Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Me 132 Report: Casting Processes Modern/ COntemporary
Hochgeladen von
Elvin Jay TesoroOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Me 132 Report: Casting Processes Modern/ COntemporary
Hochgeladen von
Elvin Jay TesoroCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
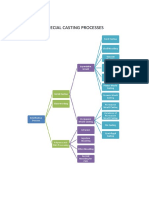
Precision
Casting
Metallic
Mold Casting
Lost Wax Method
Ceramic Shell Process Plaster Molds
Die Casting Low Pressure Casting
Gravity Mold Casting
Slush Casting Pressed Casting
Shell Molding
CO2 mold hardening process Molds of other materials
Centrifugal
Casting
True Centrifugal Semi-centrifugal Centrifuging
Continuous
Casting
Vertical
Curved Horizontal
Inclined
Hot-Chamber Die Casting
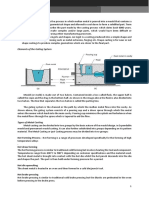
-metal is forced into the mold and pressure is maintained during solidification.
- low melting alloys are generally used in this process.
Cold-Chamber Die Casting
- metal is melted separately unlike in hotchamber die casting.
- high melting alloys are generally used.
Hot-chamber die casting:
Cold-chamber die casting:
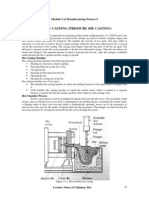
2. Low-pressure permanent-mold casting
- Uses gas pressure to fill the mold.
3. Gravity or permanent mold casting
- Utilizes a permanent mold made of metal or graphite
-Resembles both gravity and the slush casting. -Developed in France by Corthias.
A method of casting parts having axial symmetry Done by pouring the molten metal into a rotating mold. Mold rotation is continued until the metal solidified
Is used to produce hollow castings with a round hole. Characteristic feature is that hole is produced by centrifugal force alone. Mold is rotated about the axis held horizontal, inclined, or vertical. Outside surface of the job may be round, square, etc., as long as it is symmetrical to the whole axis. Speed of rotation should be high enough to hold the metal on to the mold.
Similar to TCC casting, but Only with a difference that a
central core is used to produce
holes. Generally used for articles which are more complicated than those possible in TCS.
Is employed to force metal under pressure into molds of non-symmetrical small castings having intricate details. Metal is poured along the axis of rotation through a central sprue, and made to flow into mold cavities through radial ingates.
Is a process used to cast continuous length of metal, such as in piping or tubing.
1. Molten metal is delivered to the casting equipment. 2. It then flows from a tundish into the mold. 3. The molten metal cools and partially solidifies thru the water-cooled mold. 4. The section is supported and guided below the mold by opposed rollers that contact the cast section. 5. The opposed rollers withdraw the solid cast section to a station where it is cut to desired length.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- GENERAL CHEMISTRY - Q1 - Mod1 - Properties of Matter PDFDokument17 SeitenGENERAL CHEMISTRY - Q1 - Mod1 - Properties of Matter PDFdarmaricric78% (9)
- CH 7-Methods of CastingDokument44 SeitenCH 7-Methods of CastingGosaye DesalegnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Special Casting ProcessesDokument31 SeitenSpecial Casting Processesdarshan_rudraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metal CastingDokument28 SeitenMetal CastingAngel ChanteyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pressure Die CastingDokument62 SeitenPressure Die CastingARUNSFRH83% (6)
- EngineeringDokument208 SeitenEngineeringvins4u100% (1)
- Chapter 17Dokument13 SeitenChapter 17Amit WadhelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foundry and Casting OperationDokument176 SeitenFoundry and Casting OperationABHINAV KUMAR ROY100% (26)
- Surviving Chemistry: A Workbook For High School ChemistryDokument67 SeitenSurviving Chemistry: A Workbook For High School ChemistryE3 Scholastic Publishing100% (7)
