Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Staff Development Programme: - Power Point Presentation
Hochgeladen von
GuruKPOOriginaltitel
Copyright
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenStaff Development Programme: - Power Point Presentation
Hochgeladen von
GuruKPOSTAFF DEVELOPMENT PROGRAMME
-POWER POINT PRESENTATION
BY Meenu Sharma
Inflation
is a sizeable and a rapid increase in the general price level. It is generally associated with rapidly rising prices which cause a decline in the purchasing power of money.
Prof.
Crowther, as a state in which the value of money is falling i.e. prices are rising. Prof. Kemmerer, Inflation is too much money chasing too few goods. Prof. Keynes, the rise in the price level after the point of full employment is true inflation.
Factors causing an increase in demand: Increase in public expenditure. Increase in private expenditure. Increase in exports. Reduction in taxation. Repayment of internal debts. Deficit financing.
Factors of causing a decrease in demand: Shortage of factors of supply of production Industrial disputes Natural calamities Operation of diminishing returns. Hoarding by traders. Lop-sided production
Demand
inflation: it is caused by an increase in the aggregate effective demand for goods and services. Cost inflation: also known as supply inflation. It is caused by an increase in wages , an increase in the profit margins, and imposition of heavy commodity taxes.
Effects on production :production will decline, drive out the foreign capital already invested, serious deterioration in the quality of goods produced. Effects on distribution: results in redistribution of income and wealth in favor of rich.
Other effects : Fall in consumer demand. Fall in investment demand. Fall in foreign demand.
Increased
rediscount rates. Sale of government securities in the open market. Consumer credit control. Higher reserve requirement. Reduce government expenditure. Public borrowing. Debt management. Expansion of output.
It
was given by William Phillips in 1958 The Phillip's curve is a relation between inflation and unemployment.
5 % = zero inflation
11
5 %
12
There
exists a stable relationship between the variables. The relationship has not substantially changed for over 100 years. Negative, nonlinear correlation. Wages remain stable/stationary ( =0) when unemployment is 5%.
13
From the dispersion of the data points, Phillips concluded that there was a countercyclical loop: Money wages rise faster as du/dt decreases, Money wages fall slower as du/dt increases Implies an inflationary bias, and is consistent with sticky wage theory.
dw w
faster
slower u
14
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Medical Surgical Nursing - IDokument97 SeitenMedical Surgical Nursing - IGuruKPO80% (10)
- Biyani's Think Tank: Concept Based NotesDokument49 SeitenBiyani's Think Tank: Concept Based NotesGuruKPO71% (7)
- Biyani's Think Tank: Concept Based NotesDokument49 SeitenBiyani's Think Tank: Concept Based NotesGuruKPO71% (7)
- CHP#5 Inflation, Deflation and StagflationDokument47 SeitenCHP#5 Inflation, Deflation and StagflationMuhammad HasnainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inflation Unemployment and Interest - 12&13&14 PDFDokument14 SeitenInflation Unemployment and Interest - 12&13&14 PDFDebabrattaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inflation and Deflation - 1Dokument26 SeitenInflation and Deflation - 1Dr.Ashok Kumar PanigrahiNoch keine Bewertungen
- DR A K PanigrahiDokument26 SeitenDR A K PanigrahiMannat BhallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- In de StagflationDokument24 SeitenIn de StagflationSHEKHAWAT FAMILYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inflation & UnemploymentDokument21 SeitenInflation & UnemploymentGaurav AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- DeflationDokument12 SeitenDeflationkrishna45Noch keine Bewertungen
