Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Polymers: Long Molecules
Hochgeladen von
cymyOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Polymers: Long Molecules
Hochgeladen von
cymyCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Polymers
~ 1m
03 . nm
10
4
chain units long molecules
H
C
H
H
C
H
H
C
H
H
C
H
H
C
H
H
C
H
H
C
H
H
C
H
O
CH
2
OH
HO OH
O
thin, flexible
polyethene
apolar
hydrophobic
thick, rigid
cellulose
polar
hydrophylic
~ 10nm
coiled
O
CH
2
OH
HO OH
O
O
CH
2
OH
HO OH
O
H
C
H
H
C
H
H
C
H
H
C
H
C
H
H
C
H
C
H
H
C
H
HCH
entanglement
Cross Links
cross links make a polymer insoluble
crystalline
(no diffusion)
amorphous
with some space
open, that allows
motion of permeants
0 < crystallinity < 1
depends on the
polymer and its history
dimensions ~ 10 nm
Crystalline and Amorphous
10
8
10
6
10
4
modulus of
elasticity
E
N m
2
200 300 400 500
T
g
T
m
glass rubber liquid
temperature
T
K
glass transition
melting
temperature
rigid creeping
flow
10
10
10
2
with cross
linking
Glass Transition Point
10
8
10
6
10
4
modulus of
elasticity
E
N m
2
200 300 400 500
T
g
temperature
T
K
10
10
slow cooling:
lower glass point
long in
between
short relaxation times
Freezing in
polymer (1) solvent (2)
solvent
activity
a
2
10
2
10
0
volume fraction
c
2
10
1
10
0
10
1
10
2
polymer and solvent
fit on a 3D lattice
factor 2.71
a
V
V
2 2
2
1
1
1 =
|
\
|
.
|
|
\
|
.
|
c c exp
V V
2 1
<<
linear
Flory-Huggins
V
V
2
1
10
2
10
3
10
4
solvent
activity
10
2
10
4
10
6
10
0
10
2
10
0
10
0
10
2
volume
fraction
c
2
mole
fraction x
2
a
2
activity is a simple function
of the volume fraction
strong volume and non-
ideality effects if we use
mole fractions
Do not use the
Polymer to define
Mole Fractions
a
V
V
2 2
2
1
1 1
2
1 =
|
\
|
.
|
+
(
c c _c exp
non-ideality parameter
_ > 0
solvent and polymer
dislike each other
_ = 0
solvent and polymer
are similar
solvent and polymer
attract each other
_ < 0
solvent
activity
a
2
10
2
10
0
volume fraction
c
2
10
1
10
0
10
1
10
2
_
2
1
0
-1
demixing!
Non-ideality
Swelling (1)
a B
V
V
C
2 2 1 1
2
2
1
1 3
= + +
(
c c _c c exp
B n
c
~
1
2
number of chain units
between each cross link
a cross linked polymer:
little springs under an
internal stress
solvent
Swelling (2)
1.0
0.1
0.01
0.0 1.0 2.0
0
1
2
swelling parameter
gels, protein separation media
reverse osmosis
pervaporation
gas separations
(high pressure)
_ =
c
2
B
V
V
C
2
Solubility of Vapour in Polymer
activity of vapour 2 activity of 2 in polymer
' =
-
a
p
p
2
2
2
a B
V
V
C
2 2
2
1 = + +
(
c _ exp
( )
c
1
1
equilibrium
' = a a
2 2
c
_
2 2
2
2
1
1
=
+ +
(
-
p
p B
V
V
C
exp
Henry coefficient
Distribution between Solvent and Polymer
polymer (1)
solvent (2)
solute (3)
' = c
1
0
' c
2
large
' c
3
small
c
1
c
2
c
3
equilibrium calculation:
' = a a
2 2
' = a a
3 3
a
V
V
B
V
V
C
3 3 1
3
2
2
3
1
1 3
1 = +
|
\
|
.
|
+
(
c c c c exp
swelling: Fig 15.10
' = '
|
\
|
.
