Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Dual Converter
Hochgeladen von
Udayakumar VengatesanCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Dual Converter
Hochgeladen von
Udayakumar VengatesanCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Udayakumar
M.Tech PED
SMVEC
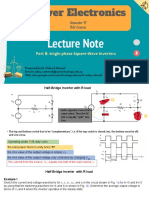
DUAL CONVERTER:
If two single phase full converters are connected in parallel
and in opposite direction (connected in back to back) across
a common load four quadrant operation is possible. Such a
converter is called as a dual converter
A Dual converter can operate in four quadrants and both
the output voltage & current can be either positive or
negative.
Dual converters are normally used in high power
variable speed drives.
If
1
&
2
are the delay angles of converters 1 & 2
respectively, the corresponding average output voltages
are V
d c
1 & V
d c
2.
The delay angles are controlled such that one converter
operates as a rectifier and the other one converter
operates as an Inverter, but both converters produce the
same average output voltage.
Waveform
Four Quadrant Operation
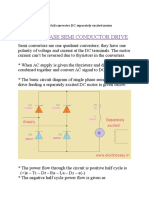
Non-circulating current mode(NCC)
Operation of NCC
only one converter is switched on at a time
converter 1 is switched ON, average output voltage
across the load, which can be varied by adjusting the
trigger angle
If
1
is less than 90
0
, the converter 1 operates as a
controlled rectifier,V
dc
and I
dc
are both positive so
Power is positive.(Source to Load)
When
1
is >90
0
converter 1 operates as a line
commutated inverter
So O/p V
dc
becomes negative so Power is
negative(Load to Source)
The converter 2 is switched ON after a small delay of
about 10 to 20 mS to allow all the thyristors of
converter 1 to turn OFF completely
2
is < 90
o
so Convt-2 act as Rectifier, V
dc
, I
dc
both are
negative , P
dc
=Positive(source-load)
When
2
is >90
0
converter 2 operates as a line
commutated inverter
So O/p V
dc
becomes Positive so Power is negative(Load
to Source)
The converter 1 is switched ON after a small delay of
about 10 to 20 mS to allow all the thyristors of
converter 2 to turn off completely
ADVANTAGE:
There is no circulating current flowing between the two
converters
No need of the series current limiting inductors
The current rating of thyristors is low in this mode
DISADVANTAGE:
Transfer characteristic becomes non linear.
The control circuit becomes complex and the output
response is slow
output dynamic response is poor
Circulating current mode(CC)
Operation of CC
Both the converters 1 and 2 are switched on and operated
simultaneously
If converter 1 is operated as a rectifier by adjusting
1
between 0 to 90
0
the converter 2 is operated as a line
commutated inverter by increasing its
2
is above 90
0
If
1
is 30
2
is 150 (
2
= -
1
)
Conv-1 feed positive power (Source to Load)
Conv-2 feeds negative power (Load to Source)
mode a current builds up between the two converters
even when the load current falls to zero.
THE AVERAGE OUTPUT VOLTAGE
V d c 1 = (2 V m / ) cos 1
V d c 2 = (2 V m / ) cos 2
Since one converter is rectifying & the other one is Inverting, so
that;
V d c 1 = V d c 2
(or) cos 1 = cos 2
cos 1 = cos ( 1)
Therefore; 2 = ( 1)
Since the instantaneous voltages of the two converters are out of
phase, there will be an instantaneous voltage difference and this
will result in circulating current between the two converters . this
circulating current will not flow through the load & is normally
limited by a circulating current Reactor L
ADVANTAGE:
faster reversal of load current
improves the dynamic response of the output
output voltage ,load current can be linearly varied
Transfer characteristic(V
o
/firing angle) is linear and hence
the output response is very fast
The load current is free to flow in either direction,reversal
of the load current can be faster and smoother.
DISADVANTAGE:
Power loss,decrease in efficiency due to series Inductor
limiting series inductors are heavier ,bulkier, So cost and
weight Increases.