- Inflation:: Types, Causes, Measurement & Philips CurveDokument22 SeitenInflation:: Types, Causes, Measurement & Philips CurveNabin SijaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inflationunemployment GMMDokument21 SeitenInflationunemployment GMMYatin GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Money and BankingDokument11 SeitenIntroduction To Money and BankingAyomikunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theory of InflationDokument12 SeitenTheory of InflationshankysmartestNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Inflation?: According To FriedmanDokument5 SeitenWhat Is Inflation?: According To FriedmanMalik Muhammad JamalNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECN405Sem: Principles of Macroeconomics: Topic 9Dokument29 SeitenECN405Sem: Principles of Macroeconomics: Topic 9aliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inflation: BY KiranDokument18 SeitenInflation: BY KiranKiran Kumar PatnaikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Macro Economics: Inflation and UnemploymentDokument11 SeitenMacro Economics: Inflation and UnemploymentHashim RiazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Macroeconomic Objectives - Low Inflation Rate - HandoutDokument48 SeitenMacroeconomic Objectives - Low Inflation Rate - Handoutdenny_sitorusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Cycles: Unit 11Dokument15 SeitenBusiness Cycles: Unit 11Ashish GahlanNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is The Difference Between Inflation and RecessionDokument1 SeiteWhat Is The Difference Between Inflation and Recessionmymail810Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Persistent Increase in The Level of Consumer Prices or A Persistent Decline in The Purchasing Power of Money... "Dokument6 SeitenA Persistent Increase in The Level of Consumer Prices or A Persistent Decline in The Purchasing Power of Money... "marketfreekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infaltion (Main Slide)Dokument27 SeitenInfaltion (Main Slide)arthonadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inflasi, Pengangguran, Dan Siklus BisnisDokument16 SeitenInflasi, Pengangguran, Dan Siklus BisnisReza AfrisalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economic 4th SemDokument9 SeitenEconomic 4th SemSomnath PahariNoch keine Bewertungen
- InflationDokument49 SeitenInflationNishant KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- C7 - InflationDokument29 SeitenC7 - InflationAnh Ôn KimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Demand Pull InflationDokument5 SeitenDemand Pull InflationHasan TareckNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inflation Its Causes and EffectsDokument28 SeitenInflation Its Causes and EffectsPoonam SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sem 2 Inflation, Unemployment and Labour MarketDokument10 SeitenSem 2 Inflation, Unemployment and Labour Marketksucheta013Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2: InflationDokument16 SeitenUnit 2: InflationKinnari SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- InflationDokument40 SeitenInflationRosebell MelgarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inflation, Deflation and StagflationDokument56 SeitenInflation, Deflation and StagflationShahjahan DashtiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economics InflationDokument14 SeitenEconomics InflationTanmay SinghalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inflation and UnemploymentDokument19 SeitenInflation and UnemploymentAnonymous Uy9aFzMdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inflation: Causes, Measures & Anti Measures by Kedar Belwalkar ITM - 13 BatchDokument11 SeitenInflation: Causes, Measures & Anti Measures by Kedar Belwalkar ITM - 13 BatchKedar BelwalkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Demand-Pull InflationDokument6 SeitenDemand-Pull InflationMalik Muhammad JamalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Cycles, Inflation and UnemploymentDokument18 SeitenBusiness Cycles, Inflation and Unemploymentrajan tiwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inflation, Deflation and StagflationDokument58 SeitenInflation, Deflation and StagflationShahjahan DashtiNoch keine Bewertungen
- InflationDokument15 SeitenInflationUsaf SalimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inflation XXDokument20 SeitenInflation XXAvdhi JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inflation & Its Impact On Pakistan EconomyDokument25 SeitenInflation & Its Impact On Pakistan EconomyMuhammadHammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business CyclesDokument18 SeitenBusiness CyclesshruthinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Inflation Unemployment BCDokument39 Seiten5 Inflation Unemployment BCSara BatoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 4 AS - Inflation and DeflationDokument20 SeitenCH 4 AS - Inflation and DeflationRabee BasitNoch keine Bewertungen
