Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Bolt Pressure Distribution
Hochgeladen von
bitconceptsCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Bolt Pressure Distribution
Hochgeladen von
bitconceptsCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
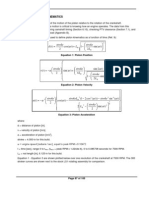
ME 307
Machine
Design I
CH-8 LEC 36 Slide 1 Dr. A. Aziz Bazoune Chapter 8: Screws, Fasteners and the Design of Nonpermanent Joints
ME 307
Machine
Design I
8-1 Thread Standards and Definitions
8-2 The Mechanics of Power Screws
8-3 Strength Constraints
8-4 Joints-Fasteners Stiffness
8-5 Joints-Member Stiffness
8-6 Bolt Strength
8-7 Tension Joints-The External Load
8-8 Relating Bolt Torque to Bolt Tension
8-9 Statically Loaded Tension Joint with Preload
8-10 Gasketed Joints
8-11 Fatigue Loading of Tension Joints
8-12 Shear Joints
8-13 Setscrews
8-14 Keys and Pins
8-15 Stochastic Considerations
CH-8 LEC 36 Slide 2 Dr. A. Aziz Bazoune Chapter 8: Screws, Fasteners and the Design of Nonpermanent Joints
ME 307
Machine
Design I
8-3 Strength Constraints
8-4 Joints-Fasteners Stiffness
8-5 Joints-Member Stiffness
8-6 Bolt Strength
CH-8 LEC 36 Slide 3 Dr. A. Aziz Bazoune Chapter 8: Screws, Fasteners and the Design of Nonpermanent Joints
ME 307
Machine
Design I
8-4 Joints: Fastener Stiffness
When a connection is desired that can be disassembled without destructive
methods and that is strong enough to resist external tensile loads, moment
loads, and shear loads, or a combination of these, then the simple bolted joint
using hardened steel washers is a good solution.
CH-8 LEC 36 Slide 4 Dr. A. Aziz Bazoune Chapter 8: Screws, Fasteners and the Design of Nonpermanent Joints
Twisting the nut stretches the bolt to
produce the clamping force. This clamping
force is called the pretention or bolt
preload.
This force exists in the connection after the
nut has been properly tightened.
Figure 8-13
A bolted connection loaded in tension by the forces P.
Note the use of two washers. Note how the threads
extend into the body of the connection. This is usual and
is desired. L
G
is the grip of the connection.
ME 307
Machine
Design I
Figure 8-14
Section of cylindrical pressure vessel.
Hexagon-head caps crews are used to
fasten the cylinder head to the body.
Note the use of an O-ring seal. LG is
the effective length of the connection
(See Table 8-7) .
Joints: Fastener Stiffness
Figure 8-14 shows another
tension-loaded connection. This
joint uses cap screws threaded
into one of the members.
CH-8 LEC 36 Slide 5 Dr. A. Aziz Bazoune Chapter 8: Screws, Fasteners and the Design of Nonpermanent Joints
ME 307
Machine
Design I
Joints: Fastener Stiffness
CH-8 LEC 36 Slide 6 Dr. A. Aziz Bazoune Chapter 8: Screws, Fasteners and the Design of Nonpermanent Joints
An alternative approach to this problem
(of not using a nut) would be to use studs.
A stud is a rod threaded on both ends. The
stud is screwed into the lower member
first; then the top member is positioned
and fastened down with hardened washers
and nuts
Studs are regarded as permanent, and so
the joint can be disassembled merely by
removing the nut and washer.
ME 307
Machine
Design I
Joints: Fastener Stiffness
CH-8 LEC 36 Slide 7 Dr. A. Aziz Bazoune Chapter 8: Screws, Fasteners and the Design of Nonpermanent Joints
Spring Rate : The ratio between the
force applied to the member and the
deflection produced by that force.
The grip L
G
of a connection is the total
thickness of the clamped material.
Total distance between the underside of
the nut to the bearing face of the bolt
head; includes washer, gasket thickness
etc.
