Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Gprs Presentation
Hochgeladen von
Manojkumar Chowdary MunnangiCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Gprs Presentation
Hochgeladen von
Manojkumar Chowdary MunnangiCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Wireless Networks
Chris Lord (cil103) An Overview of General Packet Radio Service (GPRS)
Based on information from http://www.comsoc.org/livepubs/surveys/public/3q99issue/bettstetter.html
What is GPRS?
Bearer service for GSM Packet-switched Can inter-operate with other packetswitched networks (e.g. IP, X.25) Higher data-rates and lower connection times than conventional GSM
GPRS Integration (1)
Addition of GPRS Support Nodes (GSN) All GSNs connected by IP-based GPRS backbone network
Intra-PLMN (Public Land Mobile Network) Connect GSNs on same network, private IPbased networks of the provider Inter-PLMN Connect GSNs on different PLMNs; requires a roaming agreement to be installed
GPRS Integration (2)
Serving GSN:
Authentication/charging Visited Location Registry (VLR) User profiles Packet delivery between mobile stations and external packet data networks (PDN), e.g. IP, X.25 Authentication/charging
Gateway GSN
GSM Network Interfaces (1)
Gb interface: Connects the BSC with the SGSN Gn/Gp interfaces: Transmits user data and signalling data between GSNs
Gn for transmissions on same PLMN Gp for transmissions on external PLMNs
Gf interface: IMEI queries Gi interface: Connect to external PDNs
GSM Network Interfaces (2)
Gr interface: Exchange of user information between HLR and SGSN Gc interface: Exchange of location information between GGSN and HLR Gs interface: Connects databases of SGSN and MSC/VLR to coordinate between GPRS and conventional GSM networks Gd interface: Connects SGSN with SMS Gateway MSC (SMS-GMSC)
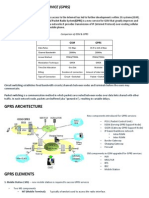
GSM System Architecture
BTS BSC BTS BSC BTS EIR AUC HLR VLR MSC GMSC
GPRS System Architecture
SMS-GMSC SMS-IWMSC BTS BSC BTS
Gb
Other GPRS PLMN
Gd Gp
GGSN
SGSN
Gs Gr
BSC BTS
Gn Gf
EIR
MSC/ VLR
HLR
D
GGSN
Gi
Gc
User/Signalling data Signalling data
PDN
Services
Bearer services for GPRS offer end-to-end packet-switched data transfer. Two types:
Point-to-point (PTP)
Internet access SMS messages Unidirectional distribution of information (e.g. weather, news) Conferencing services between multiple users
Point-to-multipoint (PTM)
Quality of Service (1)
QoS profiles can be defined using parameters derived from service precedence, reliability, delay and throughput. QoS profiles can be negotiated between the mobile user and the network, per session, depending on current resources, and can affect billing
Quality of Service (2)
Three priorities: High, Medium, Low Three reliability classes that guarantee maximum values of loss, duplication, missequencing and corruption of packets Delay defines maximum mean delay and 95-percentile delay Throughput specifies peak and mean bitrate
GPRS and Conventional GSM
GSM/GPRS services can be used in parallel. Three classes of mobile station:
Class A Simultaneous use of GSM and GPRS Class B Can register for both GSM and GPRS, but only use one at a time Class C Can attach for only either GSM or GPRS (with the exception of SMS messages)
Fin
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Ericsson GPRSDokument7 SeitenEricsson GPRSvelayyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EDGEDokument43 SeitenEDGEPramod RaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Packet Radio Service (GPRS)Dokument42 SeitenGeneral Packet Radio Service (GPRS)Santoshkumar ShelkeNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) : Adapted From A Presentation byDokument46 SeitenGeneral Packet Radio Service (GPRS) : Adapted From A Presentation byDamo DharanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gprs Architecture: General Packet Radio Service (GPRS)Dokument6 SeitenGprs Architecture: General Packet Radio Service (GPRS)Vam ArmodiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- E5-E6 - Text - Chapter 11. CM TECHNOLOGY OVERVIEW 4G 5GDokument13 SeitenE5-E6 - Text - Chapter 11. CM TECHNOLOGY OVERVIEW 4G 5Gsumit15sksNoch keine Bewertungen