- INFLATIONDokument3 SeitenINFLATIONRohan JhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- InflationDokument10 SeitenInflationData AnalystNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inflation and Monetary PolicyDokument12 SeitenInflation and Monetary Policyfarhana nasreenNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5.1 Inflation: Adigrat University Dep.T of Acfn MacroeconomicsDokument19 Seiten5.1 Inflation: Adigrat University Dep.T of Acfn Macroeconomicsabadi gebruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inflation FileDokument5 SeitenInflation FileDaliopac John PaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inflation FileDokument5 SeitenInflation FileDaliopac John PaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inflation FileDokument5 SeitenInflation FileDaliopac John PaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inflation FileDokument5 SeitenInflation FileDaliopac John PaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liquidity TrapDokument5 SeitenLiquidity TrapManish KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 6 InflationDokument26 SeitenUnit 6 InflationdawsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Lecture 8.2) Chapter 12 Unemployment and Inflation (L8 - 2)Dokument21 Seiten(Lecture 8.2) Chapter 12 Unemployment and Inflation (L8 - 2)Chen Yee KhooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effects of InflationDokument3 SeitenEffects of InflationonenumbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inflation 2Dokument19 SeitenInflation 2Salma GamalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inflation and DeflationDokument10 SeitenInflation and Deflationredsalute100% (1)
- INFLATIONDokument17 SeitenINFLATIONlillygujjarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inflation and UnemploymentDokument22 SeitenInflation and UnemploymentmenalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inflation-Conscious Investments: Avoid the most common investment pitfallsVon EverandInflation-Conscious Investments: Avoid the most common investment pitfallsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applied ElectronicsDokument37 SeitenApplied ElectronicsGuruKPO100% (2)
- Abstract AlgebraDokument111 SeitenAbstract AlgebraGuruKPO100% (5)
- Applied ElectronicsDokument40 SeitenApplied ElectronicsGuruKPO75% (4)
- Production and Material ManagementDokument50 SeitenProduction and Material ManagementGuruKPONoch keine Bewertungen
- OptimizationDokument96 SeitenOptimizationGuruKPO67% (3)
- Computer Graphics & Image ProcessingDokument117 SeitenComputer Graphics & Image ProcessingGuruKPONoch keine Bewertungen
- Algorithms and Application ProgrammingDokument114 SeitenAlgorithms and Application ProgrammingGuruKPONoch keine Bewertungen
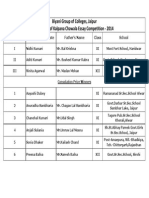
- Biyani Group of Colleges, Jaipur Merit List of Kalpana Chawala Essay Competition - 2014Dokument1 SeiteBiyani Group of Colleges, Jaipur Merit List of Kalpana Chawala Essay Competition - 2014GuruKPONoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Communication & NetworkingDokument138 SeitenData Communication & NetworkingGuruKPO80% (5)
- Think Tank - Advertising & Sales PromotionDokument75 SeitenThink Tank - Advertising & Sales PromotionGuruKPO67% (3)
- Algorithms and Application ProgrammingDokument114 SeitenAlgorithms and Application ProgrammingGuruKPONoch keine Bewertungen
- Software Project ManagementDokument41 SeitenSoftware Project ManagementGuruKPO100% (1)
- Phychology & Sociology Jan 2013Dokument1 SeitePhychology & Sociology Jan 2013GuruKPONoch keine Bewertungen
- Phychology & Sociology Jan 2013Dokument1 SeitePhychology & Sociology Jan 2013GuruKPONoch keine Bewertungen
- Paediatric Nursing Sep 2013 PDFDokument1 SeitePaediatric Nursing Sep 2013 PDFGuruKPONoch keine Bewertungen
- Business LawDokument112 SeitenBusiness LawDewanFoysalHaqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Community Health Nursing Jan 2013Dokument1 SeiteCommunity Health Nursing Jan 2013GuruKPONoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Ethics and EthosDokument36 SeitenBusiness Ethics and EthosGuruKPO100% (3)
- Product and Brand ManagementDokument129 SeitenProduct and Brand ManagementGuruKPONoch keine Bewertungen
- Legal and Constitutional History of IndiaDokument34 SeitenLegal and Constitutional History of IndiaGuruKPO86% (29)
- Data Communication & NetworkingDokument138 SeitenData Communication & NetworkingGuruKPO80% (5)
- First AidDokument58 SeitenFirst AidGuruKPO75% (4)
- Computer Graphics & Image ProcessingDokument117 SeitenComputer Graphics & Image ProcessingGuruKPONoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical Surgical Nursing - IIDokument56 SeitenMedical Surgical Nursing - IIGuruKPO33% (6)
- Mental Health of GNMDokument133 SeitenMental Health of GNMGuruKPO100% (9)