|
'
(
a
V
V
3 3
3
2
2
1 c c exp
c
c
3
3
'
=constant
volume distribution
(Nernst) coefficient
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- FM and HM 2Dokument25 SeitenFM and HM 2kishorereddy_btechNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polymer Engineering Nick DalglieshDokument2 SeitenPolymer Engineering Nick DalglieshNickolas A. DalglieshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Viscosity of Solutions of MacromoleculesDokument5 SeitenViscosity of Solutions of MacromoleculesRonald ChandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dilute: Concentrated Polymer SolutionsDokument19 SeitenDilute: Concentrated Polymer SolutionsGerald LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Models - Cfd.oldroyd B Viscoelastic PDFDokument14 SeitenModels - Cfd.oldroyd B Viscoelastic PDFHarish AkulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compressible Flow PDFDokument38 SeitenCompressible Flow PDFApple EmiratessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polymer Molar Masses and SizesDokument27 SeitenPolymer Molar Masses and Sizesfrency13Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Effective Surface AreaDokument14 SeitenThe Effective Surface Areashripathyd1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Formula Sheet CE340Dokument5 SeitenFormula Sheet CE340bilumumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Viscosity in Fluids: By: Rahim HassanzadehDokument15 SeitenViscosity in Fluids: By: Rahim Hassanzadehsharif_94Noch keine Bewertungen
- ChE354 Non NewtDokument22 SeitenChE354 Non NewtFilipe SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- RheologyDokument33 SeitenRheologyLindsey Barber100% (1)
- EN292 MaterialsDokument80 SeitenEN292 MaterialsGrant HeilemanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Viscosity LabDokument15 SeitenViscosity LabM. Fatih Doğan50% (2)
- Solutions Manual For: Multiphase Flows With Droplets and ParticlesDokument80 SeitenSolutions Manual For: Multiphase Flows With Droplets and ParticlesSarah Suelen100% (3)
- Lecture # 6-04 - 02 - 2016Dokument33 SeitenLecture # 6-04 - 02 - 2016pratapNoch keine Bewertungen
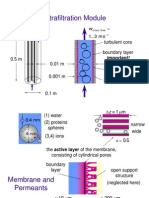
- Ultrafiltration Module: Turbulent Core Boundary LayerDokument19 SeitenUltrafiltration Module: Turbulent Core Boundary LayercymyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Light Scattering MITDokument24 SeitenLight Scattering MITYue LiuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamental PropertiesDokument8 SeitenFundamental PropertiesLogusarojNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2017 Chen3009 Chapter 1 Compressible Flow-StudentDokument38 Seiten2017 Chen3009 Chapter 1 Compressible Flow-StudentApple EmiratessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transient Analysis of Continuous Cooling Crystallizers With Needle-Shaped CrystalsDokument8 SeitenTransient Analysis of Continuous Cooling Crystallizers With Needle-Shaped CrystalsIJERDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Engineering 160/260 Polymer Science and EngineeringDokument26 SeitenChemical Engineering 160/260 Polymer Science and EngineeringUday Prakash SahuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution of Homework#2Dokument8 SeitenSolution of Homework#2丁偉庭Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Properties 2: Prof. Balázs M. FeketeDokument23 SeitenFluid Properties 2: Prof. Balázs M. FeketeaceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prepared By: Ahmed A.Maaroof Faculty of Engineering Chemical Engineering Dept. 2020-2021Dokument36 SeitenPrepared By: Ahmed A.Maaroof Faculty of Engineering Chemical Engineering Dept. 2020-2021syakoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 3 PDFDokument12 SeitenLab 3 PDFkareem el-saidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Engineering Laboratory IDokument54 SeitenChemical Engineering Laboratory IAndini DamayantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Viscosity of Liquids: PRT LVDokument7 SeitenThe Viscosity of Liquids: PRT LVSuresh VedpathakNoch keine Bewertungen
