power system is to
minimize the total cost of reactive power supply
while benefiting from transmission loss minimization
and maintaining an acceptable voltage profile.
Objective
Cost from Generator:
P
Q
Leading Lagging
If
2
Rf
Ia
2
Ra
Opportunity
Costs
Fig. 3 Reactive power cost components
Opportunity
Costs
A
B
C
Objective
Aggregating these costs, a total cost curve for reactive
power output of a synchronous generator is shown in
Fig. 4 :
Constraints that should be
satisfied:
Fig.4 The i
th
generator reactive power cost curve
1 UG
k
ik
=
QA QB QC
QG
Leading Lagging
QGC
UG
i1
UG
i2
UG
i3
UG
i4
(
s s
(
k
ik ik i
k
ik ik
QG * UG QG QG * UG
Objective
The cost of reactive power generation can be
expressed as below:
( )
=
+
NG
1 i k
ik ik ik i ik
UG * KGo UG * QG * KG
Objective
Cost from Compensators:
Cost of reactive power output from controllable
VAR sources can be expressed in general as:
Fig.5 VAR source reactive power cost curve
( )
=
+
NS
1 i
i i i i
US * KSo KS * QS
QSi
QSCi
KSi
KSoi
Objective
Cost from transformers :
Cost of shifting taps of transformers can be expressed
in general as:
=
NTR
1 i
i i
UT * KTo
Problem Statement
The non-linear mixed integer formulation can be
stated as below:
OBJ =
+
+
+ KL*PL(X , Y, o)
( )
=
+
NG
1 i k
ik ik ik i ik
UG * KGo UG * QG * KG
( )
=
+
NS
1 i
i i i i
US * KSo KS * QS
=
NTR
1 i
i i
UT * KTo
Problem Statement
Subject to:
Control Vector Constraints
Dependent Vector Constraints
Power Flow Constraints
Progress to date
Formulate the mathematical model of a Mixed Integer
LP (MILP) of reactive power optimization in
deregulated system.
Coding of MILP using MATLAB.
Thank you!
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5795)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
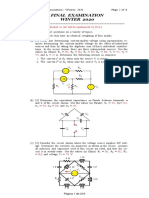
- EHV MId-2 Objective - FinalDokument22 SeitenEHV MId-2 Objective - FinalKURAKULA VIMAL KUMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Restructred Power SystemDokument14 SeitenRestructred Power SystemKURAKULA VIMAL KUMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Axioms 12 00614Dokument24 SeitenAxioms 12 00614KURAKULA VIMAL KUMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fuzzy Logic BookDokument1.004 SeitenFuzzy Logic BookKURAKULA VIMAL KUMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iare - Psoc - Lecture NotesDokument67 SeitenIare - Psoc - Lecture NotesKURAKULA VIMAL KUMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1. Introduction To Power Systems: December 2019Dokument19 SeitenChapter 1. Introduction To Power Systems: December 2019KURAKULA VIMAL KUMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Air-Insulated Substations: Koji KawakitaDokument6 SeitenIntroduction To Air-Insulated Substations: Koji KawakitaKURAKULA VIMAL KUMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grounding and BondingDokument51 SeitenGrounding and BondingKURAKULA VIMAL KUMAR100% (1)
- 2017-2018 ADMITTED BATCH R-17 Regulations: Two Year Course Structure M.TechDokument32 Seiten2017-2018 ADMITTED BATCH R-17 Regulations: Two Year Course Structure M.TechKURAKULA VIMAL KUMARNoch keine Bewertungen
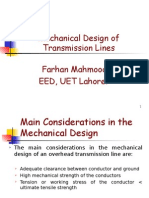
- PTR - (Mech Design) ... Mechanical Design of Transmission LinesDokument50 SeitenPTR - (Mech Design) ... Mechanical Design of Transmission LinesKURAKULA VIMAL KUMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.eligibility Criteria As in APPGECET-2015Dokument3 Seiten2.eligibility Criteria As in APPGECET-2015KURAKULA VIMAL KUMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automatic Recognition of Power Quality Disturbances: Sea LDokument52 SeitenAutomatic Recognition of Power Quality Disturbances: Sea LKURAKULA VIMAL KUMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1091)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- 3.problems SVC - Static Var or SolvedDokument19 Seiten3.problems SVC - Static Var or Solvedgonfree100% (1)
- XQ2000 Auto Paralleling - Quick Start v1.3 PDFDokument15 SeitenXQ2000 Auto Paralleling - Quick Start v1.3 PDFVictor Nunez100% (1)
- IPFC Operating CatalogueDokument20 SeitenIPFC Operating CatalogueSuresh DevarakondaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Variable Active and Reactive Power Control Using Oltc in The Power NetworkDokument10 SeitenVariable Active and Reactive Power Control Using Oltc in The Power NetworkAjay krishnan NilakantanNoch keine Bewertungen
