Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Secondary Metabolites
Hochgeladen von
Jumar CadondonCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Secondary Metabolites
Hochgeladen von
Jumar CadondonCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
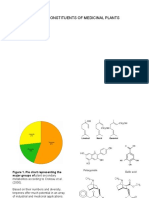
SECONDARY METABOLITES
Jumar G. Cadondon
PHYTOCHEMICALS
chemical compounds that occur naturally in plants (phyto means "plant" in Greek). non-nutritive plant chemicals that have protective or disease preventive properties. are nonessential nutrients.
How do phytochemicals work?
Hormonal action
Isoflavones, found in soy, imitate human estrogens and help to reduce menopausal symptoms and osteoporosis.
Antioxidant
protect our cells against oxidative damage and reduce the risk of developing certain types of cancer. Phytochemicals with antioxidant activity: allyl sulfides (onions, leeks, garlic), carotenoids (fruits, carrots), flavonoids (fruits, vegetables), polyphenols (tea, grapes).
Stimulation of enzymes
Indoles, which are found in cabbages, stimulate enzymes that make the estrogen less effective and could reduce the risk for breast cancer. are protease inhibitors (soy and beans), terpenes (citrus fruits and cherries)
Interference with DNA replication
Saponins found in beans interfere with the replication of cell DNA, thereby preventing the multiplication of cancer cells. Capsaicin, found in hot peppers, protects DNA from carcinogens.
Anti-bacterial effect
Destroy or inhibit the bacteria.
Physical action
bind physically to cell walls thereby preventing the adhesion of pathogens to human cell walls. Proanthocyanidins are responsible for the antiadhesion properties of cranberry. Consumption of cranberries will reduce the risk of urinary tract infections and will improve dental health.
FLAVONOIDS
plant pigments for flower coloration producing yellow or red/blue pigmentation in petals. protect plants from attacks by microbes, fungi and insects. Flavonols (queratin) helps in modulating healh health effects in animals. low toxicity modify allergens, viruses, and carcinogens. potential to be biological "response modifiers"
Health Benefits of Flavonoids
Anti-allergic Anti-inflammatory Anti-microbial (Anti-bacterial, Anti-fungal, Antiviral) Anti-cancer Anti-diarrhea Anti-oxidant
Other Potential Health Benefits
Cancer
Physiological
processing of unwanted flavonoid compounds induces so-called Phase II enzymes that also help to eliminate mutagens and carcinogens, and therefore may be of value in cancer prevention.
like rutin, monoxerutin, diosmin, troxerutin and hidrosmin have potential vasoprotective proprieties
Capillary stabilizing agents
Bioflavonoids
SAPONINS
are glucosides with foaming characteristics. consist of a polycyclic aglycones attached to one or more sugar side chains.
The aglycone part, which is also called sapogenin, is either steroid (C27) or a triterpene (C30).
The foaming ability of saponins is caused by the combination of a hydrophobic (fat-soluble) sapogenin and a hydrophilic (water-soluble) sugar part. have a bitter taste. are toxic and are known as sapotoxin.
Health Benefits of Saponins
Reduce cancer risk
antitumor and anti-mutagenic activities and canlower the risk of human cancers, by preventing cancer cells from growing.
react
with the cholesterol rich membranes of cancer cells, thereby limiting their growth and viability.
help to prevent colon cancer. can cause apoptosis of leukemia cells by inducing mitotic arrest.
Cholesterol reduction
bind with bile salt and cholesterol in the intestinal tract.
Bile
salts form small micelles with cholesterol facilitating its absorption.
cause a reduction of blood cholesterol by preventing its re-absorption.
Immunity booster
fight infections by parasites. help our immune system and to protect against viruses and bacteria.
Reduce bone loss
steroidal saponins
have
a protective role on bone loss.
Antioxidant
non-sugar part of saponins have also a direct antioxidant acitivity
reduced risk of cancer and heart diseases.
ALKALOIDS
compounds containing nitrogen in a heterocyclic ring that are common to about 15 to 20% of all vascular plants. are synthesized by plants from amino acids. bitter taste. Toxicity
help
to repel insects and herbivores.
Health Benefits of Alkaloids
ALKALOID ACTION
Ajmaline
Atropine, scopolamine,hyoscyamine Caffeine
Antiarrhythmic
Anticholinergic Stimulant, diuretic, Adenosine receptor antagonist
Codeine
Colchicine Emetine Ergot alkaloids Morphine Nicotine
Cough medicine, analgesic
Remedy for gout Antiprotozoal agent Sympathomimetic, vasodilator, antihypertensive Analgesic Stimulant, diuretic, Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor antagonist
Health Benefits of Alkaloids (cont.)