- MI 205 Luid Mechanics: B. K. GandhiDokument28 SeitenMI 205 Luid Mechanics: B. K. GandhiAshutosh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Che 518 NotebookDokument16 SeitenChe 518 NotebookNwanorim NnaemekaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp 2Dokument12 SeitenExp 2ngothihonghanh13Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pressureloss in Slurry PipesDokument10 SeitenPressureloss in Slurry PipesKarthick Velayutham100% (1)
- 5 Nov 2020Dokument25 Seiten5 Nov 2020Hadi AeNoch keine Bewertungen
- B41OA Datasheet 2016-2017Dokument11 SeitenB41OA Datasheet 2016-2017Turkan AliyevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 21: Flow Properties of Molten Polymers: PC DawsonDokument8 Seiten21: Flow Properties of Molten Polymers: PC DawsonTamalika DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intrinsic Viscosity of Macromolecular SolutionsDokument33 SeitenIntrinsic Viscosity of Macromolecular SolutionsparagdaveNoch keine Bewertungen
- B41OA Data Sheet 2015-2016Dokument10 SeitenB41OA Data Sheet 2015-2016Leanne ChewNoch keine Bewertungen
- HW 8Dokument4 SeitenHW 8azubuik0% (1)
- Introduction To Fluid MechanicsDokument49 SeitenIntroduction To Fluid MechanicsTeja Maruvada100% (1)
- Concrete Porosity (Presentation)Dokument19 SeitenConcrete Porosity (Presentation)dr_akan100% (1)
- Partial Molal QuantitiesDokument8 SeitenPartial Molal QuantitiesLheander GernaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liquid Vis Cos I TiesDokument7 SeitenLiquid Vis Cos I TiesGabriella WidjajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Mechanics: 4 Semester BS Mechanical Engineering (2009-2013)Dokument37 SeitenFluid Mechanics: 4 Semester BS Mechanical Engineering (2009-2013)Abdul AhadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch8 Steady Incompressible Flow in Pressure Conduits (PartB)Dokument66 SeitenCh8 Steady Incompressible Flow in Pressure Conduits (PartB)avinash_friends21Noch keine Bewertungen
- (CITATION Sey04 /l 1033) : ε D C C τ Z ZDokument8 Seiten(CITATION Sey04 /l 1033) : ε D C C τ Z ZPreethpalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise 2 Partition Coefficient of Succinic Acid PDFDokument4 SeitenExercise 2 Partition Coefficient of Succinic Acid PDFKeziaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MATERI - 2 Saluran Komposite & GabunganDokument14 SeitenMATERI - 2 Saluran Komposite & GabunganSandro Nainggolan BrabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical College of Engineering Department of Petrochemical Course: Kinematic Viscosity of Transparent Liquids (The Calculation of Dynamic Viscosity) D445Dokument6 SeitenTechnical College of Engineering Department of Petrochemical Course: Kinematic Viscosity of Transparent Liquids (The Calculation of Dynamic Viscosity) D445soran najebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polymer Chemistry PDFDokument31 SeitenPolymer Chemistry PDFAnonymous v6ihpntNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coeff. of ViscisityDokument5 SeitenCoeff. of ViscisityGreyscious LyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Non - Newtonian Fluids: Fluid HandlingDokument7 SeitenNon - Newtonian Fluids: Fluid Handlingbikas_sahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 1Dokument26 SeitenLab 1QUÂN LÊ MỸ KHÁNHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ceramic Phase Equilibrium Diagrams PDFDokument42 SeitenCeramic Phase Equilibrium Diagrams PDFPelita Mu'minatus SholihahNoch keine Bewertungen
- ViscosityDokument25 SeitenViscosityTRTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution Manual For Elementary Hydraulics 1st Edition by CruiseDokument8 SeitenSolution Manual For Elementary Hydraulics 1st Edition by Cruisea88756243343% (7)
- Taylor GalerkinDokument16 SeitenTaylor GalerkinAlaa AskNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resistance and Deformation of Solid Media: Pergamon Unified Engineering SeriesVon EverandResistance and Deformation of Solid Media: Pergamon Unified Engineering SeriesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportVon EverandAnalytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportNoch keine Bewertungen
