Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Types of Piles
Hochgeladen von
Sanhita S VartakOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Types of Piles
Hochgeladen von
Sanhita S VartakCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
TYPES OF PILES
Piling What is piling? Piles can be made from steel or timber although in most housing work piles are made from insitu or pre-cast reinforced concrete. They are used either to transmit loads from the building through soft or compressible ground to firmer strata below (end bearing pile), or to distribute loads into the subsoil along the length of the pile (friction pile). In housing, a concrete beam across the top of the pilesdistributes the load from the loadbearing brickwork into the piles themselves. There are a number of different piling systems. Some, (replacement piles), bore out the ground and then replace the void with concrete. A reinforcement cage is lowered into the wet concrete to resist any lateral forces in the ground which might fracture the pile, and to provide a connection for the ground beam which will support the walls. Others, (displacement piles) are forced into the ground, pushing it out of the way as the piles are driven home.
SANHITA VARTAK,45
When the piles are in position a reinforced ground beamis positioned over the top. This takes the load from the walls and distributes it into the piles. A typical house might be supported on 10-20 piles. These are pre-cast piles which are driven into the ground to a depth determined by engineers.
SANHITA VARTAK,45
SANHITA VARTAK,45
SANHITA VARTAK,45
Why is piling becoming more common? 20 or 30 years ago piling was comparatively rare for housing (other than medium and high rise flats). Since then, several factors have led to an increase in the use of piled foundations. These include: the increased pressure to re-develop 'brownfield' sites, where strip foundations may not always be appropriate increased costs of 'carting away' and tipping surplus excavation from foundation trenches (particularly in cities) the development and easy availability of smaller piling rigs and piling systems which are, nowadays, cost effective for house foundations greater understanding of piling in general (partly through better building education). Factors affecting choice There are literally dozens of piling companies in the UK each offering a number of different piling systems. In many cases more than one piling system will suit a particular set of circumstances. However, when choosing a piling system there are four main criteria to consider: building load the nature of the ground (ie, the subsoil) local environmental or physical constraints (noise restrictions, height restrictions) cost
SANHITA VARTAK,45
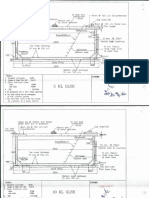
The functions of a pile cap are:
1. 2. 3.
Pile caps are thick slabs used to tie a group of piles together to support and transmit column loads to the piles.
To distribute a single load equally over the pile group and thus over a greater area of bearing potential, To laterally stabilise individual piles thus increasing overall stability of the group. And To provide the necessary combined resistance to stresses set up by the superstructure and/or ground movement.
Pile Cap Arrangement Spacing of the piles in the pile group The following should be considered when determining the spacing of the piles: 1. Overall cost of the foundation 2. Nature of the ground 3. Pile behaviour in the group 4. Resulting possible heave or compaction of ground causing damage to adjacent structures 5. Cost of pile cap 6. Size and effective length of ground beam 7. Type and size of pile SANHITA VARTAK,45
TYPICAL ARRANGEMENT OF PILES
SANHITA VARTAK,45
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- PdfstreamerDokument48 SeitenPdfstreamerAshutosh GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Fit-Out ConstructionDokument2 SeitenWhat Is Fit-Out ConstructionhieutlbkreportNoch keine Bewertungen
- Car Park Shed DrawingDokument1 SeiteCar Park Shed DrawingNizamuddin AbdullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- I. Types of Windows Used in BuildingsDokument13 SeitenI. Types of Windows Used in BuildingsAnshuman SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Division 15: Mechanical Section 15140 - SupportsDokument8 SeitenDivision 15: Mechanical Section 15140 - Supportsmdsay1975Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment IIDokument2 SeitenAssignment IIPrathyush ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Highways Department: Name of WorkDokument29 SeitenHighways Department: Name of WorkThangavel RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- PertDokument11 SeitenPertAbdulkhadir SuhairNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tenants' Repair Manual: Reporting Your RepairsDokument14 SeitenTenants' Repair Manual: Reporting Your Repairsmatthilton2005Noch keine Bewertungen
- Prestressed N Poststressed ConcreteDokument14 SeitenPrestressed N Poststressed ConcreteSameer BelimNoch keine Bewertungen
- (EIFS) WMS-A-041 R.3 and ITP-A-041 R.3 For Field Installation of STO VENTEC System in DA and AG - RequestedDokument58 Seiten(EIFS) WMS-A-041 R.3 and ITP-A-041 R.3 For Field Installation of STO VENTEC System in DA and AG - RequestedLito VasquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Free 12 X 8 Shed Plan: Click Here To Download 12,000 Shed PlansDokument24 SeitenFree 12 X 8 Shed Plan: Click Here To Download 12,000 Shed PlansRamón Baró100% (1)
- Microsoft Project Sofware Project Report PDFDokument38 SeitenMicrosoft Project Sofware Project Report PDFFarah ArishaNoch keine Bewertungen
- # # # # # # Figures BidderDokument22 Seiten# # # # # # Figures BiddersivagaaneshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 14Dokument4 SeitenChapter 14Jessa Mae CatabayNoch keine Bewertungen
- ITP AllDokument1 SeiteITP AllMuhammadIqbalMughalNoch keine Bewertungen
- MECHANICAL EQUIPMENT SCHEDULE - Aircon UpdatedDokument1 SeiteMECHANICAL EQUIPMENT SCHEDULE - Aircon UpdatedPatrick manuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- WCS 8034Dokument8 SeitenWCS 8034Sani Oghang PekanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water Tanks StructuralDesignsDokument55 SeitenWater Tanks StructuralDesignsuma venkata ramanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Description: REPAIR GUIDE Repair Type: Cosmetic Repair Cosmetic Patching Materials: ConcreteDokument2 SeitenDescription: REPAIR GUIDE Repair Type: Cosmetic Repair Cosmetic Patching Materials: ConcreteGonzalo Guerrero CáceresNoch keine Bewertungen
- PIP STS03001 (Plain & Reinforced Concrete Specification)Dokument15 SeitenPIP STS03001 (Plain & Reinforced Concrete Specification)mobin1978Noch keine Bewertungen
- Air Conditioner: PART No. 9380547105-02Dokument4 SeitenAir Conditioner: PART No. 9380547105-02Claudiu PopicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- X Specifications - Site & Buildings 02-20-09Dokument498 SeitenX Specifications - Site & Buildings 02-20-09Alexious Demide100% (1)
- Chapter 8 - Interior FinishesDokument6 SeitenChapter 8 - Interior FinishesPODNoch keine Bewertungen
- Universal Testing MachineDokument26 SeitenUniversal Testing MachineAlyan YousafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prestresed Concrete Post Tensioning PDFDokument27 SeitenPrestresed Concrete Post Tensioning PDFSathya GajjalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conc. Reinf.Dokument5 SeitenConc. Reinf.mohamed fathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ceiling Concealed Chilled Water Fan Coil UnitDokument14 SeitenCeiling Concealed Chilled Water Fan Coil UnitRodrigo Neira De FinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPHC, SPHD PDFDokument2 SeitenSPHC, SPHD PDFLê Quốc TínNoch keine Bewertungen
- SECTION 22 11 00 Facility Water Distribution: Based On DFD Master Specification Dated 10/10/17Dokument12 SeitenSECTION 22 11 00 Facility Water Distribution: Based On DFD Master Specification Dated 10/10/17Juan CarloNoch keine Bewertungen