ALKALOID Physostigmine Quinidine Quinine Reserpine Tubocurarine Vinblastine, vincristine Vincamine Yohimbine Antiarrhythmic Antipyretics, Antimalarial Antihypertensive Muscle relaxant Antitumor Vasolidating, antihypertensive Stimulant, Aphrodisiac ACTION Inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase
TANNINS
is an astringent, bitter plant polyphenolic compound binds to and precipitates proteins and various other organic compounds including amino acids and alkaloids.
Health Benefits of Tannins
Antiviral Antibacterial Antiparasitic Anti inflammatory Anti ulcer Antioxidant
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Lactone Glycosides: Pharm. D Chemical Pharmacognosy-I May 11, 2011Dokument12 SeitenLactone Glycosides: Pharm. D Chemical Pharmacognosy-I May 11, 2011ahsanonweb1983Noch keine Bewertungen
- Milk Thistle Extract PreparationDokument13 SeitenMilk Thistle Extract PreparationSinisa KusnjirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chilli CommodityDokument9 SeitenChilli CommoditySandeep LoluguNoch keine Bewertungen
- Share Resin and Resin CombinationsDokument74 SeitenShare Resin and Resin CombinationsItz Hamza100% (1)
- Flavon OidsDokument25 SeitenFlavon OidsalexpharmNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOSYNTHESIS AND ROLES OF FLAVONOIDSDokument43 SeitenBIOSYNTHESIS AND ROLES OF FLAVONOIDSpvrajivicas100% (1)
- Spectrophotometric Determination of Saponins in Antidiabetic Plant Extracts. Natalie Rivera. Mentor (A) : Jannette GavillánDokument24 SeitenSpectrophotometric Determination of Saponins in Antidiabetic Plant Extracts. Natalie Rivera. Mentor (A) : Jannette GavillánPrograma BRICNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem. of Secondary Metabolites PDFDokument62 SeitenChem. of Secondary Metabolites PDFJaimeCrispinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 23 Anthraquinone Glycosides - IIIDokument27 SeitenLecture 23 Anthraquinone Glycosides - IIIahsanonweb1983Noch keine Bewertungen
- QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE ESTIMATION OF TOTAL PHENOLICS AND TOTAL FLAVONOIDS IN LEAVES EXTRACT OF SARACA ASOCA (Roxb) .Dokument6 SeitenQUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE ESTIMATION OF TOTAL PHENOLICS AND TOTAL FLAVONOIDS IN LEAVES EXTRACT OF SARACA ASOCA (Roxb) .Baru Chandrasekhar RaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phytochemical Screening and Antioxidant Property of Chili PepperDokument31 SeitenPhytochemical Screening and Antioxidant Property of Chili PepperJeemCarloFagelaPulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essential Oil Components ChromatogramDokument3 SeitenEssential Oil Components ChromatogramMulayam Singh YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Herbal Protein ExtractionDokument33 SeitenHerbal Protein ExtractionSanjay PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Determination of the Total Phenolic Contents of Essential Oil Obtained From Cymbopogon Citratus (Lemongrass) and Persea Americana Mill (Avocado Pear Seed) and Its Bioactive Component Using Gc-Ms AnalysisDokument12 SeitenDetermination of the Total Phenolic Contents of Essential Oil Obtained From Cymbopogon Citratus (Lemongrass) and Persea Americana Mill (Avocado Pear Seed) and Its Bioactive Component Using Gc-Ms AnalysisInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aloe VeraDokument26 SeitenAloe VerasallettNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crude DrugsDokument10 SeitenCrude DrugsRahul Malik100% (2)
- Determination of Total Phenol, Flavonoid and Antioxidant ActivityDokument4 SeitenDetermination of Total Phenol, Flavonoid and Antioxidant ActivityFabi RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medicinal Plant Chemical ConstituentsDokument68 SeitenMedicinal Plant Chemical Constituentsjayaprina100% (1)
- Lecture 31 - Hydrolysable Tannins (Compatibility Mode)Dokument23 SeitenLecture 31 - Hydrolysable Tannins (Compatibility Mode)ahsanonweb1983Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rosmarinus Officinalis Essential Oil - A Review of Its Phytochemistry, Anti-Inflammatory Activity, and Mechanisms of Action InvolvedDokument17 SeitenRosmarinus Officinalis Essential Oil - A Review of Its Phytochemistry, Anti-Inflammatory Activity, and Mechanisms of Action InvolvedCarolina Rodriguez100% (1)
- Fatty Acid Profile of Spirulina Platensis Grown in Different Culture ConditionsDokument30 SeitenFatty Acid Profile of Spirulina Platensis Grown in Different Culture ConditionsFrankAyranNoch keine Bewertungen
- TanninsDokument39 SeitenTanninsUmama WarrichNoch keine Bewertungen