- E4-E5 - Text - Chapter 2. Migration To Mobile Technologies Upto 5gDokument19 SeitenE4-E5 - Text - Chapter 2. Migration To Mobile Technologies Upto 5gAGM CMS&MNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Packet Radio Service (GPRS)Dokument32 SeitenGeneral Packet Radio Service (GPRS)divyeshchauhan014Noch keine Bewertungen
- Service Excellence. Delivered: Gprs+Umts+Lte IntroDokument45 SeitenService Excellence. Delivered: Gprs+Umts+Lte IntroEmmanuel AduKissieduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gprs SlideDokument52 SeitenGprs SlideBrajendra MohanNoch keine Bewertungen
- WNM Chapter 2 FDokument14 SeitenWNM Chapter 2 Fnavteshdeore19Noch keine Bewertungen
- General Packet Radio ServiceDokument36 SeitenGeneral Packet Radio Servicegenesis619Noch keine Bewertungen
- System Architecture of GPRS: Group R1: Xiong Guangyu Nik A. SallehDokument26 SeitenSystem Architecture of GPRS: Group R1: Xiong Guangyu Nik A. SallehDinesh BabuNoch keine Bewertungen
- GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) : ArchitectureDokument7 SeitenGPRS (General Packet Radio Service) : ArchitectureSrinivas KaratlapelliNoch keine Bewertungen
- The GPRS Network: ContentsDokument13 SeitenThe GPRS Network: ContentsChidhuro OwenNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM To 3G: A Journey of Wireless CommunicationDokument45 SeitenGSM To 3G: A Journey of Wireless Communicationsrshelke100% (1)
- General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) Is ADokument8 SeitenGeneral Packet Radio Service (GPRS) Is AAjay AryaNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Packet Radio Service (GPRS)Dokument44 SeitenGeneral Packet Radio Service (GPRS)Mubassir PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- GprsDokument5 SeitenGprsRavi Ranjan KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- GPRS PresentationDokument133 SeitenGPRS PresentationNagashruthi BalasubramanyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2G/2.5G/3G Architecture: Manu MittalDokument37 Seiten2G/2.5G/3G Architecture: Manu MittalMohit VaishNoch keine Bewertungen
- IPC G Gprs S N: Onnectivity For Ateway Upport ODEDokument10 SeitenIPC G Gprs S N: Onnectivity For Ateway Upport ODEmetootheskullNoch keine Bewertungen
- GPRS PDFDokument6 SeitenGPRS PDFHandy MoseyNoch keine Bewertungen
- GPRS PDFDokument7 SeitenGPRS PDFHandy MoseyNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Packet Radio ServiceDokument21 SeitenGeneral Packet Radio ServiceNeil SidaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To 3G, GSM, GPRS, EDGE NetworkDokument22 SeitenIntroduction To 3G, GSM, GPRS, EDGE NetworkRavi YarrabothuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To 3G, GSM, GPRS, EDGE NetworkDokument22 SeitenIntroduction To 3G, GSM, GPRS, EDGE NetworkBucek BuddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wireless Access GprsDokument11 SeitenWireless Access GprsSara AbNoch keine Bewertungen
- VASDokument50 SeitenVASPrashant BediNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 4Dokument57 SeitenUnit 4Utsav SoniNoch keine Bewertungen
- GPRS Logical ArchitectureDokument4 SeitenGPRS Logical ArchitectureFaran Ul GhaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- GPRS EngDokument286 SeitenGPRS EngMd Zaki AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM P&O Training Material For Skill Certificate-GPRS Basic PrincipleDokument87 SeitenGSM P&O Training Material For Skill Certificate-GPRS Basic PrincipleObaid RaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gujarat Technological University: UNIT: 4 Third Generation CommunicationDokument65 SeitenGujarat Technological University: UNIT: 4 Third Generation CommunicationUtsav SoniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mod1 SlideDokument22 SeitenMod1 Slide2020ecpriyanshnigambNoch keine Bewertungen
- GPRS TutorialDokument25 SeitenGPRS TutorialthankhiepNoch keine Bewertungen
- GPRS Tunneling Protocol GTPDokument57 SeitenGPRS Tunneling Protocol GTPShriraj07Noch keine Bewertungen
- GGSN Pooling Support For Firewalls: Finding Feature InformationDokument18 SeitenGGSN Pooling Support For Firewalls: Finding Feature InformationAhmed Hamed DahmashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mobile Computing: Asoke KDokument45 SeitenMobile Computing: Asoke Ksadhanamca1Noch keine Bewertungen