- TTR014 - C6 - Session2018Dokument49 SeitenTTR014 - C6 - Session2018ivaneg825Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pre Lab 6Dokument4 SeitenPre Lab 6Maaz HussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Examenes TodosDokument219 SeitenExamenes TodosNuevo Milenio Centro CopiadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catalogue Mikro - PFC - 2013 PDFDokument29 SeitenCatalogue Mikro - PFC - 2013 PDFAhmad ArpaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial - ProblemsDokument7 SeitenTutorial - ProblemsSHOAIB IQBALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reactive Voltage DroopDokument2 SeitenReactive Voltage Droopwagner_guimarães_1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Protection System in Smart GridDokument55 SeitenProtection System in Smart GridJyoti Raj MahantaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sub Module 3.13 AC THEORYDokument26 SeitenSub Module 3.13 AC THEORYInterogator5Noch keine Bewertungen
- Power System Analysis Question Papers (2021-)Dokument29 SeitenPower System Analysis Question Papers (2021-)Jishnuraj KubandrarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Et 202 (B)Dokument3 SeitenEt 202 (B)murugan_collegemanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operator's Manual: User Interface Alarm List Parameter List Failure Mode and Effect Analysis (FMEA)Dokument70 SeitenOperator's Manual: User Interface Alarm List Parameter List Failure Mode and Effect Analysis (FMEA)Andreas PalalanganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power System Analysis Prof. S.N. Singh Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture - 17Dokument30 SeitenPower System Analysis Prof. S.N. Singh Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture - 17Engr Fahimuddin QureshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- EV、DV100 User's Manual V2.0Dokument64 SeitenEV、DV100 User's Manual V2.0Sang Penggila HujanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Swing Detection Using The Variation Rates of The Average Value of Apparent PowerDokument6 SeitenPower Swing Detection Using The Variation Rates of The Average Value of Apparent PowernemarjeltnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relay SuggestionDokument4 SeitenRelay SuggestionShailesh ChettyNoch keine Bewertungen
- AEC Objective Question and AnswerDokument35 SeitenAEC Objective Question and AnswerGanesan KandasamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is The Cause of Generator Overfluxing and Overcxcitation - QuoraDokument2 SeitenWhat Is The Cause of Generator Overfluxing and Overcxcitation - QuoraCharles RobiansyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Flow AnalysisDokument10 SeitenPower Flow AnalysisYusuf KayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPM D11Dokument82 SeitenSPM D11Jaweria SiddiquiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ebrit Multi Meter With Rs485Dokument10 SeitenEbrit Multi Meter With Rs485PrateekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6: Electrical and Instrumentation FacilitiesDokument47 SeitenChapter 6: Electrical and Instrumentation FacilitiesBhausaheb PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- PW466i Protective Relay Test Set BrochureDokument21 SeitenPW466i Protective Relay Test Set Brochuresunil.limaye3168Noch keine Bewertungen
- Reactive Power Compensation and Harmonic Mitigation in Single-Phase Distribution System Using Multilevel ConverterDokument6 SeitenReactive Power Compensation and Harmonic Mitigation in Single-Phase Distribution System Using Multilevel ConverterIJEACS UKNoch keine Bewertungen
- A9-1&2 SL03,04-Street Lighting Feeder Pillar Detail-A9-1Dokument1 SeiteA9-1&2 SL03,04-Street Lighting Feeder Pillar Detail-A9-1amirul aizadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relay Pqr4n 32Dokument48 SeitenRelay Pqr4n 32Dan Storytime RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 s2.0 S036031992205529X MainDokument18 Seiten1 s2.0 S036031992205529X Maintuangsiong ShuNoch keine Bewertungen