- IridoidsDokument18 SeitenIridoidspraneethasruthiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acidic PesticidesDokument15 SeitenAcidic PesticidesnikparisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 Flavonoids: Prof. Jian-Guang LuoDokument34 SeitenChapter 5 Flavonoids: Prof. Jian-Guang LuoChic Afro100% (2)
- Bearberry - Liquid Herbal Extract (Cosmetic Grade) Msds Rd28!05!2013Dokument11 SeitenBearberry - Liquid Herbal Extract (Cosmetic Grade) Msds Rd28!05!2013Meidita Aulia DanusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bioactivity Guided Isolation and Characterization of Anti-Cancer Compounds From The Stem of Musanga CecropioidesDokument5 SeitenBioactivity Guided Isolation and Characterization of Anti-Cancer Compounds From The Stem of Musanga CecropioidesT. A OwolabiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essential Oils in Foods Extraction, Stabilization, and ToxicityDokument7 SeitenEssential Oils in Foods Extraction, Stabilization, and ToxicityNajihah RamliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacognosy Lecture # 7+8 (Lipids) (By, Sir Tanveer Khan)Dokument40 SeitenPharmacognosy Lecture # 7+8 (Lipids) (By, Sir Tanveer Khan)Arslan AbdullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coumarin PDFDokument32 SeitenCoumarin PDFAulia PermataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Centella AsiaticaDokument4 SeitenCentella AsiaticahazeleyezNoch keine Bewertungen
- TanninsDokument13 SeitenTanninsharishkumar kakrani50% (2)
- Secondary Metabolites of Fungi PDFDokument19 SeitenSecondary Metabolites of Fungi PDFsatriomega100% (1)
- Lecture 21 - 23 Anthraquinone GlycosidesDokument119 SeitenLecture 21 - 23 Anthraquinone Glycosidesahsanonweb1983100% (2)
- Red Chilli PowderDokument2 SeitenRed Chilli PowderRohan MaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Implication of Pure Food Act of BDDokument50 SeitenImplication of Pure Food Act of BDNadeem Nafis100% (2)
- Lab IpmDokument9 SeitenLab IpmAmir DzarifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antioxidant 2018Dokument78 SeitenAntioxidant 2018Anum Faheem100% (1)
- Pharmacognosy Assignment 2Dokument13 SeitenPharmacognosy Assignment 2Saud AlamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Extraction and Characterization of Guava Seed Oil - A Novel Industrial ByproducDokument9 SeitenExtraction and Characterization of Guava Seed Oil - A Novel Industrial ByproducDevita AmeliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chess Insecticide MsdsDokument7 SeitenChess Insecticide MsdsssangachonuerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quality Control of Herbal Medicines and Related AreasDokument292 SeitenQuality Control of Herbal Medicines and Related AreasHarrizul RivaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Natural Enzymes and ProteinDokument11 SeitenNatural Enzymes and ProteinTria Risma100% (1)
- Effect of Spirulina (Spirulina Platensis) On Growth Performance and Haemato-Biochemical Parameters of Osmanabadi KidsDokument4 SeitenEffect of Spirulina (Spirulina Platensis) On Growth Performance and Haemato-Biochemical Parameters of Osmanabadi KidsGAJANAN JADHAVNoch keine Bewertungen
- A To Z of Enzyme TechnologyDokument303 SeitenA To Z of Enzyme TechnologyJake PoppeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adulteration in Food Is Normally Present in Its Most Crude FormDokument18 SeitenAdulteration in Food Is Normally Present in Its Most Crude Formapi-3874444100% (2)
- The Spices and Herbs Market in The Eu 2009Dokument49 SeitenThe Spices and Herbs Market in The Eu 2009Vlad KitaynikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Your Protein Not Soluble? Silica Manufacturer 3D Images of ProteinsDokument10 SeitenYour Protein Not Soluble? Silica Manufacturer 3D Images of ProteinsSanthosh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Extraction 2018Dokument7 SeitenExtraction 2018VARsha kumariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formulation and Evaluation Herbal SyrupDokument6 SeitenFormulation and Evaluation Herbal SyrupNitaParkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animal Feed Supplements, Veterinary Product Producers, Natural Veterinary Products - Arosol ChemicalsDokument30 SeitenAnimal Feed Supplements, Veterinary Product Producers, Natural Veterinary Products - Arosol ChemicalsalphafactsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synonyms-Part Used - Habitat - Chemical Tests: AsafoetidaDokument1 SeiteSynonyms-Part Used - Habitat - Chemical Tests: Asafoetidacyper zoonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quantitative Analysis of Tannins in Plant Extracts Used As Diabetes Adjuvant. Wanda Figueroa. Mentor (A) : Jannette