The grip L
G
here is the sum
of the thicknesses of both
members and both washers.
ME 307
Machine
Design I
CH-8 LEC 36 Slide 8 Dr. A. Aziz Bazoune Chapter 8: Screws, Fasteners and the Design of Nonpermanent Joints
Table 8-7
Suggested Procedure for Finding
fastener Stiffness
To find different parameters use table
8-7
ME 307
Machine
Design I
In joint under tension the members are under compression and the bolt under
tension: k
b
= equivalent spring constant of bolt composed of threaded k
t
and
unthreaded k
d
parts acting as springs in series.
CH-8 LEC 36 Slide 9 Dr. A. Aziz Bazoune Chapter 8: Screws, Fasteners and the Design of Nonpermanent Joints
1 1 1
,
b d t
d t
b
d t
d t
d t
d t
d t
b
d t t d
k k k
k k
k
k k
A E A E
k k
l l
A A E
k
A l Al
= +
=
+
= =
=
+
A
t
: tensile stress area (Tables 8-1, 8-2), l
t
: length of threaded portion of the
grip; A
d
: major diameter area of fastener; l
d
: length of unthreaded portion in
grip. k
b
: is the estimated effective stiffness of the bolt or cap screw in the
clamped zone.
For short bolts
k
b
= k
t
From Chapter 5
(Springs in series)
ME 307
Machine
Design I
CH-8 LEC 36 Slide 10 Dr. A. Aziz Bazoune Chapter 8: Screws, Fasteners and the Design of Nonpermanent Joints
8-5 Joints- Member Stiffness
ME 307
Machine
Design I
There may be more than two members included in the grip
of the fastener.
All together these act like compressive springs in series.
Equivalent spring constant k
m
If one of the members is a soft gasket, its stiffness relative
to the other members is usually so small that for all
practical purposes the others can be neglected and only
gasket stiffness used.
With no gasket, the stiffness of the members is difficult to
obtain, except by experimentation.
Compression spreads out between the bolt head and the
nut and area is not uniform.
1 2 3
1 1 1 1 1
....
m i
k k k k k
= + + +
CH-8 LEC 36 Slide 11 Dr. A. Aziz Bazoune Chapter 8: Screws, Fasteners and the Design of Nonpermanent Joints
8-5 Joints- Member Stiffness
ME 307
Machine
Design I
CH-8 LEC 36 Slide 12 Dr. A. Aziz Bazoune Chapter 8: Screws, Fasteners and the Design of Nonpermanent Joints
8-5 Joints Member Stiffness
Joint pressure distribution theoretical models
Ito used ultrasonic techniques to determine pressure distribution at
the member interface. Results show that pressure stays high out to
about 1.5 bolt radii.
Ito suggested the use of Rotschers pressure cone method for stiffness
calculations with a variable cone angle. This method is quite
complicated.
ME 307
Machine
Design I
CH-8 LEC 36 Slide 13 Dr. A. Aziz Bazoune Chapter 8: Screws, Fasteners and the Design of Nonpermanent Joints
8-5 Joints Member Stiffness
Figure 8-15
ME 307
Machine
Design I
We choose a simpler approach using a fixed
cone angle.
The contraction of an element of the cone of
thickness dx is subjected to a compressive
force P is, from Eq. (5-3),
The area of the element is
Pdx
d
EA
o =
CH-8 LEC 36 Slide 14 Dr. A. Aziz Bazoune Chapter 8: Screws, Fasteners and the Design of Nonpermanent Joints
Figure 8-15b general cone
geometry using a half-apex
angle o.
8-5 Joints Member Stiffness
( )
2 2
2 2
0
tan
2 2
tan tan
2 2
i
D d
A r r x
D d D d
x x
t t o
t o o
(
| | | |
= = +
(
| |
\ . \ .
(
+ | | | |
= + +
| |
\ . \ .