- Strategic ManagementDokument61 SeitenStrategic ManagementGuruKPONoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of NursingDokument50 SeitenFundamentals of NursingGuruKPO67% (3)
- Question:1-Explain The Role of Technology in Promoting Economic Development. While Doing So, Bring Out The Positive and Negative Role of TechnologyDokument12 SeitenQuestion:1-Explain The Role of Technology in Promoting Economic Development. While Doing So, Bring Out The Positive and Negative Role of TechnologyHashmi SutariyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic SampleDokument3 SeitenTopic SampleChanakya ResearchNoch keine Bewertungen
- Managing Financial Resources in The GovernmentDokument93 SeitenManaging Financial Resources in The GovernmentBarney's Gaming Squad100% (1)
- FAQs - On - Prize Bonds - Updated-31-12-2004Dokument11 SeitenFAQs - On - Prize Bonds - Updated-31-12-2004Shahbaz SharifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mazviita Sheanotida Mlambo R151255V Final DissertationDokument45 SeitenMazviita Sheanotida Mlambo R151255V Final DissertationColias DubeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Annual NGBIRR FY 2022.23Dokument208 SeitenFinal Annual NGBIRR FY 2022.23Dunson MuhiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- European Debt CrisisDokument21 SeitenEuropean Debt CrisisPrabhat PareekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guingona Vs CaragueDokument7 SeitenGuingona Vs CaraguePhenix Joyce PagdatoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business-Economics-Report 3000 WordsDokument19 SeitenBusiness-Economics-Report 3000 WordsRubab Kanwal100% (1)
- Finacilisationof The Wall Street ConsensusDokument37 SeitenFinacilisationof The Wall Street ConsensusLuis MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grant Thornton - Budget Booklet - 2023-24Dokument44 SeitenGrant Thornton - Budget Booklet - 2023-24sourabhshrivastava80Noch keine Bewertungen
- B5 PsafDokument926 SeitenB5 PsafIRIBHOGBE OSAJIENoch keine Bewertungen
- Treasury Securities in BangladeshDokument12 SeitenTreasury Securities in BangladeshAmit KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Eternal ZeroDokument4 SeitenThe Eternal ZeroThuy NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Papers SbotDokument13 SeitenPapers SbotTahir Hanif100% (2)
- Bank of Punjab Final Balance Sheet AnalysisDokument12 SeitenBank of Punjab Final Balance Sheet AnalysisZara SikanderNoch keine Bewertungen
- DB 45 PDFDokument120 SeitenDB 45 PDFzaheeruddin_mohdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Govt Securities MarketDokument33 SeitenGovt Securities MarketRohit BhardwajNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Tanzania: I.1 History I.1.1 Colonial PeriodDokument34 Seiten5 Tanzania: I.1 History I.1.1 Colonial PeriodJohnBenardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Latihan Ujian MacroeconomicDokument70 SeitenLatihan Ujian MacroeconomicSetiady MaruliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8 - Debt Service Funds Solutions ManualDokument30 SeitenChapter 8 - Debt Service Funds Solutions Manualgilli1trNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bond Market in IndiaDokument4 SeitenBond Market in IndiaHarsh ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Many Challenges On Indian EconomyDokument11 SeitenMany Challenges On Indian EconomyHarikrishna Malla100% (1)
- Inflation and DeflationDokument10 SeitenInflation and Deflationredsalute100% (1)
- Assignment: Name of Assignment: International Trade How OurDokument9 SeitenAssignment: Name of Assignment: International Trade How OurAmeen IslamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela: U.S.$3,000,000,000 12.75% Amortizing Bonds Due 2022 (The "Bonds")Dokument130 SeitenBolivarian Republic of Venezuela: U.S.$3,000,000,000 12.75% Amortizing Bonds Due 2022 (The "Bonds")Rafael DoblesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorialch5 MoneyfederalreserveDokument75 SeitenTutorialch5 MoneyfederalreserveRashid AyubiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project SyndicateDokument2 SeitenProject Syndicateapi-63605683Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 Securities Operations and Risk ManagementDokument32 SeitenChapter 1 Securities Operations and Risk ManagementMRIDUL GOELNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ae18-005-Central Banking and The Effects of Its Monetary Policies in Our EconomyDokument15 SeitenAe18-005-Central Banking and The Effects of Its Monetary Policies in Our EconomyLaezelie SorianoNoch keine Bewertungen