GavillánDokument20 SeitenQuantitative Analysis of Tannins in Plant Extracts Used As Diabetes Adjuvant. Wanda Figueroa. Mentor (A) : Jannette GavillánPrograma BRICNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phytochemical Screening of Coriander Sativum LinnDokument5 SeitenPhytochemical Screening of Coriander Sativum LinnMusfira Dewy SuardiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alkaloid 2Dokument6 SeitenAlkaloid 2Yenni Daen MadikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Total Phenolic Content ProtocolDokument1 SeiteTotal Phenolic Content ProtocolNor ShafiqahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Status of Neem in SenegalDokument10 SeitenStatus of Neem in SenegalVignesh MurthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHENOLIC, FLAVONOID AND DPPH RADICAL SCAVENGING ACTIVITYDokument3 SeitenPHENOLIC, FLAVONOID AND DPPH RADICAL SCAVENGING ACTIVITYHana NurvitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medicinal and Environmental Chemistry: Experimental Advances and Simulations (Part I)Von EverandMedicinal and Environmental Chemistry: Experimental Advances and Simulations (Part I)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Agricultural Benefits of Postharvest Banana PlantsVon EverandAgricultural Benefits of Postharvest Banana PlantsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Griddatareport-Surfer Uas AmdalDokument7 SeitenGriddatareport-Surfer Uas AmdalAnonymous NiipvsufNoch keine Bewertungen
- GridDataReport TangkilingDokument11 SeitenGridDataReport Tangkilingtulus_tp11Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sensors 19 00569 PDFDokument13 SeitenSensors 19 00569 PDFJumar CadondonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity No 1: Mapping Equipotential Lines and Magnetic Field LinesDokument15 SeitenActivity No 1: Mapping Equipotential Lines and Magnetic Field LinesJumar CadondonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problems (Relativity of Time)Dokument13 SeitenProblems (Relativity of Time)Jumar CadondonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science and TechnologyDokument8 SeitenScience and TechnologyJumar CadondonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetic ForcesDokument1 SeiteMagnetic ForcesJumar CadondonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problemas Resueltos Del Reichl - TMPDokument141 SeitenProblemas Resueltos Del Reichl - TMPLuis Alberto Aliaga VásquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics LabDokument12 SeitenPhysics LabJumar CadondonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Set (Series-Parallel Connections)Dokument3 SeitenProblem Set (Series-Parallel Connections)Jumar CadondonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spherical Harmonics: LM L L LM L LM M LM LDokument10 SeitenSpherical Harmonics: LM L L LM L LM M LM LJumar CadondonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q Miii NotesDokument63 SeitenQ Miii NotesJumar CadondonNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Phillip C. Wankat) Instructor's Solution ManualDokument478 Seiten(Phillip C. Wankat) Instructor's Solution ManualFranco Gates90% (39)
- Thin Lenses Physics ProblemsDokument1 SeiteThin Lenses Physics ProblemsJumar CadondonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nature and Propagation of LightDokument1 SeiteNature and Propagation of LightJumar Cadondon0% (1)
- Electricity Word ProblemsDokument1 SeiteElectricity Word ProblemsJumar CadondonNoch keine Bewertungen
- InterferenceDokument1 SeiteInterferenceJumar CadondonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Set On OpticsDokument1 SeiteProblem Set On OpticsJumar CadondonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric PotentialDokument7 SeitenElectric PotentialJumar CadondonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liquid-Liquid Extraction ExamplesDokument31 SeitenLiquid-Liquid Extraction ExamplesJeffersonPalaciosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Free Boundless Lecture Slides on MagnetismDokument31 SeitenFree Boundless Lecture Slides on MagnetismJumar Cadondon100% (1)
- Gas Absorption Problem Set 2016Dokument2 SeitenGas Absorption Problem Set 2016Jumar CadondonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final ExamDokument1 SeiteFinal ExamJumar CadondonNoch keine Bewertungen
- MagnetismDokument27 SeitenMagnetismJumar CadondonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 21 Lecture Outline - ppt52Dokument64 Seiten21 Lecture Outline - ppt52Jumar CadondonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1Dokument33 SeitenChapter 1Jumar CadondonNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHY102 TU Labmanual CapacitorDokument3 SeitenPHY102 TU Labmanual CapacitorJumar CadondonNoch keine Bewertungen