ME 307
Machine
Design I
Substituting this into the previous equation and integrating the resulting
equation from 0 to t gives.
For Members made of Aluminum, hardened steel and cast iron 25
o
<o<33
o
With o=30
o
, this becomes
CH-8 LEC 36 Slide 15 Dr. A. Aziz Bazoune Chapter 8: Screws, Fasteners and the Design of Nonpermanent Joints
8-5 Joints Member Stiffness
(2 tan )( )
ln
tan (2 tan )( )
tan
(2 tan )( )
ln
(2 tan )( )
P t D d D d
Ed t D d D d
P Ed
k
t D d D d
t D d D d
o
o
t o o
t o
o
o
o
+ +
=
+ +
= =
+ +
+ +
(8-19)
0.574
(1.55 )( )
ln
(1.55 )( )
E d
k
t D d D d
t D d D d
t
==
+ +
+ +
(8-20)
ME 307
Machine
Design I
Substituting this into the previous equation and integrating the resulting
equation from 0 to t gives.
With o=30
o
, this becomes
CH-8 LEC 36 Slide 16 Dr. A. Aziz Bazoune Chapter 8: Screws, Fasteners and the Design of Nonpermanent Joints
8-5 Joints Member Stiffness
(2 tan )( )
ln
tan (2 tan )( )
tan
(2 tan )( )
ln
(2 tan )( )
P t D d D d
Ed t D d D d
P Ed
k
t D d D d
t D d D d
o
o
t o o
t o
o
o
o
+ +
=
+ +
= =
+ +
+ +
(8-19)
0.574
(1.55 )( )
ln
(1.55 )( )
E d
k
t D d D d
t D d D d
t
==
+ +
+ +
(8-20)
ME 307
Machine
Design I
CH-8 LEC 36 Slide 17 Dr. A. Aziz Bazoune Chapter 8: Screws, Fasteners and the Design of Nonpermanent Joints
If members of the joint have the same E with symmetrical frusta (l=2t),
then they act as two identical springs in series k
m
= k/2. For o= 30 and
D = d
w
= 1.5 d, this can be written as,
Finite element analysis agree with o = 30
o
recommendation coinciding
exactly at the aspect ratio d/l = 0.4.
Additionally, FEM offered an exponential curve-fit of the form
where A and B are given in Table 8-8.
0.5774
0.5774 0.5
2ln 5
0.5774 2.5
m
E d
k
l d
l d
t
=
| |
+
|
+
\ .
(8-22)
( / ) Bd l
m
k
Ae
Ed
=
(8-23)
8-5 Joints Member Stiffness
ME 307
Machine
Design I
CH-8 LEC 36 Slide 18 Dr. A. Aziz Bazoune Chapter 8: Screws, Fasteners and the Design of Nonpermanent Joints
8-5 Joints Member Stiffness
Figure 8-16
The dimensionless plot
of stiffness versus aspect
ratio of the members of
a bolted joint, showing
the relative accuracy of
method of Rotsher,
Michke and Motosh,
compared to Finite
Element Analysis (FEA)
conducted by Wileman,
Choudury, and Green.
ME 307
Machine
Design I
CH-8 LEC 36 Slide 19 Dr. A. Aziz Bazoune Chapter 8: Screws, Fasteners and the Design of Nonpermanent Joints
8-5 Joints Member Stiffness
ME 307
Machine
Design I
Bolt strength is specified by:
1. minimum proof strength S
p
2. or minimum proof load F
p
,
3. and minimum tensile strength, S
ut
The proof load is the maximum load (force)
that a bolt can withstand without acquiring
a permanent set.
The proof strength is the quotient of the
proof load and the tensile-stress area.
The proof strength is about 90% of the 0.2%
offset yield strength.
CH-8 LEC 36 Slide 20 Dr. A. Aziz Bazoune Chapter 8: Screws, Fasteners and the Design of Nonpermanent Joints
8-6 Bolt Strength
ME 307
Machine
Design I
The SAE specifications are given in
Table 8-9 bolt grades are numbered
according to minimum tensile strength.