- General Packet Radio ServicesDokument8 SeitenGeneral Packet Radio ServicesronyiutNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Packet Radio Service (GPRS)Dokument32 SeitenGeneral Packet Radio Service (GPRS)Zatin GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GPRSDokument11 SeitenGPRSZahra ZeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) : Sylvain FIORONI Thierry BOUSSACDokument26 SeitenGeneral Packet Radio Service (GPRS) : Sylvain FIORONI Thierry BOUSSACSarita Vijay Kharia VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM Evolution SummaryDokument37 SeitenGSM Evolution SummarymseelyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agilent Testing GPRS SignallingDokument24 SeitenAgilent Testing GPRS SignallingPrasant KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Performance Evaluation For Integrated High Altitude Platforms-Terrestrial General Packet Radio Service SystemDokument6 SeitenPerformance Evaluation For Integrated High Altitude Platforms-Terrestrial General Packet Radio Service SystemHabib MohammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM/GPRS: Dr. Anil Kumar Intel CorporationDokument53 SeitenGSM/GPRS: Dr. Anil Kumar Intel CorporationIsoQuantic100% (1)
- Studdy.... 1st ReviewDokument2 SeitenStuddy.... 1st ReviewDinesh KrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MC Question Bank SolvedDokument11 SeitenMC Question Bank SolvedSAHIL LADVANoch keine Bewertungen
- SPEED: Theoretical Maximum Speeds of Up To 171.2 Kilobits Per Second (KBPS)Dokument32 SeitenSPEED: Theoretical Maximum Speeds of Up To 171.2 Kilobits Per Second (KBPS)yuben josephNoch keine Bewertungen
- GPRS For 2 Hours TrainingDokument105 SeitenGPRS For 2 Hours Trainingh_hadidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Client-Server Services, Which Enable Access To Data Stored in Databases. The Most Famous Example of ThisDokument26 SeitenClient-Server Services, Which Enable Access To Data Stored in Databases. The Most Famous Example of ThisIman AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- GPRSDokument32 SeitenGPRSSHUBHAM RANKAWAT SVNITNoch keine Bewertungen
- GPRS Basic PrincipleDokument90 SeitenGPRS Basic PrincipleMahim GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mobile Comm Short NoteDokument8 SeitenMobile Comm Short NoteSarthak BhattacharjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Expt: 3G CommunicationDokument10 SeitenExpt: 3G CommunicationSachin RuikarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overview of GPRS and UMTS: Cisco GGSN Release 10.1 Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS Release 12.4 (24) YE3 OL-19936-06Dokument10 SeitenOverview of GPRS and UMTS: Cisco GGSN Release 10.1 Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS Release 12.4 (24) YE3 OL-19936-06Ranjith VemmarathilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chinmaya Vidyalaya, Koramangala Computer Details: S.No Room Details NosDokument1 SeiteChinmaya Vidyalaya, Koramangala Computer Details: S.No Room Details NosManojkumar Chowdary MunnangiNoch keine Bewertungen
- All Computers Details - UpdatedDokument21 SeitenAll Computers Details - UpdatedManojkumar Chowdary MunnangiNoch keine Bewertungen
- C V, K, B - 34 I N D: Hinmaya Idyalaya Oramangala Angalore Ntercom Umbers EtailsDokument2 SeitenC V, K, B - 34 I N D: Hinmaya Idyalaya Oramangala Angalore Ntercom Umbers EtailsManojkumar Chowdary MunnangiNoch keine Bewertungen
- All Old & New Computers Counting DetailsDokument1 SeiteAll Old & New Computers Counting DetailsManojkumar Chowdary MunnangiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wireless Networks: Chris Lord (Cil103) An Overview of General Packet Radio Service (GPRS)Dokument13 SeitenWireless Networks: Chris Lord (Cil103) An Overview of General Packet Radio Service (GPRS)Manojkumar Chowdary MunnangiNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM Mobile Originating Call: Request AccessDokument2 SeitenGSM Mobile Originating Call: Request AccessManojkumar Chowdary MunnangiNoch keine Bewertungen