- Manufacturing Processes Ch.4 (10 and 11) CastingDokument143 SeitenManufacturing Processes Ch.4 (10 and 11) Castingashoku24007Noch keine Bewertungen
- 8 Centrifugal & Die Casting-2Dokument53 Seiten8 Centrifugal & Die Casting-2Monsieur PoopNoch keine Bewertungen
- DM-1 CO-1 Special Castings MaterialDokument9 SeitenDM-1 CO-1 Special Castings MaterialSree vishnu Sai chandan guntupalliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sheet Metalwork on the Farm - Containing Information on Materials, Soldering, Tools and Methods of Sheet MetalworkVon EverandSheet Metalwork on the Farm - Containing Information on Materials, Soldering, Tools and Methods of Sheet MetalworkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pressure Die CastingDokument62 SeitenPressure Die CastingChetan Nehete100% (2)
- Special CastingDokument46 SeitenSpecial CastingJith Viswa100% (1)
- METALLURGICAL TREATMENT DUCTILE IRONin ProgressDokument78 SeitenMETALLURGICAL TREATMENT DUCTILE IRONin ProgressVishal MaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Report Die CastingDokument12 SeitenLab Report Die CastingaaqibaminNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical Metal Plate Work - With Numerous Engravings and DiagramsVon EverandPractical Metal Plate Work - With Numerous Engravings and DiagramsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Special Casting ProcessDokument9 SeitenSpecial Casting ProcessChaitanya SadhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- AWP Course NotesDokument320 SeitenAWP Course Notesduniaadnan100% (3)
- 1.6.1 Die Casting (Pressure Die Casting) : Module-I of Manufacturing Science-IDokument8 Seiten1.6.1 Die Casting (Pressure Die Casting) : Module-I of Manufacturing Science-IChinmay Das100% (2)
- Enme 331-Fundamentals of CastingDokument48 SeitenEnme 331-Fundamentals of CastingAhmed AbdulrhmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Continuous Casting: Equipment and ProcessDokument8 SeitenContinuous Casting: Equipment and ProcessErickman Simorangkir100% (1)
- Casting TheoryDokument55 SeitenCasting TheorygggNoch keine Bewertungen
- MDSP DatabankDokument24 SeitenMDSP DatabankShapir Binyamin100% (1)
- Unit3 Part C RevisedDokument72 SeitenUnit3 Part C Revisedraymon sharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metal CastingDokument40 SeitenMetal CastingFahmi Sanji AlexanderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forging Operations - Machine Forging, Forging Dies and Special Forging OperationsVon EverandForging Operations - Machine Forging, Forging Dies and Special Forging OperationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of ASTM - Nonferrous Metal Standards and Nonferrous Alloy StandardsDokument12 SeitenList of ASTM - Nonferrous Metal Standards and Nonferrous Alloy StandardspLangpLingpLung100% (2)
- Casting ProcessesDokument42 SeitenCasting ProcessesVijay PawarNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Practical Workshop Companion for Tin, Sheet Iron, and Copper Plate Workers: Containing Rules for Describing Various Kinds of Patterns used by Tin, Sheet Iron, and Copper Plate Workers, Practical Geometry, Mensuration of Surfaces and Solids, Tables of the Weights of Metals, Lead Pipe, Tables of Areas and CircumferencesVon EverandA Practical Workshop Companion for Tin, Sheet Iron, and Copper Plate Workers: Containing Rules for Describing Various Kinds of Patterns used by Tin, Sheet Iron, and Copper Plate Workers, Practical Geometry, Mensuration of Surfaces and Solids, Tables of the Weights of Metals, Lead Pipe, Tables of Areas and CircumferencesNoch keine Bewertungen
- STP1239 Eb.1415051 1 PDFDokument283 SeitenSTP1239 Eb.1415051 1 PDFpaola100% (1)