The ASTM Specs for steel bolts (structural)
are in Table 8-10.
Metric Specs are in Table 8-11.
If S
p
not available use:
S
p
=0.85 S
y
F
p
= A
t
S
p
CH-8 LEC 36 Slide 21 Dr. A. Aziz Bazoune Chapter 8: Screws, Fasteners and the Design of Nonpermanent Joints
8-6 Bolt Strength
ME 307
Machine
Design I
CH-8 LEC 36 Slide 22 Dr. A. Aziz Bazoune Chapter 8: Screws, Fasteners and the Design of Nonpermanent Joints
8-6 Bolt Strength
ME 307
Machine
Design I
CH-8 LEC 36 Slide 23 Dr. A. Aziz Bazoune Chapter 8: Screws, Fasteners and the Design of Nonpermanent Joints
ME 307
Machine
Design I
CH-8 LEC 36 Slide 24 Dr. A. Aziz Bazoune Chapter 8: Screws, Fasteners and the Design of Nonpermanent Joints
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A - Piping Joint HandbookDokument161 SeitenA - Piping Joint HandbookCharles Tauk100% (30)
- Lightning ProtectionDokument20 SeitenLightning Protectionsofyan_shah50% (2)
- Chapter 6 ConnectionDokument30 SeitenChapter 6 ConnectionIvy SeahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Avoiding Self-Loosening Failure of Bolted Joints With NumericalDokument13 SeitenAvoiding Self-Loosening Failure of Bolted Joints With Numericalfoufoua100% (1)
- Knuckle Joints DesignDokument10 SeitenKnuckle Joints DesignKvrd Prasad100% (1)
- Analysis of Bolt TorquingDokument7 SeitenAnalysis of Bolt TorquingAlessandro Serafini100% (1)
- 171-178 EurocodeDokument8 Seiten171-178 EurocodeDeana WhiteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 10 Chemistry Workbook PDFDokument118 SeitenClass 10 Chemistry Workbook PDFSayan Dutta100% (1)
- 25 Permanent Magnet Motor Design PDFDokument39 Seiten25 Permanent Magnet Motor Design PDFbitconcepts60% (5)
- Fatigue Stress AnalysisDokument5 SeitenFatigue Stress AnalysisnareniviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tenaris University - International Standards and Recommended Practices For Assuring Structural Reliability On Octg ProductsDokument31 SeitenTenaris University - International Standards and Recommended Practices For Assuring Structural Reliability On Octg ProductsSudish Bhat100% (1)
- 28 Amazing Benefits and Uses For Hydrogen Peroxide Wake Up WorldDokument6 Seiten28 Amazing Benefits and Uses For Hydrogen Peroxide Wake Up WorldStephen AdamsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synchro and Resolver Hand BookDokument35 SeitenSynchro and Resolver Hand BookAbdul KurniadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Guide PDFDokument117 SeitenDesign Guide PDFAndres FacuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Snap-Fit Joints DesignDokument26 SeitenSnap-Fit Joints DesignDavid García SalvatierraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pipe Stress Analysis Using CAESAR IIDokument42 SeitenPipe Stress Analysis Using CAESAR IIpca97100% (1)
- DC Generator PDFDokument108 SeitenDC Generator PDFSaeed Osman MohamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical Engineering Design 8thDokument12 SeitenMechanical Engineering Design 8thStipendijeVlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- KPCL - Steam Blowing ProcedureDokument7 SeitenKPCL - Steam Blowing ProcedureAtiqur RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technology Economics Propylene Via Propane Dehydrogenation 5584a5fc359b2 PDFDokument78 SeitenTechnology Economics Propylene Via Propane Dehydrogenation 5584a5fc359b2 PDFCarolina Garzón50% (4)
- Bracing Design To Eurocode 3Dokument13 SeitenBracing Design To Eurocode 3Greg Rabulan100% (1)
- 1 Numerical Analysis of Shock ResponseDokument115 Seiten1 Numerical Analysis of Shock ResponseLeonichevNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8: Screws, Fasteners and The Design of Nonpermanent JointsDokument27 SeitenChapter 8: Screws, Fasteners and The Design of Nonpermanent JointsSandeep KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Long-Life Xlpe Insulated Power Cable PDFDokument6 SeitenLong-Life Xlpe Insulated Power Cable PDFbitconceptsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 - Design of Mechanical JointDokument26 SeitenChapter 3 - Design of Mechanical JointRaj KeeranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conveyor Pulley DrumsDokument13 SeitenConveyor Pulley DrumsriysallNoch keine Bewertungen