- DM General Surgery CurriculumDokument45 SeitenDM General Surgery CurriculumGiovanni HenryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gerry Vassilatos Lost Science Complete EditionDokument258 SeitenGerry Vassilatos Lost Science Complete EditionAnthony CaldasNoch keine Bewertungen
- JURNAL THT Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma 2 INGGRISDokument13 SeitenJURNAL THT Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma 2 INGGRISwidyalimNoch keine Bewertungen
- PAEDIATRIC HANDBOOK GUIDE FOR COMMON ILLNESSESDokument10 SeitenPAEDIATRIC HANDBOOK GUIDE FOR COMMON ILLNESSESAbdullah Al - JubairNoch keine Bewertungen
- Well Baby Screening - Educational ProgramDokument42 SeitenWell Baby Screening - Educational ProgramShwethaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiac MedicationsDokument8 SeitenCardiac Medicationsangeline totaram100% (2)
- Rabipur - (EMC) Print FriendlyDokument8 SeitenRabipur - (EMC) Print Friendlyshreyas_chandor3802Noch keine Bewertungen
- Haemodynamic MonitoringDokument128 SeitenHaemodynamic MonitoringDr. KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analgesia en Dolor Ciático Agudo Con La Cauterización Del Punto Ciático AuricularDokument68 SeitenAnalgesia en Dolor Ciático Agudo Con La Cauterización Del Punto Ciático Auricularsoyunchingon1100% (1)
- VRTS114 Final Exam-1Dokument2 SeitenVRTS114 Final Exam-1ivy bernalNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Hiv/Aids?: Human Immunodeficiency Virus (Hiv)Dokument2 SeitenWhat Is Hiv/Aids?: Human Immunodeficiency Virus (Hiv)Rockie Geronda EsmaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 Vs 14days Gram Negative SepsisDokument8 Seiten7 Vs 14days Gram Negative SepsisPavan KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- November 2, 2012 Strathmore TimesDokument32 SeitenNovember 2, 2012 Strathmore TimesStrathmore TimesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ave Lox TabsDokument5 SeitenAve Lox Tabslrdn_ghrcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular EmergenciesDokument2 SeitenCardiovascular EmergenciesAli AbdullahiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASD Overview: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and TreatmentDokument22 SeitenASD Overview: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and TreatmentHendri SaputraNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Disciples of Christ Congo Mission in the 1930sDokument20 SeitenThe Disciples of Christ Congo Mission in the 1930sHervé DisadidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- KAP Anthrax and Animal Care A Case-Control StudyDokument11 SeitenKAP Anthrax and Animal Care A Case-Control StudyAsmi AsmuNoch keine Bewertungen
- The effects of tobacco use on oral healthDokument8 SeitenThe effects of tobacco use on oral healthRivandy HolilNoch keine Bewertungen
- First Aid NotesDokument6 SeitenFirst Aid NotesDivya DhashiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stem Cell: Understanding ofDokument31 SeitenStem Cell: Understanding ofelok dyah pitalokaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument5 SeitenNotes Anatomy and PhysiologyEllah MaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chickpea: Vulgaris) and Dry Peas (Pisum Sativum L.) - Chickpea Seeds Contain On Average 18-22% ProteinDokument7 SeitenChickpea: Vulgaris) and Dry Peas (Pisum Sativum L.) - Chickpea Seeds Contain On Average 18-22% ProteinGanpat Lal SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effectiveness of Garlic (Allium Sativum) As Antimicrobial Agent Against Bacteria Causing Urinary Tract InfectionDokument4 SeitenEffectiveness of Garlic (Allium Sativum) As Antimicrobial Agent Against Bacteria Causing Urinary Tract InfectionSabrina JonesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lipids MetabolismDokument11 SeitenLipids MetabolismfakhribabikerNoch keine Bewertungen
- BQ - Medical Writing Assignment-1Dokument1 SeiteBQ - Medical Writing Assignment-1Sumeet GurnaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nakshatra DhanishtaDokument7 SeitenNakshatra DhanishtaANTHONY WRITER100% (3)
- CogwheelDokument4 SeitenCogwheelRimsha RanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Update on Lower Lid Blepharoplasty TechniquesDokument23 SeitenUpdate on Lower Lid Blepharoplasty TechniquesNur baitiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Critical Events in the COVID-19 Timeline in the PhilippinesDokument3 SeitenCritical Events in the COVID-19 Timeline in the PhilippinesChris Wilfred Estrada100% (5)