Instantaneous Circulating Current value
( )
( )
( )
1
1 2
2
1
. ;
t
r r r O O
r
i v d t v v v
L
e
t o
e
e
(
= = (
(
}
( )
1 1
sin for 2 to
O m
v V t t e t o e =
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
1 1
2 2
sin . sin .
t t
m
r
r
V
i t d t t d t
L
e e
t o t o
e e e e
e
(
= (
(
} }
( )
( )
( )
( )
1 1
2 2
cos cos
t t
m
r
r
V
i t t
L
e e
t o t o
e e
e
(
= +
(
(
( )
1
2
cos cos
m
r
r
V
i t
L
e o
e
=
The instantaneous value of the circulating current depends
on the delay angle.For trigger angle (delay angle) o
1
= 0, its
magnitude becomes minimum when
and magnitude becomes maximum when
If the peak load current is I
p
, one of the converters that
controls the power flow may carry a peak current of
4
m
p
r
V
I
L e
+ ,
( ) ( ) max max
4
, &
m m
p L r
L r
V V
I I i
R L e
= = =
, 1, 3, 5,.... t n n e t = =
, 0, 2, 4,.... t n n e t = =
Thank You . . .
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 18EE53 MODULE 4-Dual ConvertorDokument8 Seiten18EE53 MODULE 4-Dual ConvertorAshwiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 InvertersDokument136 Seiten10 InverterszapzahtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Controlled Rectifier Single Phase Full WaveDokument7 SeitenControlled Rectifier Single Phase Full WaveJesus BecerraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Electronics Lab Manual-withoutreadingsandprepostlab-EE0314Dokument69 SeitenPower Electronics Lab Manual-withoutreadingsandprepostlab-EE0314Sankaran Nampoothiri KrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MSC Rectifier CorrectedDokument53 SeitenMSC Rectifier CorrectedashammoudaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Single Phase Half Wave Controlled RectifierpdfDokument14 SeitenSingle Phase Half Wave Controlled RectifierpdfRîtzî Saxena92% (37)
- FALLSEM2012-13 CP0991 03-Aug-2012 RM01Dokument4 SeitenFALLSEM2012-13 CP0991 03-Aug-2012 RM01Ankit BhattNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 CycloconvertersDokument16 Seiten12 CycloconvertersAbdallah LotfyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Single Phase Semi Converter With R, RL Loads For Continuous Conduction ModesDokument5 SeitenSingle Phase Semi Converter With R, RL Loads For Continuous Conduction ModesSankar KaruppaiahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 3 LynchDokument26 SeitenTopic 3 Lynchsunil251Noch keine Bewertungen
- Single Transistor 12V To 230V InverterDokument7 SeitenSingle Transistor 12V To 230V Inverteryr48Noch keine Bewertungen
- Boost Converter PrinciplesDokument7 SeitenBoost Converter PrinciplesAhmed ArfaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Push Pull ConverterDokument2 SeitenThe Push Pull ConverterNader Asgar Pangarungan MamarobaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Single transistor circuit converts 12V DC to 230V ACDokument7 SeitenSingle transistor circuit converts 12V DC to 230V ACyr48Noch keine Bewertungen
- Advantages of Matrix Over CycloconvertersDokument46 SeitenAdvantages of Matrix Over CycloconvertersnazaahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3Dokument23 SeitenUnit 3Prema ElizabethNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment - 1 Single Phase Semi Controlled Converter With R and RL LoadDokument4 SeitenExperiment - 1 Single Phase Semi Controlled Converter With R and RL LoadKarthik KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Controlled Rectifiers and AC Voltage ControllersDokument35 SeitenControlled Rectifiers and AC Voltage ControllersAishwaryaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Variable DC Power Using Full Bridge ConverterDokument6 SeitenVariable DC Power Using Full Bridge Convertergoten10daNoch keine Bewertungen
- Controlled RectifiersDokument16 SeitenControlled RectifiersVishal Parekh100% (2)