- Unit-3 - Special Moulding Processes PART-2Dokument25 SeitenUnit-3 - Special Moulding Processes PART-2mahammad kamaluddeenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 4 Contemporary Casting ProcessesDokument47 SeitenTopic 4 Contemporary Casting ProcesseslucasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.14. Multiple-Use-Mould Casting ProcessesDokument3 Seiten2.14. Multiple-Use-Mould Casting Processesaman chaudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Permanent Mold Casting Processes: Usually Made From Metal Gas Pressure or A Vacuum UsedDokument57 SeitenPermanent Mold Casting Processes: Usually Made From Metal Gas Pressure or A Vacuum UsedJacob KussiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Metal Casting: - Overview of Casting Technology - Heating and Pouring - Solidification and CoolingDokument35 SeitenFundamentals of Metal Casting: - Overview of Casting Technology - Heating and Pouring - Solidification and Coolingb0zzch4Noch keine Bewertungen
- Centrifugal CastingDokument18 SeitenCentrifugal CastingArijit PatraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metal Casting ProcessesDokument29 SeitenMetal Casting ProcessesVisvas RajyaguruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 2 Manufacturing ProcessDokument31 SeitenLecture 2 Manufacturing Processكل ما يريده القلبNoch keine Bewertungen
- Centrifugal CastingDokument18 SeitenCentrifugal CastingBhushan Shankar KambleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metal Casting: Compiled By: Norliana Mohd AbbasDokument34 SeitenMetal Casting: Compiled By: Norliana Mohd AbbasAziful AimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Casting FormingDokument40 SeitenCasting FormingA PRATYUSHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Casting, Rolling, Forging, ExtrusionDokument60 SeitenCasting, Rolling, Forging, ExtrusionHARIKRISHNAN SRNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 CastingDokument90 SeitenChapter 4 CastingA TalkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Permanent Mold CastingDokument4 SeitenPermanent Mold CastingcpprodNoch keine Bewertungen
- CC NotesDokument12 SeitenCC Notesr v raoNoch keine Bewertungen
- MP - R18-1.1 Casting2-Spl Casting & Furnaces-190801Dokument12 SeitenMP - R18-1.1 Casting2-Spl Casting & Furnaces-190801Vikranth MadarapuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Centrifugal Casting Process by AakankshaDokument18 SeitenCentrifugal Casting Process by AakankshaAakanksha RamtekeNoch keine Bewertungen
- MODULE 1 - Other Casting ProcessesDokument78 SeitenMODULE 1 - Other Casting ProcessesrishavrajbabaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Special Casting MethodsDokument73 SeitenSpecial Casting Methods359 Srinivasa RamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Continuous Casting ReportDokument9 SeitenContinuous Casting ReportAkriti KumariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metallurgy CH 12 and 13 Lecture NotesDokument6 SeitenMetallurgy CH 12 and 13 Lecture Notesayaan.works76Noch keine Bewertungen
- Material Processing DefectsDokument52 SeitenMaterial Processing DefectsAmeem TariqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slush CastingDokument20 SeitenSlush Castingamt938100% (1)
- Manufacturing Summaries: Expendable Mold and Permanent MoldDokument4 SeitenManufacturing Summaries: Expendable Mold and Permanent MoldSanguinius28Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 5Dokument39 SeitenLec 5Omar AssalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foundry Technology SlidesDokument123 SeitenFoundry Technology SlidesSeth Aboagye JnrNoch keine Bewertungen
- CONTINUOUS CASTING ColloquiumDokument18 SeitenCONTINUOUS CASTING ColloquiumakritiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fabrication of MetalDokument22 SeitenFabrication of MetalaurangzaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Long AnswerDokument3 SeitenLong AnswerVarinder MouryaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Metal Casting: 1. Overview of Casting Technology 2. Heating and Pouring 3. Solidification and CoolingDokument32 SeitenFundamentals of Metal Casting: 1. Overview of Casting Technology 2. Heating and Pouring 3. Solidification and CoolingAkash GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manuf ProcessDokument15 SeitenManuf ProcessKaruppiah ArunachalamNoch keine Bewertungen