- Live Solution Tank ExampleDokument6 SeitenLive Solution Tank ExamplecymyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nox Kinetics Calculations - : Cvode Starts at Line 100 On Excel SheetDokument13 SeitenNox Kinetics Calculations - : Cvode Starts at Line 100 On Excel SheetcymyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Transfer FinDokument10 SeitenHeat Transfer FincymyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nox Kinetics Calculations - : Cvode Starts at Line 100 On Excel SheetDokument13 SeitenNox Kinetics Calculations - : Cvode Starts at Line 100 On Excel SheetcymyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Combustion Equilibrium Calculations: A1 A2 A3 A4Dokument6 SeitenCombustion Equilibrium Calculations: A1 A2 A3 A4cymyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Installed Flow CharacteristicsDokument4 SeitenInstalled Flow CharacteristicscymyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Counter Current Heat Exchanger CarnahanDokument4 SeitenCounter Current Heat Exchanger CarnahancymyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 10.9bDokument2 SeitenProblem 10.9bcymyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 8.6 DewDokument10 SeitenProblem 8.6 DewcymyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air Standard Cycle - Design Conditions: W - AC (KJ/S)Dokument6 SeitenAir Standard Cycle - Design Conditions: W - AC (KJ/S)cymyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 8.6 BubbleDokument10 SeitenProblem 8.6 BubblecymyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 8.6 L (160.67F)Dokument3 SeitenProblem 8.6 L (160.67F)cymyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Example 8.5a (Vapor Ethane)Dokument4 SeitenExample 8.5a (Vapor Ethane)cymyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mass Flowrates and Weight %: Styrene FlowsheetDokument1 SeiteMass Flowrates and Weight %: Styrene FlowsheetcymyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air Standard Cycle With HRSG Supplemental Firing: Overall Energy Balance MethodDokument6 SeitenAir Standard Cycle With HRSG Supplemental Firing: Overall Energy Balance MethodcymyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air Standard Cycle - Off Design 2: W - AC (KJ/S)Dokument8 SeitenAir Standard Cycle - Off Design 2: W - AC (KJ/S)cymyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linear Data Reconciliation: Narasimhan and Jordache (2000)Dokument1 SeiteLinear Data Reconciliation: Narasimhan and Jordache (2000)cymyNoch keine Bewertungen
- SI - Real Gas - Design: VariablesDokument9 SeitenSI - Real Gas - Design: VariablescymyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Example 2.16 BDokument1 SeiteExample 2.16 BcymyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Example 6.16aDokument1 SeiteExample 6.16acymyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Example 8.6c (Vapor Condenser)Dokument2 SeitenExample 8.6c (Vapor Condenser)cymyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Example 2.14Dokument1 SeiteExample 2.14cymyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air Standard Cycle - Design Conditions: W - AC (KJ/S)Dokument6 SeitenAir Standard Cycle - Design Conditions: W - AC (KJ/S)cymyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Example 2.16 ADokument1 SeiteExample 2.16 AcymyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Feed Reactor in Reactor Out Product Vapor Out Recycle Purge RHSDokument1 SeiteFeed Reactor in Reactor Out Product Vapor Out Recycle Purge RHScymyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Example 5.6aDokument1 SeiteExample 5.6acymyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Example 2.17 ADokument2 SeitenExample 2.17 AcymyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Example 2.17 BDokument2 SeitenExample 2.17 BcymyNoch keine Bewertungen
- X (0) X (1) X (2) RHS X X X: Newton-Raphson Method All VBA CodeDokument1 SeiteX (0) X (1) X (2) RHS X X X: Newton-Raphson Method All VBA CodecymyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0.25 Reaction N + 3H NH: Ammonia Material Balance Using Gauss Jordan Elimination and Newton RaphsonDokument1 Seite0.25 Reaction N + 3H NH: Ammonia Material Balance Using Gauss Jordan Elimination and Newton RaphsoncymyNoch keine Bewertungen