- 5 - AC-AC Converters (Compatibility Mode)Dokument32 Seiten5 - AC-AC Converters (Compatibility Mode)OmkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Line or Naturally Commutated ConvertersDokument32 SeitenLine or Naturally Commutated ConvertersMichael Adu-boahenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tan Kien Hau (01Dem16F1004) ONG KANG WEI (01DEM16F1006) Lee Zhi Shern (01Dem16F1038) Zulhilmi (01Dem16F1007)Dokument18 SeitenTan Kien Hau (01Dem16F1004) ONG KANG WEI (01DEM16F1006) Lee Zhi Shern (01Dem16F1038) Zulhilmi (01Dem16F1007)Eden HazardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hafta1.compressedDokument28 SeitenHafta1.compressedSersio BordiosNoch keine Bewertungen
- AC-DC Converter - Single PhaseDokument16 SeitenAC-DC Converter - Single Phasebishnu prasad muniNoch keine Bewertungen
- L3. Single Phase Ac Voltage ControllersDokument68 SeitenL3. Single Phase Ac Voltage ControllersSourabh KhandelwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Single Phase Midpoint Controlled Rectifier SetupDokument3 SeitenSingle Phase Midpoint Controlled Rectifier Setupshameem v.pNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ac Fundamnetals ManualDokument12 SeitenAc Fundamnetals ManualRaj Mehra MeharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Electronics 1: ENEL371S2Dokument30 SeitenPower Electronics 1: ENEL371S2bpd21Noch keine Bewertungen
- PEI Mod2@AzDOCUMENTS - inDokument68 SeitenPEI Mod2@AzDOCUMENTS - inINDIAN LEGENDSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 4 InvertersDokument86 SeitenUnit 4 InvertersHaritha RkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Single Phase RectifiersDokument11 SeitenSingle Phase RectifiersMiguel MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simulation of Single Phase Full Bridge Converter Using LTspiceDokument9 SeitenSimulation of Single Phase Full Bridge Converter Using LTspicegoten10daNoch keine Bewertungen
- L11 Single Phase Half Controlled Bridge ConverterDokument19 SeitenL11 Single Phase Half Controlled Bridge Converterapi-19951707Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 2B - Single-Phase Square-Wave InvertersDokument41 SeitenLecture 2B - Single-Phase Square-Wave Invertersسجاد عباسNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question BankDokument11 SeitenQuestion BankRohini MukunthanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dr. Tejas N. Zaveri Pro. Rashmi K. PatelDokument17 SeitenDr. Tejas N. Zaveri Pro. Rashmi K. PatelKaustubh UradeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dual Transistor Multivariate Circuit.Dokument3 SeitenDual Transistor Multivariate Circuit.sbpatel123Noch keine Bewertungen
- DUAL CONVERTER GUIDEDokument16 SeitenDUAL CONVERTER GUIDERavinandan PathakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wound-Field Synchronous Machine DrivesDokument62 SeitenWound-Field Synchronous Machine DrivesKorlpate BhaskarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dual converters provide four-quadrant operationDokument9 SeitenDual converters provide four-quadrant operationJackson MtongaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp. 5 - Terminal Characteristis and Parallel Operation of Single Phase Transformers.Dokument7 SeitenExp. 5 - Terminal Characteristis and Parallel Operation of Single Phase Transformers.AbhishEk SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 - Ac To Ac ConverterDokument43 SeitenChapter 5 - Ac To Ac Converterapolloroka100% (1)
- The Buck ConverterDokument6 SeitenThe Buck ConverterjiggywiggyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aim - Theory - : Multivibrator Has Automatic Built in Triggering Which Switches It Continuously Between ItsDokument6 SeitenAim - Theory - : Multivibrator Has Automatic Built in Triggering Which Switches It Continuously Between ItsShahrukh PinjariNoch keine Bewertungen
- S6 PE Lab Manual 2018 MATLAB PDFDokument27 SeitenS6 PE Lab Manual 2018 MATLAB PDFhariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Electronics 1-2015bjrDokument80 SeitenPower Electronics 1-2015bjrNurAdiFirawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dual ConvertersDokument10 SeitenDual ConvertersAlexNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2095784617.power Electronics Unit IiDokument59 Seiten2095784617.power Electronics Unit IiSaranya. M SNSNoch keine Bewertungen