- Condenser Design in Aspen PlusDokument9 SeitenCondenser Design in Aspen Plusvsraochemical1979100% (7)
- SKF Manual de ApertosDokument44 SeitenSKF Manual de ApertosA RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical Engineering Design Chapter 8 CompressDokument24 SeitenMechanical Engineering Design Chapter 8 Compressfog900Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical Engineering Design Chapter 8 CompressDokument24 SeitenMechanical Engineering Design Chapter 8 Compressfog900Noch keine Bewertungen
- B Screws & Bolted JointsDokument54 SeitenB Screws & Bolted Jointsfog900Noch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Machine Elements (Fasteners)Dokument39 SeitenDesign of Machine Elements (Fasteners)Nauman KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8: Screws, Fasteners and The Design of Nonpermanent JointsDokument27 SeitenChapter 8: Screws, Fasteners and The Design of Nonpermanent JointsErcüment KayacıkNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME-328 Machine Design - Lecture 7Dokument21 SeitenME-328 Machine Design - Lecture 7sksiddiqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- SYS Bolt ManualDokument64 SeitenSYS Bolt ManualNoppolNorasriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fastner ch2Dokument62 SeitenFastner ch2Tki NeweNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8: Screws, Fasteners and The Design of Nonpermanent JointsDokument35 SeitenChapter 8: Screws, Fasteners and The Design of Nonpermanent JointsمحمدالنوبىNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Analysis of COTTER JOINT Using Autodesk Inventor 2013 and ANSYS WorkbenchDokument22 SeitenDesign and Analysis of COTTER JOINT Using Autodesk Inventor 2013 and ANSYS WorkbenchamuNoch keine Bewertungen
- LEC 31 CH-18 Shafts and AxlesDokument34 SeitenLEC 31 CH-18 Shafts and AxlesJoe Hosny100% (1)
- Couchaux Et Al-2017-Ce/papersDokument10 SeitenCouchaux Et Al-2017-Ce/papersCuneyt VatanseverNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dr. A. Aziz Bazoune: King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals Mechanical Engineering DepartmentDokument34 SeitenDr. A. Aziz Bazoune: King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals Mechanical Engineering Departmentashray_111Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3Dokument25 SeitenChapter 3Fadhiran YahyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE470MidExam SolutionsDokument12 SeitenCE470MidExam SolutionsTefera TemesgenNoch keine Bewertungen
- FEA Mesh Convergence and Singularity in Connecting LugDokument11 SeitenFEA Mesh Convergence and Singularity in Connecting LugDarshanPatel100% (1)
- Design and Fabrication of Toggle JackDokument30 SeitenDesign and Fabrication of Toggle JackJitendra Rout0% (1)
- Fatigue in Engine Connecting Rod Bolt Due To Forming LapsDokument7 SeitenFatigue in Engine Connecting Rod Bolt Due To Forming LapsRoberto Polo BrunoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experimental Investigation On Torsional Rigidity of Power ScrewsDokument4 SeitenExperimental Investigation On Torsional Rigidity of Power ScrewsIOSRJEN : hard copy, certificates, Call for Papers 2013, publishing of journalNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENCE 455 Design of Steel StructuresDokument6 SeitenENCE 455 Design of Steel StructuresTooraj RoozkhoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Belt AnalysisDokument4 SeitenBelt AnalysisMaheswaran MuthaiyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contact Stress Analysis of Barrel CouplingDokument8 SeitenContact Stress Analysis of Barrel CouplingBruno SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- MEL311Dokument281 SeitenMEL311Shiri ShaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MOM Chapter 3-Mechanical Properties of MaterialsDokument22 SeitenMOM Chapter 3-Mechanical Properties of MaterialsezoramajnunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dr. A. Aziz Bazoune: King Fahd University of Petroleum & MineralsDokument37 SeitenDr. A. Aziz Bazoune: King Fahd University of Petroleum & MineralsVikram BorkhediyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tension Member 19.3.2023Dokument85 SeitenTension Member 19.3.2023Akib IslamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Use of Strain Gauge Rosette To Investigate Stress Concentration in Isotropic and Orthotropic Plate With Circular HoleDokument5 SeitenUse of Strain Gauge Rosette To Investigate Stress Concentration in Isotropic and Orthotropic Plate With Circular HoleHako KhechaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mace 60035Dokument7 SeitenMace 60035eng_ayman_H_MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Piston Kinematics & Rod Bolt PreloadDokument5 SeitenPiston Kinematics & Rod Bolt PreloadRezinTexasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cad & Component DrawingDokument36 SeitenCad & Component DrawingkousikkumaarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tasc 15-101Dokument9 SeitenTasc 15-101HAitham Abd El-hameedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effects of Stacking Sequence and Clamping Forceon The Bearing Strength of Mechanically Fastened Joints in Composite LaminatesDokument9 SeitenEffects of Stacking Sequence and Clamping Forceon The Bearing Strength of Mechanically Fastened Joints in Composite Laminateskhudhayer1970Noch keine Bewertungen
- Connection ReportDokument20 SeitenConnection Reportapi-570030183Noch keine Bewertungen
- Theory of Machines & Machine DesignDokument3 SeitenTheory of Machines & Machine DesignAvilash JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cat 3176c Montagem Da Cabeça.Dokument7 SeitenCat 3176c Montagem Da Cabeça.César PérezNoch keine Bewertungen
- TE - 2019 - Design of Machine Elements PDFDokument4 SeitenTE - 2019 - Design of Machine Elements PDFonkar nikamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modeling and Analysis of Cotter Joint REPORT R20ER055Dokument21 SeitenModeling and Analysis of Cotter Joint REPORT R20ER055Akash AkashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Optimization of Power Screw JackDokument7 SeitenDesign Optimization of Power Screw JackTd DammikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TrussDokument12 SeitenTrussAmirullah Adnan100% (1)
- Flexible Mechanical ElementsDokument36 SeitenFlexible Mechanical ElementsFadi W MoussaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Me331-Design of Machine Elements Unit Iii Design of Fasteners and JointsDokument21 SeitenMe331-Design of Machine Elements Unit Iii Design of Fasteners and JointsMuthuvel MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fatigue of Textile and Short Fiber Reinforced CompositesVon EverandFatigue of Textile and Short Fiber Reinforced CompositesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fatigue Life Estimation Non Linear System Random 2008 FDokument11 SeitenFatigue Life Estimation Non Linear System Random 2008 FbitconceptsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Role of Additives in XLPE PDFDokument5 SeitenRole of Additives in XLPE PDFbitconceptsNoch keine Bewertungen
- WTR XLPE - Development PDFDokument4 SeitenWTR XLPE - Development PDFbitconceptsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04-0507-Electronics Packaging Considerations For Space ApplicationsDokument6 Seiten04-0507-Electronics Packaging Considerations For Space ApplicationsbitconceptsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solder ReliabilityDokument12 SeitenSolder ReliabilitybitconceptsNoch keine Bewertungen