- CastingDokument20 SeitenCastingCHANDRAJEET AMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manufacturing Processes Manufacturing Processes ME ME - 222 222Dokument66 SeitenManufacturing Processes Manufacturing Processes ME ME - 222 222shahnawaz875Noch keine Bewertungen
- MP-I-Lecture No. 15-16Dokument27 SeitenMP-I-Lecture No. 15-16Osaid AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME - 32021 Chapter (3) Hard Mold Casting ProcessesDokument26 SeitenME - 32021 Chapter (3) Hard Mold Casting ProcessesWILYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec2 Centrifugal CastingDokument15 SeitenLec2 Centrifugal CastingMuhammad IshaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASTM D 524 Residuo Carbonoso PDFDokument8 SeitenASTM D 524 Residuo Carbonoso PDFMaria BradaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mbb-Gold Process FlowDokument1 SeiteMbb-Gold Process FlowPemburu EmasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tugas B.ing Bab 2 PDFDokument13 SeitenTugas B.ing Bab 2 PDFdimas arifiyantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Is 14688 1999Dokument10 SeitenIs 14688 1999saeedahmad901Noch keine Bewertungen
- Removal of Heavy Metals Using Waste EggshellDokument6 SeitenRemoval of Heavy Metals Using Waste EggshellangelbroderNoch keine Bewertungen
- High Rise Building (Part I) Group 2Dokument39 SeitenHigh Rise Building (Part I) Group 2TAWDE KOMALNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 TH V-I ModifiedDokument151 Seiten12 TH V-I ModifiedAkash VigneshwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2-Inorganic Chemistry Chapter 11 - The Alkali Metals: Chemistry - Grade 10I Lesson 1Dokument3 SeitenUnit 2-Inorganic Chemistry Chapter 11 - The Alkali Metals: Chemistry - Grade 10I Lesson 1Help GloPosNetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tin Plating: Michael CaranoDokument2 SeitenTin Plating: Michael CaranoVaidas JukneviciusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corrosion Inhibition by Various Plant Products at Mild Steel Surfaces in Acidic and Basic MediaDokument4 SeitenCorrosion Inhibition by Various Plant Products at Mild Steel Surfaces in Acidic and Basic MediaEditor IJTSRDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eimn2 Chapter: Marine Engineering MaterialsDokument2 SeitenEimn2 Chapter: Marine Engineering MaterialsenglisgoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASNT Level IIIDokument17 SeitenASNT Level IIIryearly100% (1)
- Orbital Diagrams Valance Electrons Electron Dot StructuresDokument20 SeitenOrbital Diagrams Valance Electrons Electron Dot StructuresKieth ObaobNoch keine Bewertungen
- Petersen mst15Dokument8 SeitenPetersen mst15api-271093465Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Reactivity Series of Metals and Its ApplicationsDokument14 SeitenThe Reactivity Series of Metals and Its ApplicationsSaadiah MohammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Periodic Table Knowledge OrganiserDokument1 SeiteThe Periodic Table Knowledge OrganiserLaundry VendingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Belzona 1321 (Ceramic S-Metal) : Key BenefitsDokument22 SeitenBelzona 1321 (Ceramic S-Metal) : Key BenefitsIrvansyah RazadinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inorganic Chemistry Chem-318 Lec 1Dokument30 SeitenInorganic Chemistry Chem-318 Lec 1Mahnoor ShakeelNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Novel Approach To Updating The Corrosiveness Maps of IndiaDokument9 SeitenA Novel Approach To Updating The Corrosiveness Maps of IndiaNeha KhairwaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIO218 Test 10Dokument5 SeitenBIO218 Test 10Egi SugianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Non Ferrous Metals FinalDokument89 SeitenNon Ferrous Metals FinalAstilbe AlairNoch keine Bewertungen