- PC-EE-504-Module 5 Power Electronics: InvertersDokument39 SeitenPC-EE-504-Module 5 Power Electronics: InvertersSanjoy PathakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Series Inverter ExptDokument4 SeitenSeries Inverter Exptmoreh8515Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sandy 123Dokument9 SeitenSandy 123Sandy RonaldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cycle 1 Exp 2Dokument9 SeitenCycle 1 Exp 2Agnivesh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module BuckDokument13 SeitenModule BuckShankara BNoch keine Bewertungen
- Half Wave and Full Wave RectifiersDokument5 SeitenHalf Wave and Full Wave RectifiersRajesh PylaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Full Wave Rectifier: Convert AC to DC Efficiently in 40 CharactersDokument21 SeitenFull Wave Rectifier: Convert AC to DC Efficiently in 40 CharactersbaradhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp 2Dokument6 SeitenExp 2College ISMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Von EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Bewertung: 2.5 von 5 Sternen2.5/5 (3)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Von EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Noch keine Bewertungen
- JCSSP 2011 179 187Dokument9 SeitenJCSSP 2011 179 187Udayakumar VengatesanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recent Trends in FACTS ControllerDokument8 SeitenRecent Trends in FACTS ControllerUdayakumar VengatesanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Modeling of DC MachinesDokument12 Seiten2 Modeling of DC MachinesUdayakumar VengatesanNoch keine Bewertungen
- TQMDokument93 SeitenTQMUdayakumar VengatesanNoch keine Bewertungen
- BasicThermal AnalysisDokument24 SeitenBasicThermal AnalysisUdayakumar VengatesanNoch keine Bewertungen
- L09 Power Amplifier (Class B and C)Dokument21 SeitenL09 Power Amplifier (Class B and C)Joshua DuffyNoch keine Bewertungen
- MMPA Standard Specs for Permanent MagnetsDokument28 SeitenMMPA Standard Specs for Permanent MagnetsWVP100% (1)
- Igbt Theory Pe14Dokument10 SeitenIgbt Theory Pe14Vikash YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Quick GuideDokument39 SeitenElectrical Quick GuideMelvin EsguerraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coolong of Power Semiconductor DevicesDokument13 SeitenCoolong of Power Semiconductor DevicesUdayakumar VengatesanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.2 Electric Motors - Revised (Table Format)Dokument8 Seiten3.2 Electric Motors - Revised (Table Format)Sumit AgrawalNoch keine Bewertungen
- IMPORTANT QUESTION IN ELECTRICAL ENGG FOR ASSISTANT ENGINEER EXAMS OF UPRVUNL, UPPCL, MPPKVVNL, HPPSC, IES, GATE and Other State Psus.Dokument223 SeitenIMPORTANT QUESTION IN ELECTRICAL ENGG FOR ASSISTANT ENGINEER EXAMS OF UPRVUNL, UPPCL, MPPKVVNL, HPPSC, IES, GATE and Other State Psus.Rishi Kant Sharma100% (1)
- Staff CivilDokument61 SeitenStaff CivilUdayakumar VengatesanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pipeline ArchitectureDokument4 SeitenPipeline ArchitectureUdayakumar VengatesanNoch keine Bewertungen
- (ELD) Problem For Finding The Optimal Combination of The Output PowerDokument45 Seiten(ELD) Problem For Finding The Optimal Combination of The Output PowerUdayakumar VengatesanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eto Coc Written Examination Questions & Answers Part-1: by Minbox - February 11, 2020Dokument15 SeitenEto Coc Written Examination Questions & Answers Part-1: by Minbox - February 11, 2020Gokul RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCR / Thyristor: - Circuit Symbol and Terminal IdentificationDokument13 SeitenSCR / Thyristor: - Circuit Symbol and Terminal IdentificationlubnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power ElectronicsDokument29 SeitenPower ElectronicsMoiz Amjad50% (2)