- WFM 5101 Watershed Hydrology: Shammi HaqueDokument18 SeitenWFM 5101 Watershed Hydrology: Shammi HaquejahirNoch keine Bewertungen
- L5T-112 Manual - 2007 - Issue 1.1 PDFDokument16 SeitenL5T-112 Manual - 2007 - Issue 1.1 PDFfluidaimaginacionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vtoris 100% Clean Paypal Transfer Guide 2015Dokument8 SeitenVtoris 100% Clean Paypal Transfer Guide 2015Sean FrohmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of Bird Sanctuaries in India (State-Wise)Dokument6 SeitenList of Bird Sanctuaries in India (State-Wise)VISHRUTH.S. GOWDANoch keine Bewertungen
- R, Axn: Housingand RegulatoryDokument5 SeitenR, Axn: Housingand RegulatoryAce RamosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter I. Scope of Distributive Trade StatisticsDokument11 SeitenChapter I. Scope of Distributive Trade StatisticsNguyễn Hà Diệu LinhNoch keine Bewertungen
- OM Part B - Rev1Dokument45 SeitenOM Part B - Rev1Redouane BelaassiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kamal: Sales and Marketing ProfessionalDokument3 SeitenKamal: Sales and Marketing ProfessionalDivya NinaweNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - DIASS Trisha Ma-WPS OfficeDokument2 Seiten1 - DIASS Trisha Ma-WPS OfficeMae ZelNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5000-5020 en PDFDokument10 Seiten5000-5020 en PDFRodrigo SandovalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Small Data, Big Decisions: Model Selection in The Small-Data RegimeDokument10 SeitenSmall Data, Big Decisions: Model Selection in The Small-Data Regimejuan carlos monasterio saezNoch keine Bewertungen
- NJEX 7300G: Pole MountedDokument130 SeitenNJEX 7300G: Pole MountedJorge Luis MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annex A - Scope of WorkDokument4 SeitenAnnex A - Scope of Workمهيب سعيد الشميريNoch keine Bewertungen
- OMM 618 Final PaperDokument14 SeitenOMM 618 Final PaperTerri Mumma100% (1)
- Chapter 10 OutlineDokument3 SeitenChapter 10 OutlineFerrari75% (4)
- Ep Docx Sca SMSC - V2Dokument45 SeitenEp Docx Sca SMSC - V290007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Work Permits New Guideline Amendments 2021 23.11.2021Dokument7 SeitenWork Permits New Guideline Amendments 2021 23.11.2021Sabrina BrathwaiteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project On Mahindra BoleroDokument35 SeitenProject On Mahindra BoleroViPul75% (8)
- NCPDokument6 SeitenNCPJoni Lyn Ba-as BayengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Pyqs NsejsDokument3 SeitenHeat Pyqs NsejsPocketMonTuberNoch keine Bewertungen
- Altos Easystore Users ManualDokument169 SeitenAltos Easystore Users ManualSebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Turnbull CV OnlineDokument7 SeitenTurnbull CV Onlineapi-294951257Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vertical Cutoff WallsDokument18 SeitenVertical Cutoff WallsMark LaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study in Architectural Structures: A-7E Avionics System - ADokument36 SeitenCase Study in Architectural Structures: A-7E Avionics System - Ajckz8Noch keine Bewertungen
- Verilog A Model To CadenceDokument56 SeitenVerilog A Model To CadenceJamesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hauling AgreementDokument2 SeitenHauling AgreementE.A. Francisco Trucking100% (3)
- ISSA2013Ed CabinStores v100 Часть10Dokument2 SeitenISSA2013Ed CabinStores v100 Часть10AlexanderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subject: PSCP (15-10-19) : Syllabus ContentDokument4 SeitenSubject: PSCP (15-10-19) : Syllabus ContentNikunjBhattNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skilled Worker Overseas FAQs - Manitoba Immigration and Economic OpportunitiesDokument2 SeitenSkilled Worker Overseas FAQs - Manitoba Immigration and Economic OpportunitieswesamNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 AcmeCorporation Fullstrategicplan 06052015 PDFDokument11 Seiten3 AcmeCorporation Fullstrategicplan 06052015 PDFDina DawoodNoch keine Bewertungen