- XMR AzDokument9 SeitenXMR AzbitconceptsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermoelectric Cooling WhitepaperDokument9 SeitenThermoelectric Cooling WhitepaperbitconceptsNoch keine Bewertungen
- CFX TutDokument149 SeitenCFX Tutthiagopalmieri3253Noch keine Bewertungen
- Labview Modbus EngDokument6 SeitenLabview Modbus EngSri Natha DesikanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basics of Heat Transfer - Water Cooling Systems, PC Liquid Cooling Kit, Cpu, Video Card, Hard DriveDokument2 SeitenBasics of Heat Transfer - Water Cooling Systems, PC Liquid Cooling Kit, Cpu, Video Card, Hard DrivebitconceptsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indonesian Mineral Deposits - IntroductoryDokument11 SeitenIndonesian Mineral Deposits - IntroductoryridofambudiNoch keine Bewertungen
- DCC Technicals For All MachinesDokument38 SeitenDCC Technicals For All MachinesKareem TrainmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculate The Mole ConceptDokument1 SeiteCalculate The Mole ConceptRajiv Shankar SinhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1995 Review - Aqueous Tape Casting of Ceramic PowdersDokument12 Seiten1995 Review - Aqueous Tape Casting of Ceramic PowdersFreudensteinitzNoch keine Bewertungen
- BTech (Mechanical With Specialization in Energy Engineering) Curriculum For AY2012-13Dokument8 SeitenBTech (Mechanical With Specialization in Energy Engineering) Curriculum For AY2012-13Akshat GargNoch keine Bewertungen
- 22 6Dokument13 Seiten22 6Francisco M. RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problemas Geotecniafree1Dokument46 SeitenProblemas Geotecniafree1Dickey Design100% (3)
- Chemicals Zetag MSDS Inverse Emulsion Zetag 8849 FS - 0710Dokument6 SeitenChemicals Zetag MSDS Inverse Emulsion Zetag 8849 FS - 0710PromagEnviro.comNoch keine Bewertungen
- PG 91Dokument1 SeitePG 91Shahruzi MahadzirNoch keine Bewertungen
- IISER Pune Semester IIDokument12 SeitenIISER Pune Semester IIAnmol SahuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Periodicity Review SL KeyDokument4 SeitenPeriodicity Review SL KeyYeyoung ParkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pressure-Enthalpy Diagrams: Aturation Ubcooling AND UperheatDokument35 SeitenPressure-Enthalpy Diagrams: Aturation Ubcooling AND UperheatAbdul RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schultz 1987Dokument18 SeitenSchultz 1987Ruiz ManuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- AspenTech HYSYS Pipe ModelsDokument23 SeitenAspenTech HYSYS Pipe ModelswidhisaputrawijayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Report: Organic Chemistry I CHM3201Dokument5 SeitenLab Report: Organic Chemistry I CHM3201Sehnegha KasirajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Docu Tips-24972ukqualsgcebiologyas804224972Dokument52 SeitenDocu Tips-24972ukqualsgcebiologyas804224972Rafid HaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1st Preliminary Exam (Science 6) 2021-2022 - Google FormsDokument4 Seiten1st Preliminary Exam (Science 6) 2021-2022 - Google FormsEl CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fuelless GeneratorDokument20 SeitenFuelless GeneratorazoubraNoch keine Bewertungen
- JUM RF Technical DocumentDokument2 SeitenJUM RF Technical DocumentMaxime HullmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gate 1990Dokument12 SeitenGate 1990Akhil TiwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Juba Form Two ExamDokument8 SeitenJuba Form Two ExamHossam Abdalla SalehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group Two'S Seminar Work: Topic: Enzyme Regulation Allosteric Regulation and Models OutlineDokument13 SeitenGroup Two'S Seminar Work: Topic: Enzyme Regulation Allosteric Regulation and Models OutlineOluwasegun ModupeNoch keine Bewertungen
- BenzilDokument5 SeitenBenzildeviycNoch keine Bewertungen
- B SC Analytical ChemDokument82 SeitenB SC Analytical ChemEngineering PhysicistNoch keine Bewertungen