- HVDC Terminal StationDokument28 SeitenHVDC Terminal Stationmaka27Noch keine Bewertungen
- Put PDFDokument4 SeitenPut PDFyuj oNoch keine Bewertungen
- Differences between GTO and IGBT devicesDokument3 SeitenDifferences between GTO and IGBT devicesDevarshi GaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Single-phase half-bridge inverter modes and componentsDokument18 SeitenSingle-phase half-bridge inverter modes and components03 Anton P JacksonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power ElectronicsDokument2 SeitenPower ElectronicspakalagopalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Commutation Circuits PDFDokument2 SeitenCommutation Circuits PDFRalphNoch keine Bewertungen
- Karavia: SVC For Dynamic Voltage Control of A 220 KV Transmission System Fed by The Inga-Kolwesi HVDC LinkDokument2 SeitenKaravia: SVC For Dynamic Voltage Control of A 220 KV Transmission System Fed by The Inga-Kolwesi HVDC LinkDaniel ChristianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transistor DatasheetDokument12 SeitenTransistor Datasheetrevanthkumar80Noch keine Bewertungen
- Emtp PDFDokument34 SeitenEmtp PDFagkacdm1163100% (1)
- 1975 RCA Thyristors RectifiersDokument505 Seiten1975 RCA Thyristors RectifiersPaulo De Amorim CostaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8 Solid State Relays ContactorsDokument74 SeitenChapter 8 Solid State Relays ContactorsAndi KaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transient Stability Improvement of SMIB With Unified Power Flow ControllerDokument78 SeitenTransient Stability Improvement of SMIB With Unified Power Flow ControllerRagesh OdungattuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Redressement Contrôlé Monophasé Simple Alternance: Exercice 1Dokument4 SeitenRedressement Contrôlé Monophasé Simple Alternance: Exercice 1Ay OùbNoch keine Bewertungen
- EPower 029669 5 PDFDokument14 SeitenEPower 029669 5 PDFrajabharath12Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lab RecordDokument48 SeitenLab Recordanshuman.sahanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Harmonic Generation and Analysis of Non-Linear LoadsDokument20 SeitenHarmonic Generation and Analysis of Non-Linear Loadsue06037Noch keine Bewertungen
- BT151Dokument7 SeitenBT151FredericoAffonsoBuenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course Plan: American International University-Bangladesh (Aiub)Dokument12 SeitenCourse Plan: American International University-Bangladesh (Aiub)kazi AlviNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10ee81 Electrical Design, Estimating and CostingDokument16 Seiten10ee81 Electrical Design, Estimating and CostingFzs LohiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Single Phase Semi Converter DC Motor DriveDokument3 SeitenSingle Phase Semi Converter DC Motor DriveHeliosAlaricNoch keine Bewertungen
- HVDC StationDokument26 SeitenHVDC StationRajmohan100% (1)
- Power Electronics: Faculty-In-Charge: Dr. Sitangshu BhattacharyaDokument27 SeitenPower Electronics: Faculty-In-Charge: Dr. Sitangshu BhattacharyaShivanshu TrivediNoch keine Bewertungen
- IGBTs (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors) vs MOSFET vs GTO vs TRIAC vs IGCTDokument4 SeitenIGBTs (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors) vs MOSFET vs GTO vs TRIAC vs IGCTvikas bhaskarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control 3V DC Voltage from 9V Battery Using SwitchesDokument15 SeitenControl 3V DC Voltage from 9V Battery Using Switchesraghu_chandra_3Noch keine Bewertungen
- 620a Rap enDokument283 Seiten620a Rap enStefan Tudorache100% (1)
- Guide to AC Diesel-Electric HaulersDokument39 SeitenGuide to AC Diesel-Electric HaulersVentasVarias Antofa100% (1)
- Flexible Ac Transmitter System Using TSR For Controlling Voltage and CurrentDokument21 SeitenFlexible Ac Transmitter System Using TSR For Controlling Voltage and Currentعبدالله نافعNoch keine Bewertungen